1 min read
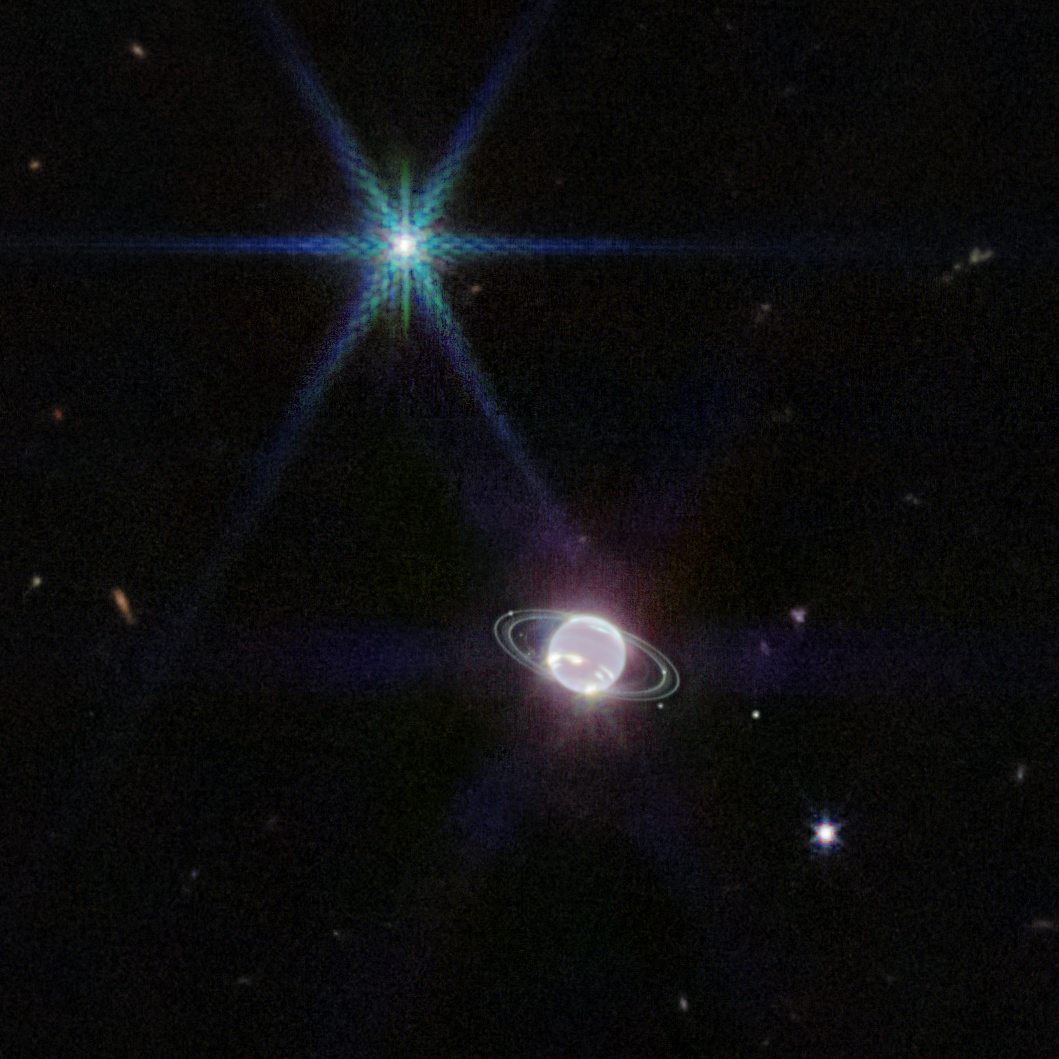
Neptune Wide Field (NIRCam)

In this image by Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), a smattering of hundreds of background galaxies, varying in size and shape, appear alongside the Neptune system.
Neptune, when compared to Earth, is a big planet. If Earth were the size of a nickel, Neptune would be as big as a basketball. In most portraits, the outer planets of our solar system reflect this otherworldly size. However, Neptune appears relatively small in a wide-field view of the vast universe.
Towards the bottom left of this image, a barred spiral galaxy comes into focus. Scientists say this particular galaxy, previously unexplored in detail, may be about a billion light-years away. Spiral galaxies like this are typically dominated by young stars that appear blueish in these wavelengths.
NIRCam was built by a team at the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced Technology Center.
About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Neptune's average distance from Earth is 2.7 billion miles
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from JWST data from proposal: 2739 (K. Pontoppidan).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.12 July 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F140M, F210M, F300M, F460M
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Neptune
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Gas giant
- Release DateSeptember 21, 2022
- Science ReleaseNew Webb Image Captures Clearest View of Neptune’s Rings in Decades
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI; Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Naomi Rowe-Gurney (NASA-GSFC)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample different infraraed wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Red: F460M Orange: F300M Green: F210M Blue: F140M

Related Images & Videos
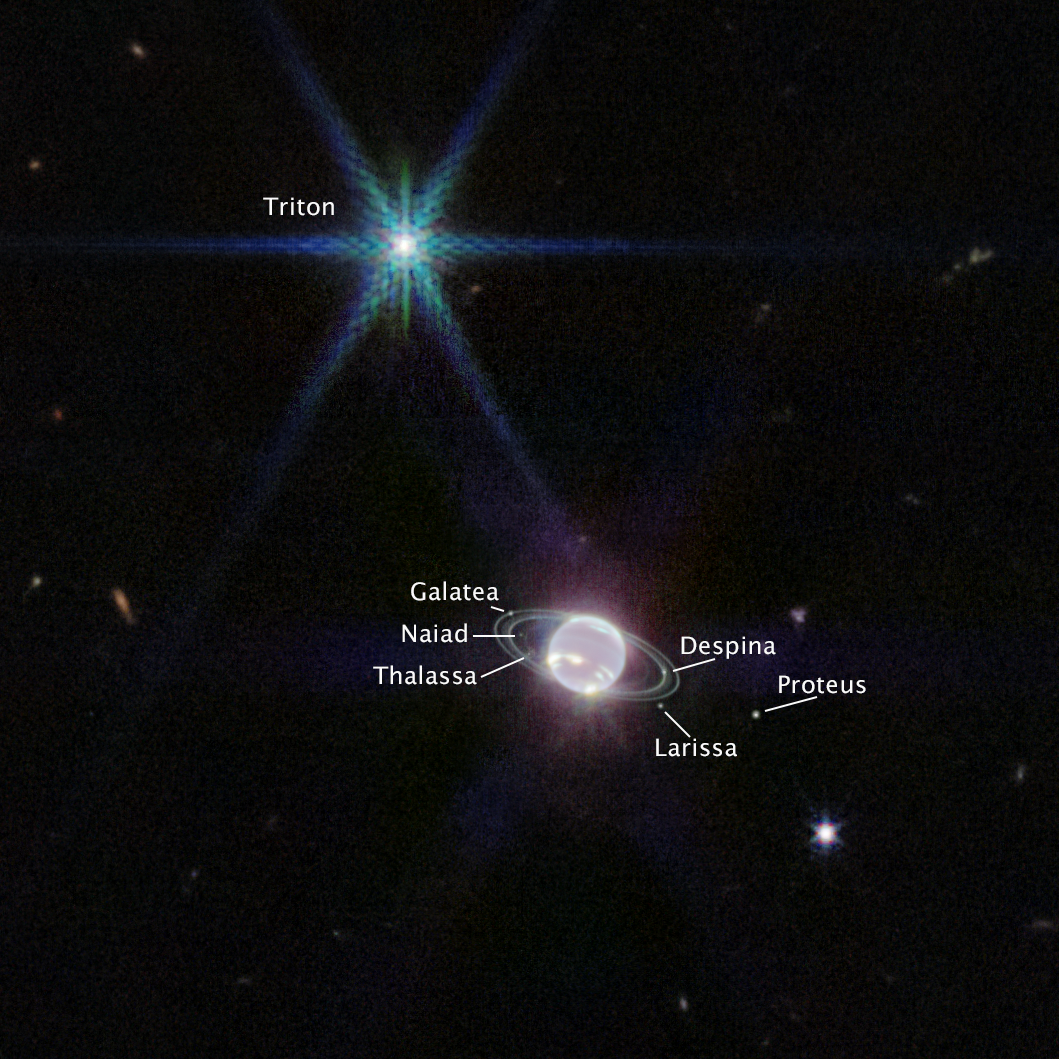
Neptune (NIRCam) Labeled
In this version of Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) image of Neptune, the planet’s visible moons are labeled. Neptune has 14 known satellites, and seven of them are visible in this image. Triton, the bright spot of light in the upper left of this image, far outshines Neptune...
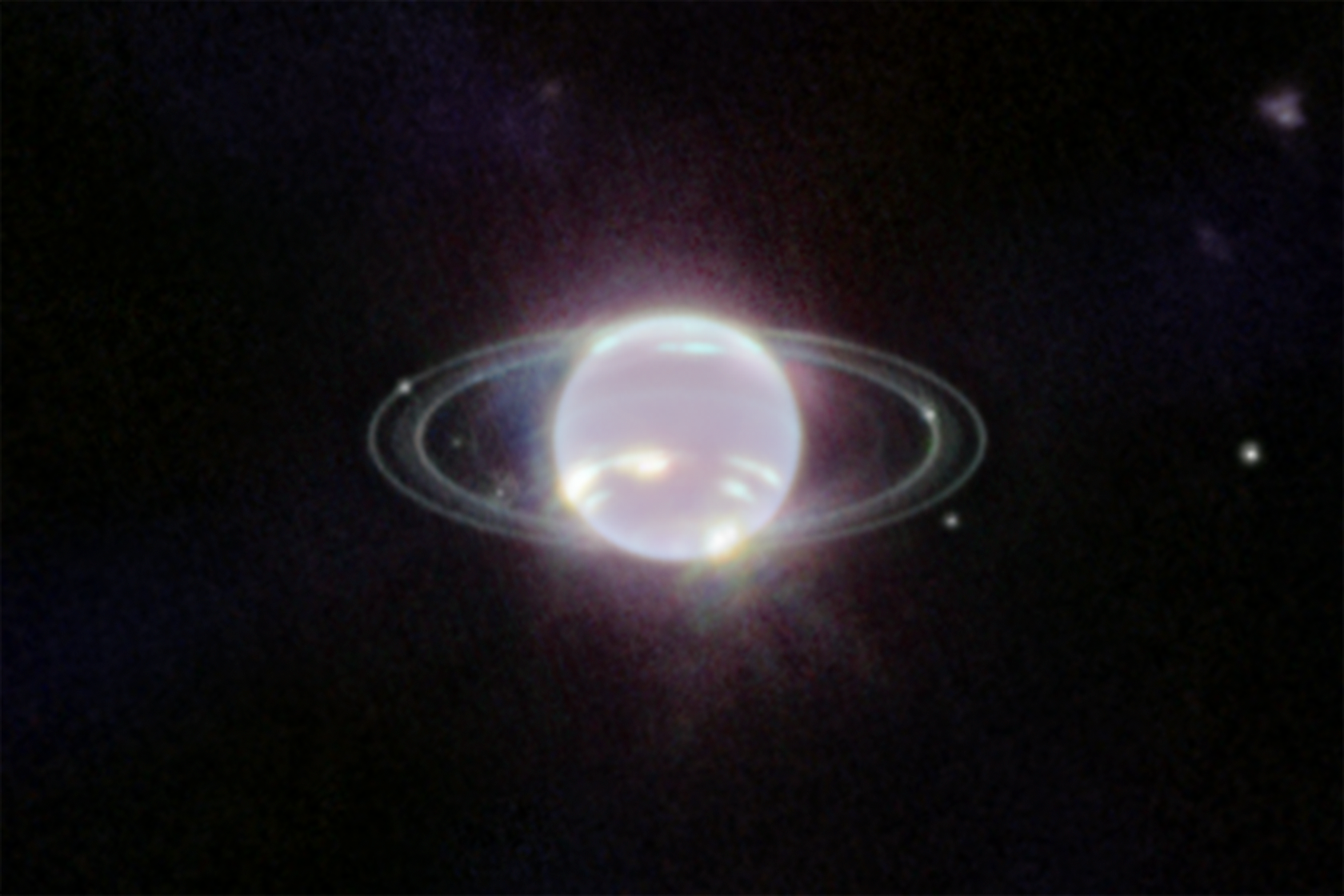

Neptune Close Up (NIRCam)
Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) image of Neptune, taken on July 12, 2022, brings the planet’s rings into full focus for the first time in more than three decades. The most prominent features of Neptune’s atmosphere in this image are a series of bright patches in the...

Neptune Wide Field (NIRCam Compass Image)
This image of Neptune and its rings and moons, captured by Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), shows compass arrows and a color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Naomi Rowe-Gurney (NASA-GSFC)

































