1 min read
Crab Nebula (NIRCam and MIRI Image)
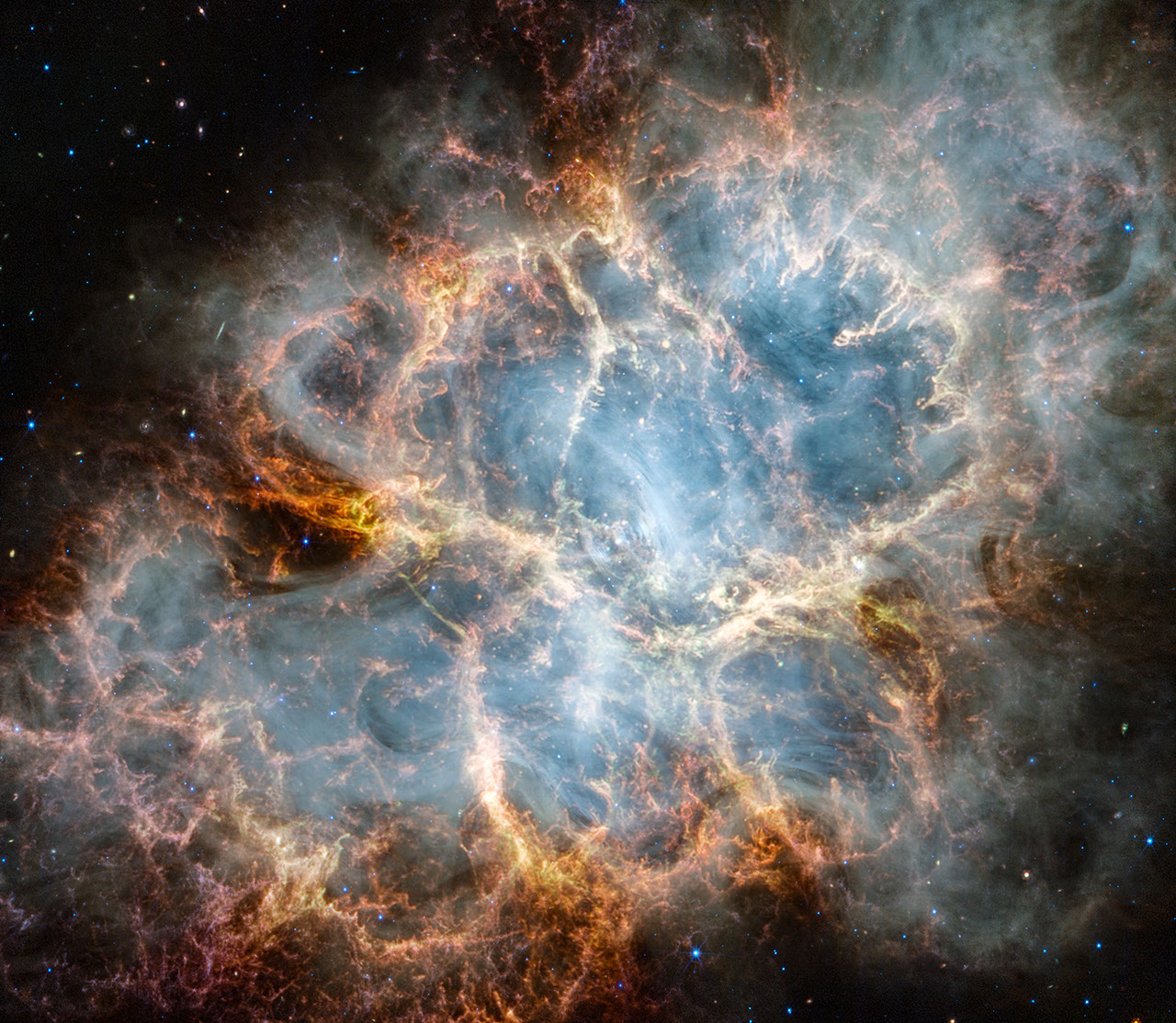

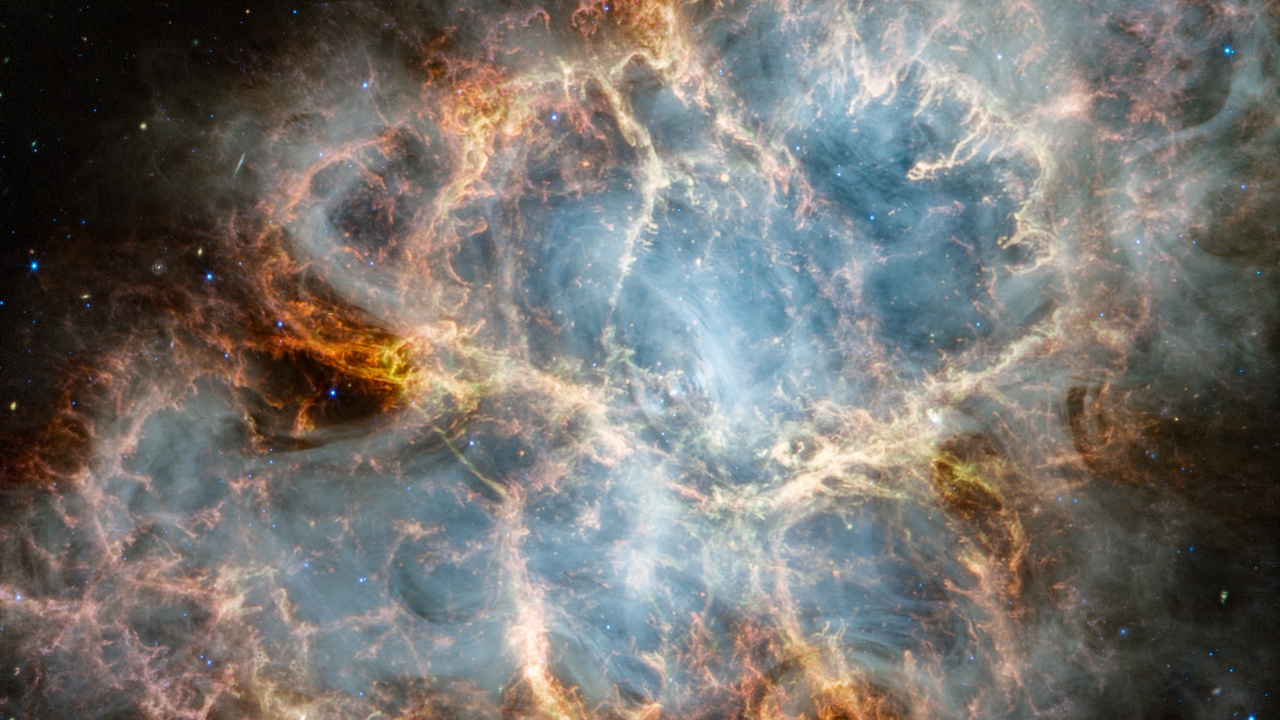
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has gazed at the Crab Nebula in the search for answers about the supernova remnant’s origins. Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) have revealed new details in infrared light.
Similar to the Hubble optical wavelength image released in 2005, with Webb the remnant appears comprised of a crisp, cage-like structure of fluffy red-orange filaments of gas that trace doubly ionized sulfur (sulfur III). Among the remnant’s interior, yellow-white and green fluffy ridges form large-scale loop-like structures, which represent areas where dust particles reside.
The area within is comprised of translucent, milky material. This white material is synchrotron radiation, which is emitted across the electromagnetic spectrum but becomes particularly vibrant thanks to Webb’s sensitivity and spatial resolution. It is generated by particles accelerated to extremely high speeds as they wind around magnetic field lines. Trace the synchrotron radiation throughout the majority of the Crab Nebula’s interior.
Locate the wisps that follow a ripple-like pattern in the middle. In the center of this ring-like structure is a bright white dot: a rapidly rotating neutron star. Further out from the core, follow the thin white ribbons of the radiation. The curvy wisps are closely grouped together, following different directions that mimic the structure of the pulsar’s magnetic field. Note how certain gas filaments are bluer in color. These areas contain singly ionized iron (iron II).
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05:34:32
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+22:00:52
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Taurus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.6500 light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 5.5 arcmin across (about 10 light-years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 1714 (T. Temim) - Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam, MIRI
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.31 Oct 2022, 24 Feb 2023, 17 Mar 2023
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.NIRCam: F162M, F480M; MIRI: F560W, F1130W, F1800W, F2100W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Crab Nebula, M1, NGC 1952
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Remnant, Pulsar
- Release DateOctober 30, 2023
- Science ReleaseThe Crab Nebula Seen in New Light by NASA’s Webb
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Tea Temim (Princeton University); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam and MIRI instruments. Several filters were used to sample specific wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F162M, Light Blue: F480M, Cyan: F560W, Green: F1130W, Orange: F1800W, Red: F2100W

Related Images & Videos
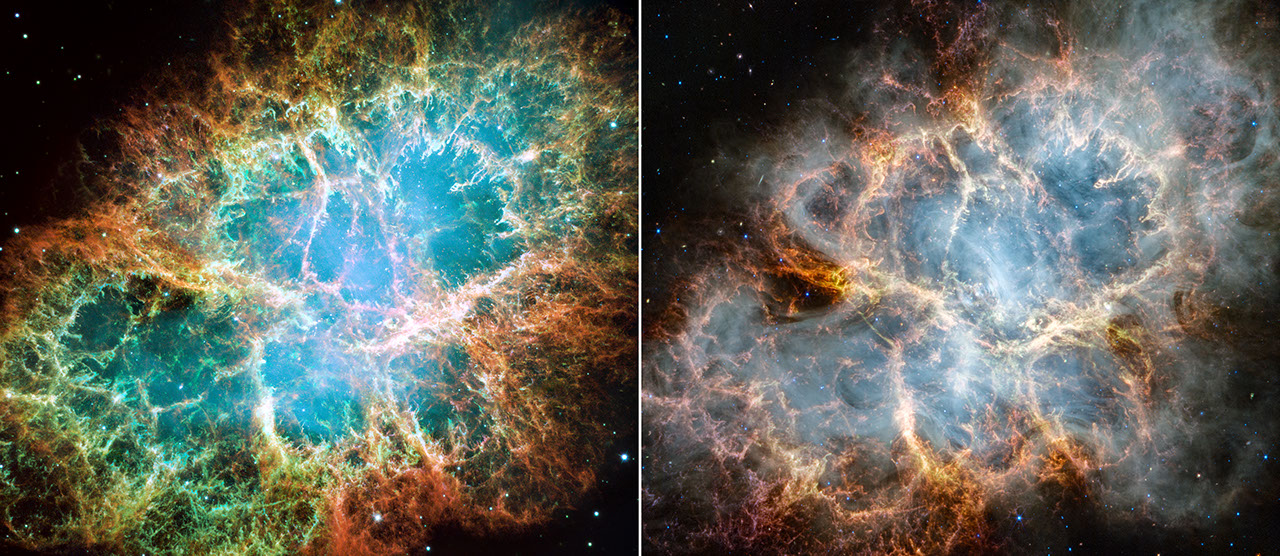
Crab Nebula (Webb and Hubble Comparison)
A side-by-side comparison of the Crab Nebula as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope in optical light (left) and the James Webb Space Telescope in infrared light (right). The Hubble image was released in 2005, while astronomers have recently used Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared...

Crab Nebula (NIRCam and MIRI Compass Image)
Image of the Crab Nebula captured by Webb’s NIRCam and MIRI, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Tea Temim (Princeton University)
Joseph DePasquale (STScI)





























