1 min read
Hubble Interacting Galaxy Arp 220

Arp 220 appears to be a single, odd-looking galaxy, but is in fact a nearby example of the aftermath of a collision between two spiral galaxies. It is the brightest of the three galactic mergers closest to Earth, about 250 million light-years away in the constellation of Serpens, the Serpent. The collision, which began about 700 million years ago, has sparked a cracking burst of star formation, resulting in about 200 huge star clusters in a packed, dusty region about 5,000 light-years across (about 5 percent of the Milky Way's diameter). The amount of gas in this tiny region equals the amount of gas in the entire Milky Way Galaxy. The star clusters are the bluish-white bright knots visible in the Hubble image. Arp 220 glows brightest in infrared light and is an ultra-luminous infrared galaxy. Previous Hubble observations, taken in the infrared at a wavelength that looks through the dust, have uncovered the cores of the parent galaxies 1,200 light-years apart. Observations with NASA s Chandra X-ray Observatory have also revealed X-rays coming from both cores, indicating the presence of two supermassive black holes. Arp 220 is the 220th galaxy in Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.
This image is part of a large collection of 59 images of merging galaxies taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and released on the occasion of its 18th anniversary on 24th April 2008.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.15h 34m 57.28s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.23° 30' 9.5"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Serpens
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.250 million light-years (100 million parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.HST Proposal: 10592 A. Evans (University of Virginia, Charlottesville/NRAO/Stony Brook University) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.January 6, 2006, Exposure Time: 33 minutes
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B) and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Arp 220, IC 1127, VV 540, KPG 470, UGC 09913
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Interacting Galaxies
- Release DateApril 24, 2008
- Science ReleaseCosmic Collisions Galore!
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

Cosmic Collisions Galore!
Astronomy textbooks typically present galaxies as staid, solitary, and majestic island worlds of glittering stars. But galaxies have a dynamical side. They have close encounters that sometimes end in grand mergers and overflowing sites of new star birth as the colliding galaxies...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 6786
This Hubble image displays a beautiful pair of interacting spiral galaxies with swirling arms. The smaller of the two, dubbed LEDA 62867 and positioned to the left of the frame, seems to be safe for now, but will probably be swallowed by the larger spiral galaxy, NGC 6786 (to...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IC 1623
IC 1623 is an interacting galaxy system that is very bright when observed in the infrared. One of the two galaxies, the infrared-bright, but optically obscured galaxy VV 114E, has a substantial amount of warm and dense gas. Warm and dense gas is also found in the overlap region...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IC 883
IC 883 displays a very disturbed, complex central region with two tidal tails of approximately the same length emerging at nearly right angles: one diagonally to the top right of the frame and the other to the bottom right. The twin tidal tails suggest that IC 883 is the remnant...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 7469
This is a stunning pair of interacting galaxies, the barred spiral Seyfert 1 galaxy NGC 7469 (Arp 298, Mrk 1514), a luminous infrared source with a powerful starburst deeply embedded into its circumnuclear region, and its smaller companion IC 5283. This system is located about...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IRAS 18090
This system consists of two interacting spiral galaxies. The galaxy to the left displays a dim plume of luminosity that extends to the right in the direction of the second spiral. Both galaxies are partly obscured by dust lanes. The galaxy at center is adorned with blue knots of...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 69-6
The galaxies of this beautiful interacting pair bear some resemblance to musical notes on a stave. Long tidal tails sweep out from the two galaxies: gas and stars were stripped out and torn away from the outer regions of the galaxies. The presence of these tails is the unique...
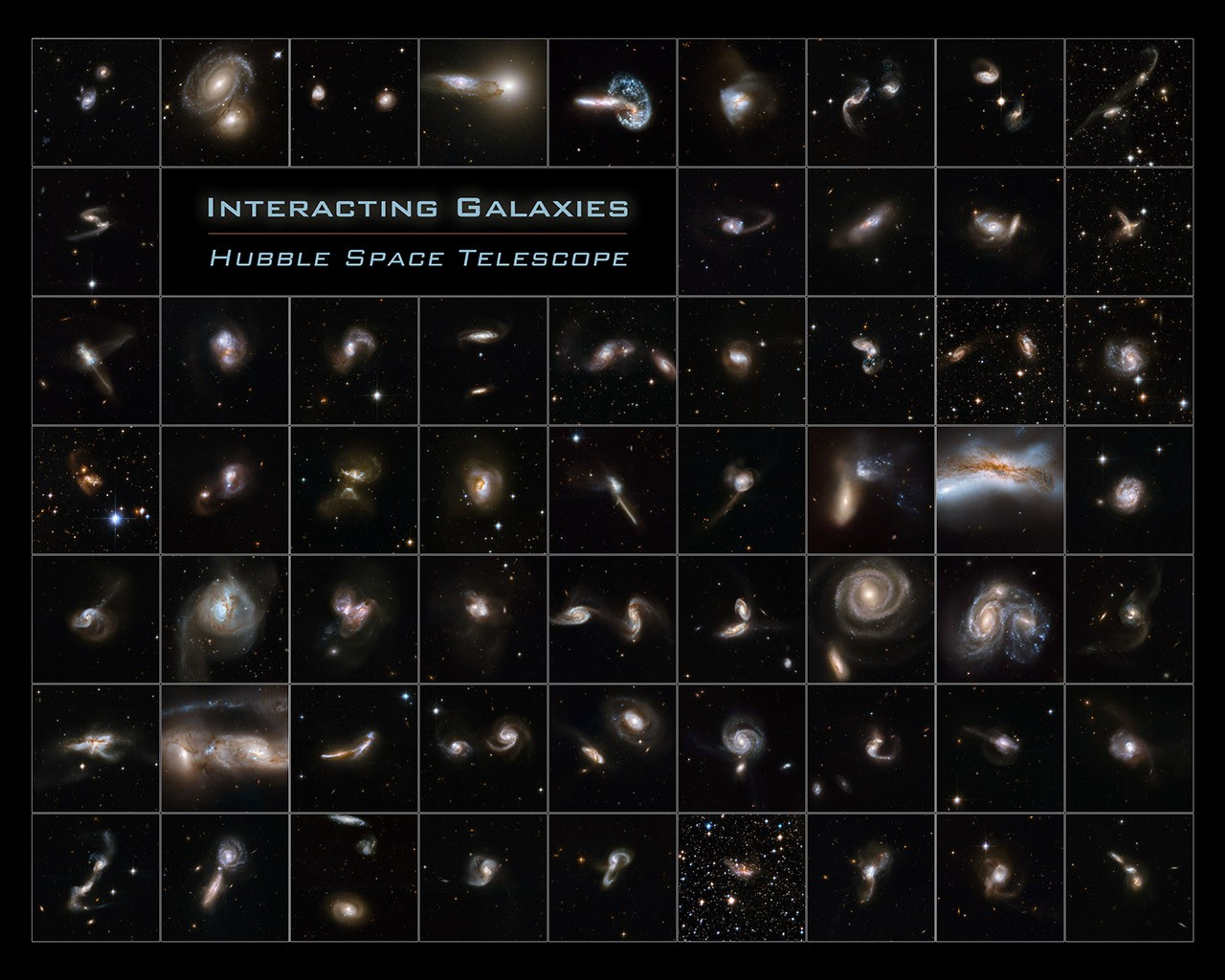

Hubble Interacting Galaxies Poster
Astronomy textbooks typically present galaxies as staid, solitary, and majestic island worlds of glittering stars. But galaxies have a dynamical side. They have close encounters that sometimes end in grand mergers and overflowing sites of new star birth as the colliding galaxies...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 5256
NGC 5256, also known as Markarian 266, is a striking example of two disk galaxies that are about to merge. Spectacular streamers of gas surround the two nuclei and eye-catching blue spiral trails indicate recent star formation. The shape of the object is highly disturbed and...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 5257
NGC 5257/8 (Arp 240) is an astonishing galaxy pair, composed of spiral galaxies of similar mass and size, NGC 5257 and NGC 5258. The galaxies are visibly interacting with each other via a bridge of dim stars connecting the two galaxies, almost like two dancers holding hands...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy II Zw 96
This is a system of merging galaxies with a bizarre shape. Powerful young starburst regions hang as long threadlike structures between the main galaxy cores. The system almost qualifies as an ultra-luminous system, but has not yet reached the late stage of coalescence that is...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IRAS F10565
IRAS F10565+2448 is a system that appears to consist of two colliding galaxies. The larger galaxy has dust lanes, while the smaller galaxy has a pronounced curved tail that has been pulled away from the center (downwards as seen here). IRAS F10565+2448 is located in the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 286-19
ESO 286-19 is a peculiar galaxy that consists of what were originally two disk galaxies that are now in the midst of an ongoing collision. It has undergone a burst of star formation that ended about eight million years ago. ESO 286-19 has a long tail to the right of the main...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 6670
NGC 6670 is a gorgeous pair of overlapping edge-on galaxies resembling a leaping dolphin. Scientists believe that NGC 6670 has already experienced at least one close encounter and is now in the early stages of a second. The nuclei of the two galaxies are approximately 50,000...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy CGCG 436-030
CGCG 436-030, the eye-catching spiral galaxy in the image, shows a very pronounced curling tail. The companion galaxy, located to the bottom-right of the image, displays an intricate structure, including a number of trails that extend quite far out from its core. The bright star...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 7674
NGC 7674 (seen just above the center), also known as Markarian 533, is the brightest and largest member of the so-called Hickson 96 compact group of galaxies, consisting of four galaxies. This stunning Hubble image shows a spiral galaxy nearly face-on. The central bar-shaped...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IC 2545
IC 2545 is a beautiful, but deceptive object that appears to be a single S-shaped galaxy, but is actually a pair of merging galaxies. The two cores of the parent galaxies are still visible in the central region. Other telltale markers for the collision include two pronounced...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 550-2
ESO 550-2 shows a pair of spiral galaxies, the larger nearly face-on and accompanied by a smaller, highly tilted partner. Tidal interaction from the smaller companion has clearly deformed one arm of the larger galaxy. Strong star formation continues both in the deformed arm and...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy VV 705
VV 705, or Markarian 848, consists of two galaxies that seem to be embracing each other. Two long, highly curved arms of gas and stars emerge from a central region with two cores. One arm, curving clockwise, stretches to the top of the image where it makes a U-turn and...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy UGC 5101
UGC 5101 is a peculiar galaxy with a single nucleus contained within an unstructured main body that suggests a recent interaction and merger. UGC 5101 is thought to contain an active galactic nucleus an extremely bright, compact core - buried deep in the gas and dust. A...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 1614
The galaxy system NGC 1614 has a bright optical center and two clear inner spiral arms that are fairly symmetrical. It also has a spectacular outer structure that consists principally of a large one-sided curved extension of one of these arms to the lower right, and a long,...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy 2MASX J09133888-1019196
2MASX J09133888-1019196 comprises two interacting galaxies that are both disturbed by gravitational interaction. The wide separation of the pair - approximately 130,000 light-years - suggests that the galaxies are just beginning to merge. Together the two galaxies form an...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy AM 1316-241
AM 1316-241 is made up of two interacting galaxies - a spiral galaxy (on the left of the frame) in front of an elliptical galaxy (on the right of the frame). The starlight from the background galaxy is partially obscured by the bands and filaments of dust associated with the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy UGC 8335
UGC 8335 is a strongly interacting pair of spiral galaxies resembling two ice skaters. The interaction has united the galaxies via a bridge of material and has yanked two strongly curved tails of gas and stars from the outer parts of their bodies . Both galaxies show dust lanes...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy Mrk 273
Markarian 273 is a galaxy with a bizarre structure that somewhat resembles a toothbrush. The Hubble image shows an intricate central region and a striking tail that extends diagonally towards the bottom-right of the image. The tail is about 130 thousand light-years long and is...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 5754
This beautiful pair of interacting galaxies consists of NGC 5754, the large spiral on the right, and NGC 5752, the smaller companion in the bottom left corner of the image. NGC 5754's internal structure has hardly been disturbed by the interaction. The outer structure does...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy Arp 148
Arp 148 is the staggering aftermath of an encounter between two galaxies, resulting in a ring-shaped galaxy and a long-tailed companion. The collision between the two parent galaxies produced a shockwave effect that first drew matter into the center and then caused it to...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 6090
NGC 6090 is a beautiful pair of spiral galaxies with an overlapping central region and two long tidal tails formed from material ripped out of the galaxies by gravitational interaction. The two visible cores are approximately 10,000 light-years apart, suggesting that the two...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 6240
NGC 6240 is a peculiar, butterfly- or lobster-shaped galaxy consisting of two smaller merging galaxies. It lies in the constellation of Ophiuchus, the Serpent Holder, some 400 million light-years away. Observations with NASA s Chandra X-ray Observatory have disclosed two giant...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 5331
NGC 5331 is a pair of interacting galaxies beginning to hold their arms . There is a blue trail which appears in the image flowing to the right of the system. NGC 5331 is very bright in the infrared, with about a hundred billion times the luminosity of the Sun. It is located in...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IRAS 20351
IRAS 20351+2521 is a galaxy with a sprawling structure of gas, dust and numerous blue star knots. IRAS 20351+2521 is located in the constellation of Vulpecula, the Fox, 450 million light-years away from Earth. This image is part of a large collection of 59 images of merging...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 507-70
ESO 507-70 is an odd-looking galaxy that is probably the remnant of an earlier merger process. It is a chaotic swirl of gas, dust and stars with no sign of the conjectured original spiral or elliptical structure, now lost and distorted beyond recognition in a gravitational...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy UGC 8058
The extraordinary galaxy UGC 8058, also known as Markarian 231, was discovered in 1969 as part of a survey searching for galaxies with strong ultraviolet radiation. It has long tidal tails and a disturbed shape. Results from the first spectrum showed clear signs of the presence...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 593-8
ESO 593-8 is an impressive pair of interacting galaxies with a feather-like galaxy crossing a companion galaxy. The two components will probably merge to form a single galaxy in the future. The pair is adorned with a number of bright blue star clusters. ESO 593-8 is located in...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 3256
NGC 3256 is an impressive example of a peculiar galaxy that is actually the relict of a collision of two separate galaxies that took place in a distant past. The telltale signs of the collision are two extended luminous tails swirling out from the galaxy. NGC 3256 belongs to the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy VV 283
VV 283 looks like a single peculiar galaxy, but is in fact a pair of merging galaxies. A tidal tail swirls out from a messy central region and splits into two branches. The upward twisting branch is brightened by luminous blue star knots. Like many merging systems, VV 283 is a...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy UGC 12812
UGC 12812, also known as Markarian 331, is a spiral galaxy with no obvious tidal tails. It is located in the lower part of the Hubble image. Two neighboring blue galaxies are seen at the top of the frame. The galaxy at the very top is embellished by a remarkable number of blue...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy UGC 9618
UGC 9618, also known as VV 340 or Arp 302 consists of a pair of very gas-rich spiral galaxies in their early stages of interaction: VV 340A is seen edge-on to the left, and VV 340B face-on to the right. An enormous amount of infrared light is radiated by the gas from massive...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 99-4
ESO 99-4 is a galaxy with a highly peculiar shape that is probably the remnant of an earlier merger process that has deformed it beyond visual recognition, leaving the main body largely obscured by dark bands of dust. ESO 99-4 lies in a rich field of foreground stars, in the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy AM 0702-601
AM 0702 consists of a couple of detached galaxies, far apart and probably only just beginning to interact. The first signs of the interaction are visible in the galaxy on the left, where the outer structure of the spiral arms is starting to expand, extending a tidal tail of...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 77-14
This Hubble image of ESO 77-14 is a stunning snapshot of a celestial dance performed by a pair of similar sized galaxies. Two clear signatures of the gravitational tug of war between the galaxies are the bridge of material that connects them and the disruption of their main...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IRAS 21101
This system is an interacting galaxy pair. The interaction has disturbed both galaxies: the lower galaxy has a bizarre structure and a tidal tail emerges from the main body of the upper galaxy. The galaxy pair lies in a crowded field of Milky Way stars. IRAS 21101+5810 is...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy AM 0500-620
AM 0500-620 consists of a highly symmetric spiral galaxy seen nearly face-on and partially backlit by a background galaxy. The foreground spiral galaxy has a number of dust lanes between its arms. The background galaxy was earlier classified as an elliptical galaxy, but Hubble...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 454
NGC 454 is galaxy pair comprising a large red elliptical galaxy and an irregular gas-rich blue galaxy. The system is in the early stages of an interaction that has severely distorted both components. The three bright blue knots of very young stars to the right of the two main...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 6621
NGC 6621/2 (VV 247, Arp 81) is a strongly interacting pair of galaxies, seen about 100 million years after their closest approach. It consists of NGC 6621 (to the right) and NGC 6622 (to the left). NGC 6621 is the larger of the two, and is a very disturbed spiral galaxy. The...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy UGC 4881
UGC 4881, known as the "The Grasshopper," is a stunning system consisting of two colliding galaxies. It has a bright curly tail containing a remarkable number of star clusters. The galaxies are thought to be halfway through a merger the cores of the parent galaxies are still...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy MCG02-001
MCG+12-02-001 consists of a pair of galaxies visibly affected by gravitational interaction as material is flung out in opposite directions. A large galaxy can be seen at the top of the frame and a smaller galaxy resembling an erupting volcano is at the bottom. The bright core of...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IC 5298
IC 5298 is a beautiful face-on spiral galaxy with two long arms extending from the central bulge and curving back amongst the scattered stars, gas and dust. A nearby smaller companion is linked by a bridge of matter to the principal galaxy in an interaction reminiscent of the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 3690
This system consists of a pair of galaxies, dubbed NGC 3690 (or Arp 299), which made a close pass some 700 million years ago. As a result of this interaction, the system underwent a fierce burst of star formation. In the last fifteen years or so six supernovae have popped off in...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 17
This galaxy features a single nucleus, containing a blue central disk with delicate fine structure in the outer parts, and tidal tails indicative of two former disk galaxies. At present these galaxies appear to have completed their merger. The remnant shows clear signs that the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 6050
NGC 6050/IC 1179 (Arp 272) is a remarkable collision between two spiral galaxies, NGC 6050 and IC 1179, and is part of the Hercules Galaxy Cluster, located in the constellation of Hercules. The galaxy cluster is part of the Great Wall of clusters and superclusters, the largest...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 695
NGC 695 is a peculiar galaxy which looks like a revolving tornado. It is a disturbed spiral galaxy, seen face-on, with loosely wound spiral arms. Knotty star-forming regions are tangled in a mesh of dust and gas. NGC 695 is in an interaction with a small companion located just...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy Arp 256
Arp 256 is a stunning system of two spiral galaxies in an early stage of merging. The Hubble image displays two galaxies with strongly disrupted shapes and an astonishing number of blue knots of star formation that look like exploding fireworks. The galaxy to the left has two...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 148-2
ESO 148-2 is a beautiful object that resembles an owl in flight. It consists of a pair of former disk galaxies undergoing a collision. The cores of the two individual galaxies - seen at the center of the image - are embedded in hot dust and contain a large number of stars. Two...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 255-7
ESO 255-7 consists of a quartet of interacting galaxies. Three or four galaxies are embedded in a common structure with an arc-like shape. The upper part of this structure appears almost like one single galaxy but has in fact two component galaxies. The lowest galaxy is...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IC 2810
IC 2810 is a disk galaxy viewed nearly edge-on. It is slightly disturbed by gravitational interaction with a smaller, dusty companion (located to the bottom of the image). The larger galaxy shows blue knots of star formation. Although the pair has no overlapping region at...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy MCG11-002
MCG+08-11-002 is an odd-looking galaxy with a spectacular dark band of absorbing dust in front of the galaxy's center, making it resemble a "Black Eye". Scientists believe that it is the remnant of an earlier collision of two separate galaxies. This peculiar galaxy is at the...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy IC 4687
IC 4687 forms a triplet with two other galaxies: IC 4686 to the right and IC 4689 further to the right. IC 4687 has a chaotic body of stars, gas and dust and a large curly tail to the left. The two companions are partially obscured by dark bands of dust. The interacting triplet...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy NGC 520
NGC 520 is the product of a collision between two disk galaxies that started 300 million years ago. It exemplifies the middle stages of the merging process: the disks of the parent galaxies have merged together, but the nuclei have not yet coalesced. It features an odd-looking...

Hubble Interacting Galaxy ESO 239-2
ESO 239-2 is most likely the result of a cosmic collision or a lengthy merger process that will eventually result in an elliptical galaxy. The messy intermediate stage, captured here, is a galaxy with long, tangled tidal tails that envelope the galaxy's core. This image is part...
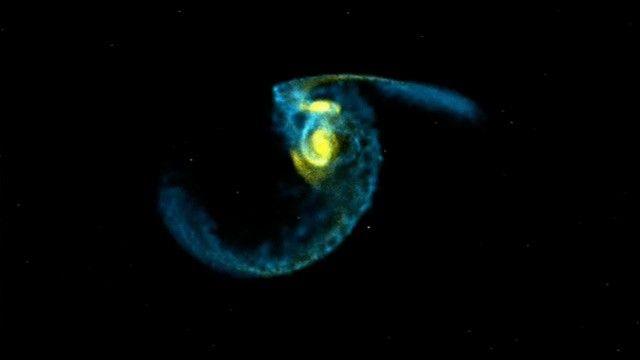
Hubble Gives Glimpse of Milky Way's Future
With the release of dozens of images showing how galaxies collide with each other, astronomers are piecing together details of how mega-galaxies form. Our nearest galaxy neighbor, Andromeda, will be colliding with our own Milky Way in about 5 billion years.

Hubble Studies Different Stages in the Collision Between Galaxies (Visualization)
An image of a galaxy collision captures only one stage of billion-year-long collision process. This visualization of a galaxy collision supercomputer simulation shows the entire collision sequence, and compares the different stages of the collision to different interacting...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov