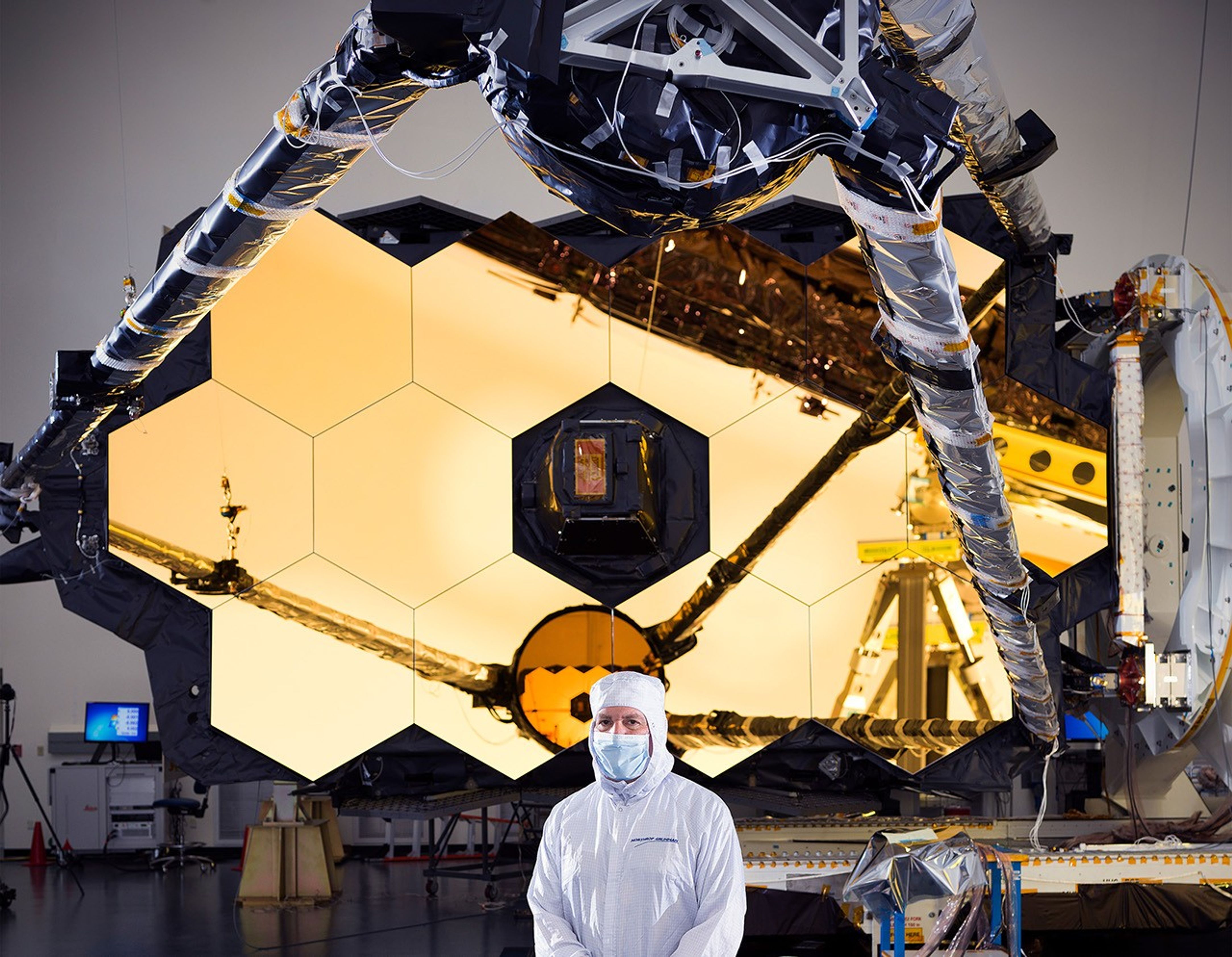
James Webb Space Telescope
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the history of our Universe.

Key Facts
Featured Image

NASA’s Webb Examines Cranium Nebula
Two heads are better than one in the latest images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, which reveal new detail…
Read the Story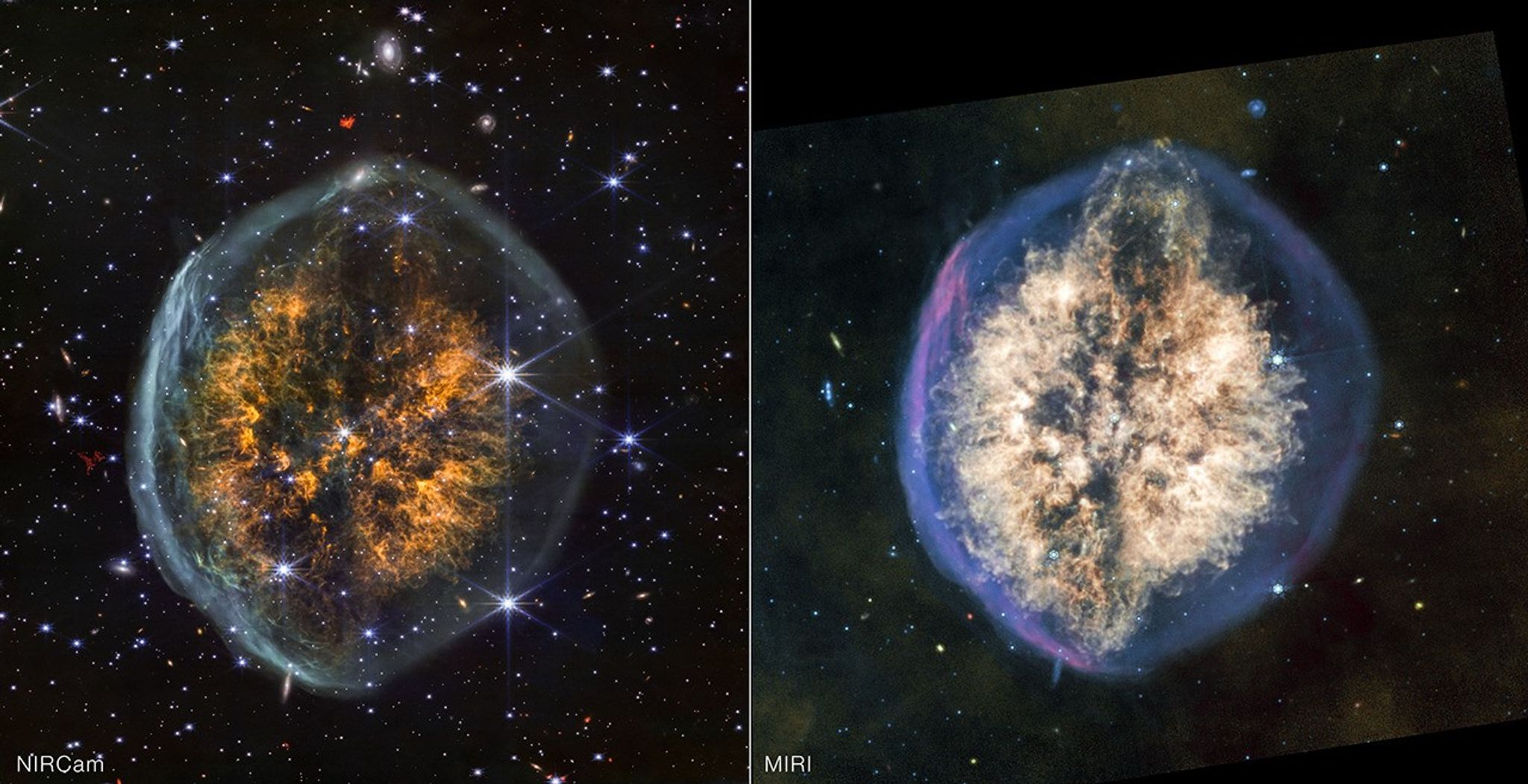
Featured Webb Award
Jan 7, 2026
Webb Receives the SPIE 2026 George W. Goddard Award in Space and Airborne Optics
Awarded to Lee Feinberg, recognizing outstanding leadership through the design, integration, and delivery of optical systems that brought the objectives of the Webb and Hubble space telescopes into clear focus.
Latest News
The feed below is a mix of Webb Science Releases and associated images/videos, Webb Science Blogs, Webb press releases and articles tagged with "James Webb Space Telescope". To filter out everything except the Webb Science Releases (or Science Blogs) - simply select that filter check box. Webb Science Releases, images, videos and Webb's Science Blogs can also be filtered by Webb's four primary science themes.
Filter, Search and Sort Notes: Initial filtered results displayed below show all articles that match ANY of the filters for all dates. Once one or more filter options are checked , only articles that MATCH ANY (logical OR) of the checked filters are displayed within the date range selected. The MATCH ALL (logical AND) filter operator will reduce the matching set to only those articles that match ALL checked filters within the date range. The "Search Latest Content" box searches for the terms entered within the subset of filtered articles. You can also sort the results by date in descending (newest first) or ascending (oldest first).
Filters

Two heads are better than one in the latest images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, which reveal new detail…

The differences in what Webb’s infrared instruments reveal and conceal within the PMR 1 “Exposed Cranium” nebula is apparent in…

These images of the “Exposed Cranium” nebula PMR 1, captured by the James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and…

This video compares infrared views of the PMR 1 “Exposed Cranium” nebula taken by NASA’s retired Spitzer Space Telescope, as…
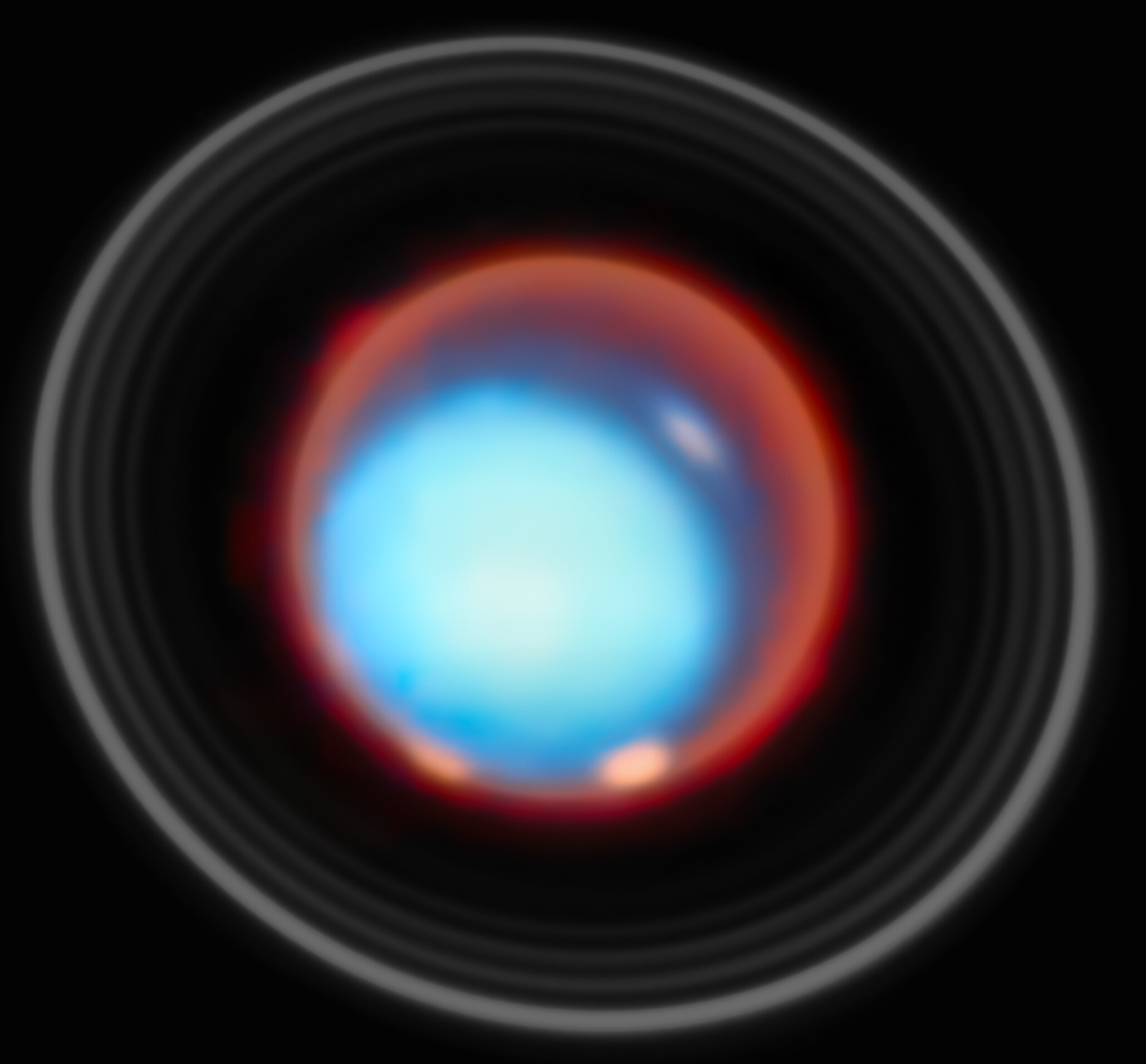

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope provided the first vertical view of Uranus’s ionosphere in this image released on Feb. 19,…

Forty million years ago, a star in a nearby galaxy exploded, spewing material across space and generating a brilliant beacon…

The main image at left shows a combined Webb and Hubble view of spiral galaxy NGC 1637. Panels at right…

Image of galaxy NGC 1637 captured by Hubble’s WFC3 and Webb’s NIRCam, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key…

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has “supercharged” what astronomers know about star formation with its sharp near- and mid-infrared observations.…
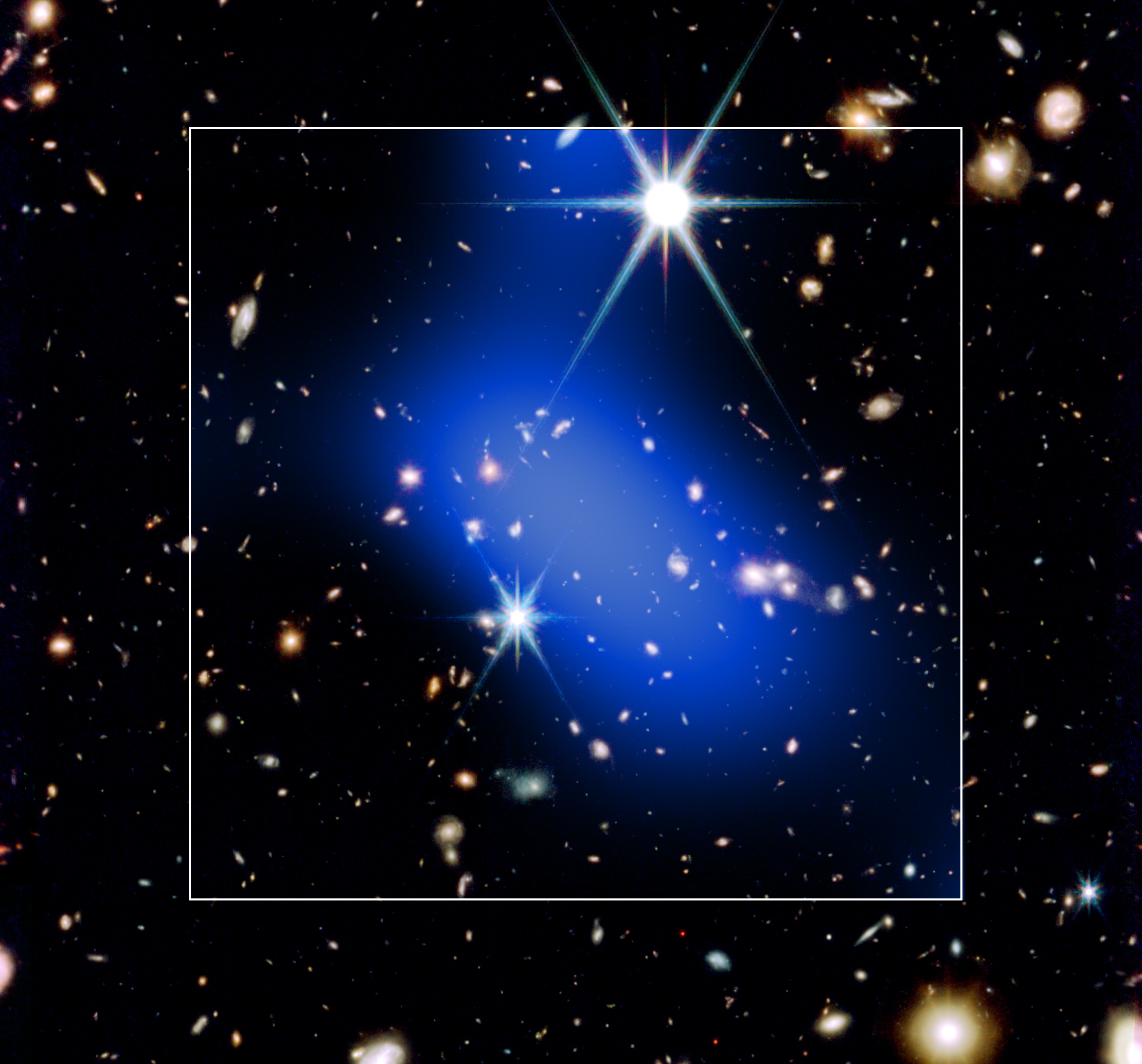

A new discovery captures the cosmic moment when a galaxy cluster – among the largest structures in the universe –…

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has topped itself once again, delivering on its promise to push the boundaries of the…

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope shows galaxy MoM-z14 as it appeared in the distant past, only 280 million years after…

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope shows galaxy MoM-z14 as it appeared in the distant past, only 280 million years after…

With the Webb telescope’s unprecedented sensitivity, scientists are learning more about dark matter’s influence on stars, galaxies, and even planets…

Astronomers have long sought evidence to explain why comets at the outskirts of our own solar system contain crystalline silicates,…
Webb's Blog
Webb's Blog offers an insider's point of view covering a variety of topics. The feed below supports a deeper dive into Webb's Blog which contains early release science (not yet peer reviewed) as well as Webb Mission Operations and Webb Engineering posts - you can filter on any/all of these post types as well as filter Webb Science Blogs by Webb's four primary science themes.
Filter, Search and Sort Notes: Initial filtered results displayed below show all articles that match ANY of the filters for all dates. Once one or more filter options are checked , only articles that MATCH ANY (logical OR) of the checked filters are displayed within the date range selected. The MATCH ALL (logical AND) filter operator will reduce the matching set to only those articles that match ALL checked filters within the date range. The "Search Latest Content" box searches for the terms entered within the subset of filtered articles. You can also sort the results by date in descending (newest first) or ascending (oldest first).
Filters
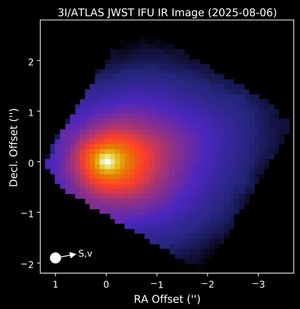
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope observed interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS Aug. 6, with its Near-Infrared Spectrograph instrument. The research team has…

Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process.…

Editor’s Note: This post highlights a combination of peer-reviewed results and data from Webb science in progress, which has not…

While asteroid 2024 YR4 is currently too distant to detect with telescopes from Earth, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope collected one…
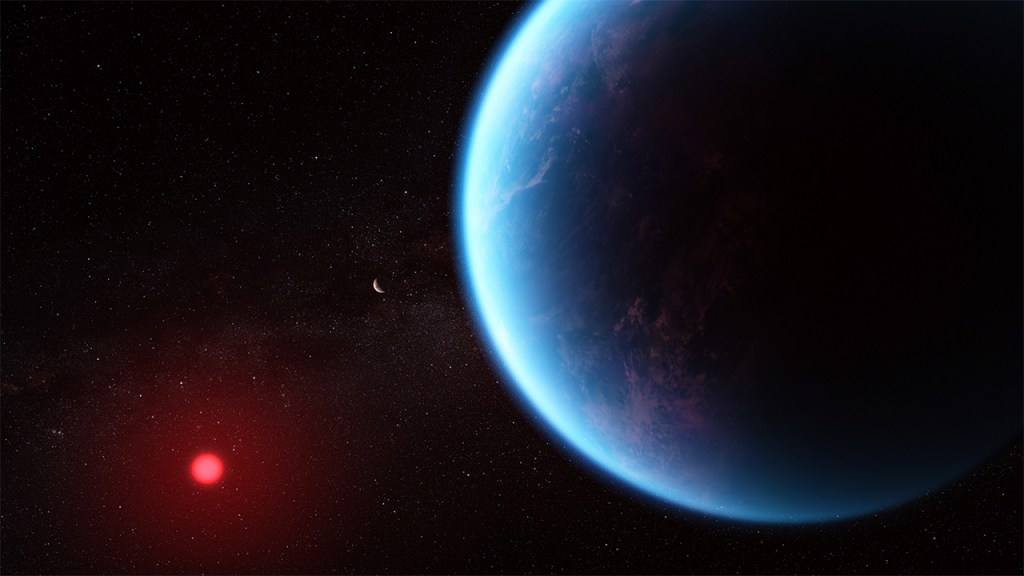

This artist’s concept shows what exoplanet K2-18 b could look like based on science data. K2-18 b, an exoplanet 8.6…

Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process. These…

Trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) are icy bodies ranging in size from Pluto and Eris (dwarf planets with diameters of about 1,500…

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is the largest and most powerful telescope ever launched to space. Its mirror is composed…
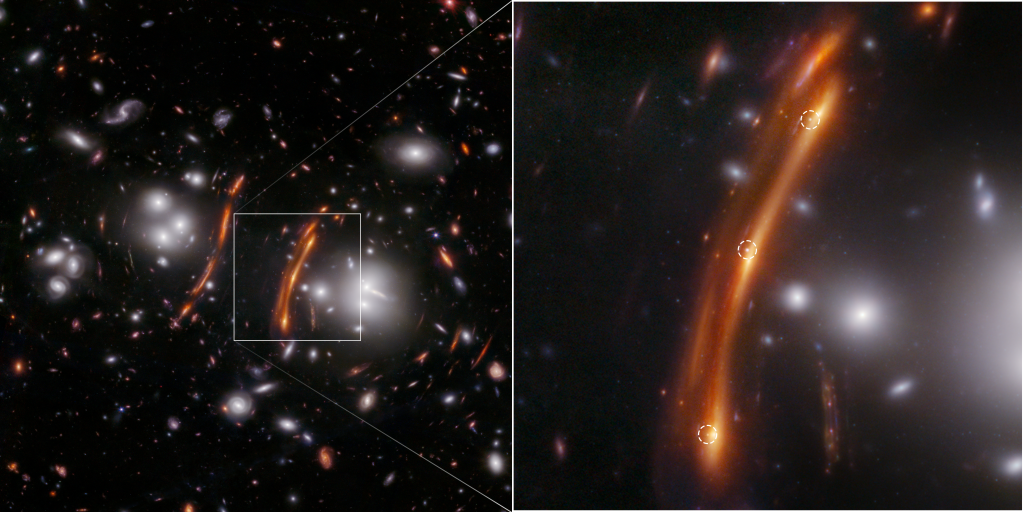

Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process. Measuring…
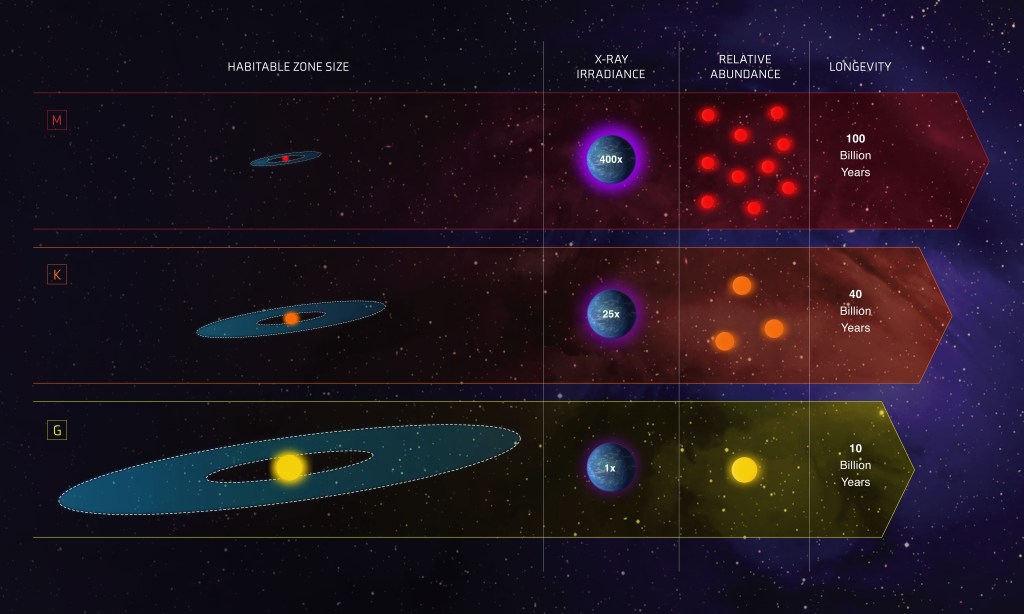
Exoplanets are common in our galaxy, and some even orbit in the so-called habitable zone of their star. NASA’s James…
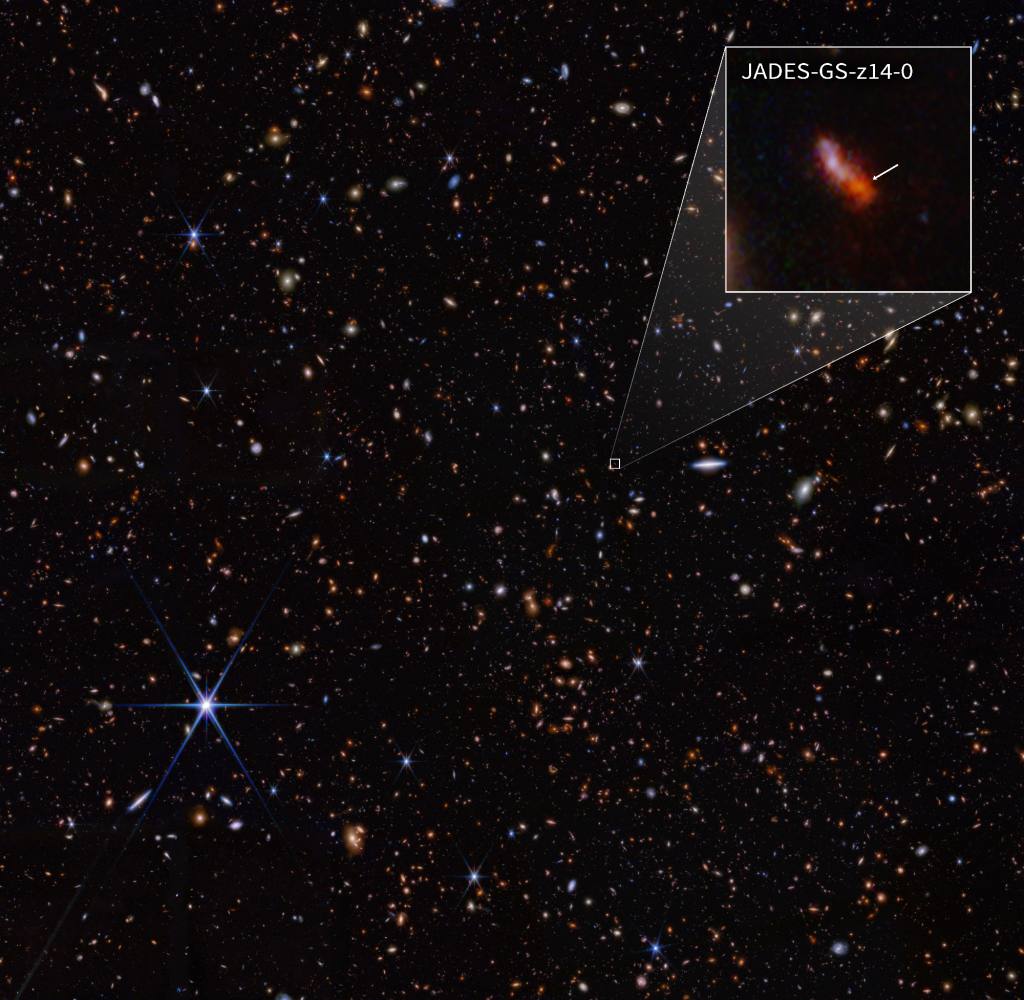

