1 min read
Rho Ophiuchi (NIRCam Image)
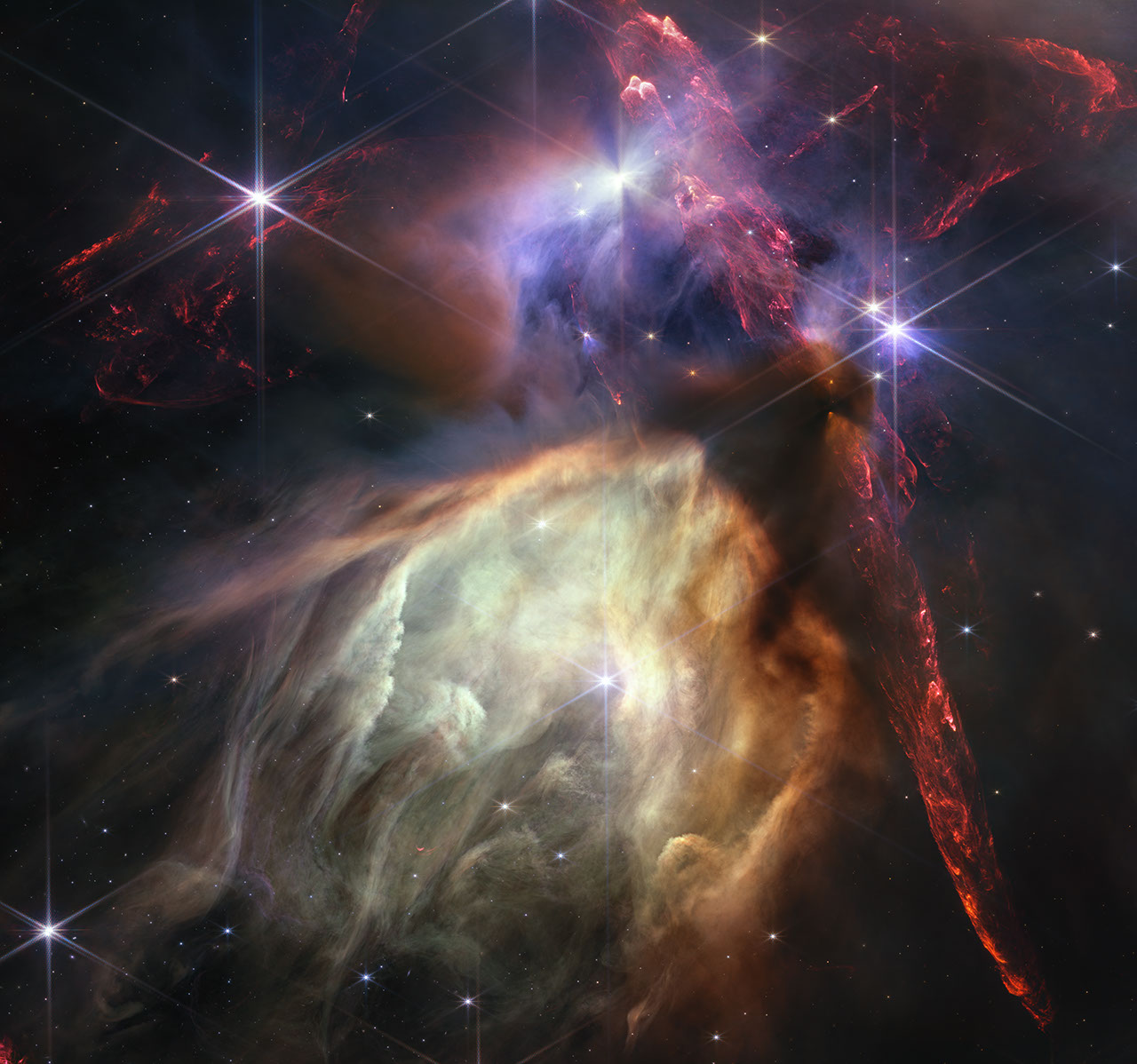

The first anniversary image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope displays star birth like it’s never been seen before, full of detailed, impressionistic texture. The subject is the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex, the closest star-forming region to Earth. It is a relatively small, quiet stellar nursery, but you’d never know it from Webb’s chaotic close-up. Jets bursting from young stars crisscross the image, impacting the surrounding interstellar gas and lighting up molecular hydrogen, shown in red. Some stars display the telltale shadow of a circumstellar disk, the makings of future planetary systems.
The young stars at the center of many of these disks are similar in mass to the Sun, or smaller. The heftiest in this image is the star S1, which appears amid a glowing cave it is carving out with its stellar winds in the lower half of the image. The lighter-colored gas surrounding S1 consists of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, a family of carbon-based molecules that are among the most common compounds found in space.
For more detail on what is happening where in Webb’s image of Rho Ophiuchi, watch the video tour and read the press release.
Extended Description and Image Alt Text
Extended Description
An active star-forming region. Red dual opposing jets coming from young stars fill the darker top half of the image, while a glowing pale-yellow, cave-like structure is bottom center, tilted toward two o’clock, with a bright star at its center. The dust of the cave structure becomes wispy toward eight o’clock, trailing off and allowing stars and distant galaxies to show through.
Above the arched top of the dust cave three groupings of stars with diffraction spikes are arranged. Smaller stars are scattered around the image. A dark cloud sits at the top of the arch of the glowing dust cave, with one streamer curling down the right-hand side. The dark shadow of the cloud appears pinched in the center, with light emerging in a triangle shape above and below the pinch, revealing the presence of a star inside the dark cloud.
The image’s largest jets of red material emanate from within this dark cloud, thick and displaying structure like the rough face of a cliff, glowing brighter at the edges. At the top center of the image, a star displays another, larger pinched dark shadow, this time vertically. To the left of this star is a more wispy, indistinct region, like this star is also beginning to clear out space around itself like the one at the center of the dusty cave below.
Image Alt Text
Red dual opposing jets coming from young stars fill the darker top half of the image, while a glowing pale-yellow, cave-like structure is bottom center, tilted toward two o’clock, with a bright star at its center. The dust of the cave structure becomes wispy toward eight o’clock. Above the arched top of the dust cave three groupings of stars with diffraction spikes are arranged. A dark cloud sits at the top of the arch of the glowing dust cave, with one streamer curling down the right-hand side. The dark shadow of the cloud appears pinched in the center, with light emerging in a triangle shape above and below the pinch, revealing the presence of a star inside the dark cloud. The image’s largest jets of red material emanate from within this dark cloud, thick and displaying structure like the rough face of a cliff, glowing brighter at the edges. At the top center of the image, a star displays another, larger pinched dark shadow, this time vertically. To the left of this star is a more wispy, indistinct region.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.16:26:30.56
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-24:23:04.16
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ophiuchus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.390 light-years away
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 0.7 light-years across (6.4 arcminutes)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 2739 (K. Pontoppidan)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.07 March 2023, 4-6 April 2023
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F187N, F200W, F335W, F444W, F470N
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Rho Ophiuchi
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Star-forming region
- Release DateJuly 12, 2023
- Science ReleaseWebb Celebrates First Year of Science With Close-up on Birth of Sun-like Stars
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide and narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F187N, Light Blue: F200W, Cyan: F335W, Yellow: F444W, Red: F470N

Related Images & Videos

Rho Ophiuchi (NIRCam Compass Image)
Image of star formation in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from...
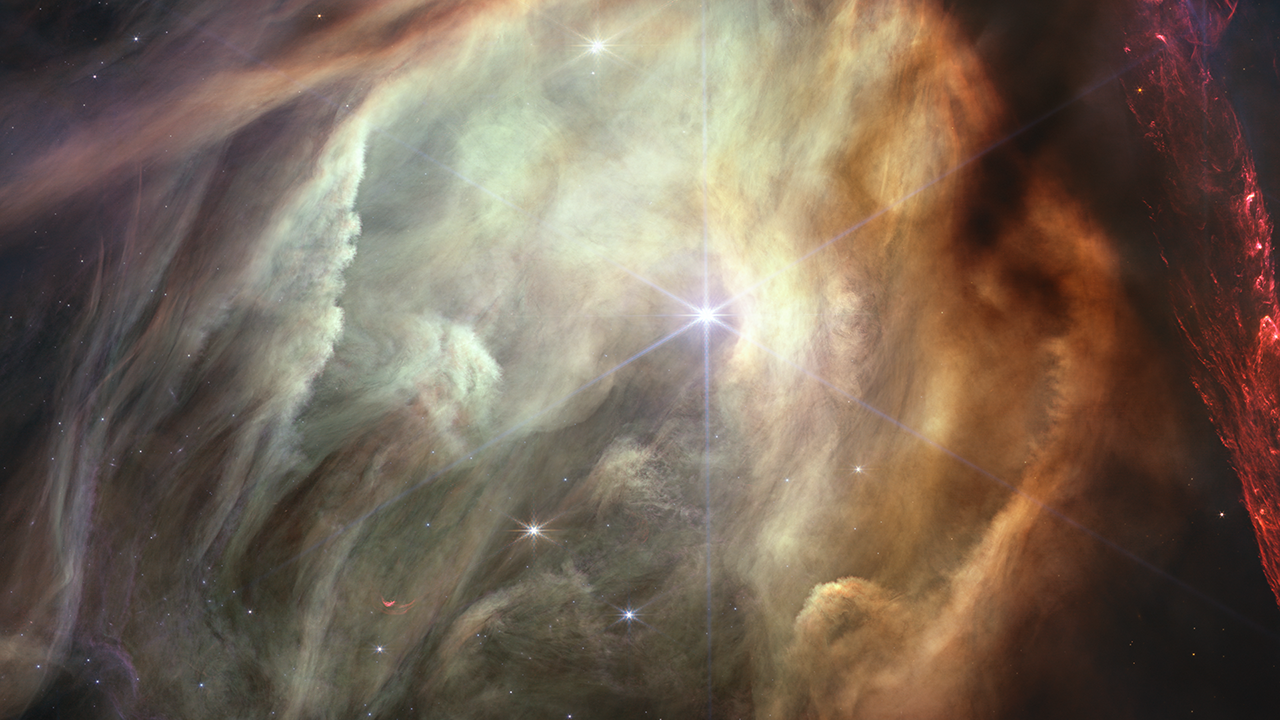
Zoom in to Rho Ophiuchi
Travel to the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex. The journey begins with a ground-based image by astrophotographer Akira Fujii, then transitions into a plate from the Digitized Sky Survey. Next a two-color image from the now-retired infrared NASA Spitzer Space Telescope appears, and...

Rho Ophiuchi Video Tour
This video tours a portion of the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex, the closest star-forming region to Earth. The image was taken to celebrate the first anniversary of the start of science operations for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Jets bursting from young stars crisscross the...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Klaus Pontoppidan (STScI)
Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
































