1 min read
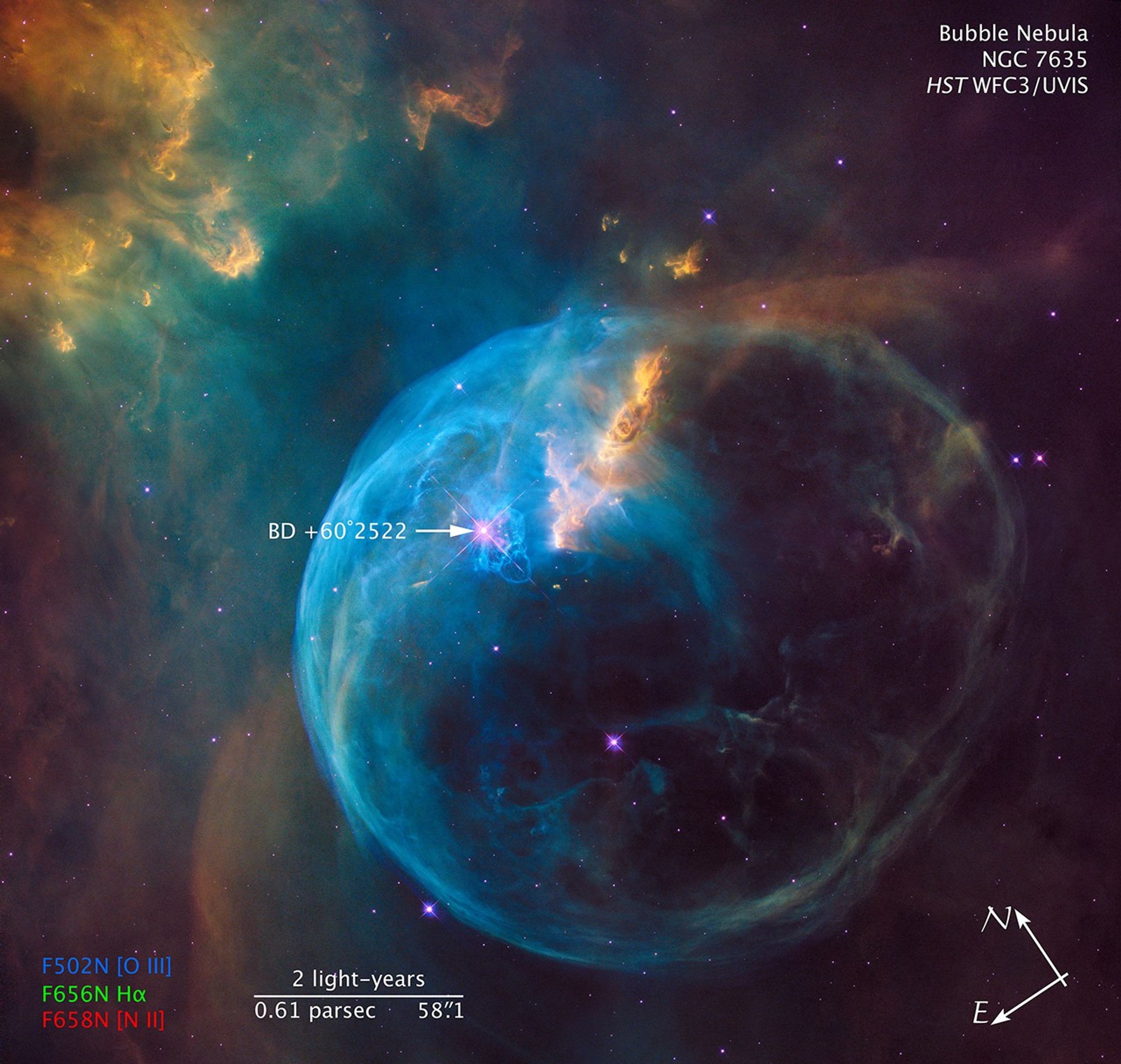
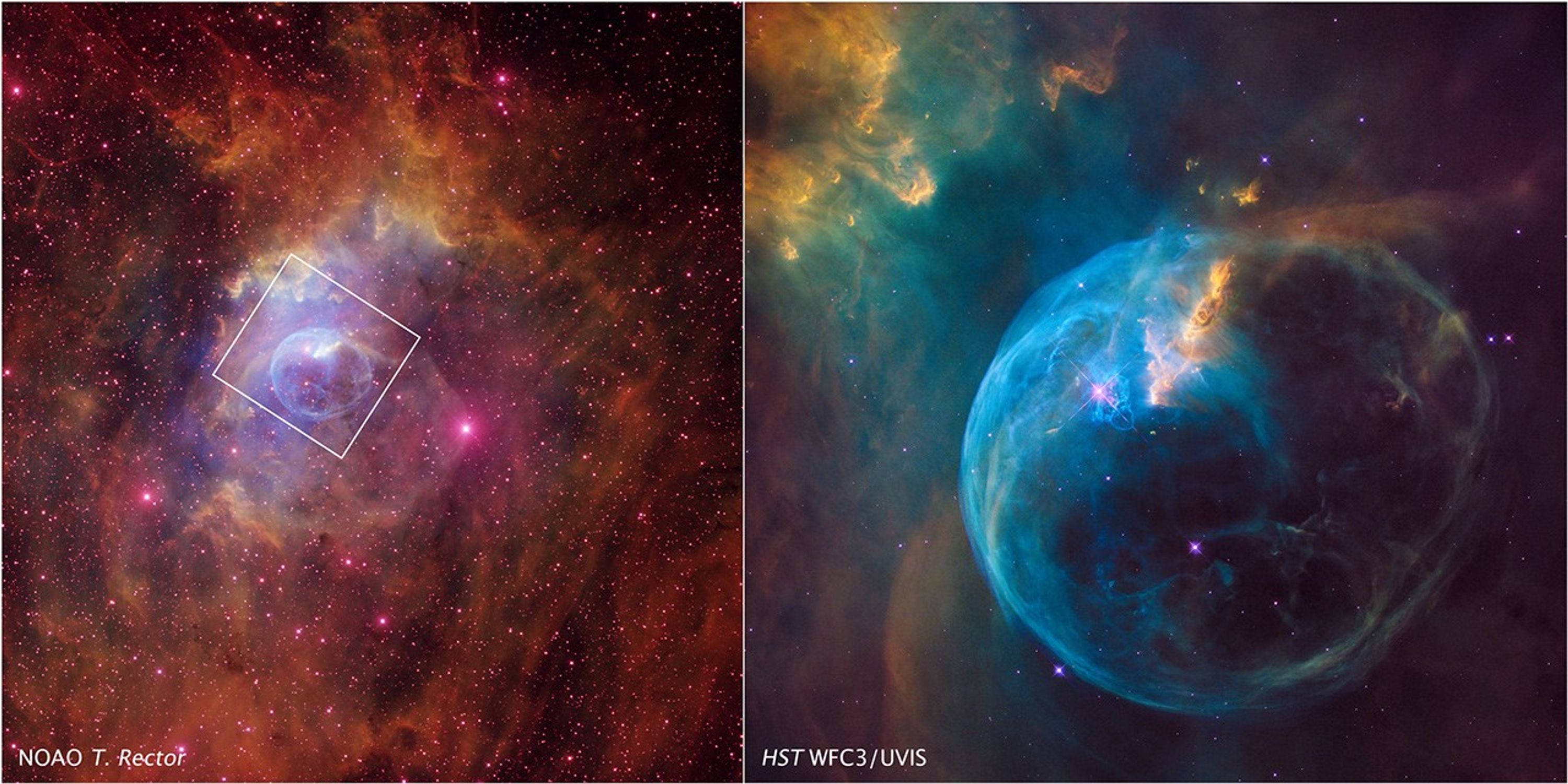
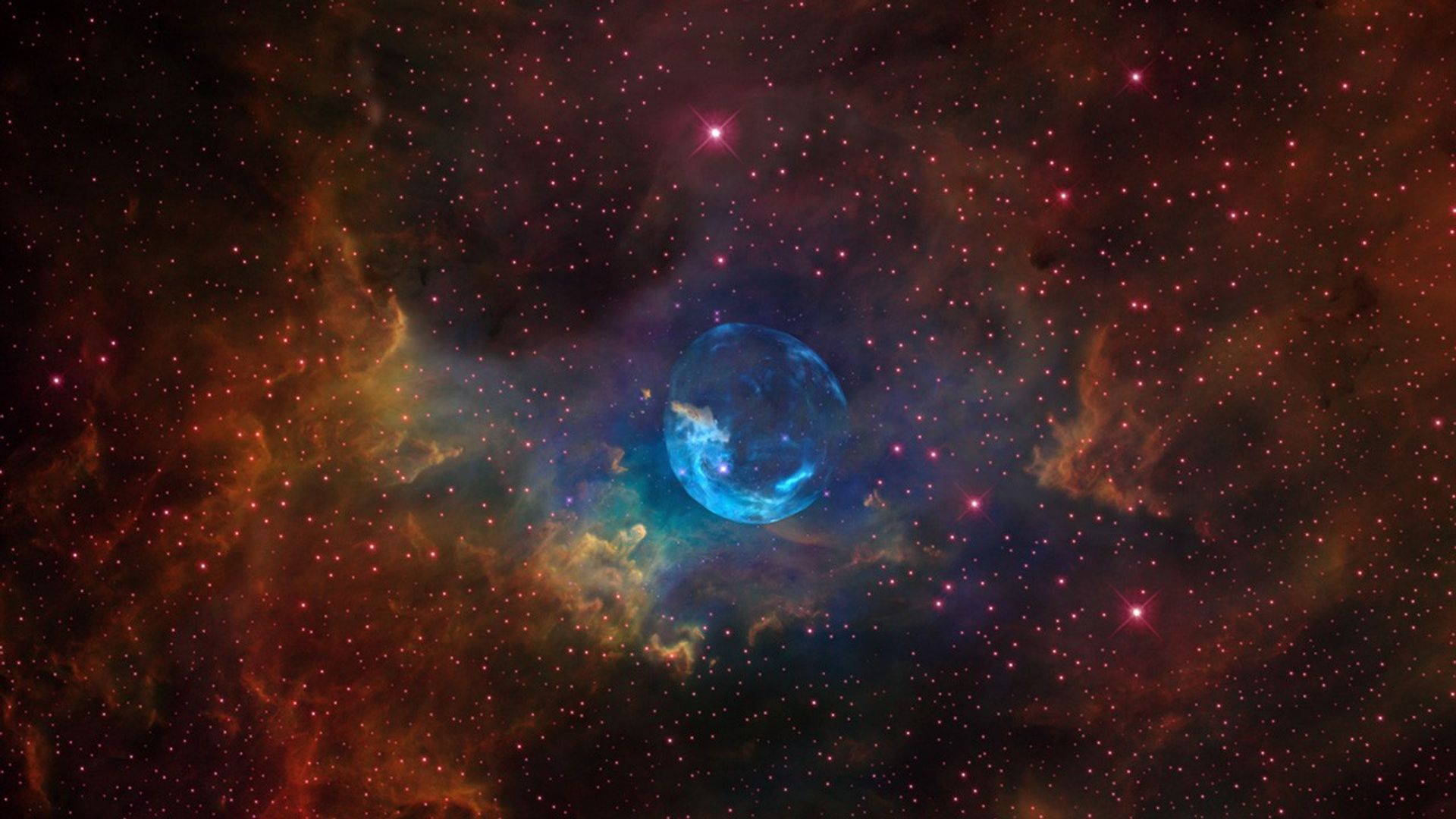
Ground-based Field of View and Location of the Bubble Nebula
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.23h 20m 48.3s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.61° 12' 6.12"
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.7,100 light-years (2,100 parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble data were provided by the HST proposal 14471 taken by the Hubble Heritage Team: Z. Levay, R. Avila, C. Christian, L. Frattare, J. Green, J. Mack, C. Martlin, S. Meyett, M. Mutchler, and S. Porter (STScI/AURA), and K. Noll (NASA/GSFC). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NOAO (left) and HST>WFC3/UVIS (right)
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 25/26, 2016, Exposure Time: 3.5 hours (HST)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.HST: F502N ([O III]), F656N (H-alpha), and F658N ([N II])
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Bubble Nebula, NGC 7635
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Emission nebula, O 6.5 Star
- Release DateApril 21, 2016
- Science ReleaseHubble Sees a Star ‘Inflating’ a Giant Bubble
- CreditT. Rector/University of Alaska Anchorage, H. Schweiker/WIYN and NOAO/AURA/NSF, NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

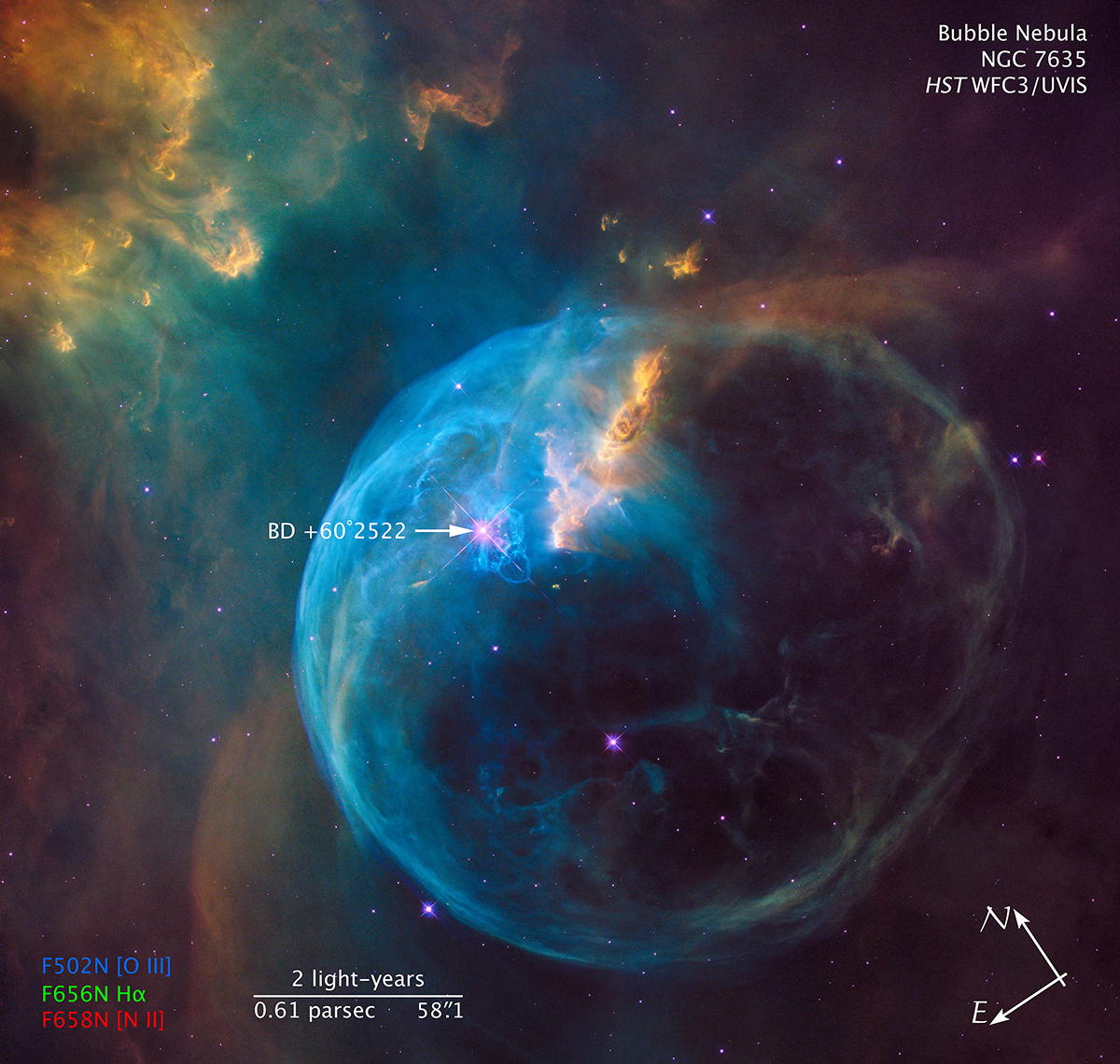
The Hubble image (right) is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3/UVIS instrument. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F502N ([O III]) Green: F656N (H-alpha) Red: F658N ([N II])
Related Images & Videos

Bubble Nebula (NGC 7635)
For the 26th birthday of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers are highlighting a Hubble image of an enormous bubble being blown into space by a super-hot, massive star. The Hubble image of the Bubble Nebula, or NGC 7635, was chosen to mark the 26th anniversary of the...

Animation Approaching the Bubble Nebula
This visualization of the Bubble Nebula begins with a ground-based view that encompasses the glowing cloud. The high-energy light from the Wolf-Rayet star, BD +60°2522, is responsible for ionizing the entire region. The virtual camera flies through the foreground stars and...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov