1 min read
Hubble View of Eris and Dysnomia
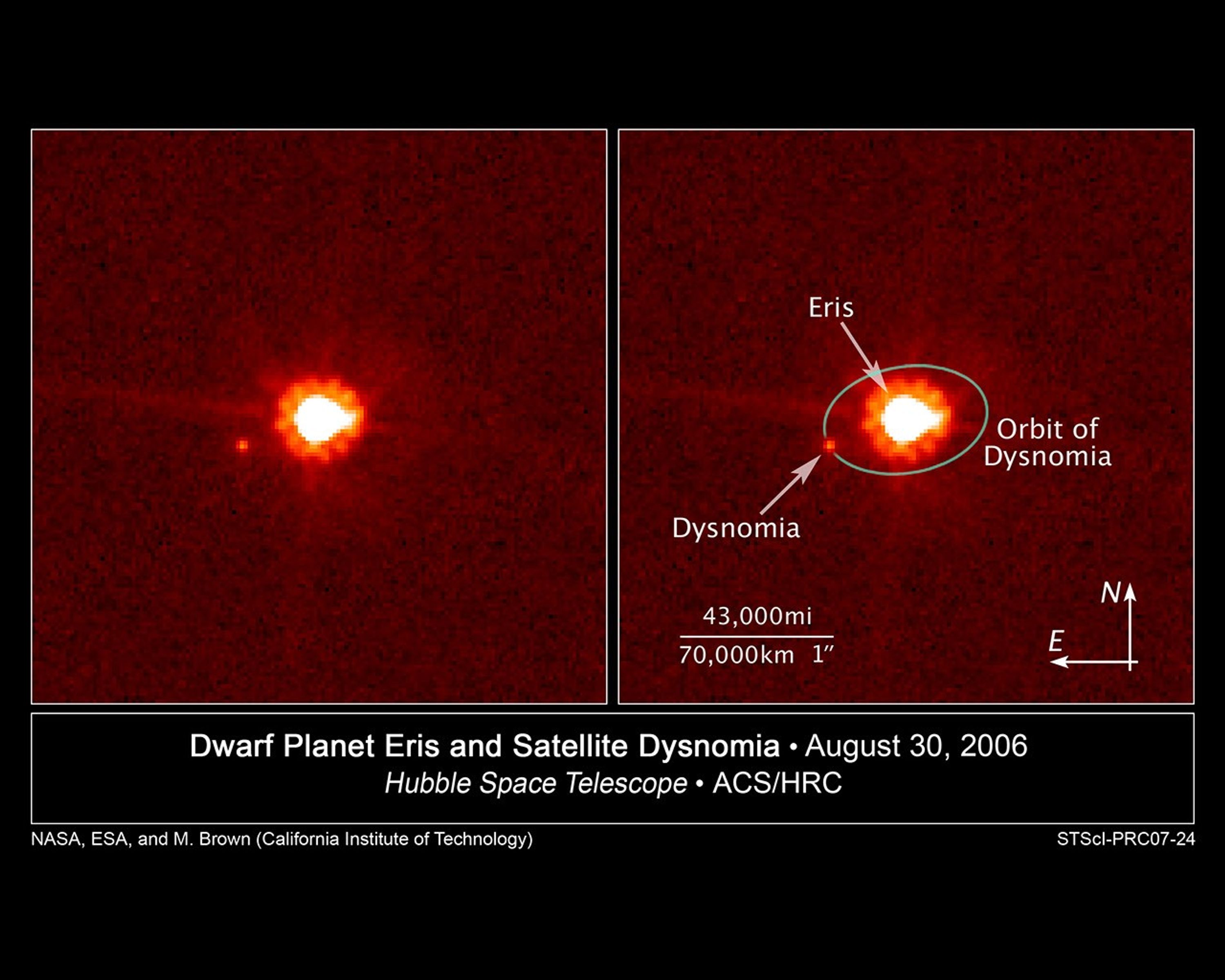
[Left] - This is an image of the dwarf planet Eris (center) and its satellite Dysnomia (at 9 o'clock position) taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on Aug. 30, 2006. Hubble observations were obtained on Dec. 3, 2005 and Aug. 30, 2006 using the Advanced Camera for Surveys. The Hubble images were combined with images from the Keck telescopes taken on Aug. 20, 21, 30, and 31 to measure the satellite's orbit and calculate a mass for Eris, which is the largest dwarf planet in the solar system.
[Right] - Labeled version of the above mentioned image of dwarf planet Eris and its satellite Dysnomia taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on Aug. 30, 2006. Dysnomia's projected orbit around Eris is superimposed on the image.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.01h 39m 24.33s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-5° 10' 10.99"
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.10 billion miles away (16 billion kilometers)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposals 10759: M. Brown (California Institute of Technology), D. Rabinowitz (Yale University) and C. Trujillo (Gemini Observatory); and 10860: M. Brown, H. Roe, K. Barkume, and E. Schaller (California Institute of Technology) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/HRC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.December 9-10, 2005 and August 30, 2006, Exposure Time: 4.3 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F606W (V)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Eris, 2003 UB313
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Dwarf Planet with Satellite
- Release DateJune 14, 2007
- Science ReleaseAstronomers Measure Mass of Largest Dwarf Planet
- Credit

Related Images & Videos

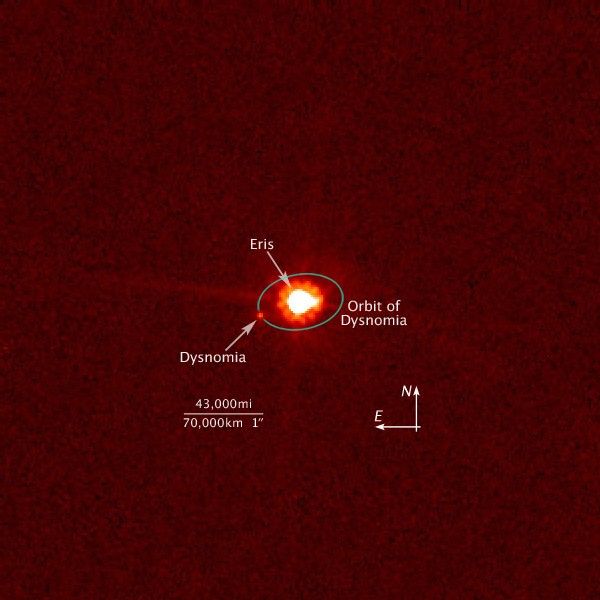
Hubble View of Eris and Dysnomia (Unannotated)
This is an image of the dwarf planet Eris (center) and its satellite Dysnomia (at 9 o'clock position) taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on Aug. 30, 2006. Hubble observations were obtained on Dec. 3, 2005 and Aug. 30, 2006 using the Advanced Camera for Surveys. The Hubble...

Hubble View of Eris and Dysnomia (Annotated)
This is an image of the dwarf planet Eris (center) and its satellite Dysnomia (at 9 o'clock position) taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope on Aug. 30, 2006. Hubble observations were obtained on Dec. 3, 2005 and Aug. 30, 2006 using the Advanced Camera for Surveys. The Hubble...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov