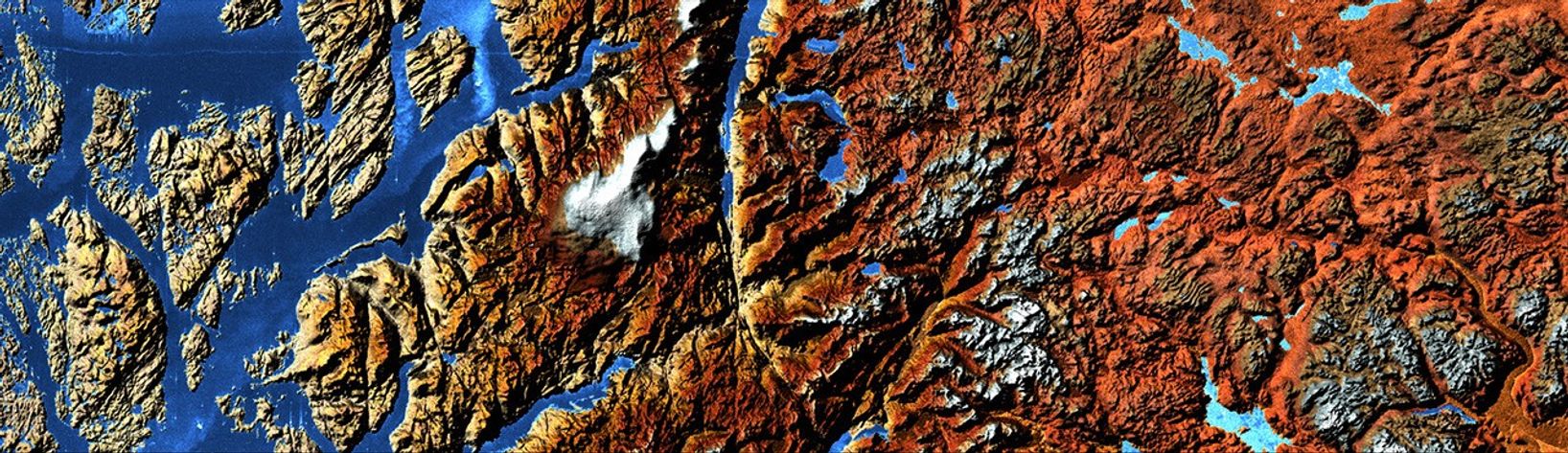
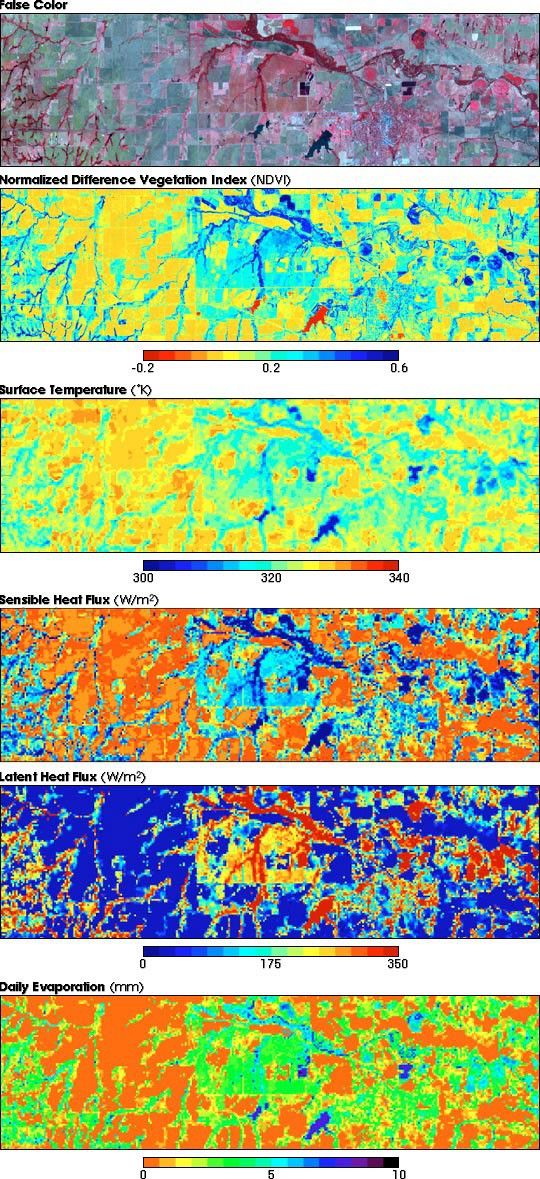
The Norwegian Fjords are steep, ice-carved valleys that stretch from the landout into the sea. Fjords are created not solely by glacier erosion, butalso by the high-pressure melt water that flows beneath the ice. Fjordvalleys can be carved hundreds to thousands of meters below sea level. TheHardangerfjorden shown in this image is about 179 km long, and reaches itsmaximum depth of more than 800 m about 100 km inland.
In the above image, based on elevation data collected by theShuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), beige and yellow represent low elevations,while red, brown and white represent progressively higher elevations. Shades of blue representwater. The Hardangerfjord is left of center, and extends off the top of theimage. Sorfjorden is towards the right edge of the image.
The location of a fjord may be due to pre-glacial valleys, bedrockcharacteristics, or fractures in the Earth's crust. Fjords typically have U-shaped cross-sectional profiles, with the valley floor being flat or onlyslightly rounded. The fjord's longitudinal profile usually consists of aseries of basins separated by rock barriers or moraine sills (glacialdebris). Fjord entrances are usually quite shallow with shoals and smallislands. Usually the deep basins are situated some distance inland from themouth of the fjord. The shallow mouths are places where the glaciers thatonce filled the valley either began to float, or else had room to spreadout. Inland, the glaciers were more confined, and so they carved more deeplyinto the Earth.
About 10,000 years ago, at the end of the last major glaciation, theScandinavian land mass began slowly rising up as warmer temperatures freedit from the enormous weight of glacial ice, a process called glacialrebound. However, the land's increased buoyancy did not keep pace with therising sea level, and the lower parts of formerly glaciated valleys becameflooded. The glacial rebound of the Scandinavian land mass is stilloccurring.
References & Resources
Image courtesy German Remote Sensing Data Center, based on data from the SRTM.