1 min read
Wolf-Rayet 140 (MIRI Compass Image)

This 2023 image of Wolf-Rayet 140, a system of dust shells ejected by two massive stars at the center, was captured by the James Webb Space Telescope’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument).
The image shows a scale bar, compass arrows, and color key for reference.
The scale bar is labeled in light-years along the bottom, which is the distance that light travels in one Earth-year. One light-year is equal to about 5.88 trillion miles or 9.46 trillion kilometers. The scale bar is also labeled in arcminutes, which is a measure of angular distance on the sky. One arcsecond is equal an angular measurement of 1/3600 of one degree. There are 60 arcminutes in a degree and 60 arcseconds in an arcminute. (The full Moon has an angular diameter of about 30 arcminutes.) The actual size of an object that covers one arcsecond on the sky depends on its distance from the telescope.
The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative to direction arrows on a map of the ground (as seen from above).
This image shows mid-infrared wavelengths of light that have been translated into visible-light colors. The color key shows which MIRI filters were used when collecting the light. The color of each filter name is the visible-light color used to represent the infrared light that passes through that filter.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.20:20:27.98
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+43:51:16.28
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Cygnus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.5,600 light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from JWST data from proposals 1349 and 3823 (R. Lau); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.MIRI
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.27 July 2022 and 9 September 2023
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F770W, F1500W, F2100W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Wolf-Rayet 140; WR 140
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Wolf-Rayet Star
- Release DateJanuary 13, 2025
- Science ReleaseWebb Watches Carbon-Rich Dust Shells Form, Expand in Star System
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI; Science: Emma Lieb (University of Denver), Ryan Lau (NSF's NOIRLab), Jennifer Hoffman (University of Denver)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the MIRI instrument. Several filters were used to sample different infraraed wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Red: F2100W Green: F1500W Blue: F770W
Related Images & Videos
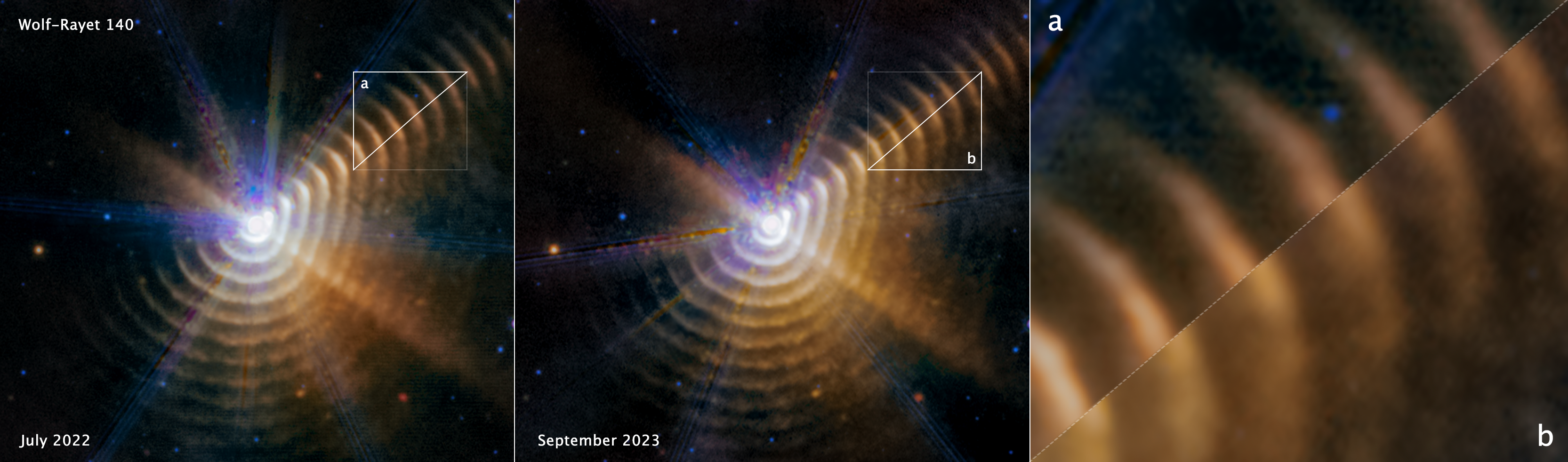
Compare Observations of Wolf-Rayet 140 (MIRI Images)
Watch dust move in space! Compare the two mid-infrared images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope of Wolf-Rayet 140, a system of dust shells ejected by two massive stars that are in an elongated orbit. Look to the top right of the first two images. Two triangles are matched...