Editor’s Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process.…
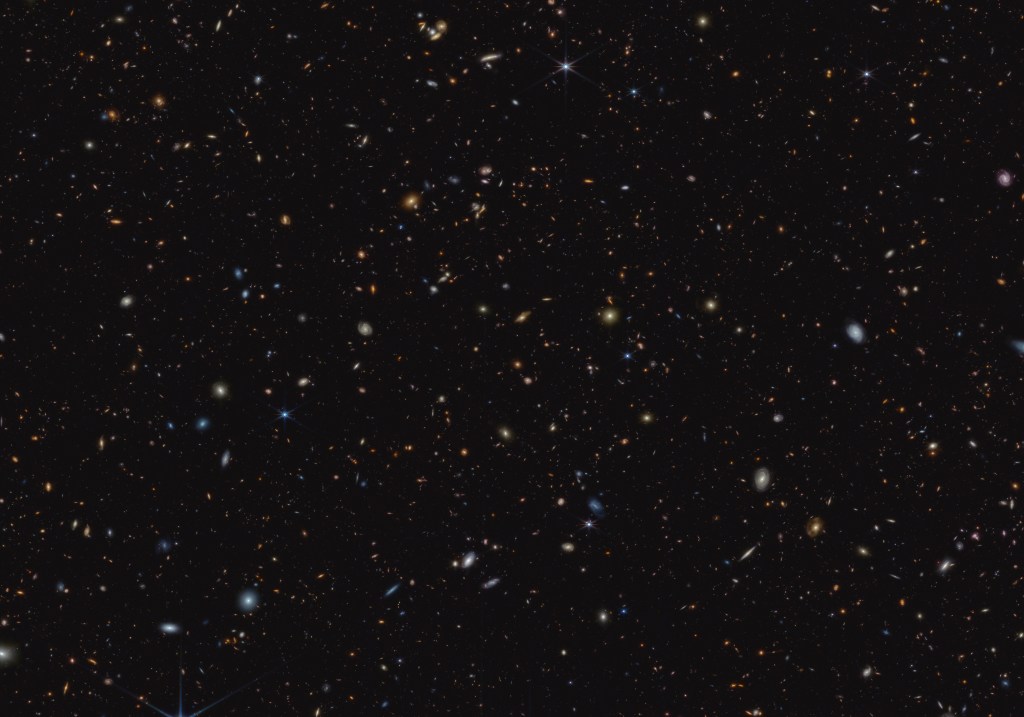

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is delivering on its promise to explore the farthest reaches of the universe, looking back…

Editor's Note: This post highlights data from Webb science in progress, which has not yet been through the peer-review process.…

One of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's science goals is to understand how galaxies in the early universe formed and…

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope observed the exoplanet WASP-80 b as it passed in front of and behind its host…
Latest 2026 Images
The image below is a SLIDESHOW. Hover over the image to see the image title and controls. Click the image to go to a detail page with more info and the ability to download the image at various resolutions (click the downward arrow icon in lower right corner).
More Webb Images
What is Webb Observing?
See current, upcoming and recent past observations scientists are making with the Webb Space Telescope. View details about each observation's science focus areas, the instruments used and more.
View the Tool
The Webb Mission
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the history of our Universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own Solar System.
Learn More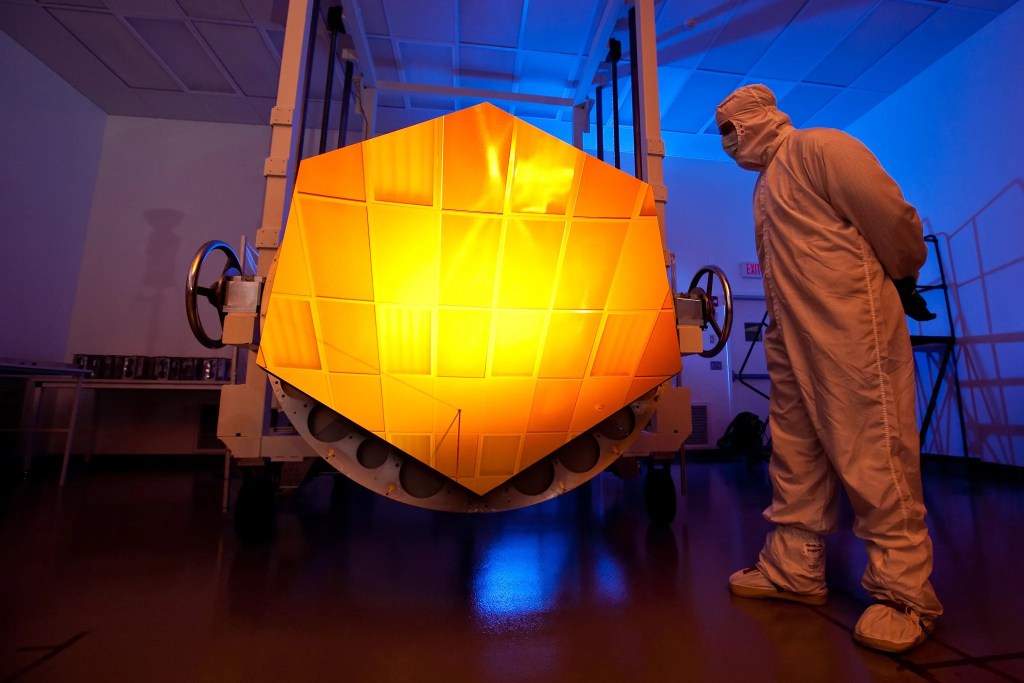
Webb's Science Goals
The James Webb Space Telescope is a giant leap forward in our quest to understand the Universe and our origins. Webb is examining every phase of cosmic history: from the first luminous glows after the Big Bang to the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets to the evolution of our own solar system. Learn about the 4 main science themes for Webb.
Learn More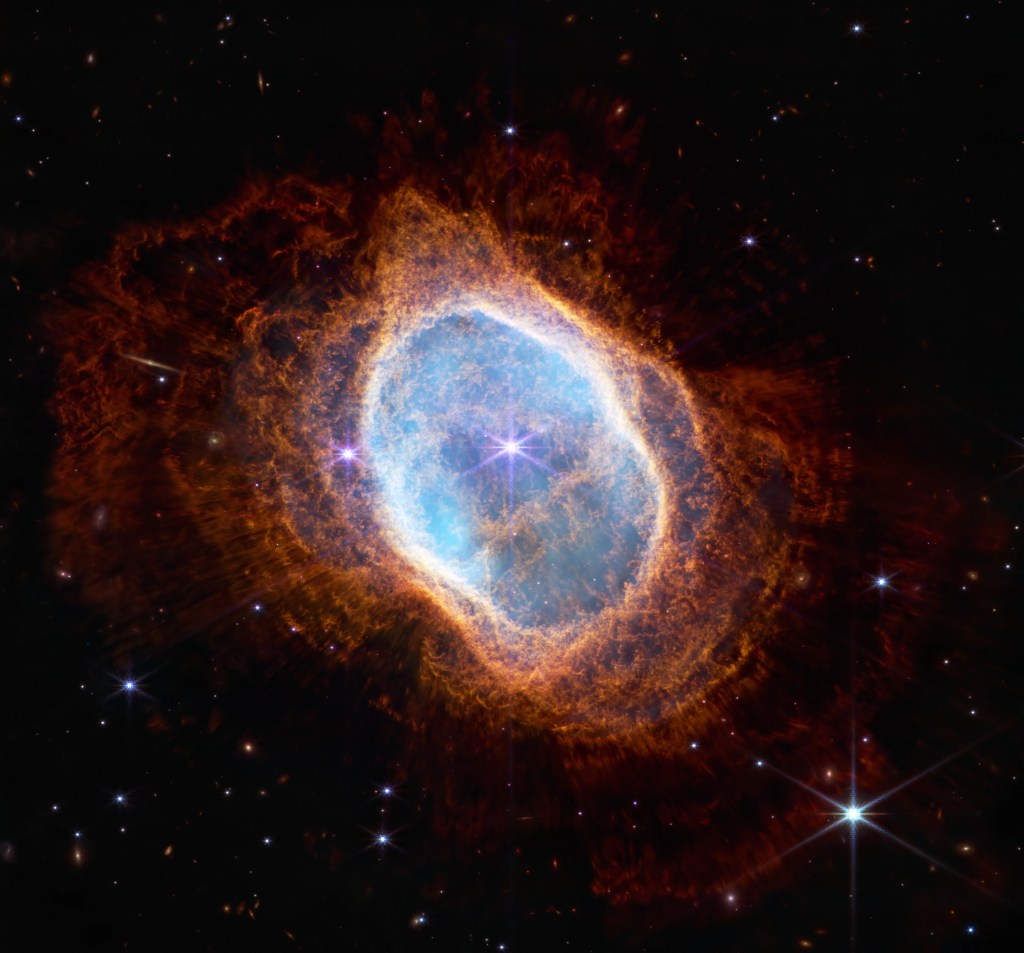
The Spacecraft
The Webb Space Telescope is the largest, most powerful and most complex telescope ever launched into space . It's design and development history stretches back before the Hubble Space Telescope was launched. Learn about the design, the major components and subsystems of Webb and see Webb in 3d in a 3d Solar System.
Learn More
The International Webb Team
Webb is for the world, and from the world. Thousands of skilled scientists, engineers and technicians from 14 countries (and more than 29 U.S. states, and Washington, D.C.) contributed to the design, build, test, integration, launch, commissioning and operations of Webb. It is a joint NASA/ESA/CSA mission. Assembly and testing of the mirror and instruments occurred at NASA Goddard (GSFC).
Learn More
Do NASA Science with Galaxy Zoo!
-
Join NASA researchers and help discover the secrets of the universe.
NASA invites people of all ages and backgrounds to participate in authentic NASA research via "citizen science" or "participatory science" projects, where volunteers and amateurs have helped make thousands of important scientific discoveries! As a part of the Galaxy Zoo project, you can help classify the latest images of galaxies from NASA's Webb telescope.









































