Science Highlights
Hubble has affected every area of astronomy. Its most notable scientific discoveries reflect the broad range of research and the breakthroughs it has achieved.
Quick Facts
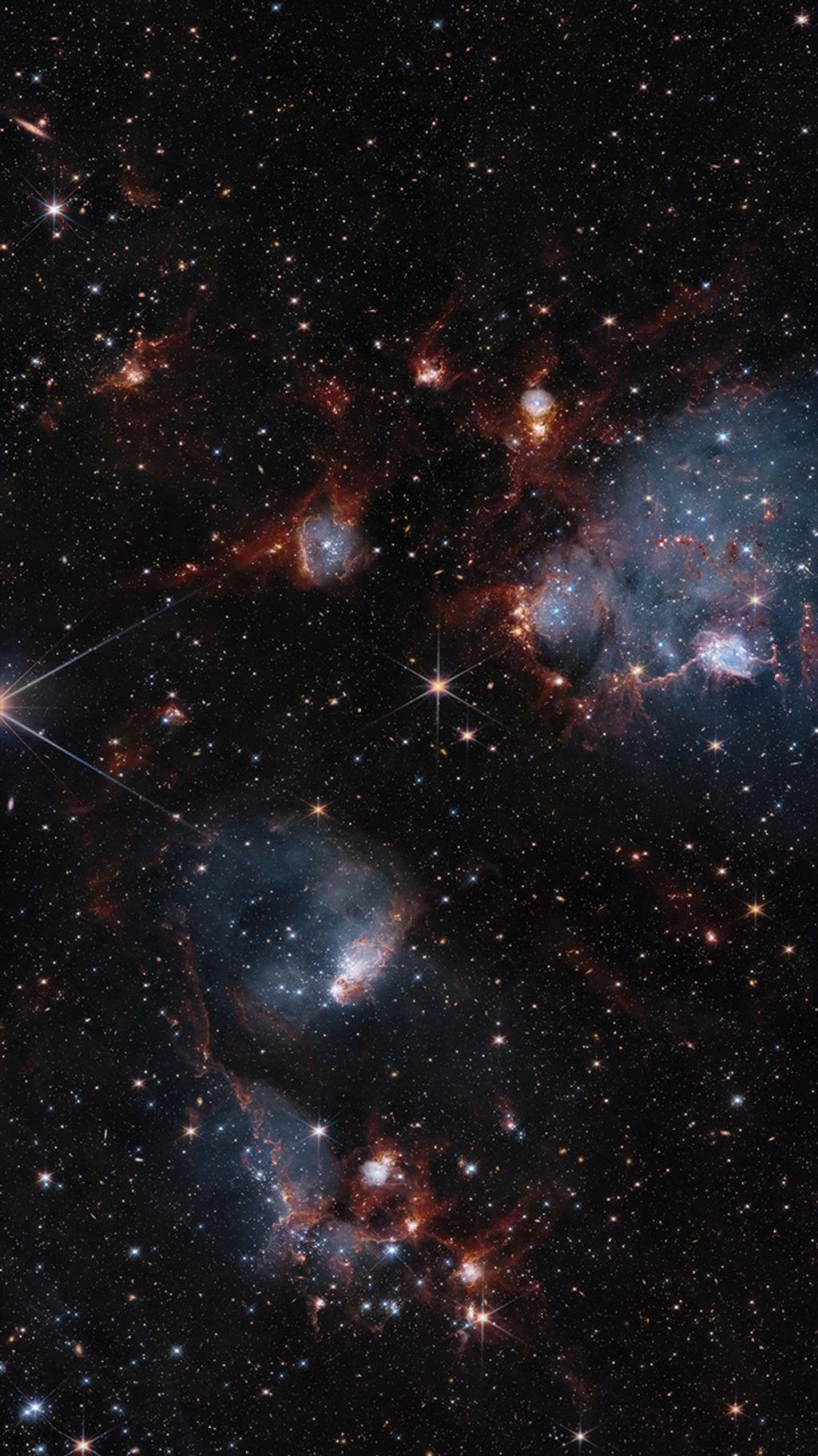
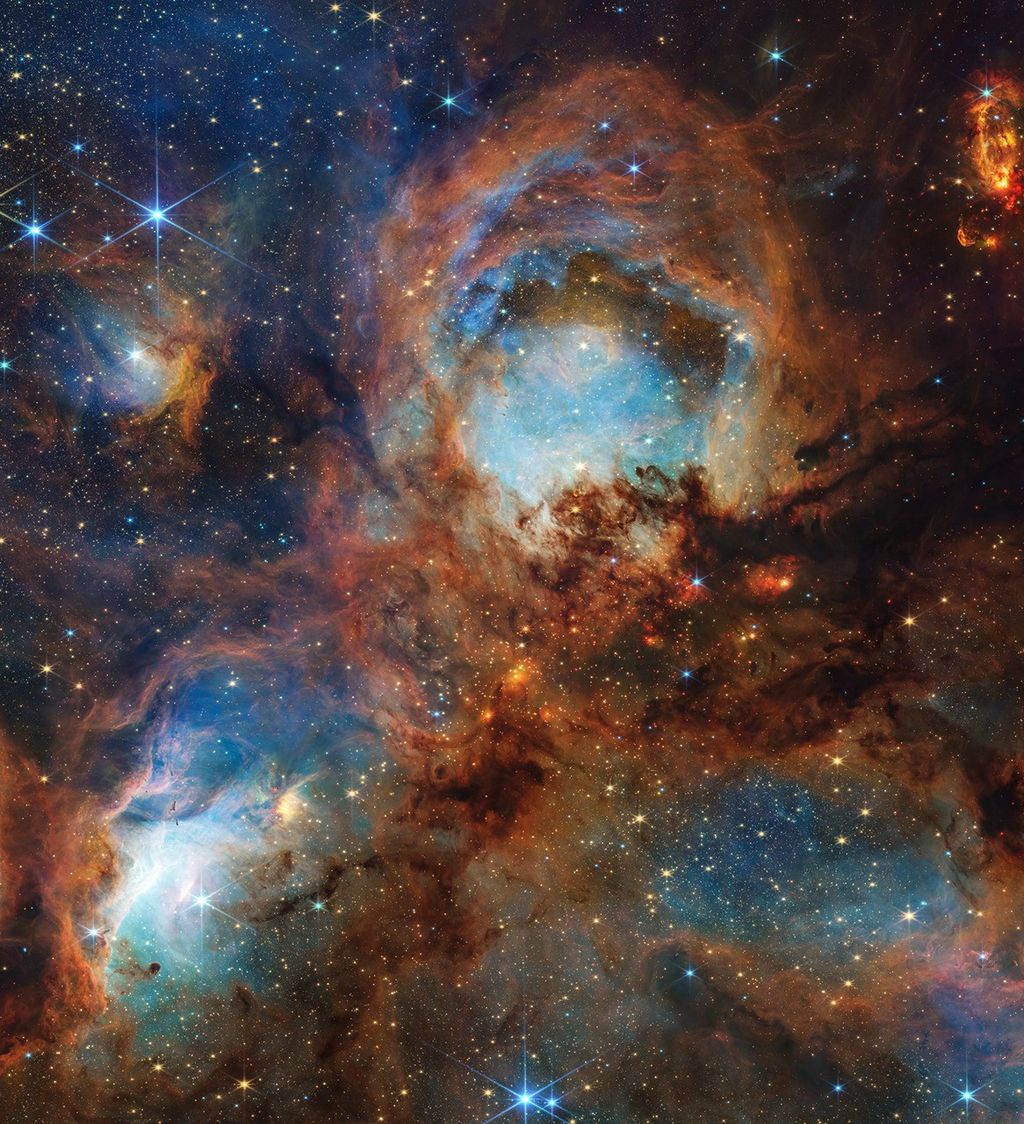
Since its launch in 1990, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has offered us stunning images that capture the awe-inspiring beauty of the universe, but Hubble is far more than pretty pictures. In its three-plus decades of exploration, Hubble has generated as many questions as it has answered — uncovering new mysteries while expanding our understanding of the universe in ways we never imagined. Its scientific instruments gather wavelengths of light from ultraviolet, through visible, and into the near-infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble’s sensitivity to such a broad range of wavelengths makes it one of the most valuable and productive observatories in the history of astronomy. As of February 2024, it exceeds one million observations, from which astronomers have written more than 21,000 peer-reviewed scientific papers. More than 1.2 million publications reference those original papers — a number that increases by an average exceeding 150 per day. Hubble’s extensive archive of observations also allows astronomers to study astronomical objects that display subtle changes over time; these have helped shape our understanding of the very nature and evolution of the universe. Every modern astronomy textbook includes contributions from Hubble.
Developed as a partnership between the United States space program and the European Space Agency, Hubble orbits 320 miles (515 km) above Earth’s surface. Its location above the distorting effects of our atmosphere allows Hubble to observe astronomical objects and phenomena more consistently and with better detail than is attainable from most ground-based observatories. The telescope's sensitive instruments can view objects near and far — from small colliding asteroids in our solar system, to distant star-forming galaxies that date back to when the universe was only three percent of its current age. Hubble observations have made key discoveries that characterize the structure and evolution of the universe, galaxies, nebulae, stars, exoplanets, and our solar system neighbors.
Well into its third operational decade, Hubble continues to be extremely productive. It exceeds one million observations, from which astronomers have written more than 21,000 peer-reviewed scientific papers. More than 1.2 million publications reference those original papers – a number that increases by an average exceeding 150 per day. Every current astronomy textbook includes contributions from Hubble.
Hubble's observations have pushed the boundaries of our knowledge and have created a string of accomplishments that are unparalleled. The following list holds just a few examples of those scientific achievements:
- First time elements detected from early universe
- First confirmation that supermassive black holes exist
- First to prove that black holes are at the cores of almost all galaxies
- First images of the collision of two astronomical objects
- First to detect oxygen in a satellite’s atmosphere
- First images of a star's surface other than our Sun
- First visual evidence of planetary building blocks
- First exoplanet atmosphere detected and elements determined
- First visual evidence of a planet’s atmosphere evaporating away into space
- First organic molecules detected in an exoplanet atmosphere
- First photographs of an asteroid with tails
- First to detect water vapor plumes off of Europa
- First space-based images of an asteroid breaking
- First image of the first-ever predicted supernova
- Farthest galaxy ever imaged at the time
- Farthest individual star ever imaged at the time
- First detection of water vapor on an exoplanet in the habitable zone
- First ultraviolet image of an exoplanet in formation
- First detection of a possible moon around an exoplanet
- First precision measurement of the expansion rate of the universe
- First confirmation that the Andromeda Galaxy may collide with our Milky Way Galaxy, and Hubble Casts Doubt on Certainty of Galactic Collision
In its three-plus decades of exploration, Hubble has generated as many questions as it has answered – uncovering new mysteries while expanding our understanding of the universe in ways we never imagined.
The stories you find here represent a small sample of Hubble’s thought-provoking discoveries and images. Selecting this set from the thousands of awe-inspiring Hubble observations was difficult, but they serve to highlight some of Hubble’s greatest scientific achievements to date.
Hubble Science Highlights
The stories you find here represent a small sample of Hubble’s thought-provoking discoveries and images. Selecting this set from the thousands of awe-inspiring Hubble observations was difficult, but they serve to highlight some of Hubble’s greatest scientific achievements to date.
Our Solar System
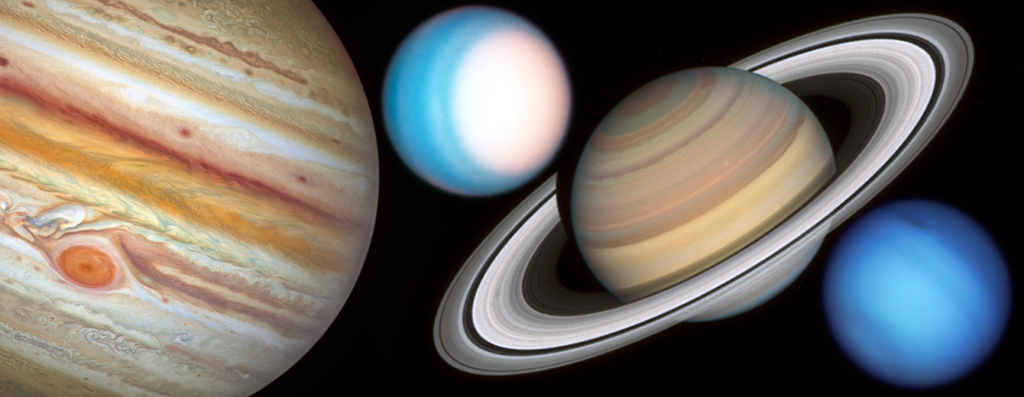
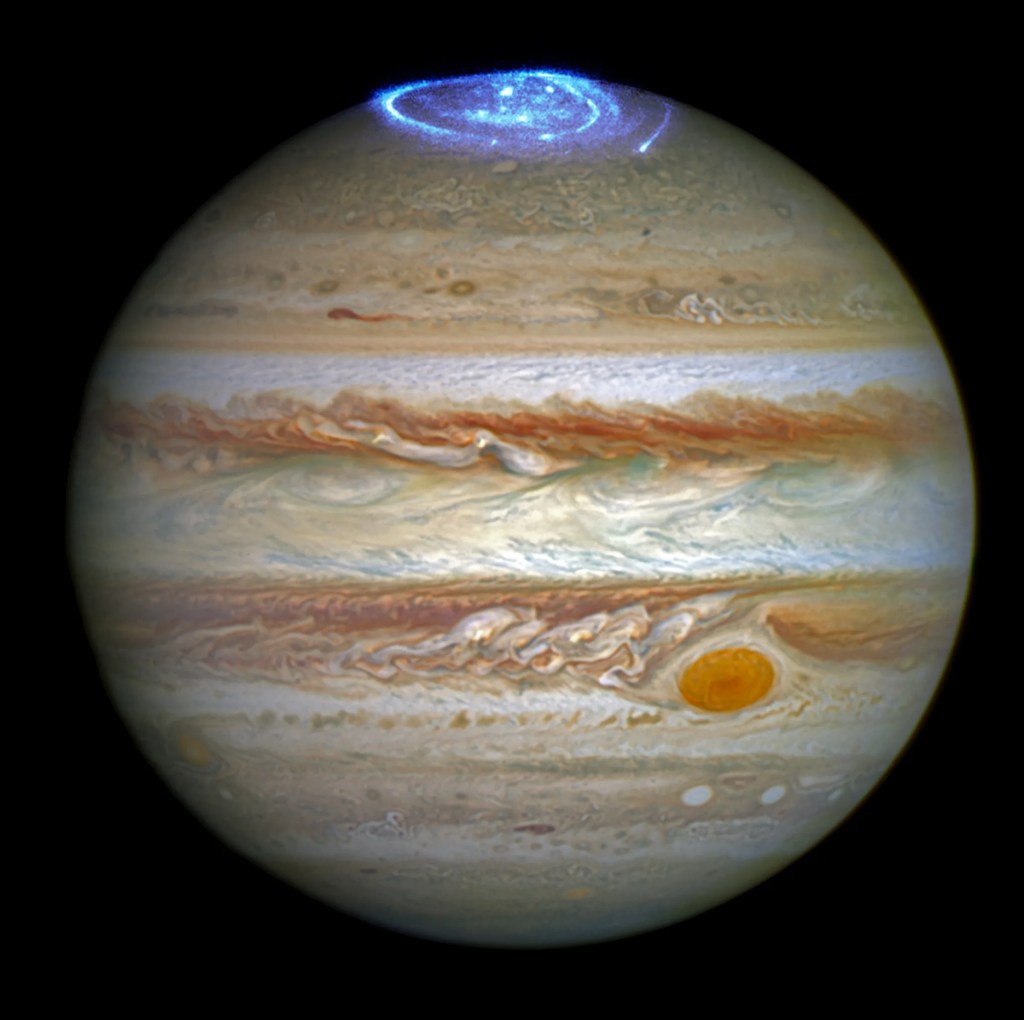
Studying the Planets and Moons
Hubble’s systematic observations chart the ever-changing environments of our solar system's planets and their moons.

Tracking Evolution in the Asteroid Belt
These conglomerates of rock and ice may hold clues to the early solar system.
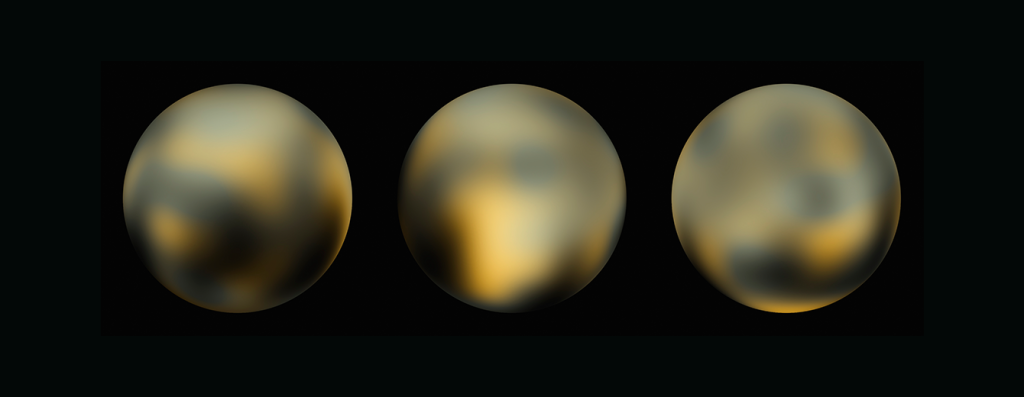
Uncovering Icy Objects in the Kuiper Belt
Hubble’s discoveries helped NASA plan the New Horizon spacecraft’s flyby of Pluto and beyond.
Our Galaxy
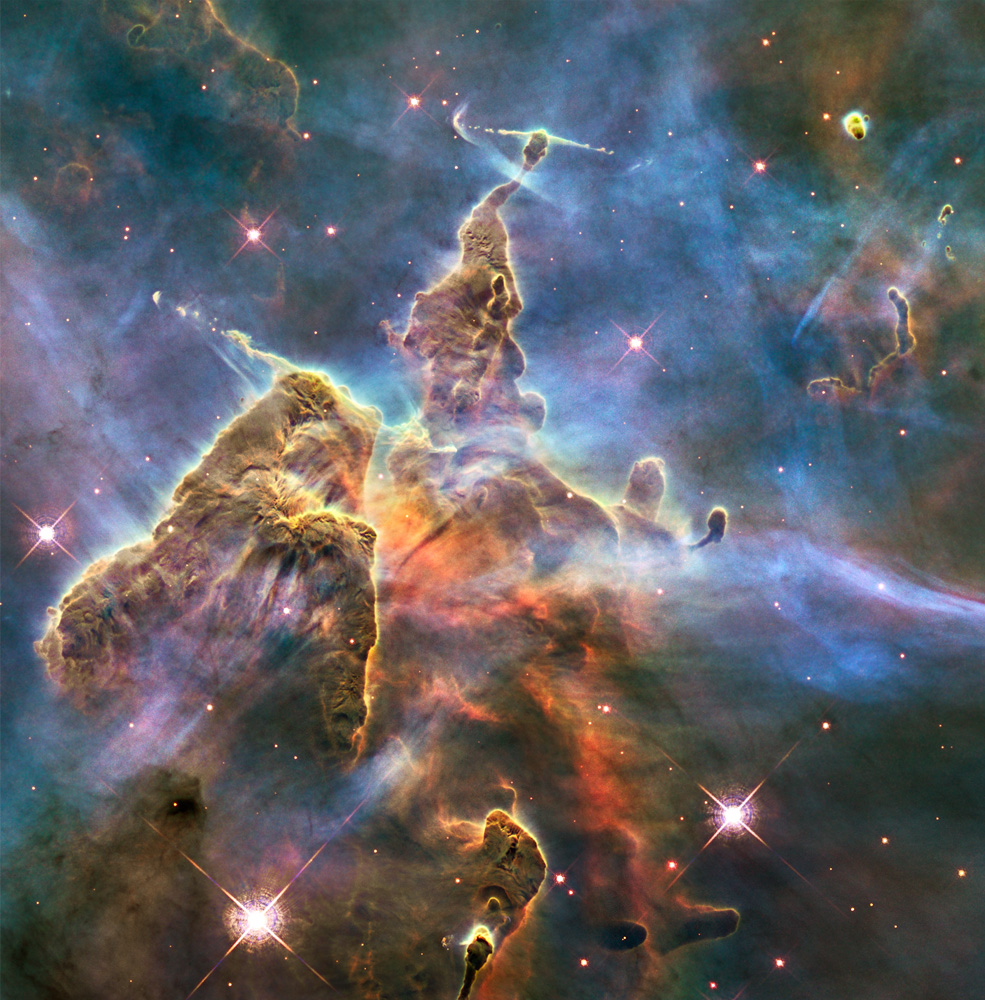

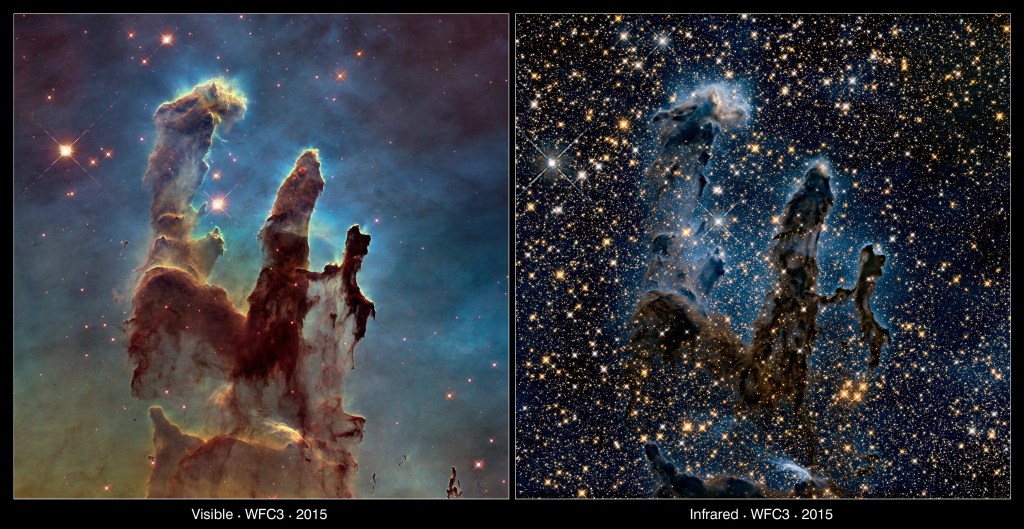
Exploring the Birth of Stars
Seeing ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light helps Hubble uncover the mysteries of star formation.
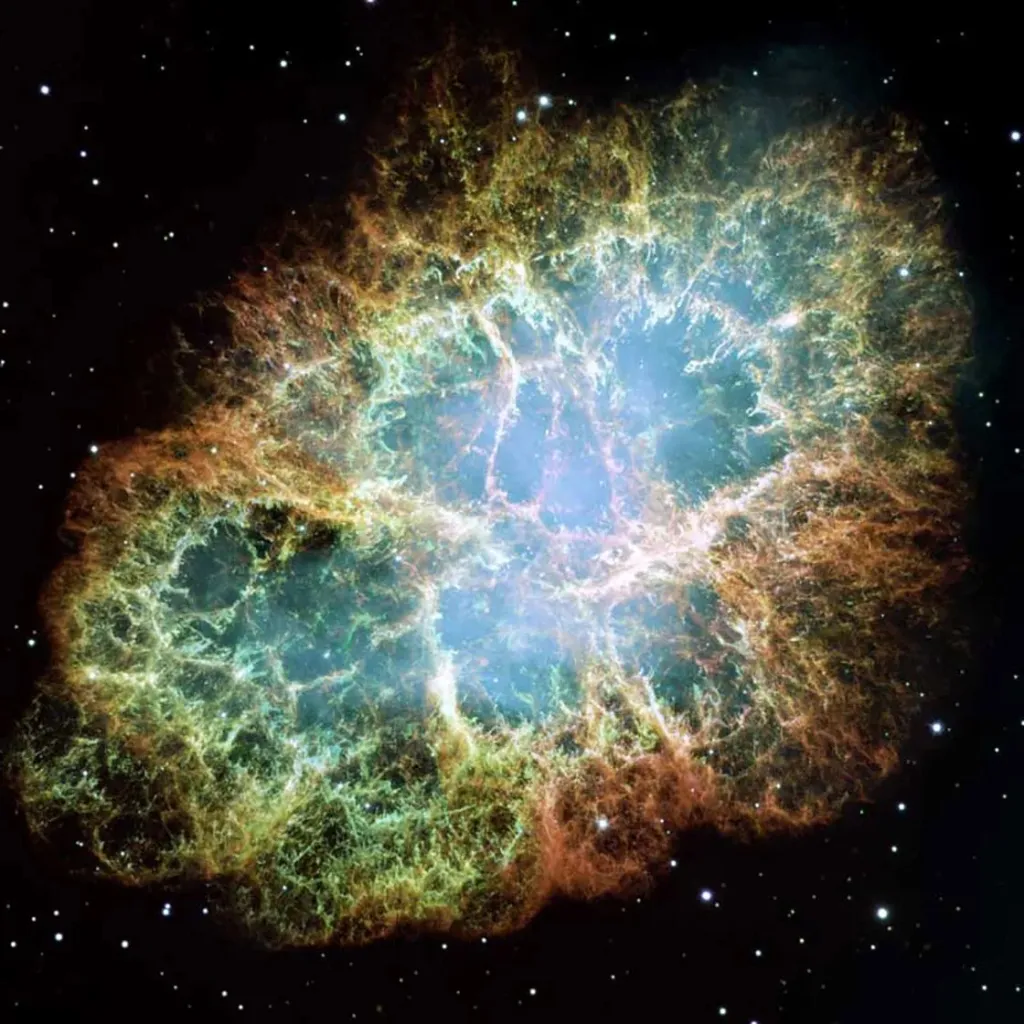

The Death Throes of Stars
When stars die, they throw off their outer layers, creating the clouds that birth new stars.
