1 min read
A “Rose” Made of Galaxies Highlights Hubble’s 21st Anniversary

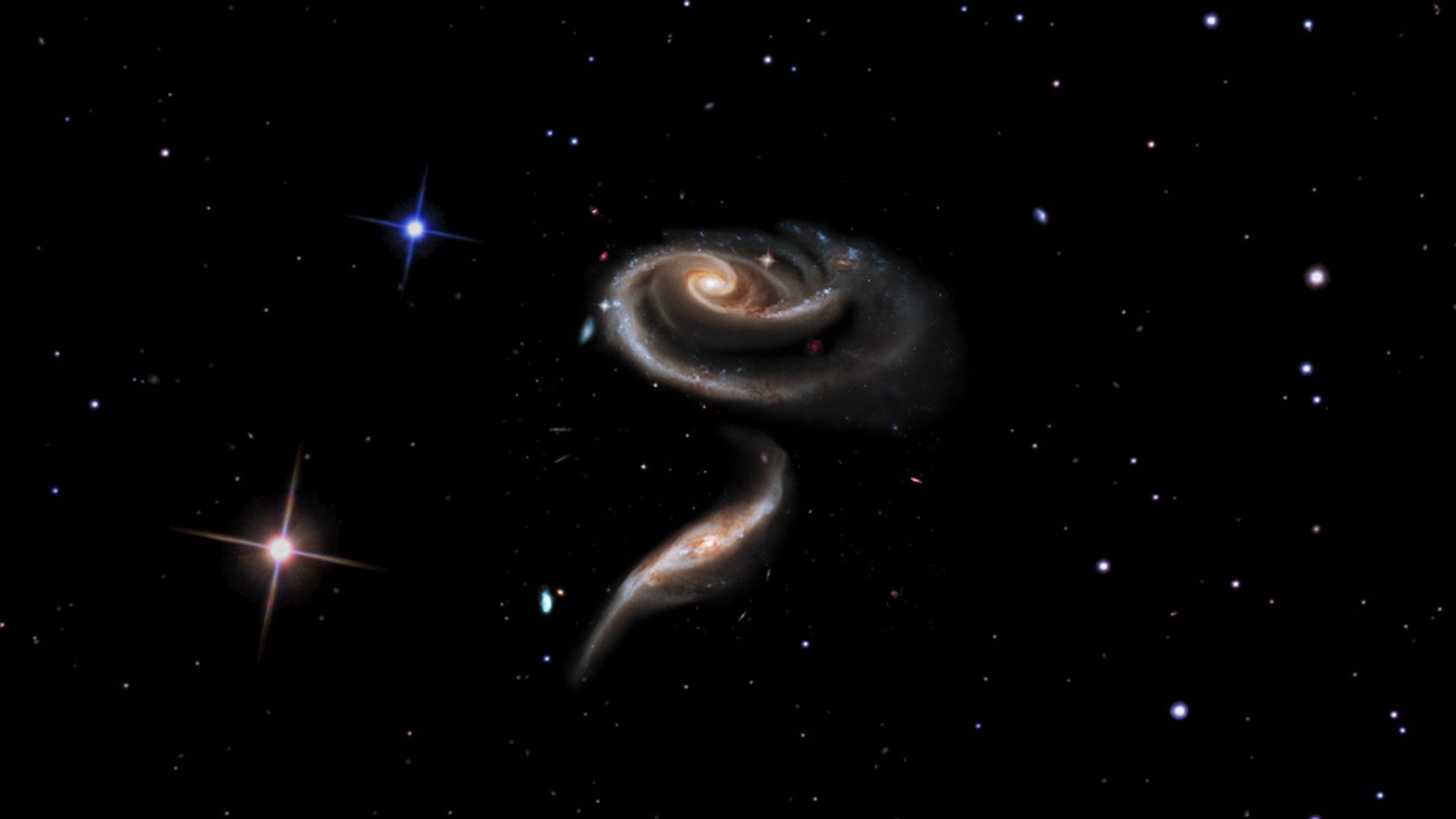
In celebration of the 21st anniversary of the Hubble Space Telescope's deployment into space, astronomers at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md., pointed Hubble's eye to an especially photogenic group of interacting galaxies called Arp 273.
