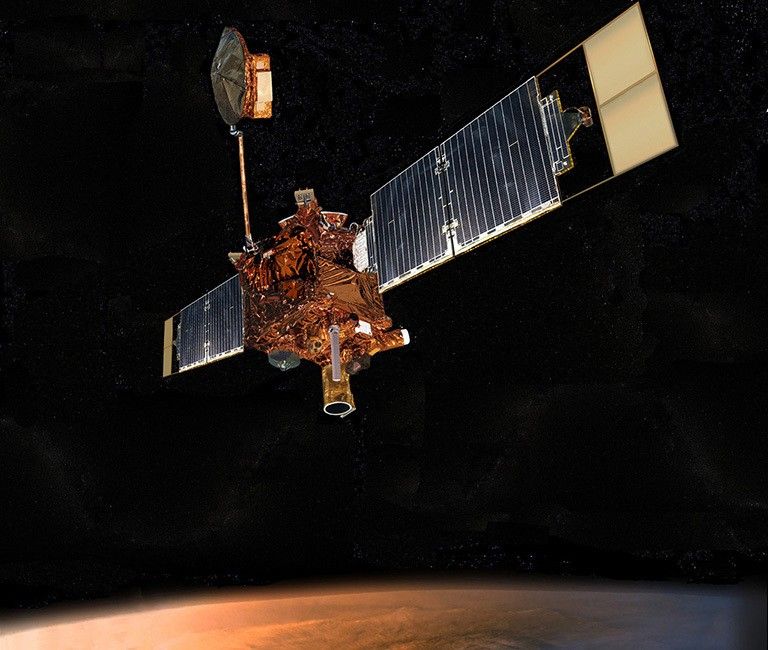
Mars Global Surveyor
Mars Global Surveyor
Type
Launch
Target
Mission End
What was Mars Global Surveyor?
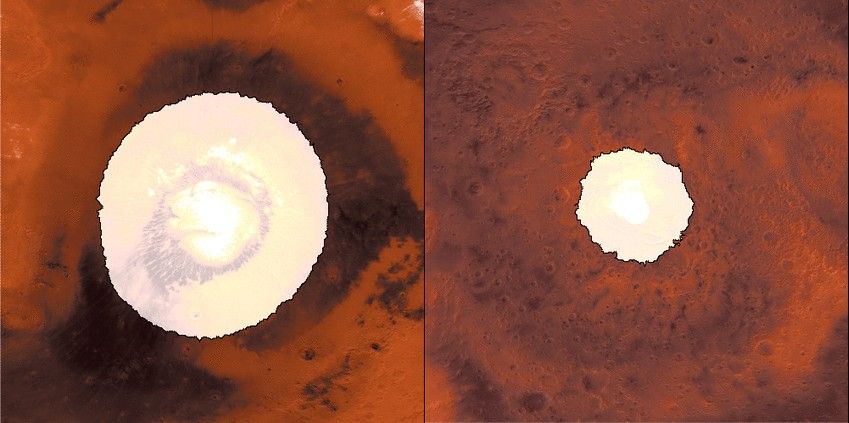
Mars Global Surveyor was an orbiting spacecraft that looped around the Red Planet for a decade. The mission overhauled scientists' understanding of Mars by studying the entire Martian surface, atmosphere, and interior. Major findings included dramatic evidence that water still flows on Mars in short bursts down hillside gullies, and the identification of water-related mineral deposits leading to selection of a Mars rover landing site for a subsequent mission.
The mission continued sending images and other data until November 2006, when it went silent due to a series of events linked to a computer error likely caused by battery failure.
| Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| MIssion Type | Orbiter |
| Spacecraft Mass | 2,272 pounds (1,030.5 kilograms) |
| Launch Vehicle | Delta 7925 (no. D239) |
| Scientific Instruments | 1. Mars Orbital Camera (MOC) 2. Mars Orbital Laser Altimeter (MOLA) 3. Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES) 4. Magnetometer/Electron Reflectometer (MAG/ER) 5. Radio Science Experiment (RS) 6. Mars Relay Antenna (MR) |
Key Dates
Launch Date: Nov. 7, 1996 UTC
Orbit Insertion: Sept. 12, 1997
End of Mission: Nov. 14, 2006
Technologies of Broad Benefit
Each Mars mission is part of a continuing chain of innovation: each relies on past missions to identify needed new technologies and each contributes its own innovations to benefit future missions. This chain allows NASA to continue to push the boundaries of what is currently possible, while relying on proven technologies.
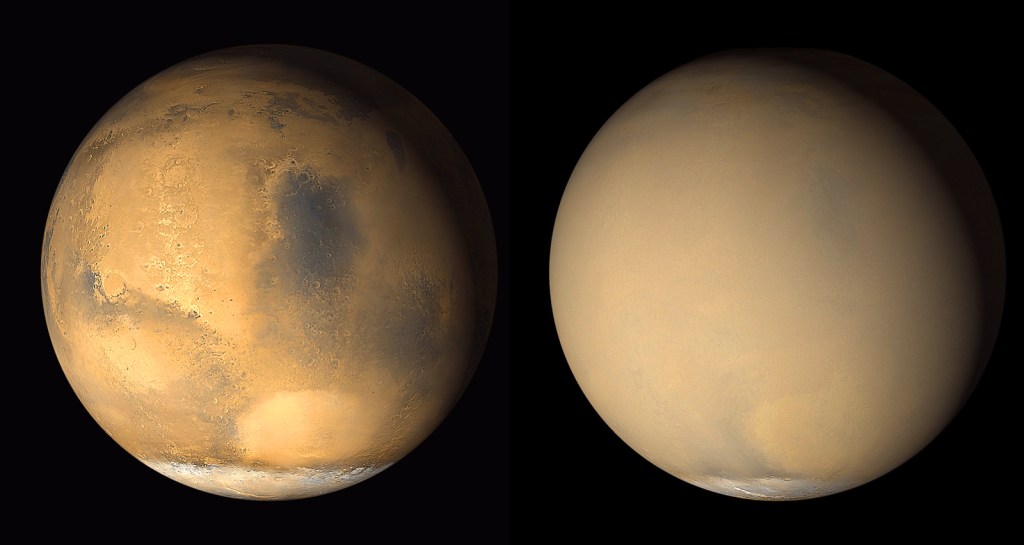
Science
Mars Global Surveyor was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet – from the ionosphere (an envelope of charged particles surrounding Mars) down through the atmosphere to the surface, and deep into Mars' interior. As part of the larger Mars Exploration Program, Mars Global Surveyor performed atmospheric monitoring for sister orbiters during aerobraking, and it helped rovers and lander missions by identifying potential landing sites and relaying surface telemetry.
Science Instruments
Mars Global Surveyor carried a complement of six scientific investigations to perform atmospheric monitoring for sister orbiters during aerobraking, and it helped subsequent rover and lander missions by identifying potential landing sites and relaying surface telemetry.