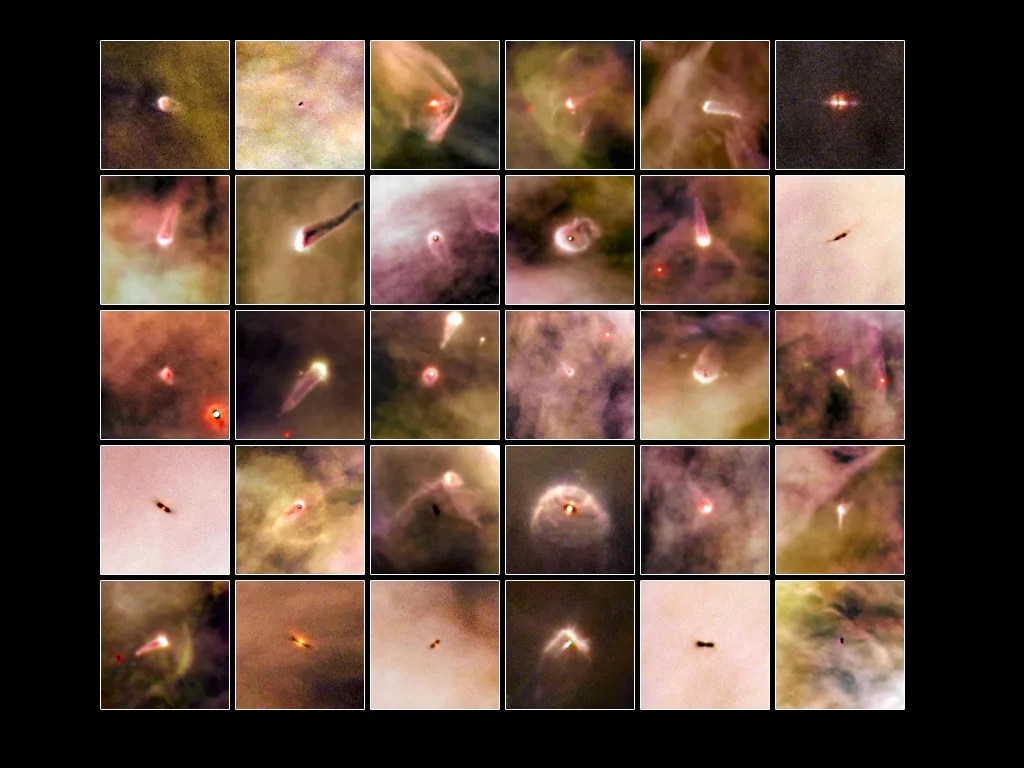

Finding Planetary Construction Zones
Hubble’s sensitivity uncovers the seeds of planets in enormous disks of gas and dust around young stars.
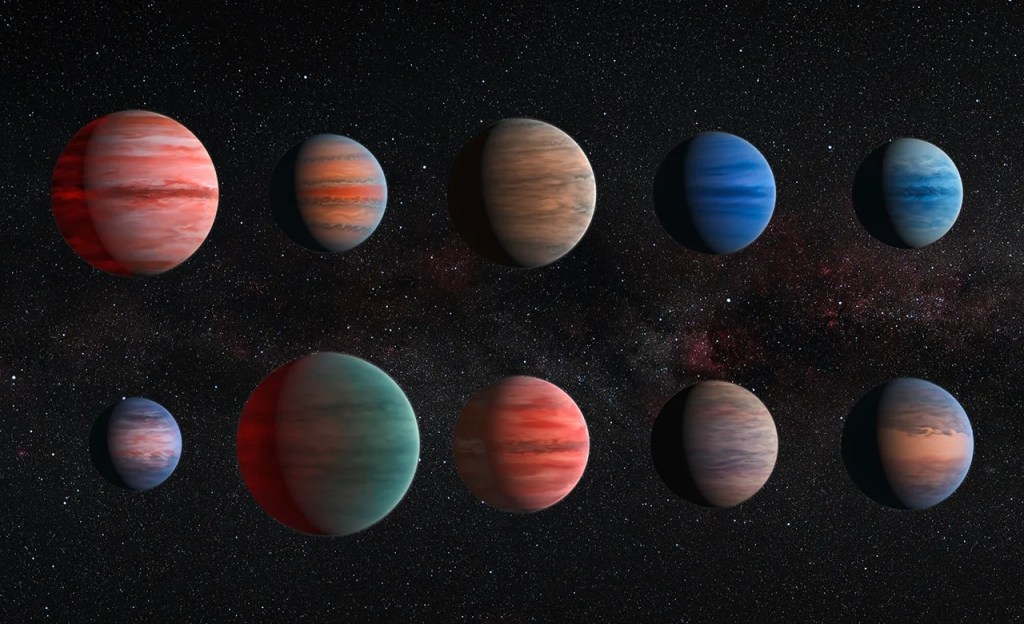

Recognizing Worlds Beyond Our Sun
Hubble can detect and measure the basic organic components for life on planets orbiting other stars.
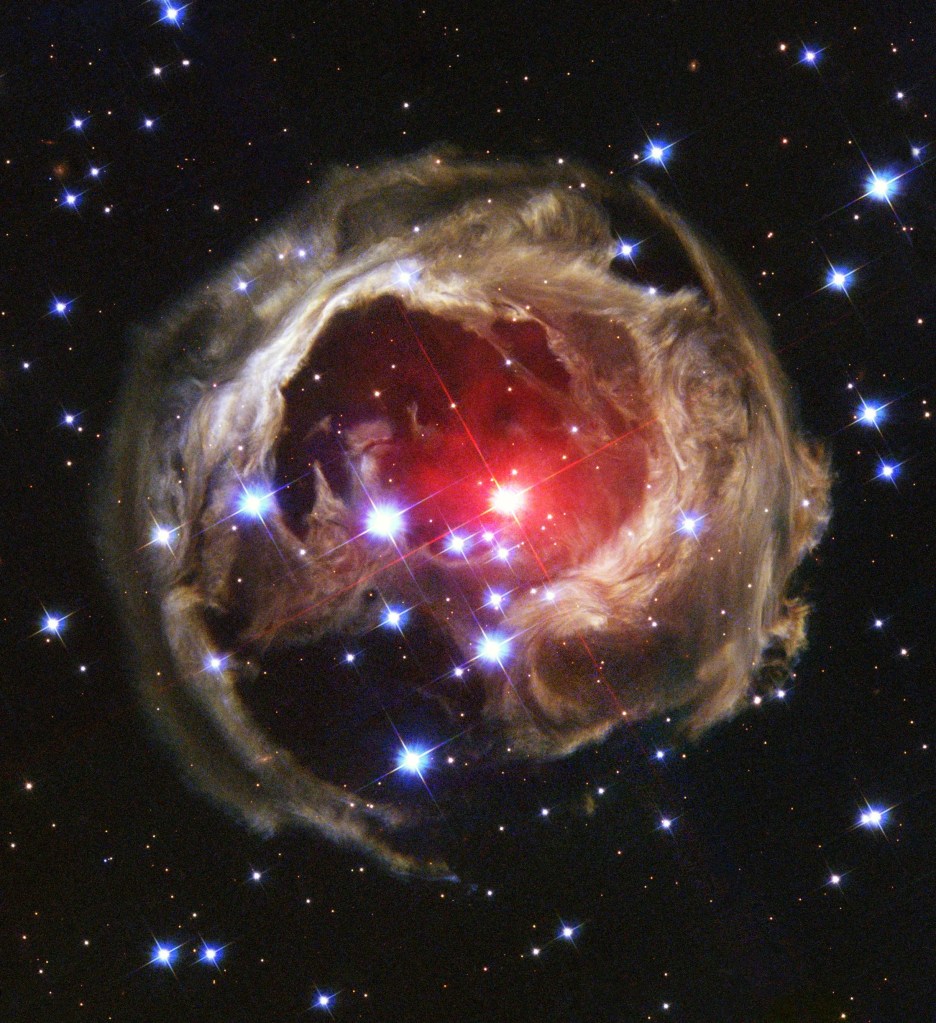

Seeing Light Echoes
Like ripples on a pond, pulses of light reverberate through cosmic clouds forming echoes of light.
The Universe
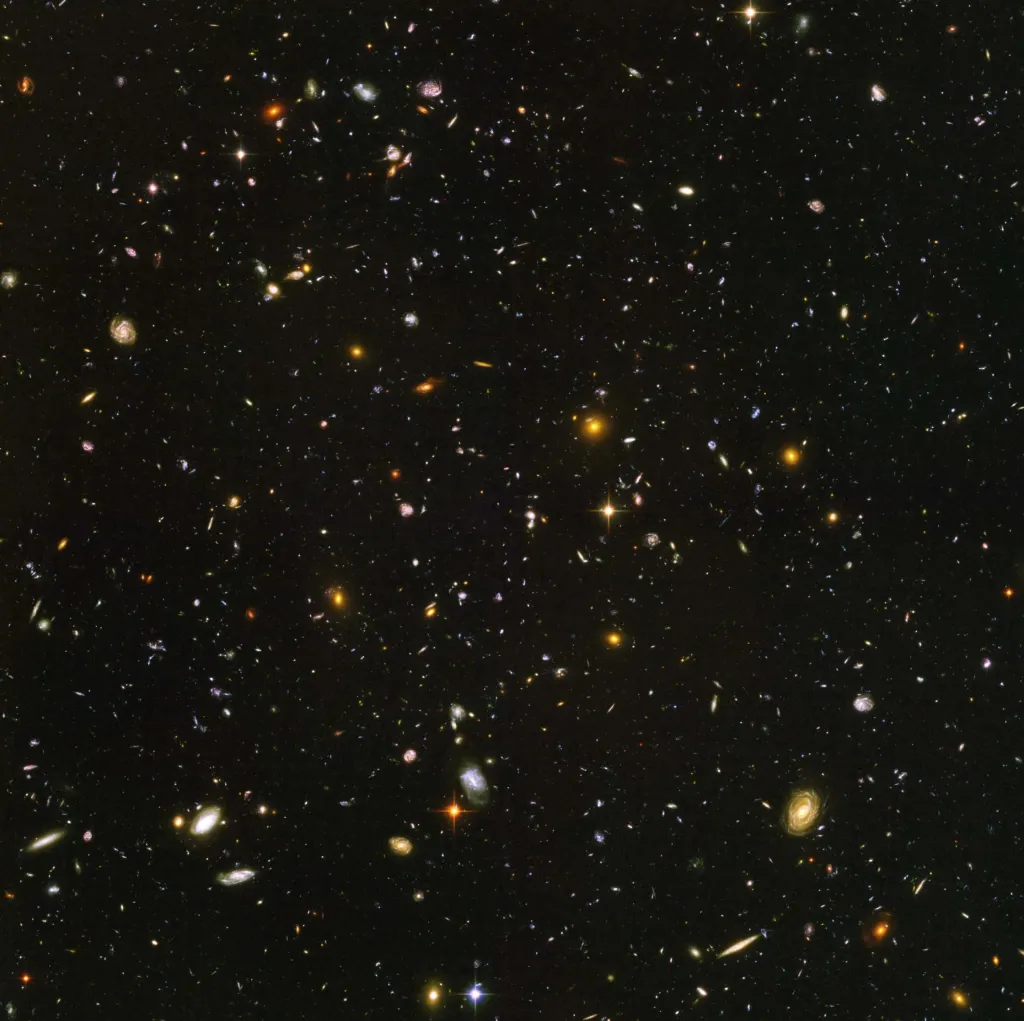

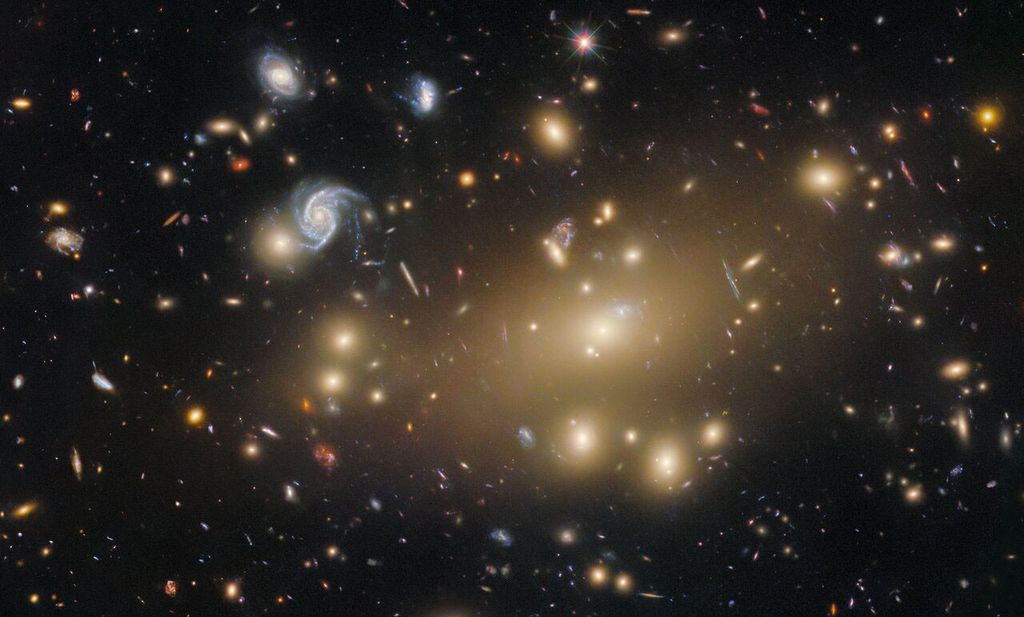
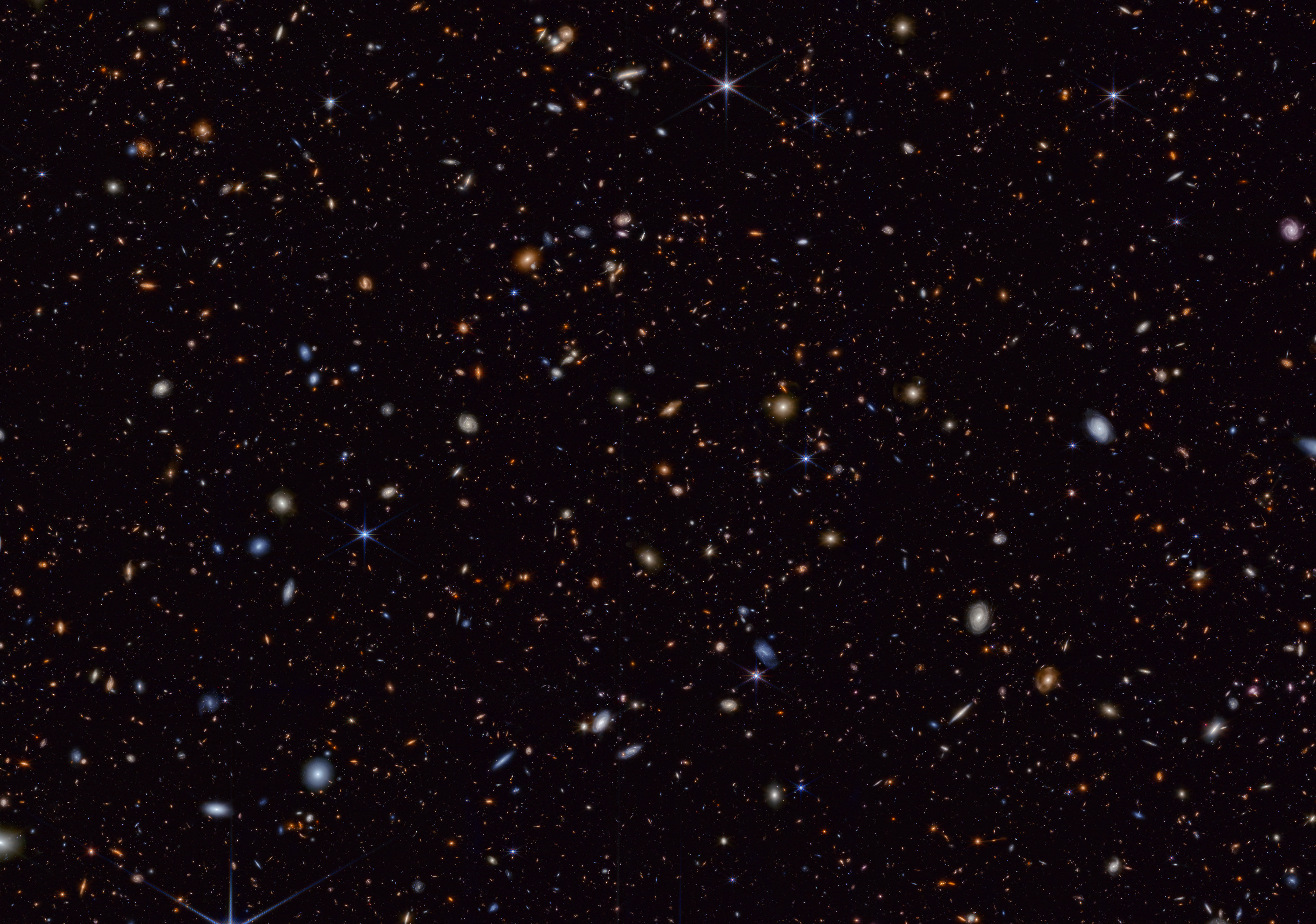
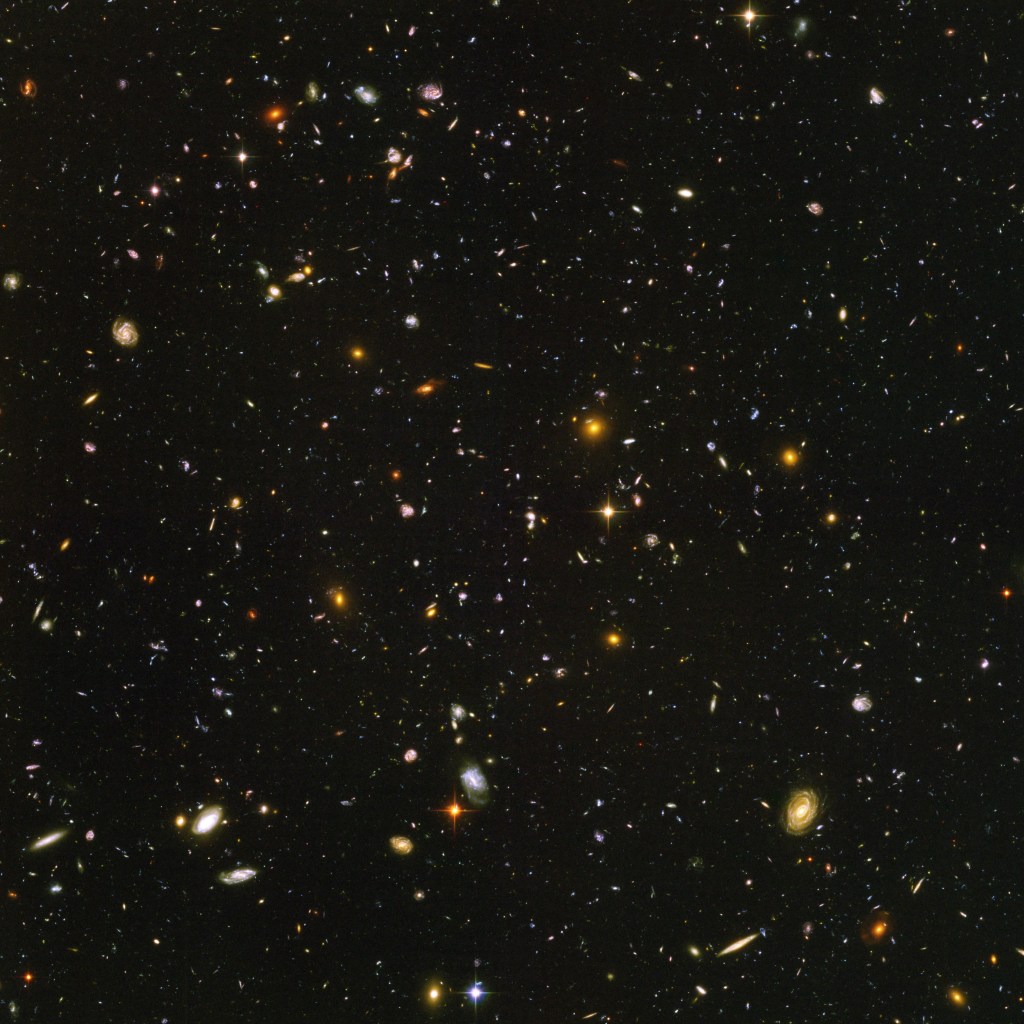
Tracing the Growth of Galaxies
Hubble's Deep Field observations are instrumental in tracing the growth of galaxies.
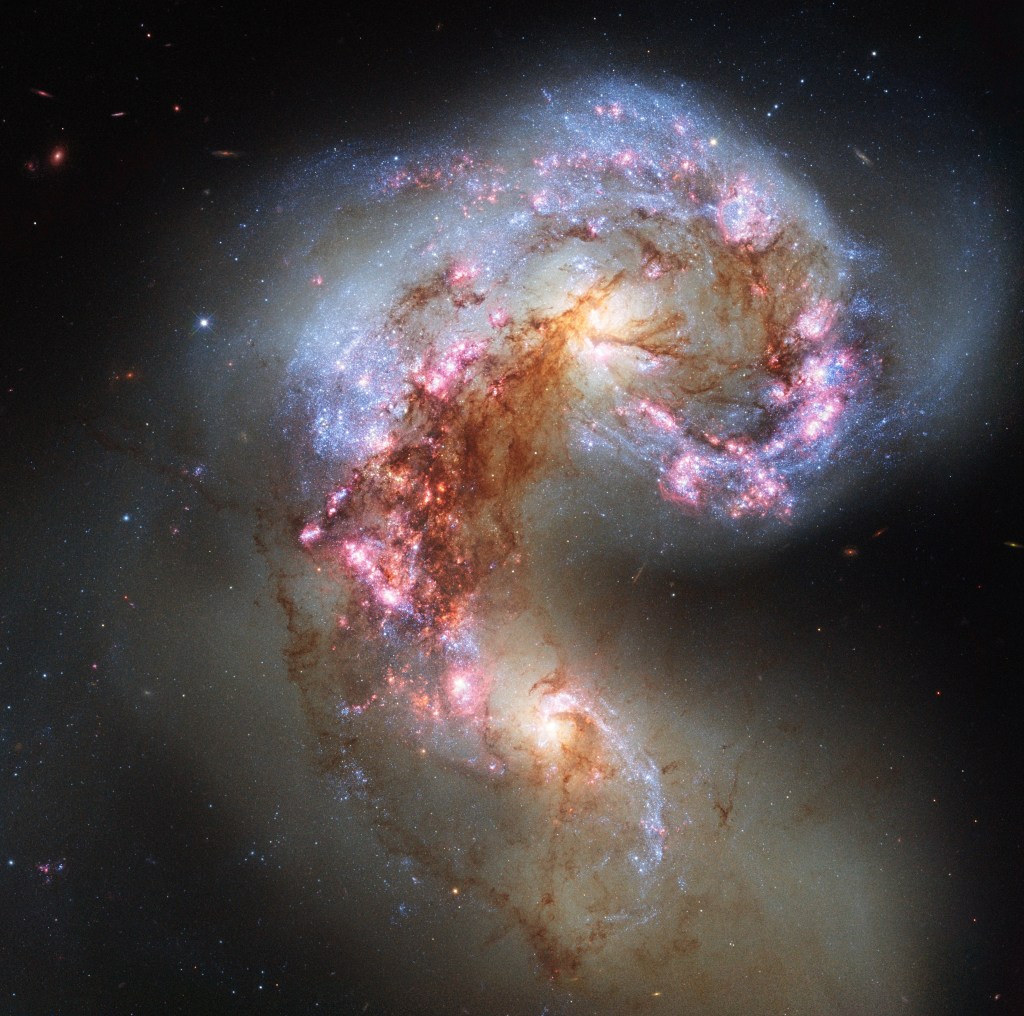

Galaxy Details and Mergers
Galaxies evolve through gravitational interaction with their neighbors, creating a menagerie of forms.
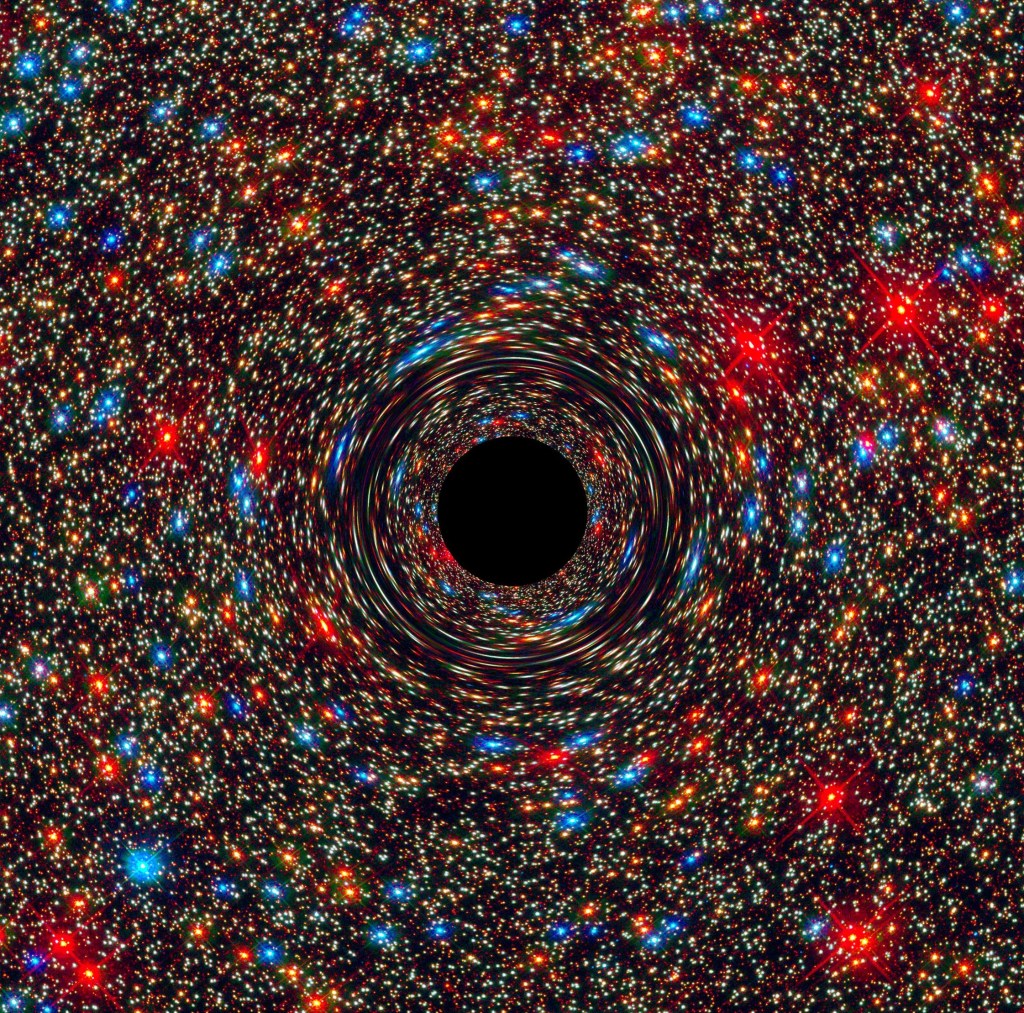

Monster Black Holes are Everywhere
Supermassive black holes lie at the heart of nearly every galaxy.
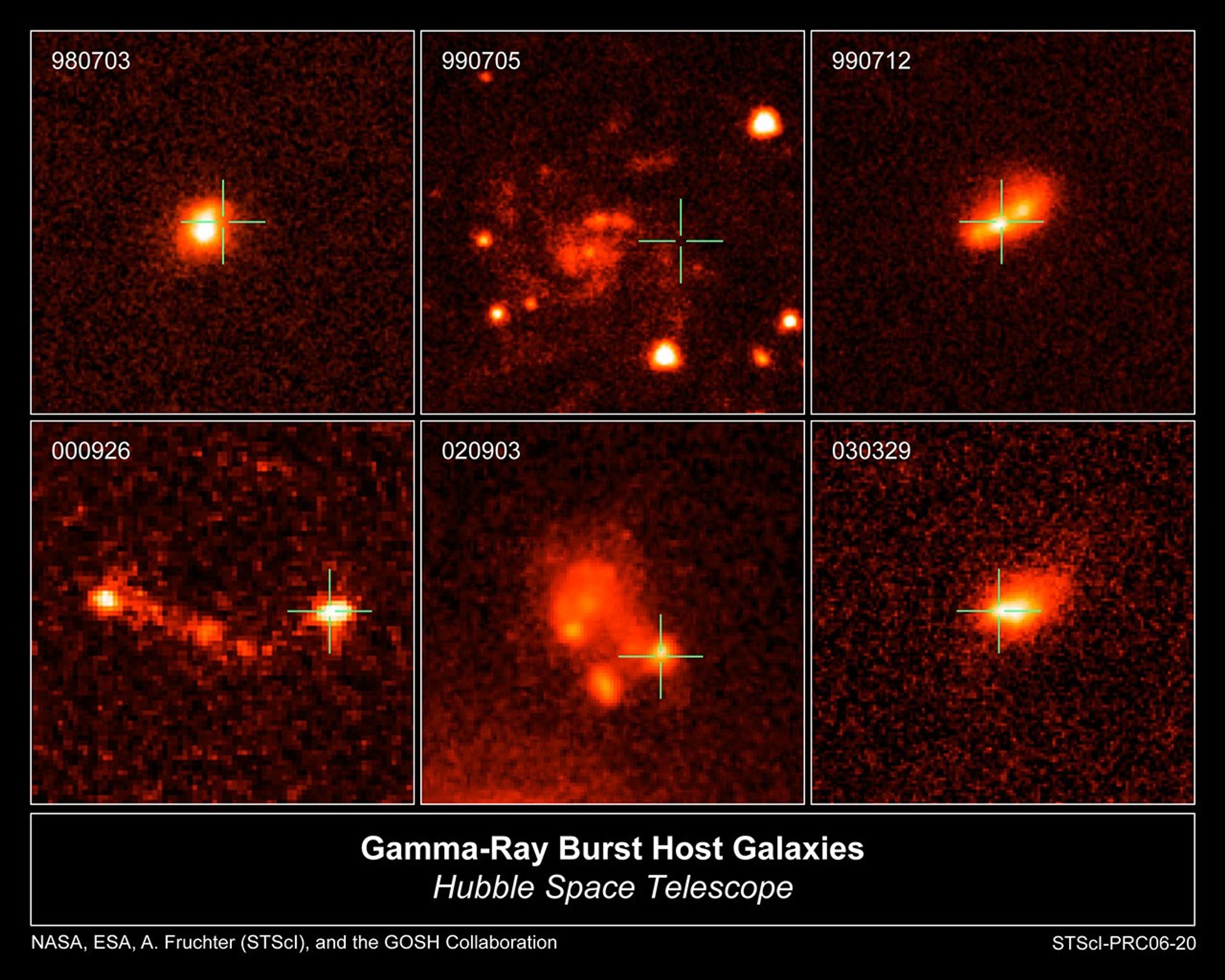
Homing in on Cosmic Explosions
Hubble helps astronomers better understand and define some of the largest explosions in the universe.
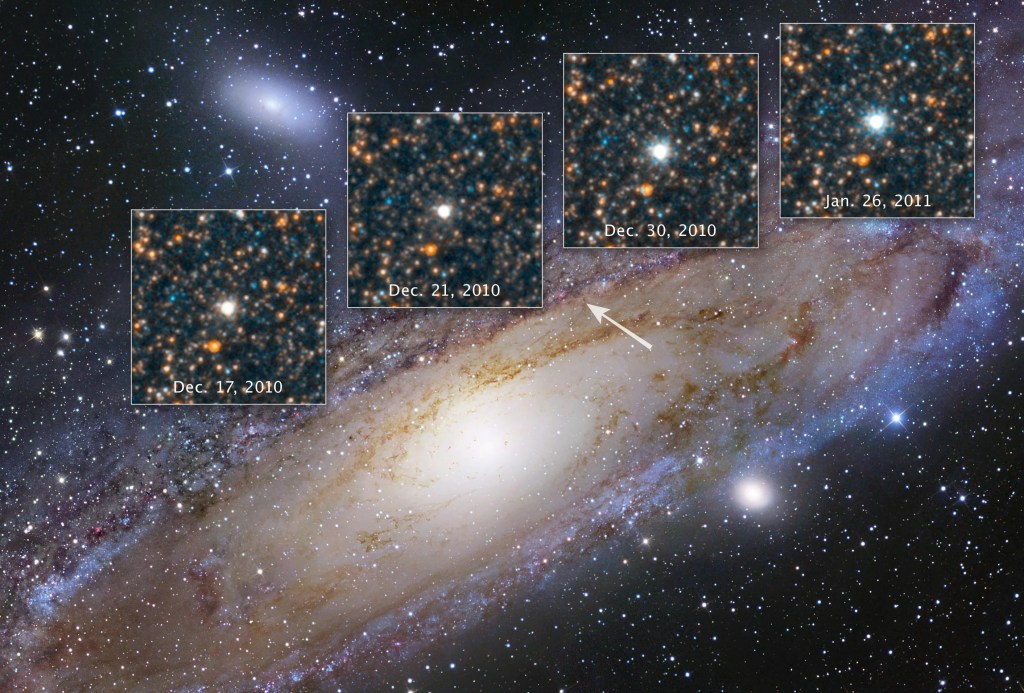

Discovering the Runaway Universe
Our cosmos is growing, and that expansion rate is accelerating.
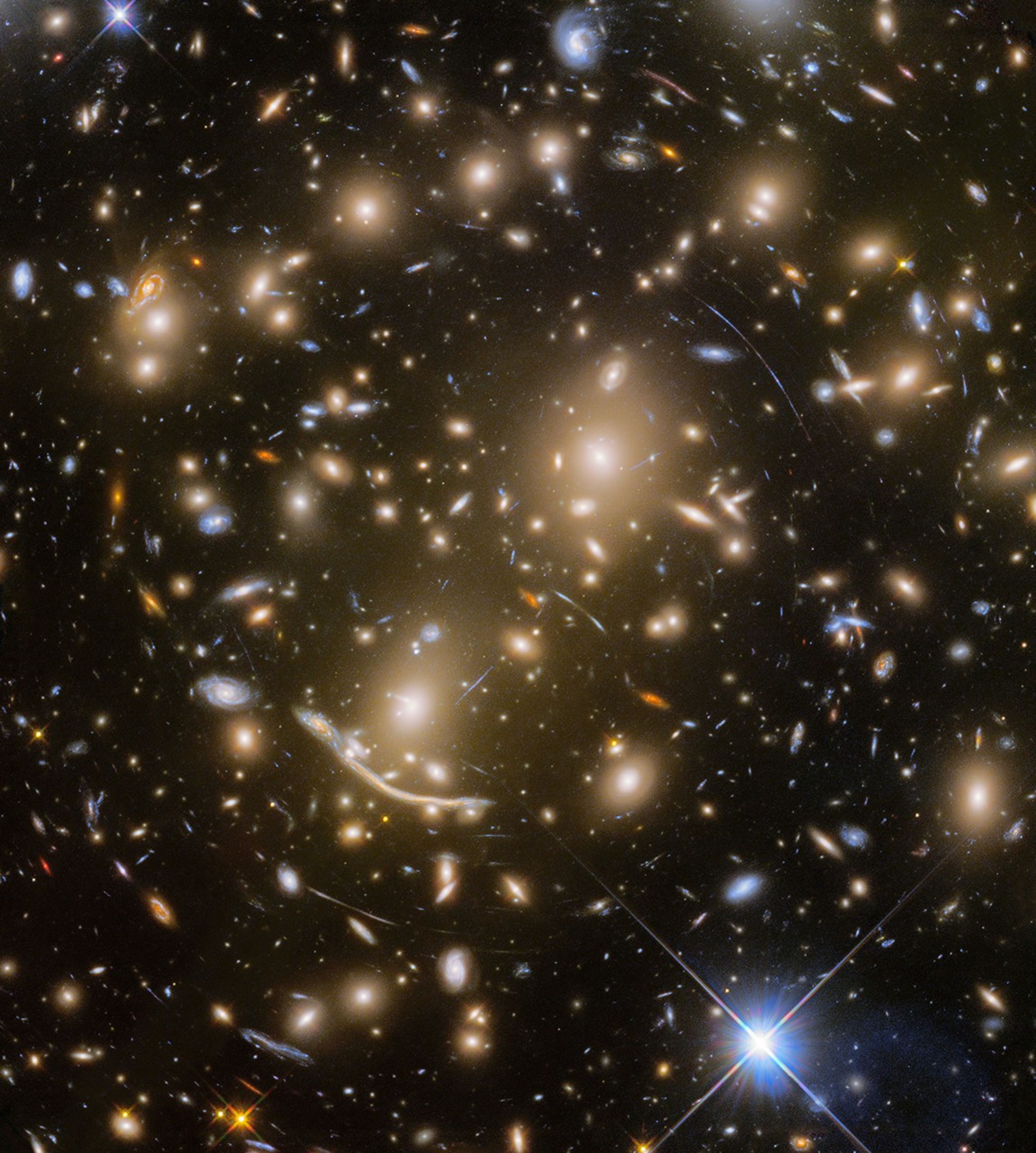

Focusing in on Gravitational Lenses
Gravitational lenses are 'Nature's Boost', expanding our view deeper into space and farther back in time.
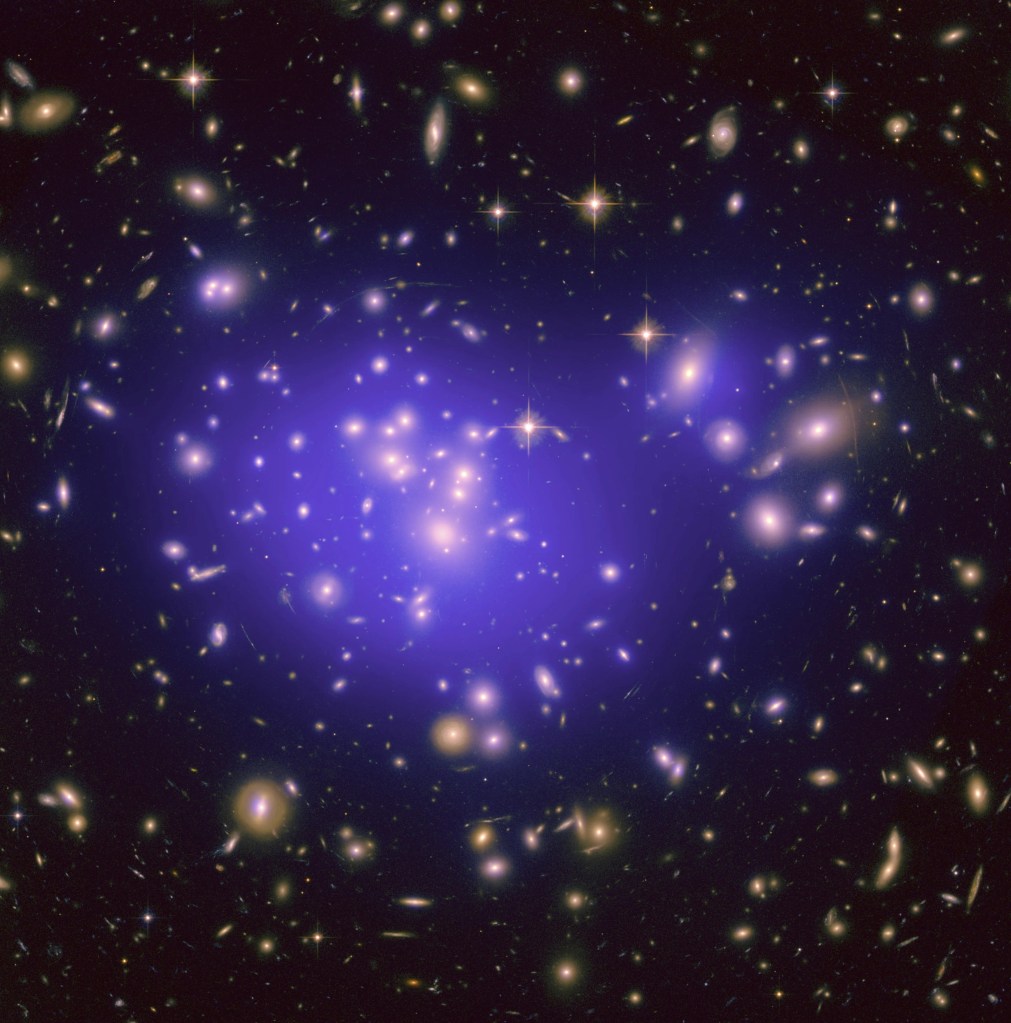

Shining a Light on Dark Matter
The gravitational pull of dark matter guides the formation of everything we can see in the universe.

Mapping the Cosmic Web
Filaments and sheets of matter create an interconnected web that forms the large-scale structure of the universe.
Reshaping Our Cosmic View
This downloadable e-book showcases some of Hubble’s ground-breaking discoveries over its more than three decades of observations.
Learn More and Download













