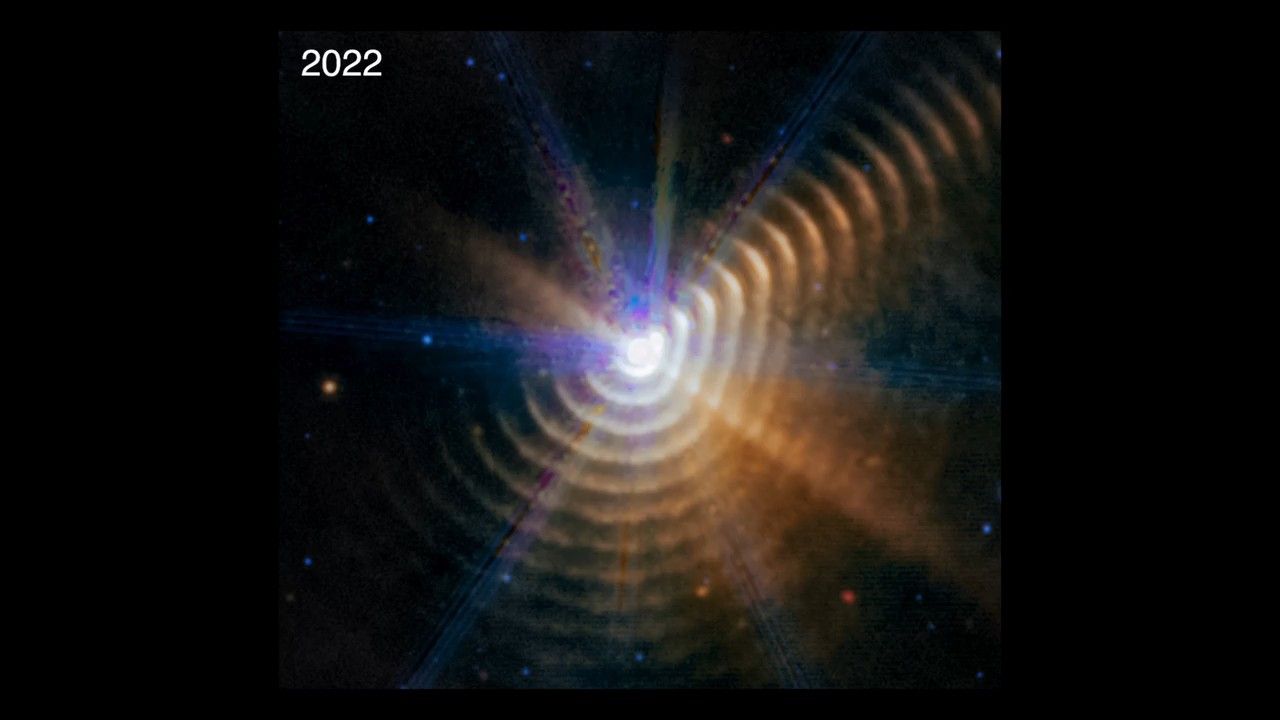

Fade Between 2022 and 2023 Observations of Wolf-Rayet 140
This video alternates between two James Webb Space Telescope observations of Wolf-Rayet 140, a two-star system that has sent out more than 17 shells of dust over 130 years. Mid-infrared light observations highlight them with excellent clarity. By comparing this pair of...
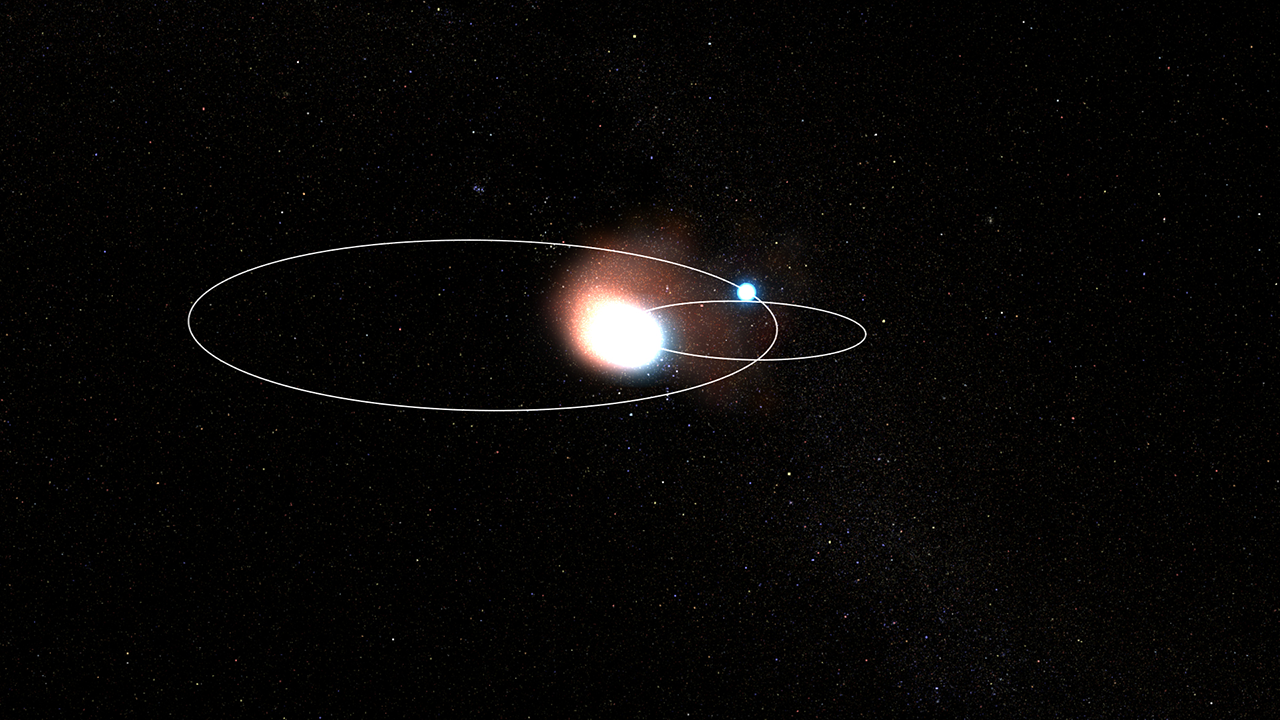
Stars’ Orbits in Wolf-Rayet 140 (Visualization)
When the two massive stars in Wolf-Rayet 140 swing past one another, their winds collide, material compresses, and carbon-rich dust forms. The stronger winds of the hotter Wolf-Rayet star blow behind its slightly cooler (but still hot) companion. The stars create dust for...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
Emma Lieb (University of Denver), Ryan Lau (NSF’s NOIRLab), Jennifer Hoffman (University of Denver)
































