1 min read
Secondary Eclipse Light Curve
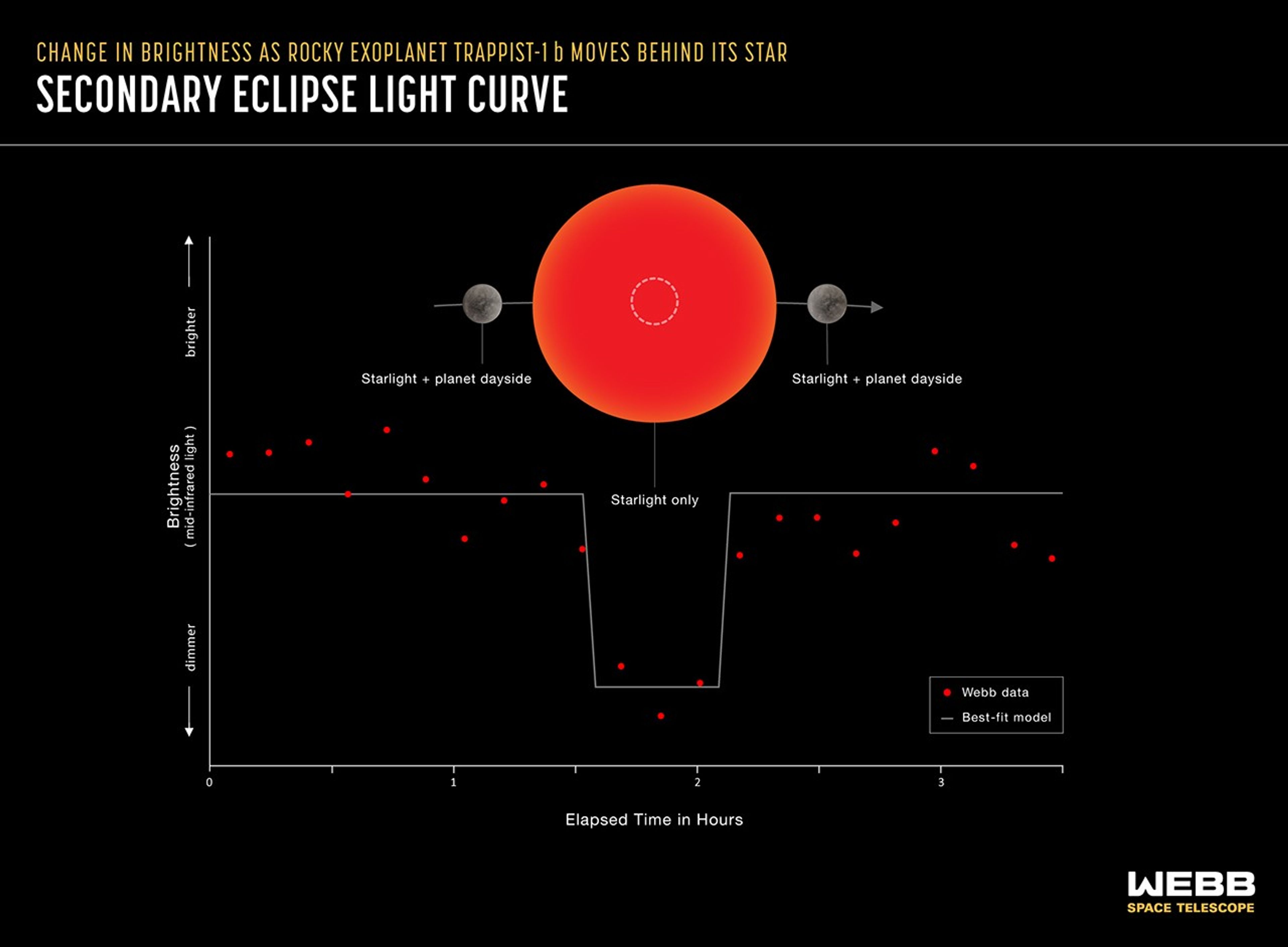
A secondary eclipse light curve shows the decrease in brightness of a star-planet system as the planet moves behind the star. The amount of light contributed by the planet is the difference between the brightness of the star and planet combined (as observed before and after the secondary eclipse) and the brightness of the star on its own (during the secondary eclipse). This light curve shows real Webb data from TRAPPIST-1 b, a rocky planet orbiting a red dwarf star 40 light-years from Earth. TRAPPIST-1 b is not part of the Rocky Worlds program.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.23h 06m 30s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-05d 02m 30s
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Aquarius
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.40 light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.time-series photometry of secondary eclipse
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.MIRI
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.2022: November 8, 12, 20, 24, and December 3
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F1500W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.TRAPPIST-1 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Rocky exoplanet orbiting red dwarf (M-dwarf) star
- Release DateSeptember 30, 2025
- CreditIllustration: NASA, ESA, CSA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI), Andi James (STScI); Science: Thomas Greene (NASA Ames)
Share
Details
Last Updated
Sep 30, 2025
Contact
Media
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov




