The larger of the spiral galaxies, known as UGC 1810, has a disk that is tidally distorted into a rose-like shape by the gravitational tidal pull of the companion galaxy below it, known as UGC 1813. A swath of blue jewels across the top is the combined light from clusters of intensely bright and hot young blue stars. These massive stars glow fiercely in ultraviolet light.
The smaller, nearly edge-on companion shows distinct signs of intense star formation at its nucleus, perhaps triggered by the encounter with the companion galaxy.
A series of uncommon spiral patterns in the large galaxy is a tell-tale sign of interaction. The large, outer arm appears partially as a ring, a feature seen when interacting galaxies actually pass through one another. This suggests that the smaller companion actually dived deep, but off-center, through UGC 1810. The inner set of spiral arms is highly warped out of the plane with one of the arms going behind the bulge and coming back out the other side. How these two spiral patterns connect is still not precisely known.
A possible mini-spiral may be visible in the spiral arms of UGC 1810 to the upper right. It is noticeable how the outermost spiral arm changes character as it passes this third galaxy, from smooth with lots of old stars (reddish in color) on one side to clumpy and extremely blue on the other. The fairly regular spacing of the blue star-forming knots fits with what is seen in the spiral arms of other galaxies and is predictable based on instabilities in the gas contained within the arm.
The larger galaxy in the UGC 1810 - UGC 1813 pair has a mass that is about five times that of the smaller galaxy. In unequal pairs such as this, the relatively rapid passage of a companion galaxy produces the lopsided or asymmetric structure in the main spiral. Also in such encounters, the starburst activity typically begins in the minor galaxies earlier than in the major galaxies. These effects could be due to the fact that the smaller galaxies have consumed less of the gas present in their nucleus, from which new stars are born.
Arp 273 lies in the constellation Andromeda and is roughly 300 million light-years away from Earth. The image shows a tenuous tidal bridge of material between the two galaxies that are separated by tens of thousands of light-years from each other.
The interaction was imaged on December 17, 2010, with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
This Hubble image is a composite of data taken with three separate filters on WFC3 that allow a broad range of wavelengths covering the ultraviolet, blue, and red portions of the spectrum.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.02h 21m 30.6s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.39° 21' 57.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Andromeda
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 340 million light-years (105 million parsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is 2.6 arcminutes (260,000 light-years or 80,000 parsecs) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 12326: K. Noll (PI), Z. Levay, M. Mutchler, T. Borders, L. Frattare, M. Livio, C. Christian, and H. Bond (Hubble Heritage Team/STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.December 17, 2010, Exposure Time: 5.9 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F390W (U), F475X (g), and F600LP (Red Longpass)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Arp 273, UGC 1810
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Interacting Galaxies
- Release DateApril 20, 2011
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Celebrates 21st Anniversary with “Rose” of Galaxies
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3 instrument on HST. Several filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F390W (U) Green: F475X (g) Red: F600LP (Red Longpass)

Related Images & Videos

Rendezvous with Interacting Galaxies Arp 273
This movie presents a visualization of the interacting galaxy group known as Arp 273. This unique three-dimensional view presents a visual reminder that the objects in Hubble images are not all at the same distance, but rather spread across light-years of space. The...
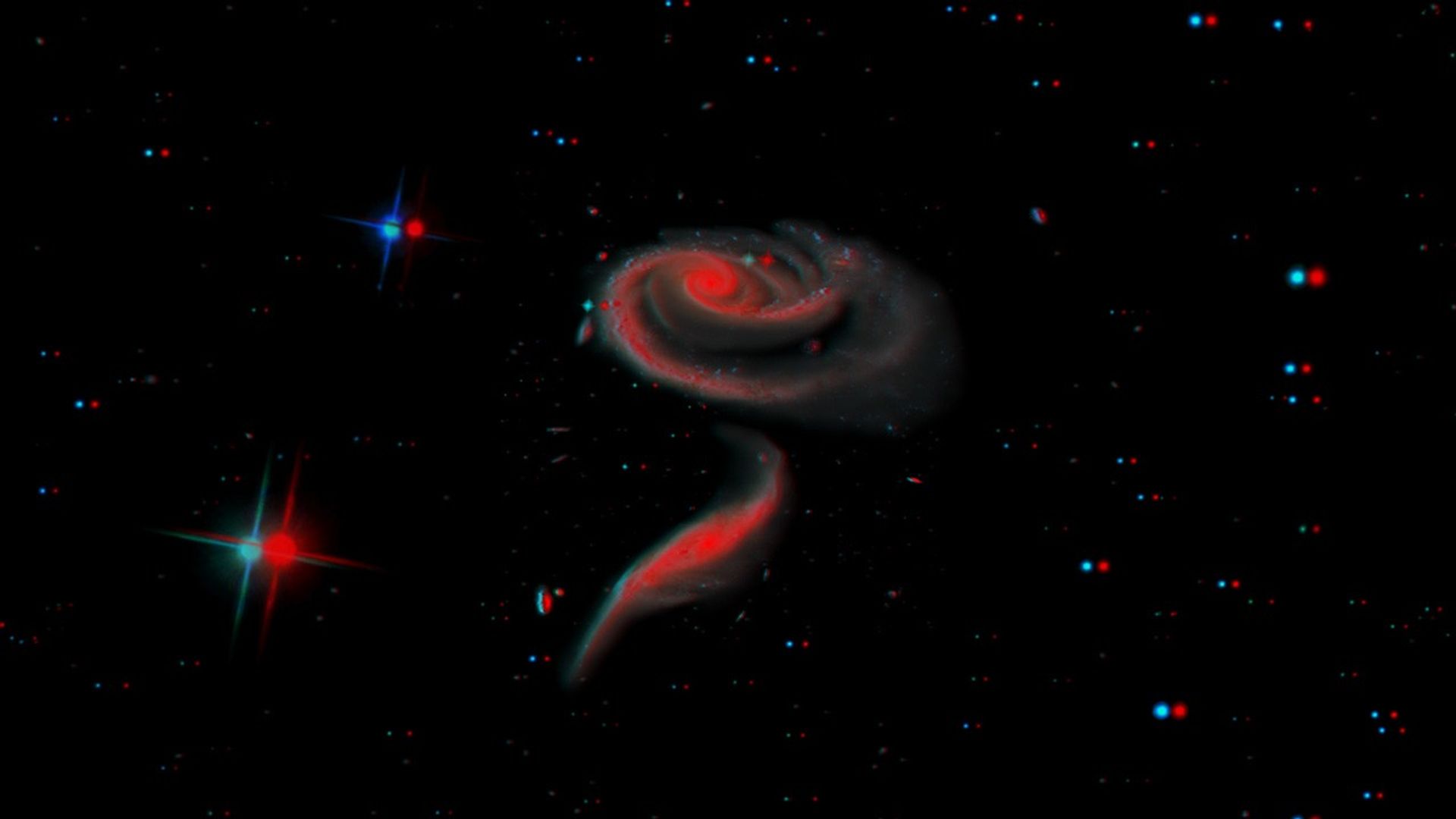

Stereo 3-D Rendezvous with Interacting Galaxies Arp 273
This movie presents a visualization of the interacting galaxy group known as Arp 273. This unique three-dimensional view presents a visual reminder that the objects in Hubble images are not all at the same distance, but rather spread across light-years of space. The...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov