1 min read
Warm Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-107 b (Artist’s Concept)
This artist’s concept shows what the exoplanet WASP-107 b could look like based on recent data gathered by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, along with previous observations from Hubble and other space- and ground-based telescopes.
WASP-107 b is a “warm Neptune” exoplanet orbiting a relatively small and cool star approximately 210 light-years from Earth, in the constellation Virgo. The planet is about 80% the size of Jupiter in terms of volume, but has a mass less than 10% of Jupiter, making it one of the least dense exoplanets known.
WASP-107 b orbits its star at a distance of about 5 million miles (0.055 astronomical units, or AU), completing one circuit in 5.72 days. The planet is tidally locked: It rotates at the same rate that it orbits the star, which means that one side is permanently lit, with the other in continuous darkness, with no day-night cycle. The orbit of WASP-107 b is slightly elliptical, which means that the gravitational pull between the star and planet changes continuously as the planet moves toward and away from the star during its orbit.
Observations of 0.8- to 12-micron infrared light captured by Hubble’s WFC3 (Wide Field Camera 3), and Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph), and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), suggest that the planet has a relatively large core surrounded by a relatively small mass of hydrogen and helium gas, which has been inflated due to tidal heating of the interior.
WASP-107 b has not been directly imaged by any telescope.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h33m32.74s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-10d08m46.37s
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Virgo
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.210 light-years
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.WASP-107 b
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Warm Neptune Exoplanet
- Release DateMay 20, 2024
- Science ReleaseWebb Cracks Case of Inflated Exoplanet
- CreditArtwork: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)
Related Images & Videos
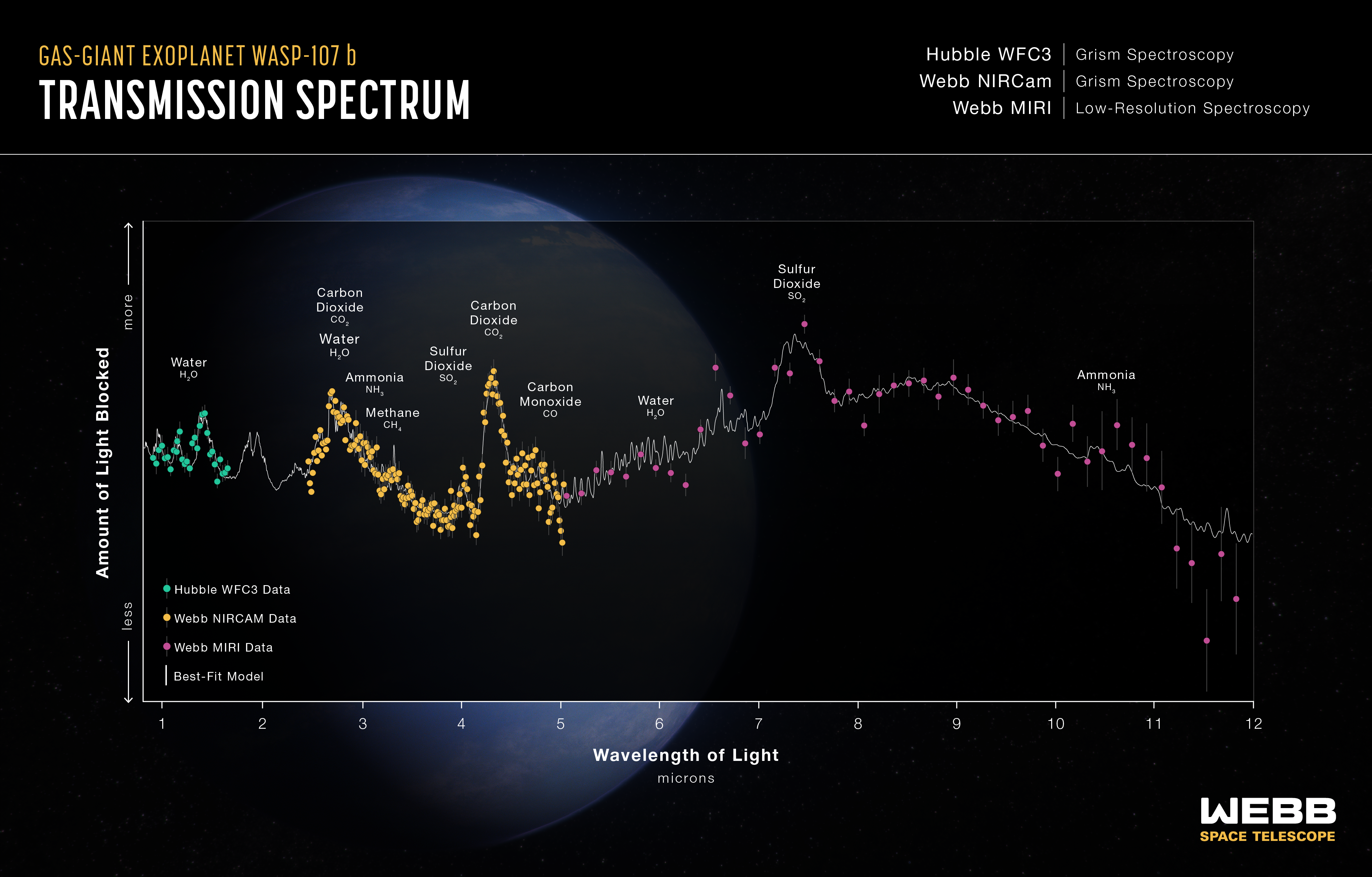
Warm Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-107 b Transmission Spectrum (Hubble WFC3, Webb NIRCam, Webb MIRI)
This transmission spectrum, captured using NASA’s Hubble and James Webb space telescopes, shows the amounts of different wavelengths (colors) of starlight blocked by the atmosphere of the gas-giant exoplanet WASP-107 b . The spectrum includes light collected over five separate...
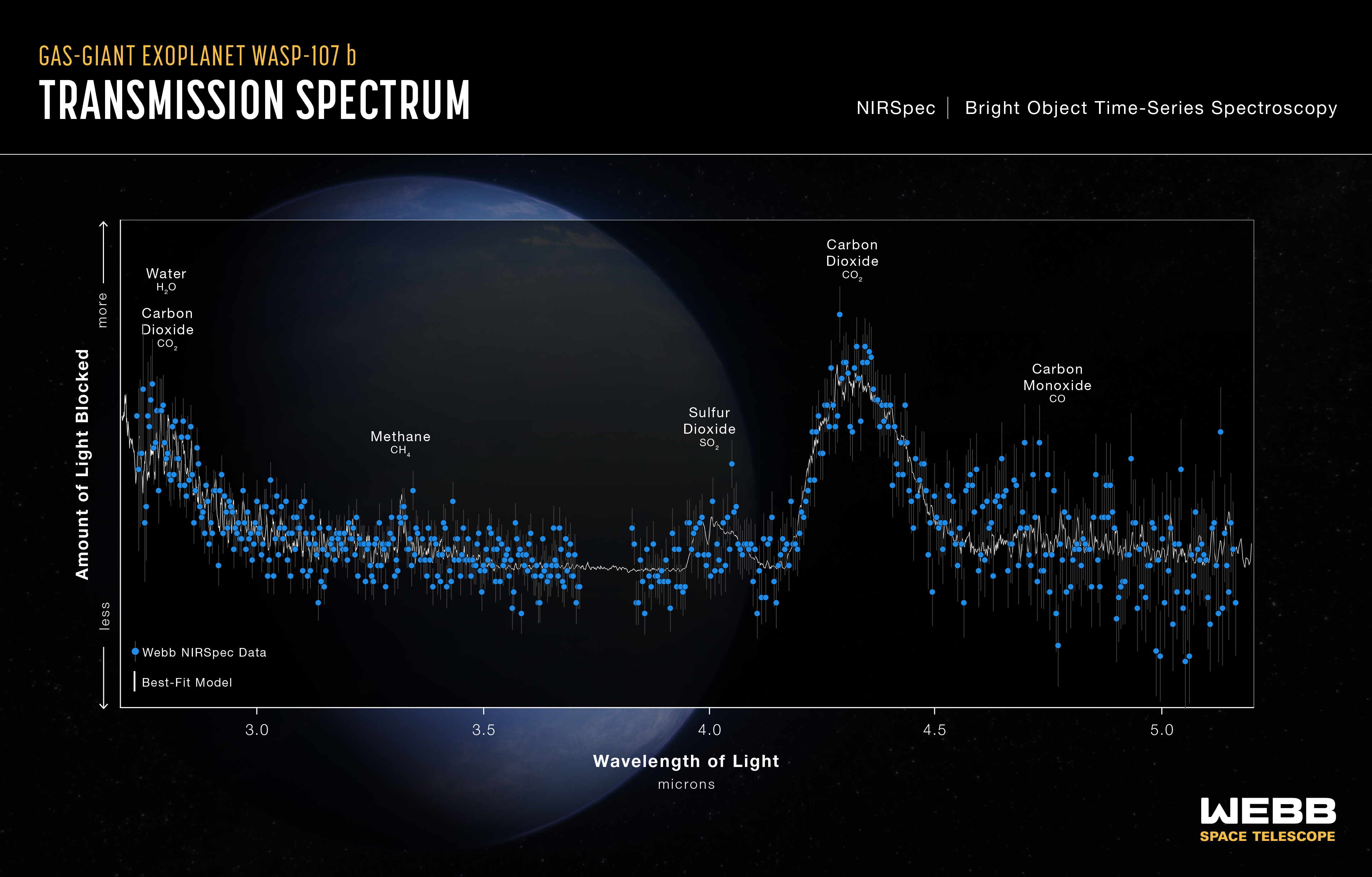
Warm Gas-Giant Exoplanet WASP-107 b Transmission Spectrum (NIRSpec)
This transmission spectrum, captured using Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph), shows the amounts of different wavelengths (colors) of near-infrared starlight blocked by the atmosphere of the gas-giant exoplanet WASP-107 b . The spectrum was made by observing the...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)

























