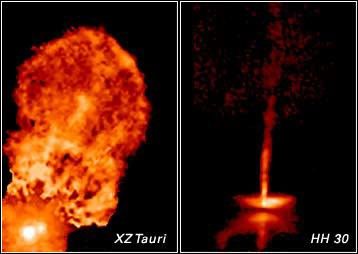
Time-lapse movies made from a series of pictures taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope are showing astronomers that young stars and their surroundings can change dramatically in just weeks or months. As with most children, a picture of these youngsters taken today won't look the same as one snapped a few months from now. The movies show jets of gas plowing into space at hundreds of thousands of miles per hour and moving shadows billions of miles in size. The young star systems featured in the movies, XZ Tauri and HH 30, reside about 450 light-years from Earth in the Taurus-Auriga molecular cloud, one of the nearest stellar nurseries to our planet. Both systems are probably less than a million years old, making them relative newborns, given that stars typically live for billions of years.
1 min read
Movies from Hubble Show the Changing Faces of Infant Stars
Related Images & Videos
Movies from Hubble Show the Changing Faces of Infant Stars
Time-lapse movies made from a series of pictures taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope are showing astronomers that young stars and their surroundings can change dramatically in just weeks or months. As with most children, a picture of these youngsters taken today won't look...

Hot Gas Bubble Ejected by Young Binary Star System XZ Tauri
These images taken with the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 reveal the evolution of bubbles of glowing gas being blown out from the young binary star system XZ Tauri. Gas from an unseen disk around one or both of the stars is channeled through magnetic...

Young Star HH30's Dynamic Disk and Jets
These images of HH 30 show changes over only a five-year period in the disk and jets of this newborn star, which is about half a million years old. The pictures were taken between 1995 and 2000 with the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope....
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
XZ Tauri image: NASA, John Krist (Space Telescope Science Institute), Karl Stapelfeldt (Jet Propulsion Laboratory), Jeff Hester (Arizona State University), Chris Burrows (European Space Agency/Space Telescope Science Institute);
HH 30 image: NASA, Alan Watson (Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico), Karl Stapelfeldt (Jet Propulsion Laboratory), John Krist (Space Telescope Science Institute) and Chris Burrows (European Space Agency/ Space Telescope Science Institute)