Tharsis Volcano
| Credit | NASA/JPL-Caltech/USGS |
|---|---|
| Language |
|
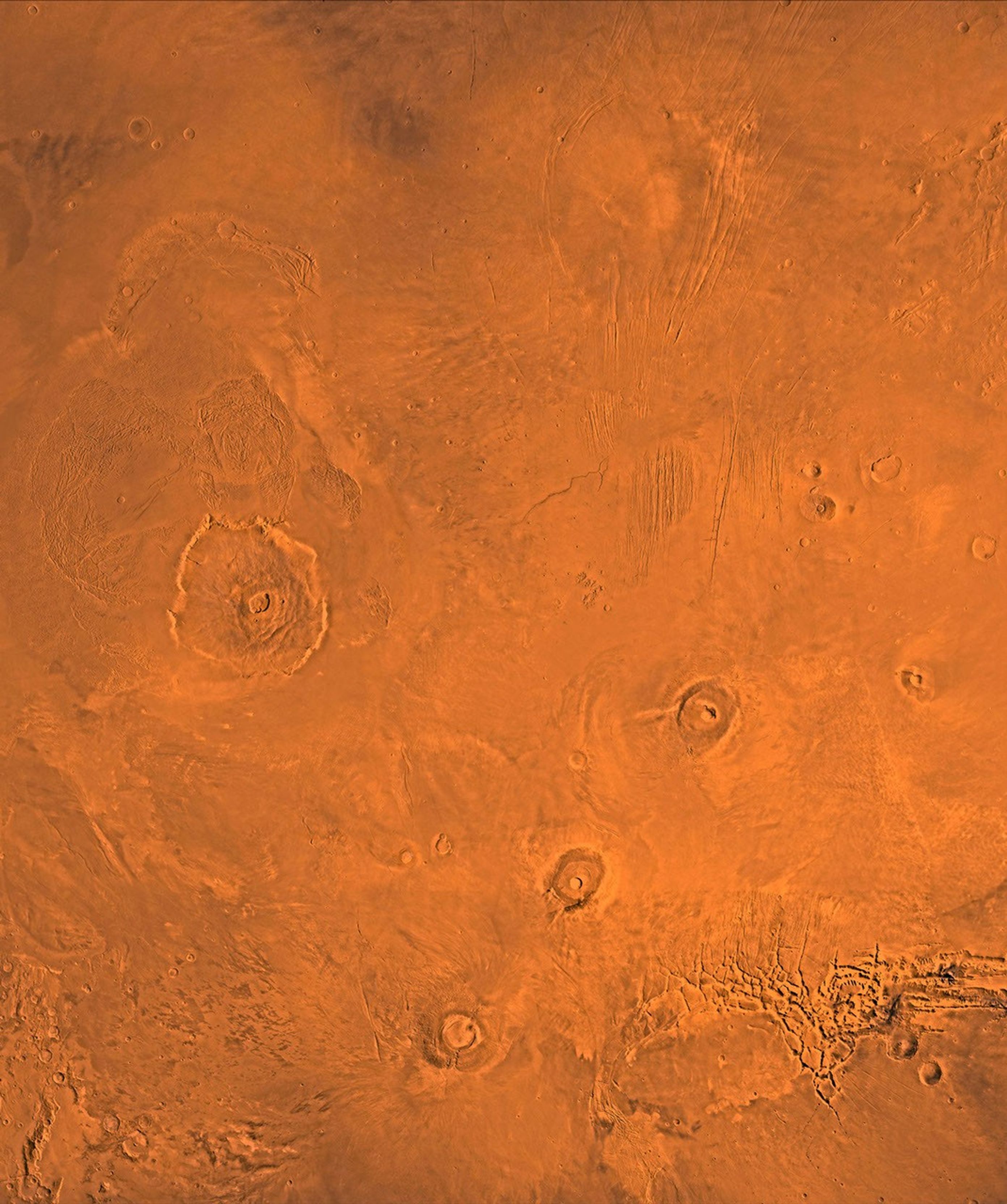
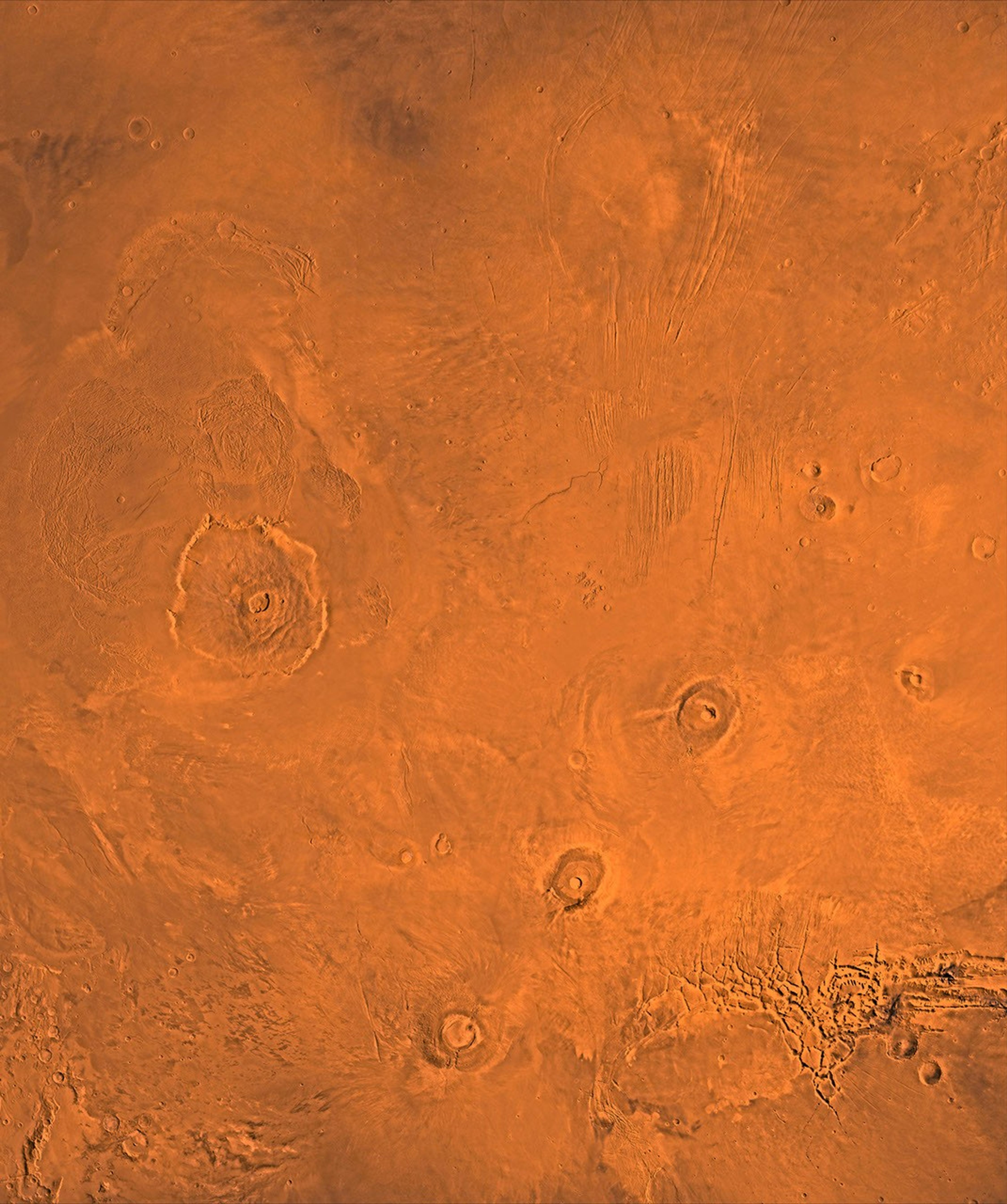
A color image of the Tharsis region of Mars; north toward top. The scene shows the Tharsis bulge, a huge ridge covered by the 3 large aligned Tharsis Montes shield volcanoes (from lower left to right): Arsia, Pavonis, and Ascraeus Mons. To the left of the Tharsis Montes lies the huge Olympus Mons shield volcano, followed clockwise by Alba Patera (north center), several smaller volcanoes, and the linear depressions of Mareotis and Tempe Fossae (upper right).
This image is a composite of Viking medium-resolution images in black and white and low-resolution images in color. The image extends from latitude 50 degrees N. to 20 degrees S. and from longitude 85 degrees to 150 degrees. Mercator projection is used between latitudes 20 degrees S. and 30 degrees N.; Lambert projection is used above latitude 30 degrees N.
The Tharsis bulge encompasses the most intensely and most recently active volcanic region of the planet. Each Tharsis Montes volcano is 350-400 km in diameter and about 17 km above the surrounding plain. The volcanoes are about 700 km apart and appear to be above a major northeast-trending fracture zone along the bulge, now buried by volcanic deposits. Olympus Mons (left center) is the largest known volcano in the Solar System. It is 27 km high, over 600 km at the base, and is surrounded by a well-defined scarp that is up to 6 km high. The summit calderas (central depressions) of all four volcanoes probably formed from recurrent collapse following drainage of magma resulting from flank eruptions. 1,600-km-diameter Alba Patera (north center) far exceeds any other known volcano in areal extent; it covers eight times the area of Olympus Mons but reaches only about 6 km in height. Fossae (linear depressions) of the Tharsis area are fault-bound graben formed by upwarping of the Tharsis bulge.