1 min read
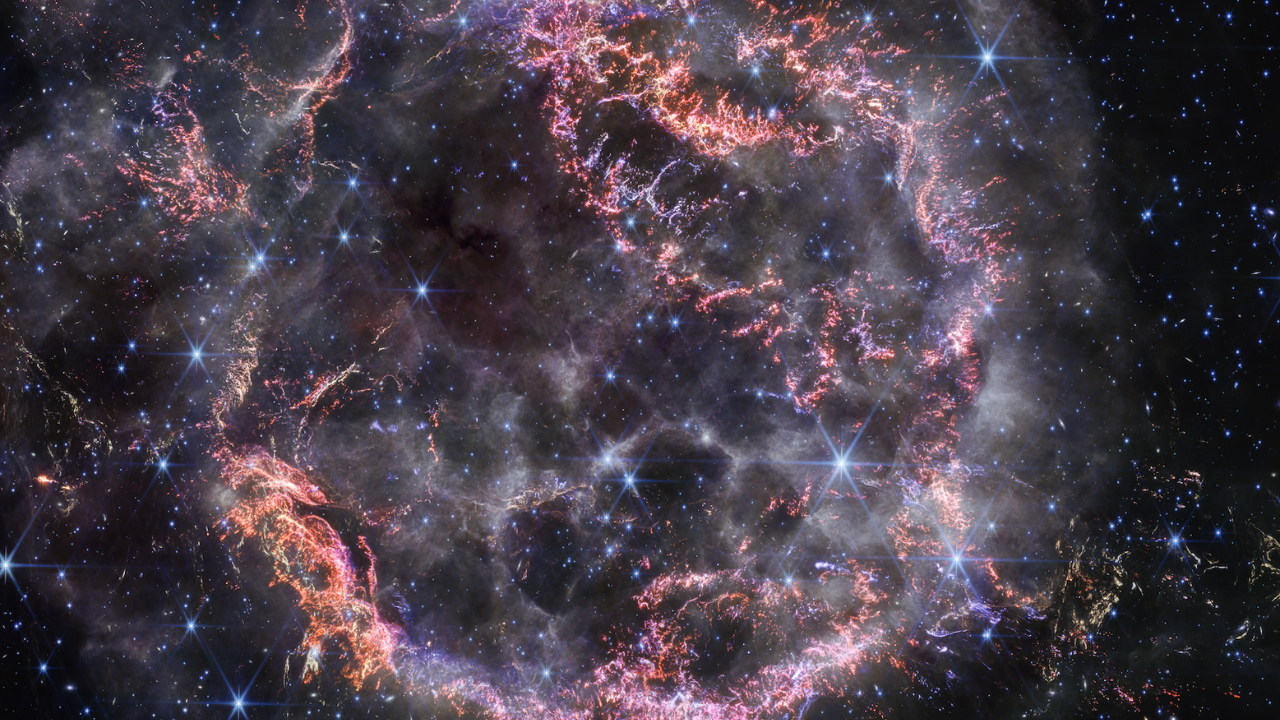
Cassiopeia A Close-ups (NIRCam Image)
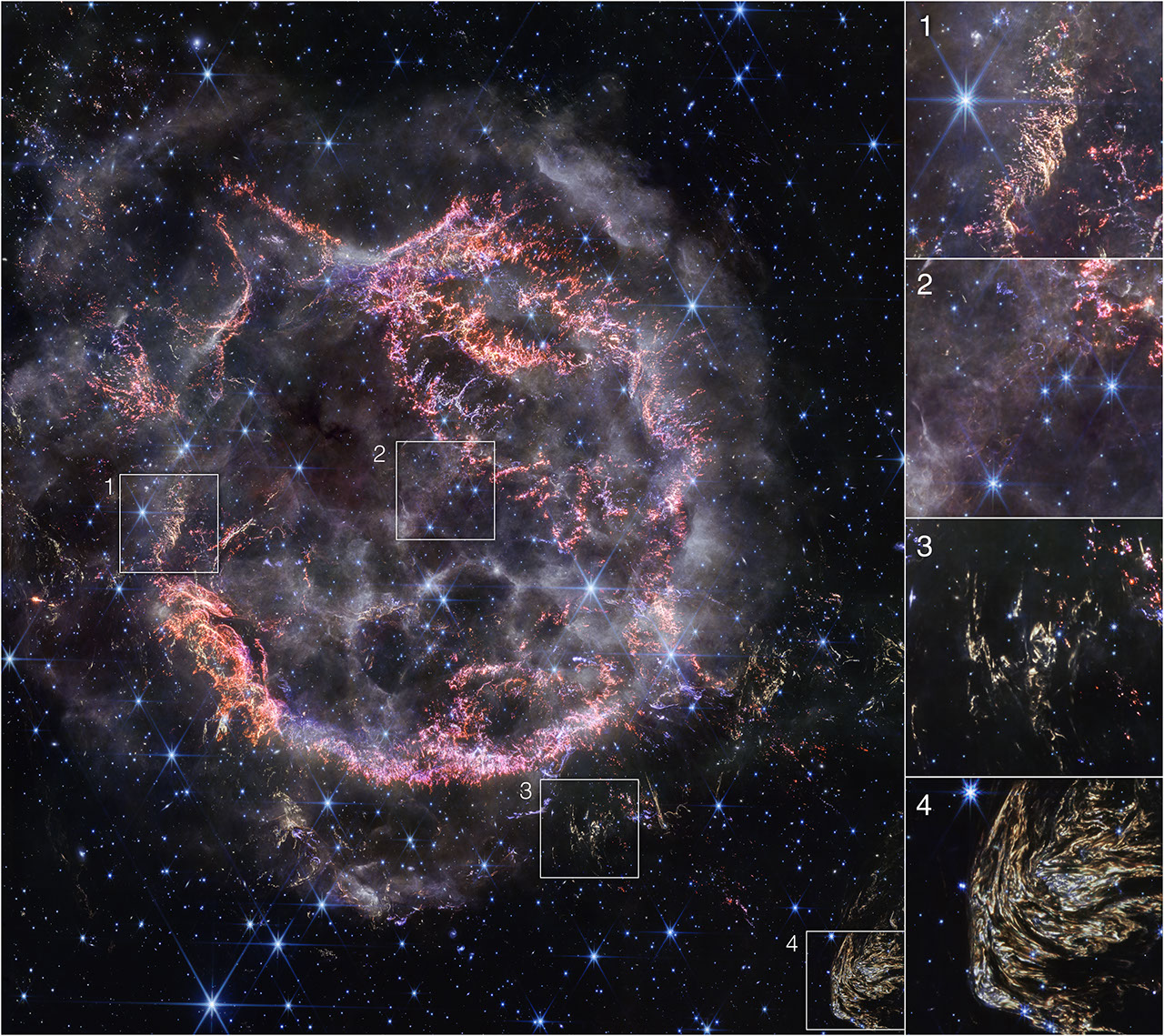

This image highlights several interesting features of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A as seen with Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera):
- NIRCam’s exquisite resolution is able to detect tiny knots of gas, comprised of sulfur, oxygen, argon, and neon from the star itself. Some filaments of debris are too tiny to be resolved even by Webb, meaning they are comparable to or less than 10 billion miles across (around 100 astronomical units). Researchers say this represents how the star shattered like glass when it exploded.
- Circular holes visible in the MIRI image within the Green Monster, a loop of green light in Cas A’s inner cavity, are faintly outlined in white and purple emission in the NIRCam image—this represents ionized gas. Researchers believe this is due to the supernova debris pushing through and sculpting gas left behind by the star before it exploded.
- This is one of a few light echoes visible in NIRCam’s image of Cas A. A light echo occurs when light from the star’s long-ago explosion has reached, and is warming, distant dust, which is glowing as it cools down.
- NIRCam captured a particularly intricate and large light echo, nicknamed Baby Cas A by researchers. It is actually located about 170 light-years behind the supernova remnant.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.23:23:24.00
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+58:48:54.00
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Cassiopeia
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.11,090 light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Main image is about 5.8 arcminutes across (19 light-years).
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 1947 (D. Milisavljevic).
Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.05 November 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F162M, F356W, F444W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Cassiopeia A; SNR G111.7-02.1
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova remnant
- Release DateDecember 10, 2023
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Stuns With New High-Definition Look at Exploded Star
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Danny Milisavljevic (Purdue University), Ilse De Looze (UGhent), Tea Temim (Princeton University)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample specific wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F162M, Green: F356W, Red: F444W
Related Images & Videos
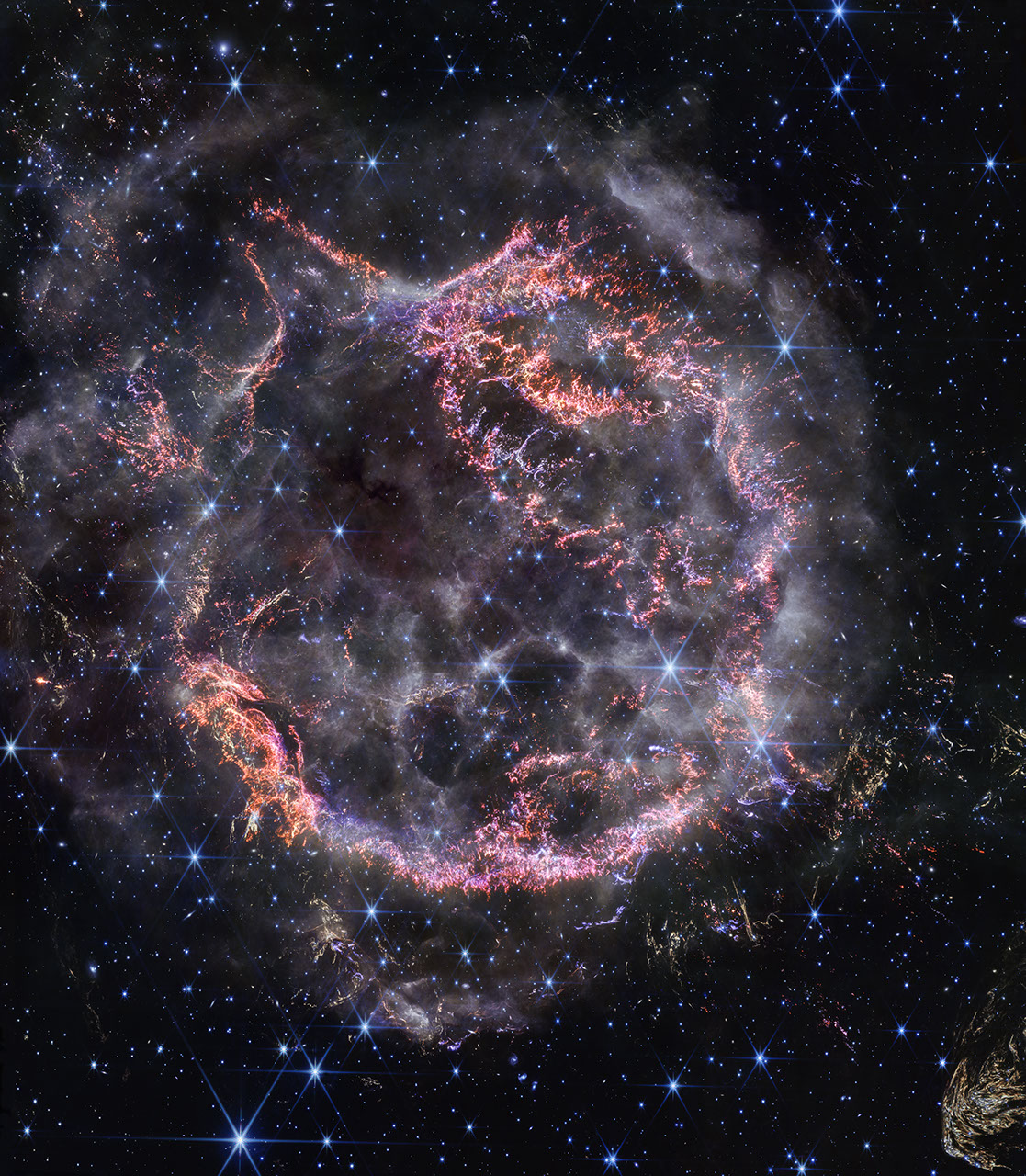

Cassiopeia A (NIRCam Image)
A new high-definition image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) unveils intricate details of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A), and shows the expanding shell of material slamming into the gas shed by the star before it exploded. The most...
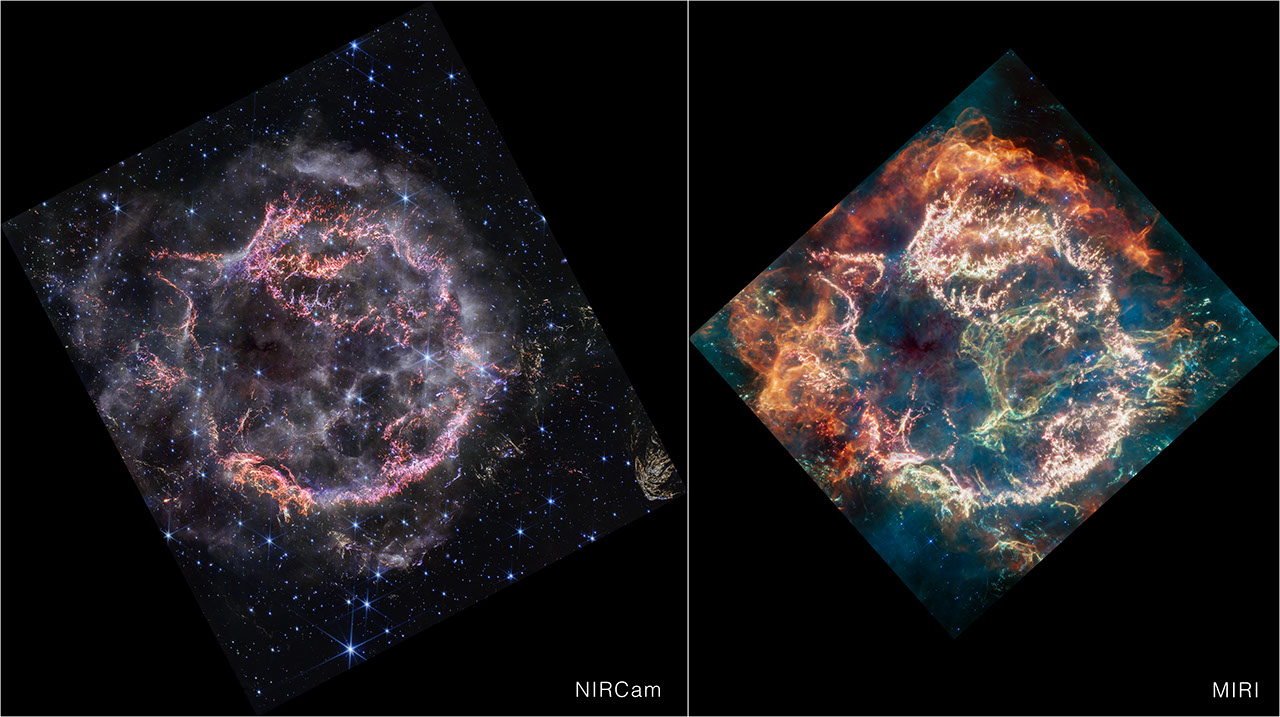
Cassiopeia A (NIRCam and MIRI side by side)
This image provides a side-by-side comparison of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A) as captured by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument). At first glance, Webb’s NIRCam image appears less colorful than the MIRI...
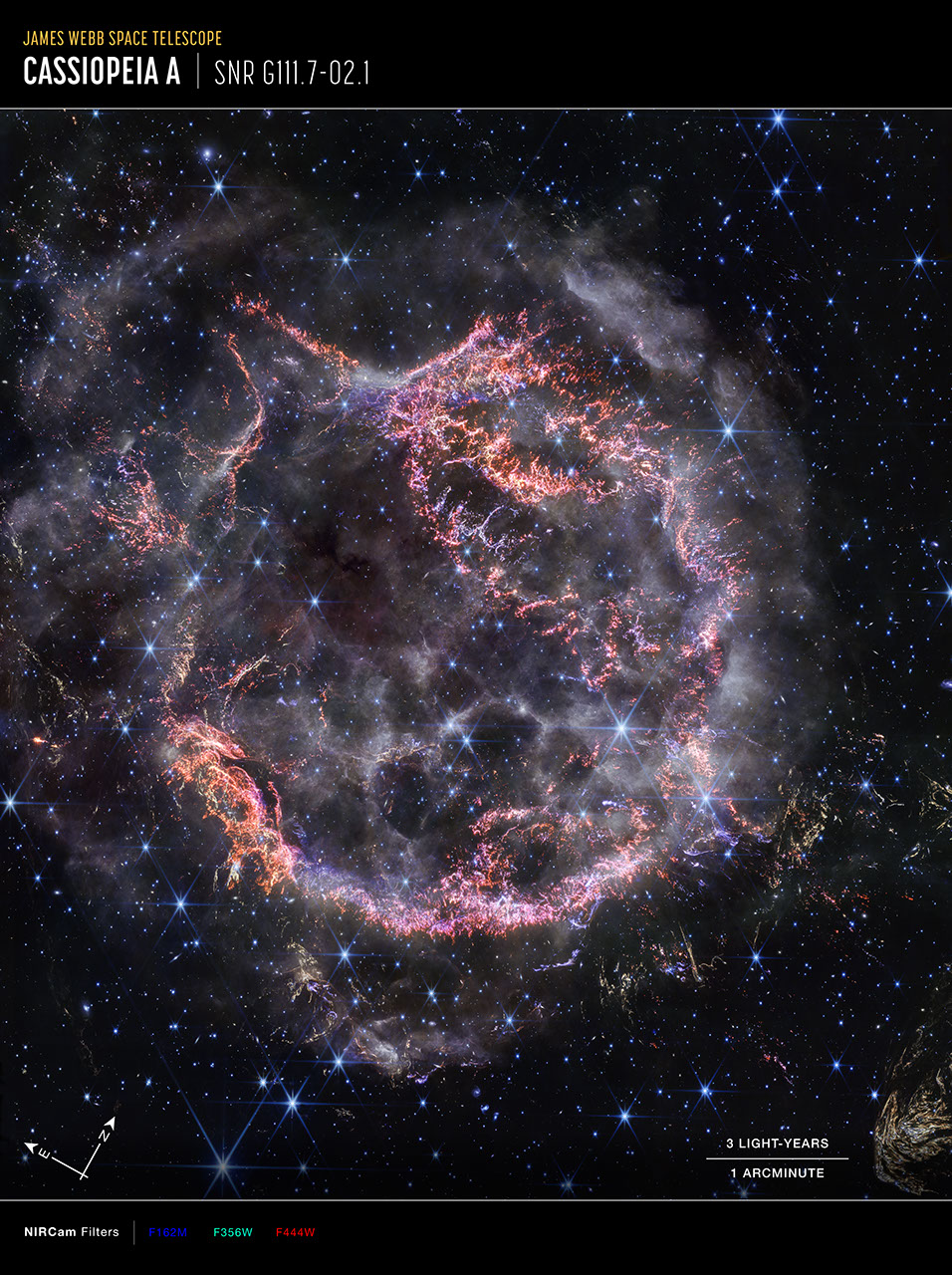

Cassiopeia A (NIRCam Compass Image)
This image of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant, captured by Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) shows compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. The scale bar is labeled in...
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Danny Milisavljevic (Purdue University), Ilse De Looze (UGhent), Tea Temim (Princeton University)