1 min read
SN 1987A (NIRCam, MIRI and NIRSpec Images)
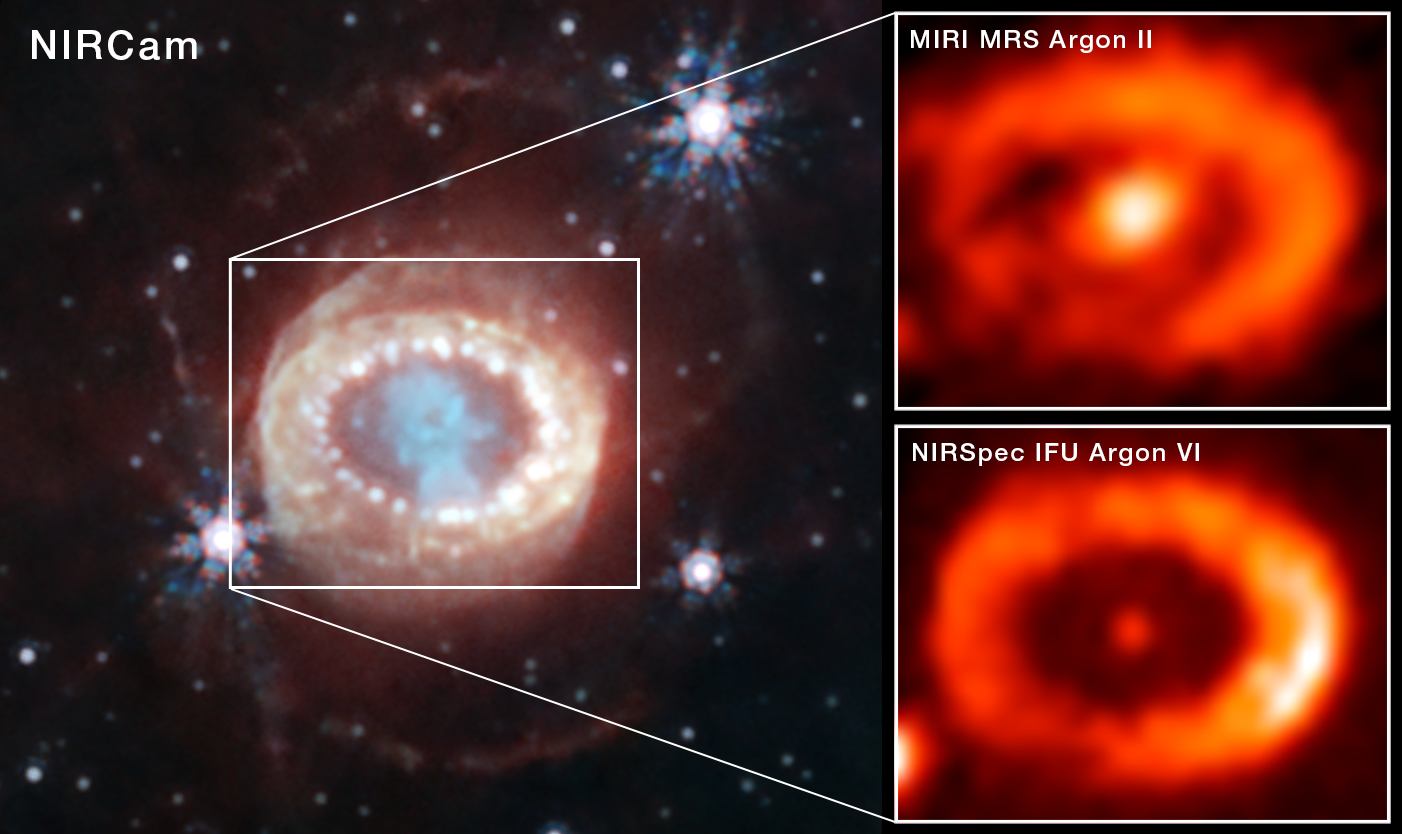
The James Webb Space Telescope has observed the best evidence yet for emission from a neutron star at the site of a well-known and recently-observed supernova known as SN 1987A. At left is a NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) image released in 2023. The image at top right shows light from singly ionized argon (Argon II) captured by the Medium Resolution Spectrograph (MRS) mode of MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). The image at bottom right shows light from multiply ionized argon captured by the NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph). Both instruments show a strong signal from the center of the supernova remnant. This indicated to the science team that there is a source of high-energy radiation there, most likely a neutron star.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05:35:28.03
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-69:16:11.8
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Dorado
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Approximately 160,000 light-years away
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam, MIRI, NIRSpec
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.1-2 September 2022, 16 July 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.NIRCam > F150W; F164N; F200W; F323N; F405N; F444W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.SN 1987A
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Remnant
- Release DateFebruary 22, 2024
- Science ReleaseWebb Finds Evidence for Neutron Star at Heart of Young Supernova Remnant
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Claes Fransson (Stockholm University), Mikako Matsuura (Cardiff University), M. Barlow (UCL), Patrick Kavanagh (Maynooth University), Josefin Larsson (KTH)

The main image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample specific wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F150W, Cyan: F164N, Cyan: F200W, Yellow: F323N, Orange: F405N, Red: F444W
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Claes Fransson (Stockholm University), Mikako Matsuura (Cardiff University), M. Barlow (UCL), Patrick Kavanagh (Maynooth University), Josefin Larsson (KTH)




























