1 min read
Globular Star Cluster NGC 1466

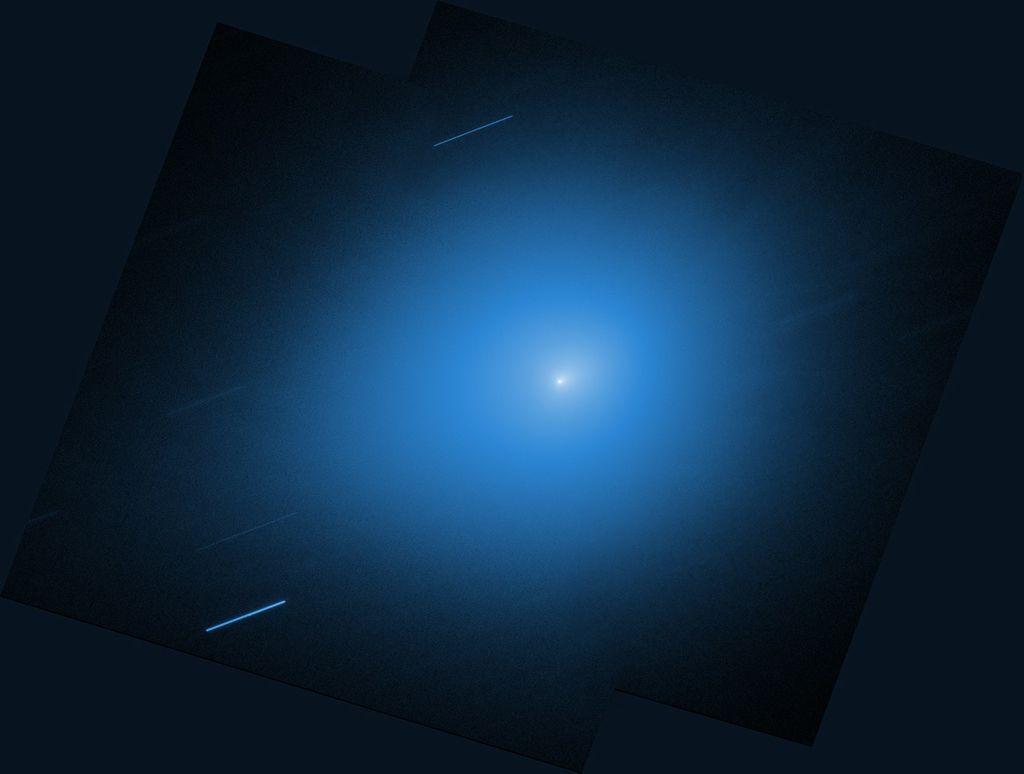
This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reveals an ancient, glimmering ball of stars called NGC 1466. It is a globular cluster — a gathering of stars all held together by gravity — that is slowly moving through space on the outskirts of the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of our closest galactic neighbors.
Blue straggler stars are blue, bright stars, with a higher mass than the average for a cluster, and they are expected to sink towards the center of a star cluster over time. Those closest to the cluster core are the first to migrate inwards, with more distant blue stragglers progressively moving inwards over time.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03:44:32.99
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.71:40:15.92
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Hydrus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The star cluster is located 160,000 light-years away from Earth.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 2.66 arcmin across (about 124 light-years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST observations include those from program 14164 (A. Sarajedini). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS; HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February and July 2016
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.WFC3/UVIS: F336W and ACS/WFC: F606W, and F814W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 1466
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Globular Star Cluster
- Release DateSeptember 9, 2019
- Science ReleaseHubble Explores Formation and Evolution of Star Clusters in Large Magellanic Cloud
- Credit

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3/UVIS and the ACS/WFC instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample narrow and wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F336W Green = F606W Red = F814W

Related Images & Videos

NGC 1466 Compass Image
This image from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reveals an ancient, glimmering ball of stars called NGC 1466. It is a globular cluster — a gathering of stars all held together by gravity — that is slowly moving through space on the outskirts of the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov