1 min read
Mars Opposition 2018

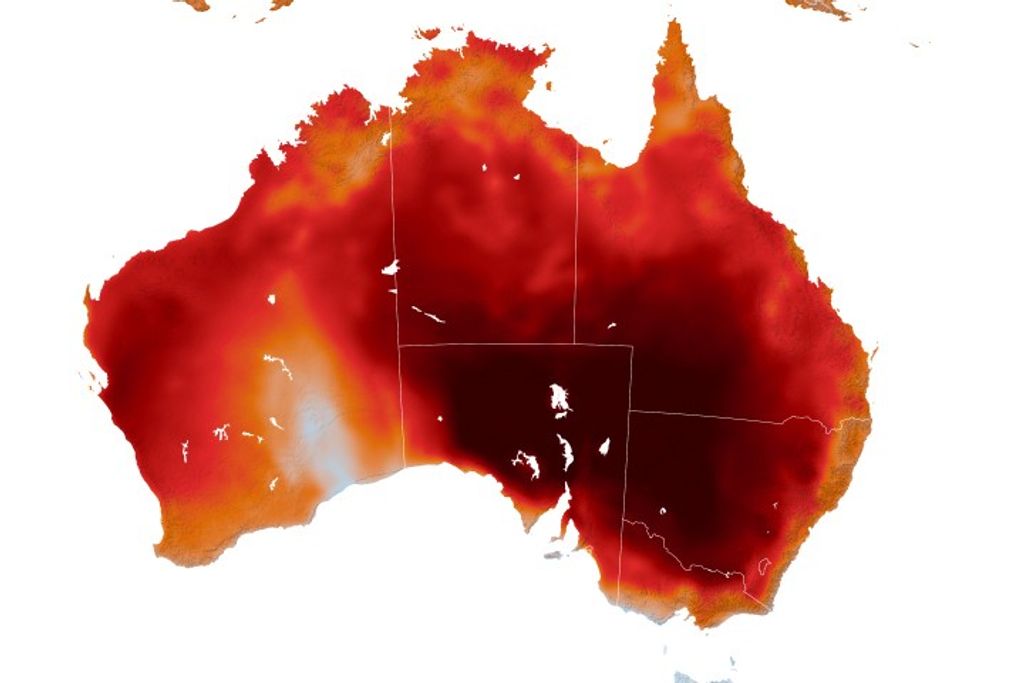
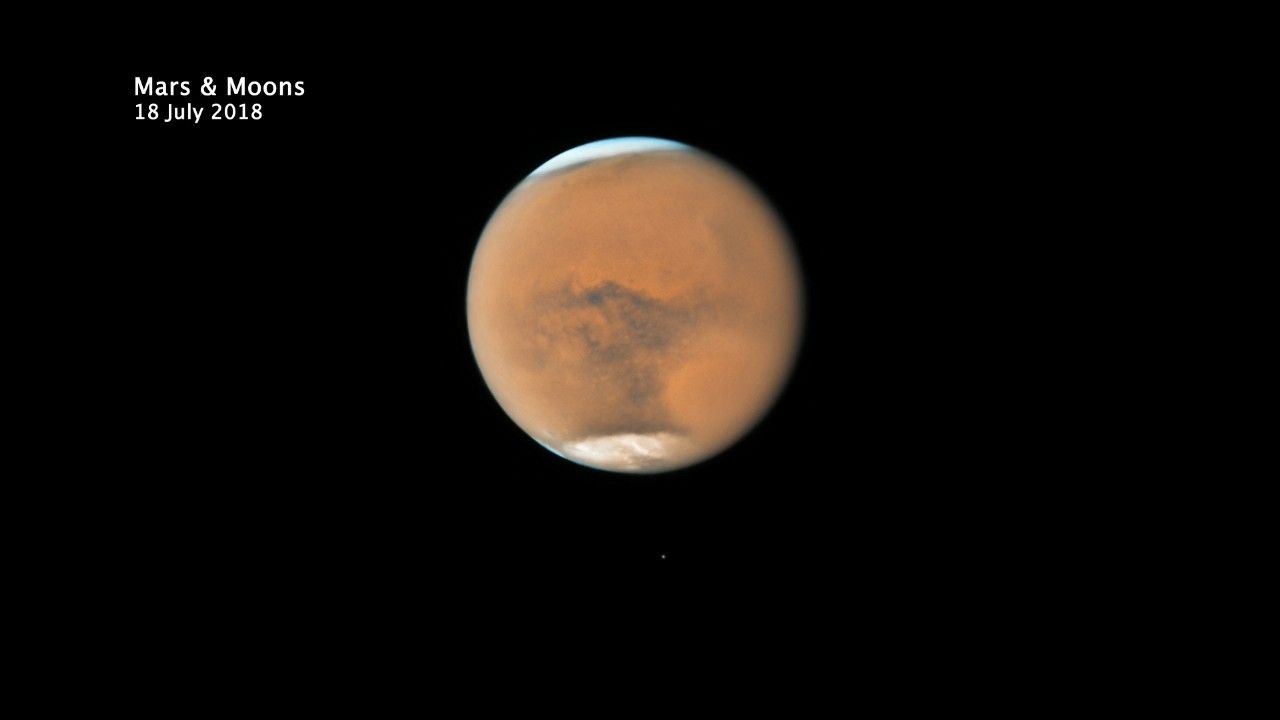
Hubble’s Close-up View of Mars Dust Storm
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope photographed Mars on July 18, near its closest approach to Earth since 2003. The planet was observed near opposition, when the Sun, Earth and Mars are lined up, with Earth sitting in between the Sun and Mars. This proximity gives the Red Planet its brightest appearance in the night sky since the 2003 opposition.
It’s springtime in Mars’ southern hemisphere, where a dust storm erupted and ballooned into a global event that is now blanketing the entire planet. Even so, several distinctive features can be identified.
The large oval area at the lower right is the bright Hellas Basin. About 1,400 miles across and nearly five miles deep, it was formed about 4 billion years ago by an asteroid impact. Many global dust storms originate in this region, the deepest feature on Mars. The orange area in the upper center of the image is Arabia Terra, a vast upland region in northern Mars that covers about 2,800 miles. The landscape is densely cratered and heavily eroded, indicating that it could be among the oldest terrains on the planet.
South of Arabia Terra, running east to west along the equator, are the long dark features known as Sinus Sabaeus (to the east) and Sinus Meridiani (to the west). NASA’s Mars rover Opportunity landed in the western portion of Sinus Meridiani, while its twin, Spirit, landed on the other side of the planet.
The darker regions of Sinus Sabaeus and Sinus Meridiani are covered by dark bedrock and fine-grained sand deposits ground down from ancient lava flows and other volcanic features. These sand grains are coarser and less reflective than the fine dust that gives the brighter regions of Mars their rusty appearance. Because it is autumn in the northern hemisphere, a bright blanket of clouds covers the north polar region. Clouds also can be seen over the southern polar cap.
The two small moons of Mars, Phobos (right) and Deimos (left), appear in the lower half of the image.
This picture of Mars was captured on July 18, at just 36.9 million miles from Earth, near its July 27 opposition. The biennial close approaches between Mars and Earth are not all the same. Mars’ orbit around the Sun is markedly elliptical; the proximity to Earth can range from 35 million miles to 63 million miles. Data from Hubble and the missions studying Mars will provide greater insight into the processes that cause the Martian dust storms.
Oppositions occur because about every two years Earth’s orbit catches up to Mars’ orbit, aligning the Sun, Earth, and Mars in a straight line, so that Mars and the sun are on “opposing” sides of Earth. This phenomenon is a result of the difference in orbital periods between Earth’s orbit and Mars’ orbit. While Earth takes the familiar 365 days to travel once around the Sun, Mars takes 687 Earth days to make its trip around our star. As a result, Earth makes almost two full orbits in the time it takes Mars to make just one, resulting in the occurrence of Martian oppositions about every 26 months.
About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.On July 18, 2018, Mars was 0.39 astronomical unit (37 million miles or 59 million kilometers) away from Earth.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST observations include those from program 15456 (M. Mutchler) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.July 18, 2018
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F275W, F410M, F502N, F673N
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Mars near opposition
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateJuly 26, 2018
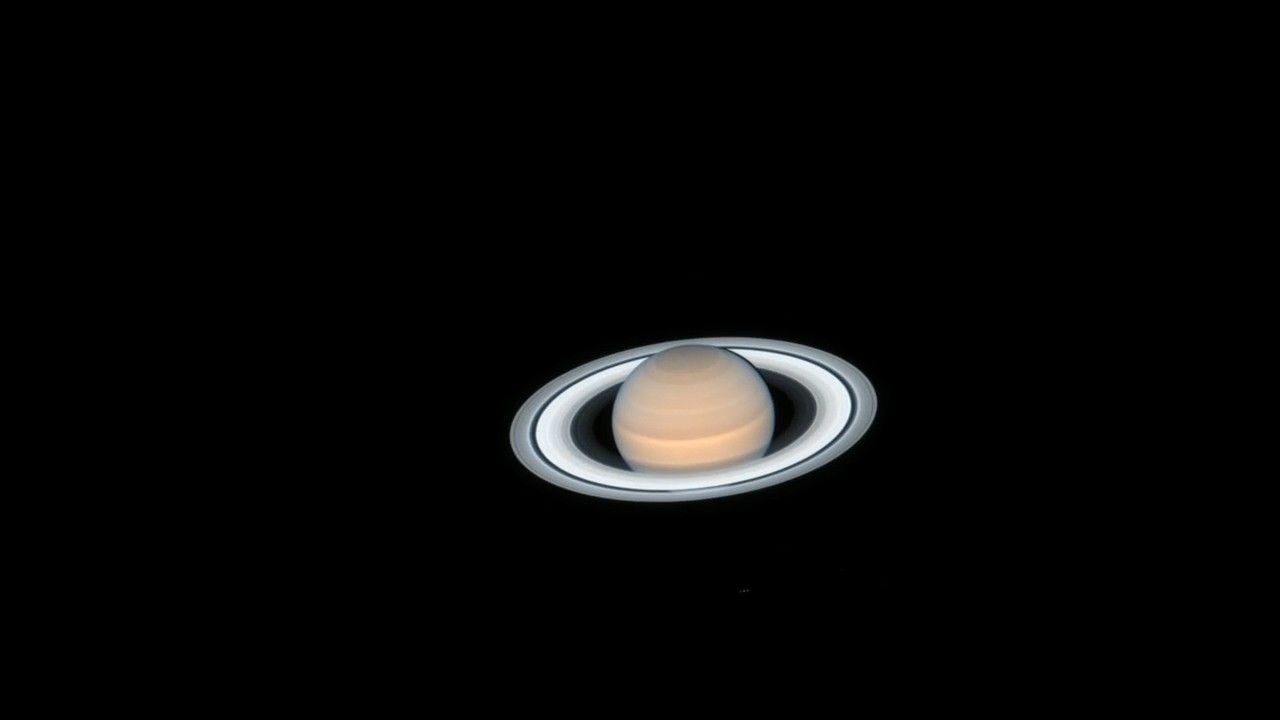
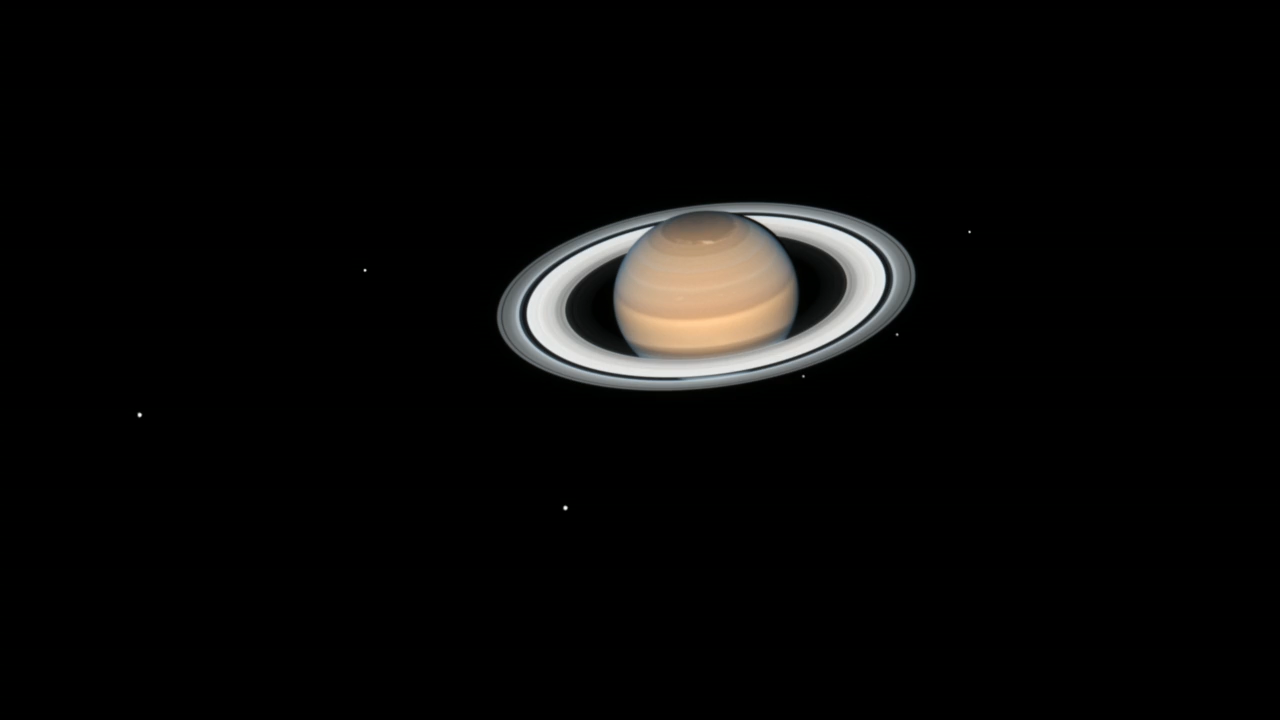
- Science ReleaseSaturn and Mars Team Up to Make Their Closest Approaches to Earth in 2018
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3/UVIS instrument. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Purple: F275W Blue: F410M Green: F502N Red: F673N

Related Images & Videos

Saturn and Mars at Opposition
Hubble’s Latest Portraits of Saturn and Mars NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has photographed Saturn, left, and Mars, right, near their closest approaches to Earth in June and July 2018. The planets were photographed near opposition, when the Sun, Earth and an outer planet are...

Saturn Opposition 2018
Hubble Takes Portrait of Opulent Ring World Saturn is by far the solar system’s most photogenic planet, and in this latest Hubble Space Telescope snapshot it is especially so because Saturn’s magnificent ring system is near its maximum tilt toward Earth (which was in 2017)....

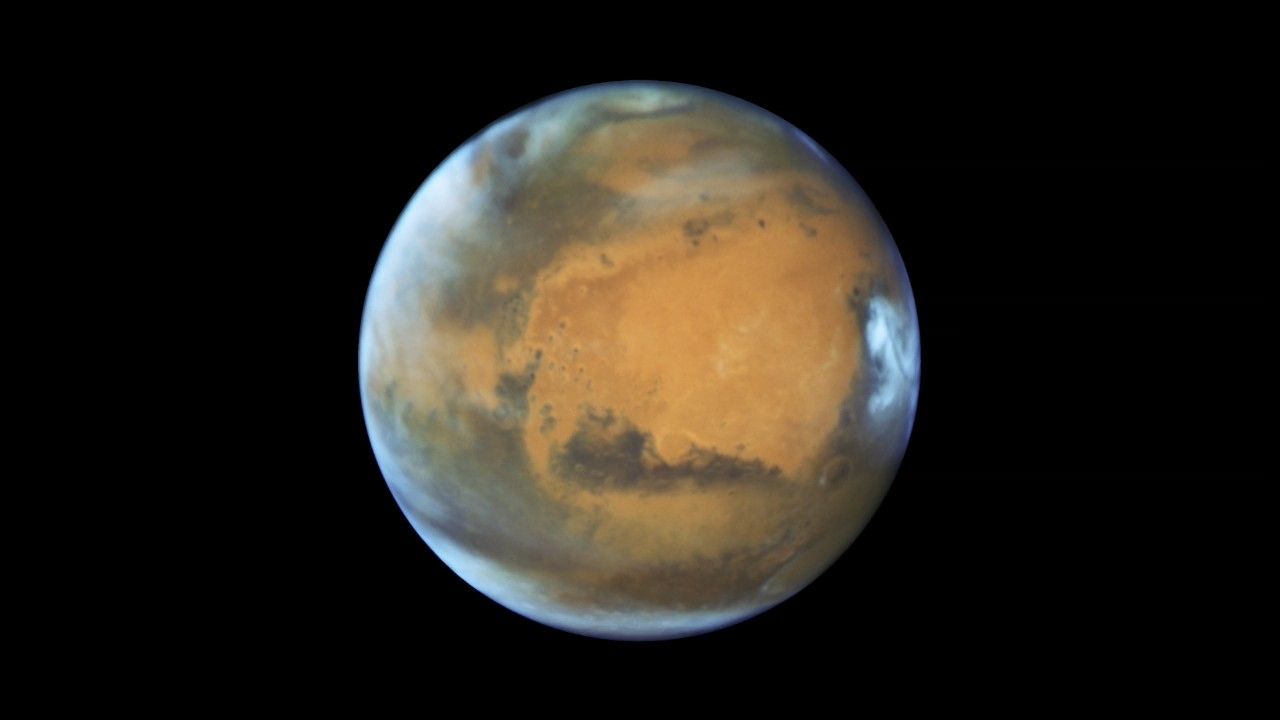
Mars Oppositions 2016 and 2018
Mars Seen in Clear and Dusty Conditions These side-by-side images of Mars, taken roughly two years apart, show very different views of the same hemisphere of Mars. Both were captured when Mars was near opposition, which occurs about every two years, when Earth’s orbit catches up...
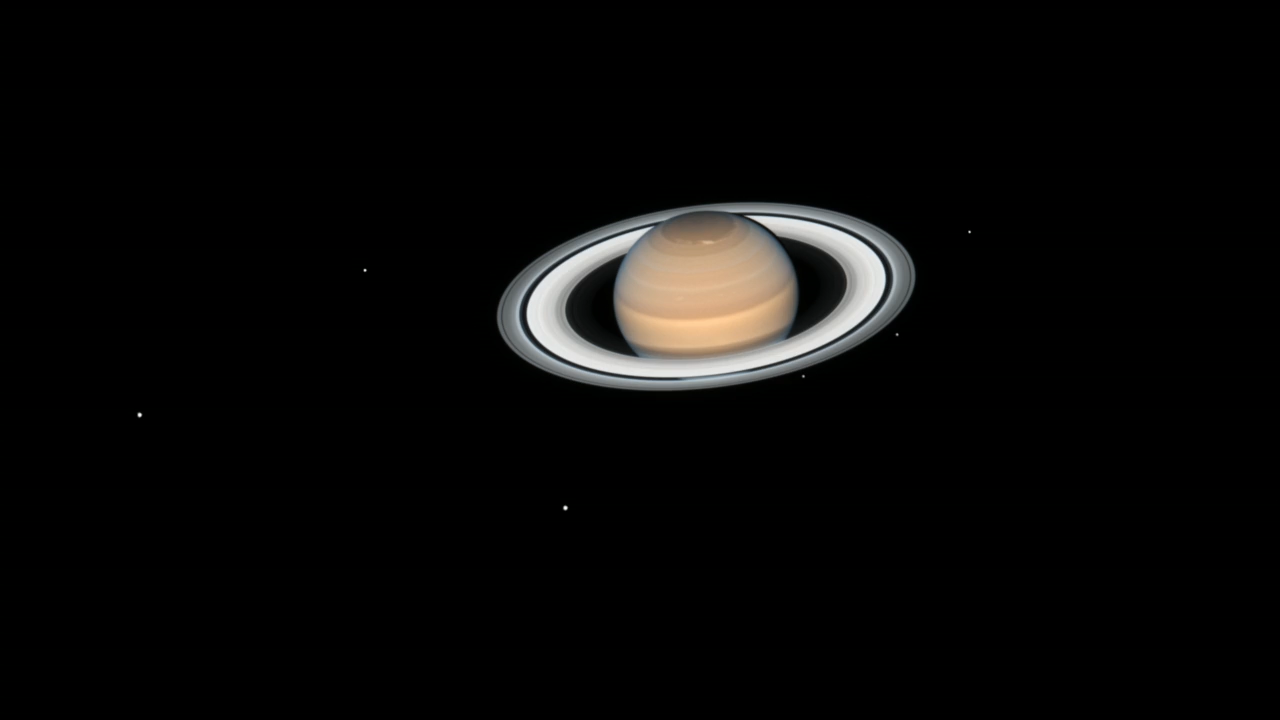
Saturn and Six of Its Moons (Annotated)
This annotated time-lapse animation of Hubble observations shows the rotation of Saturn and six of its moons over roughly 20 hours. In a textbook demonstration of Keplerian motion, the moons closer to the planet orbit more rapidly, while those farther away move more slowly. This...

Mars and Its Moons (Annotated)
This time-lapse animation of Hubble images shows Mars rotating over 43 minutes. The video begins with the moon Deimos traveling from right to left as it orbits Mars. Then Phobos makes an appearance from the right before disappearing behind the Red Planet’s shadow. The...

Mars at Opposition (2016 and 2018)
This video shows the difference in orientation of Mars between the 2016 and 2018 observations, and it also illustrates the obscuration by the 2018 dust storm. The opening image, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope on May 12, 2016, shows a clear atmosphere. Three-dimensional...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov