1 min read
Polaris A and Polaris Ab

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.02h 31m 49s.08
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+89° 15' 50".8
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Minor
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The distance to the star system is 430 light-years or 132 parsecs.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Polaris (star Aa) and star Ab are on average18.5 Astronomical Units from each other. Polaris (star Aa) and star B are on average 2,400 Astronomical Units from each other.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble image was created from HST data from proposal 10593: N.R. Evans (Harvard Smithsonian/CfA), H.E. Bond (STScI), G. Bono (INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma), M. Karovska (Harvard Smithsonian/CfA), E. Nelan (STScI), D.D. Sasselov (Harvard University), and G. Schaefer (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/HRC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.August 2-3, 2005
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F220W (Near UV)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Polaris, Alpha Ursae Minoris, North Star
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Triple Star System
- Release DateJanuary 9, 2006
- Science ReleaseThere’s More to the North Star Than Meets the Eye
- Credit
Related Images & Videos
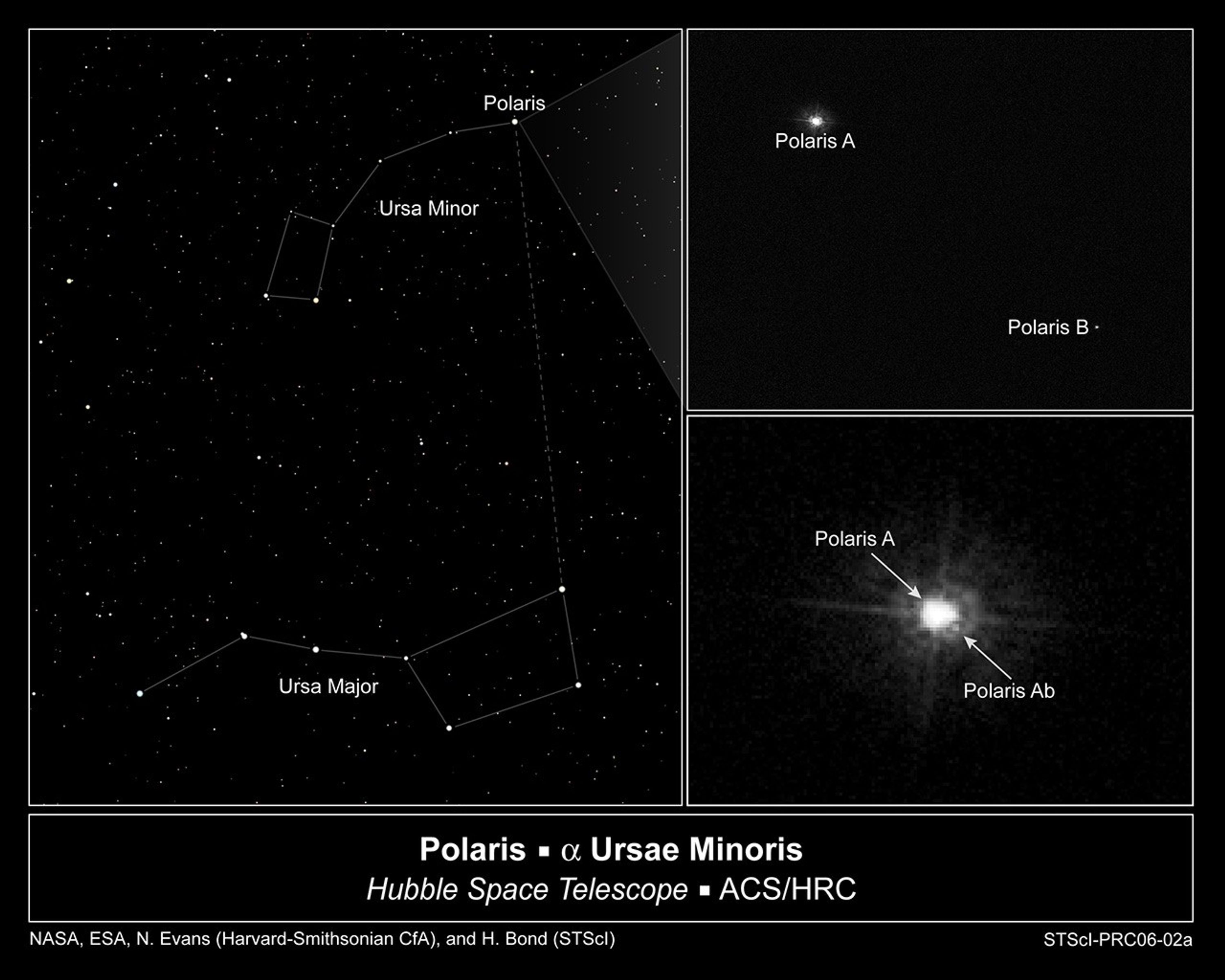
Hubble Images Polaris's Companion
This sequence of images shows that the North Star, Polaris is really a triple star system. For the first time, the close companion of Polaris has been seen directly. The left frame shows Polaris's location very close to the position of Earth's north celestial pole in Ursa Minor...

Artist's Concept of Polaris System
This is a view from within the Polaris triple star system. The North Star, Polaris A is a bright supergiant variable star. Just above Polaris is a small companion, Polaris Ab, which is 2 billion miles from Polaris. Much farther away, near the top of the illustration, is the wide...

Artist's Concept of Polaris System - Annotated
This is a view from within the Polaris triple star system. The North Star, Polaris A is a bright supergiant variable star. Just above Polaris is a small companion, Polaris Ab, which is 2 billion miles from Polaris. Much farther away, near the top of the illustration, is the...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov































