1 min read
Hubble’s Largest Galaxy Portrait Offers a New High-Definition View

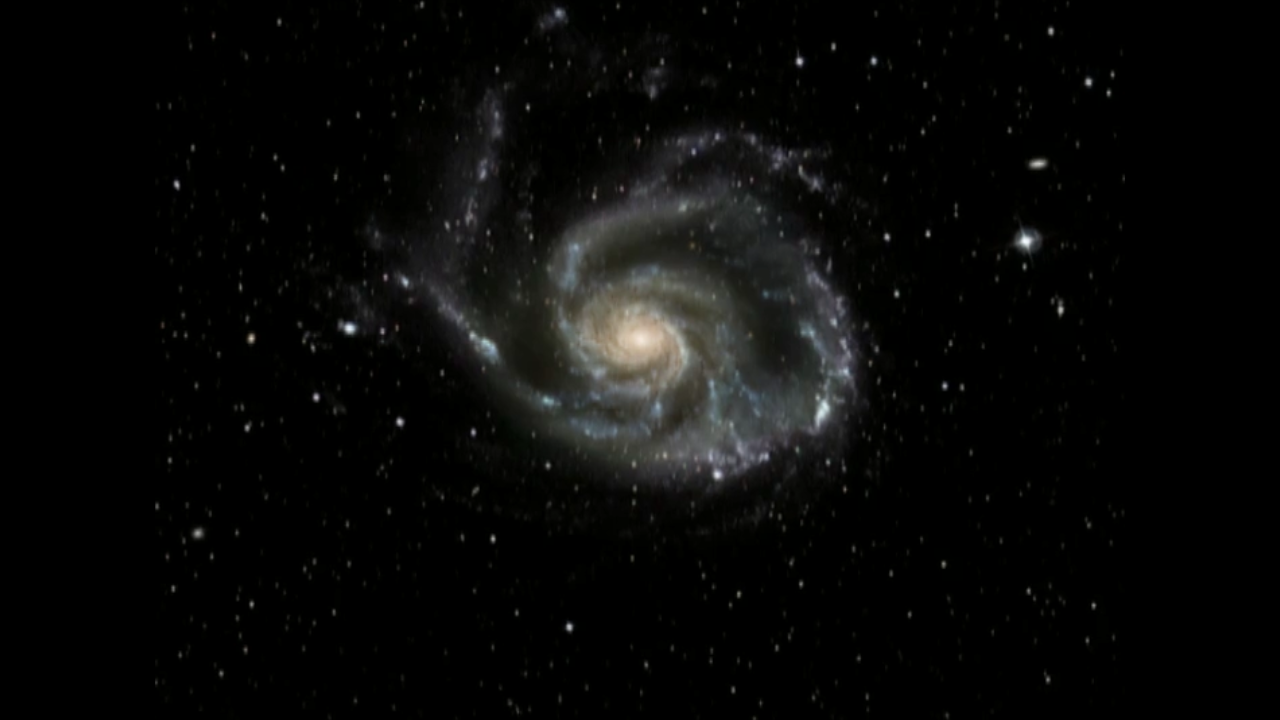
Giant galaxies weren't assembled in a day. Neither was this Hubble Space Telescope image of the face-on spiral galaxy Messier 101 (M101). It is the largest and most detailed photo of a spiral galaxy that has ever been released from Hubble. The galaxy's portrait is actually composed of 51 individual Hubble exposures, in addition to elements from images from ground-based photos. The final composite image measures a whopping 16,000 by 12,000 pixels.
The Hubble archived observations that went into assembling this image were originally acquired for a range of Hubble projects: determining the expansion rate of the universe, studying the formation of star clusters in the giant star birth regions, finding the stars responsible for intense X-ray emission, and discovering blue supergiant stars.
The giant spiral disk of stars, dust, and gas is 170,000 light-years across or nearly twice the diameter of our galaxy, the Milky Way. M101 is estimated to contain at least one trillion stars. Approximately 100 billion of these stars could be like our Sun in terms of temperature and lifetime.
The galaxy's spiral arms are sprinkled with large regions of star-forming nebulae. These nebulae are areas of intense star formation within giant molecular hydrogen clouds. Brilliant young clusters of hot, blue, newborn stars trace out the spiral arms. The disk of M101 is so thin that Hubble easily sees many more distant galaxies lying behind the galaxy.
M101 (also nicknamed the Pinwheel Galaxy) lies in the northern circumpolar constellation, Ursa Major (The Great Bear), at a distance of 25 million light-years from Earth. Therefore, we are seeing the galaxy as it looked 25 million years ago - when the light we're receiving from it now was emitted by its stars - at the beginning of Earth's Miocene Period, when mammals flourished and the Mastodon first appeared on Earth. The galaxy fills a region in the sky equal to one-fifth the area of the full moon.
The newly composed image was assembled from Hubble archived images taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys and the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over nearly 10 years: in March 1994, September 1994, June 1999, November 2002, and January 2003. The Hubble exposures have been superimposed onto ground-based images, visible at the edge of the image, taken at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope in Hawaii, and at the 0.9-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory, part of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory in Arizona. The final color image was assembled from individual exposures taken through blue, green, and red (infrared) filters.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.14h 3m 13.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.54° 20' 52.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Major
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.25 million light-years (8 Megaparsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposals 9490: K.D. Kuntz (JHU/GSFC), P. Barmby and J.P. Huchra (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), K. Mukai, S.L. Snowden, and W.D. Pence (Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics, GSFC), and J.P. Brodie (University of California, Santa Cruz). Other proposals used include: • Fabio Bresolin (proposal 9492) • John Trauger (proposal 5210) • Jeremy Mould (proposal 5397) • You-Hou Chu (proposal 6829) The Hubble exposures have been superimposed onto ground-based images, visible at the edge of the image, taken at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope in Hawaii, and at the 0.9-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory, part of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory in Arizona. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC and HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.March 1994, September 1994, June 1999, November 2002, and January 2003
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F555W (V), and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.M101, NGC 5457, The Pinwheel Galaxy
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Face-on Spiral Galaxy
- Release DateFebruary 28, 2006
- Science ReleaseHubble’s Largest Galaxy Portrait Offers a New High-Definition View
- CreditHubble Image: NASA, ESA, K. Kuntz (JHU), F. Bresolin (University of Hawaii), J. Trauger (Jet Propulsion Lab), J. Mould (NOAO), Y.-H. Chu (University of Illinois, Urbana), and STScI; CFHT Image: Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope/ J.-C. Cuillandre/Coelum; NOAO Image: G. Jacoby, B. Bohannan, M. Hanna/ NOAO/AURA/NSF

Blue: F435W (B) Green: F555W (V) Red: F814W (I)

Related Images & Videos

A Detailed Look at Spiral Galaxy M101
A close cropping of spiral galaxy M101 shows an array of stunning details that may be overlooked when viewing the full image. Due to the high sensitivity and fine resolution of Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys, one can clearly see individual dust lanes in the spiral arms as...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov