1 min read
ACS Images of KBO “Quaoar”
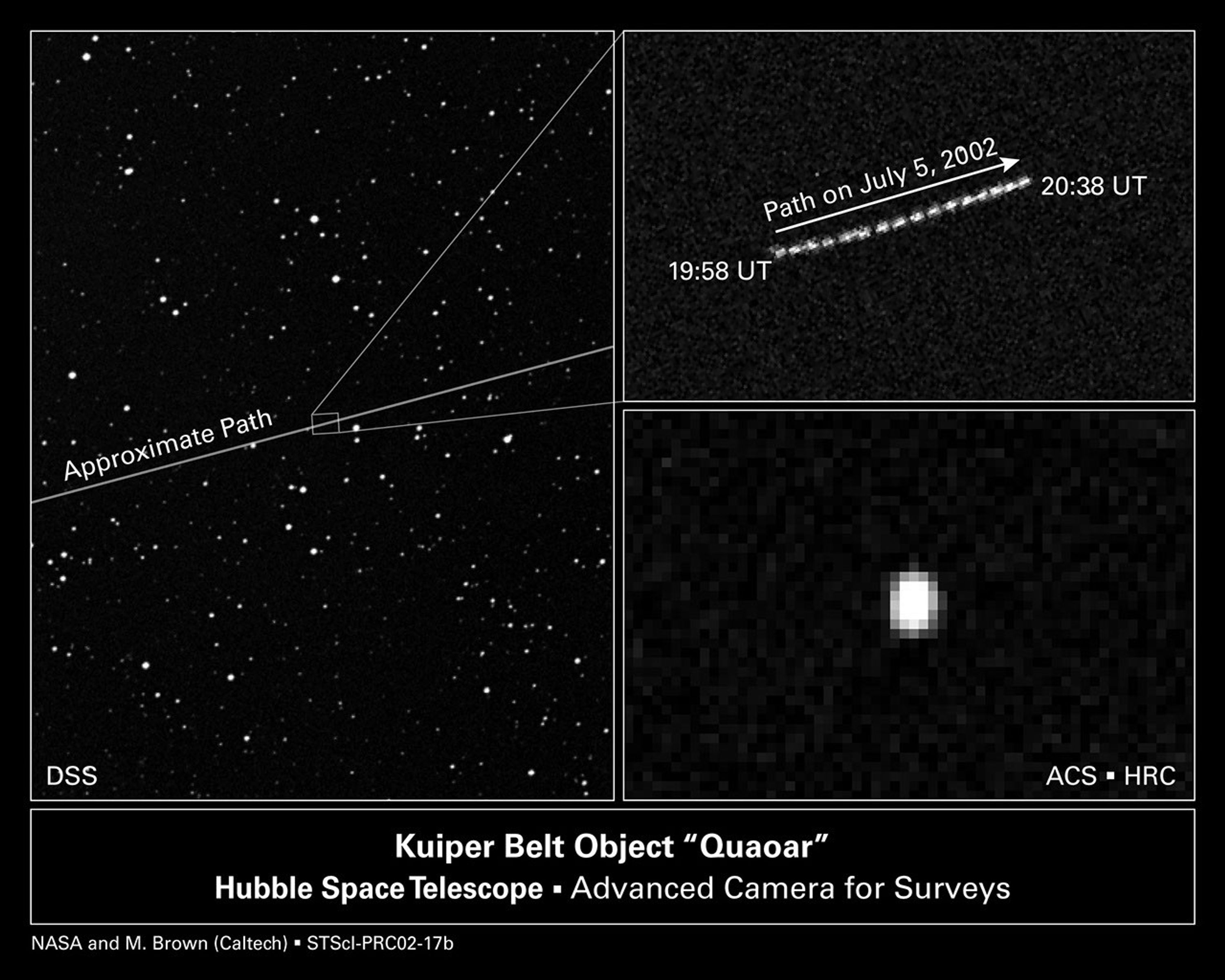

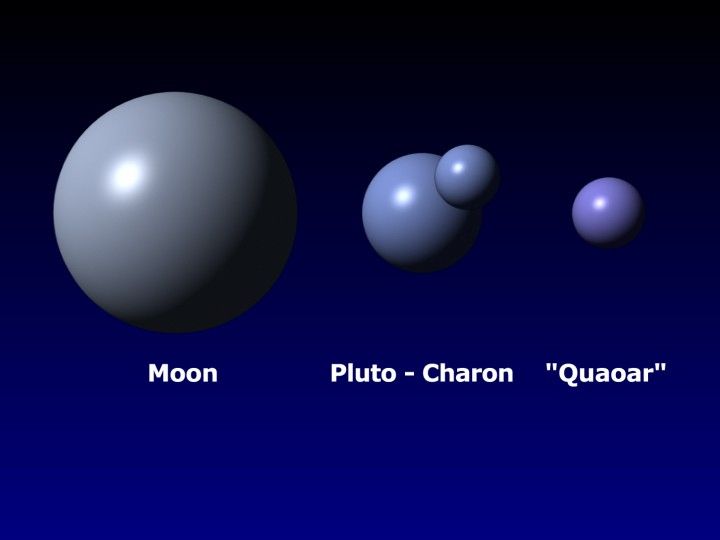
With the help of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have determined that 2002 LM60, an icy Kuiper belt object dubbed "Quaoar," by its discoverers, is the largest body found in the solar system since the discovery of Pluto 72 years ago. Quaoar (pronounced kwa-whar) is about half the size of Pluto. Like Pluto, Quaoar dwells in the Kuiper belt, an icy debris field of comet-like bodies extending 7 billion miles beyond Neptune's orbit.
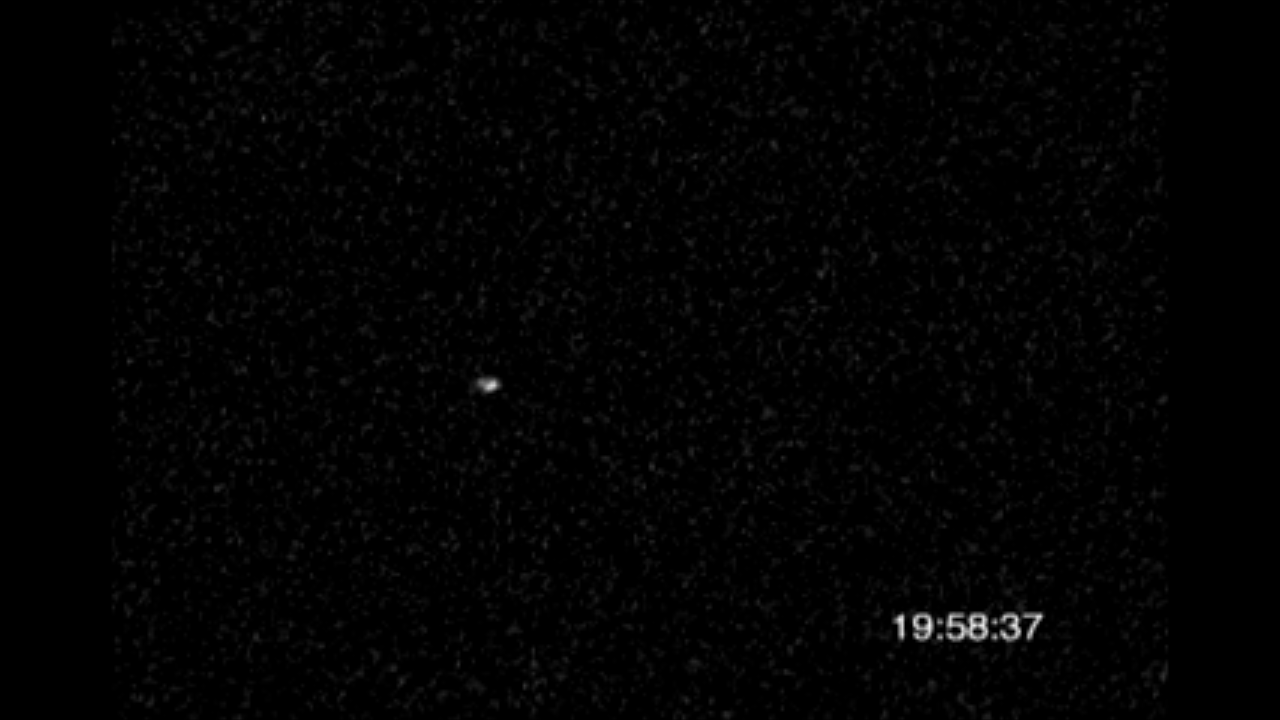
The photograph at bottom right, taken by Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys, is a close-up view of the icy world. Only Hubble's sharp vision can resolve the disk of this distant world, leading to the first-ever direct measurement of the true size of a Kuiper belt object. Quaoar's diameter is about 800 miles (1300 kilometers). It is the farthest object in the solar system ever to be resolved by a telescope. The Hubble photo does not show details of Quaoar's icy surface because the object is too far away. Quaoar is about 4 billion miles (6.5 billion kilometers) from Earth, more than 1 billion miles farther than Pluto. The photograph was made by assembling 16 pictures of the object. Observations were made July 5, 2002 and Aug. 1, 2002.
The image at upper right is a composite of 16 snapshots of the object as it traveled across the sky. Quaoar is in a circular orbit around the Sun. The snapshots were taken over a 29- minute span on July 5.
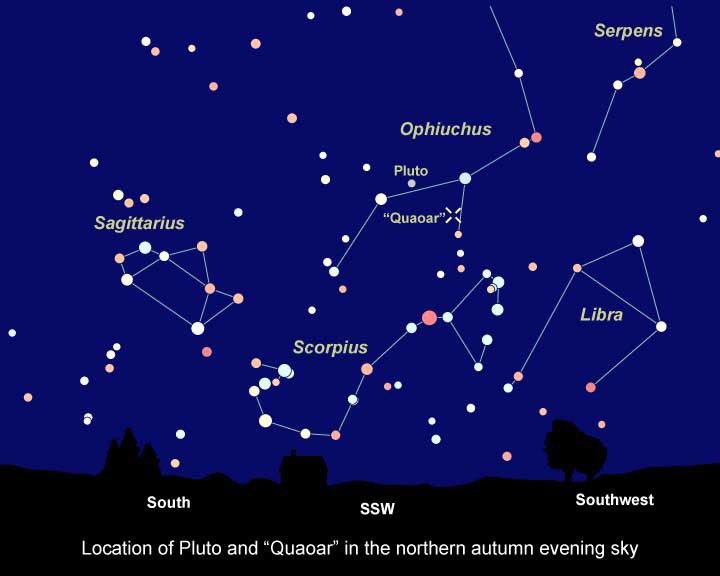
The photograph at left, part of the Digitized Sky Survey, shows the Kuiper belt object's approximate path across the summer constellation Ophiuchus. The small box in the center defines Hubble's narrow view, an area devoid of stars.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.16h 36m 18s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-14° 48' 0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ophiuchus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 43 astronomical units (about 4 billion miles or 6.5 billion kilometers)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Approximately 800 miles in diameter (about 1300 kilometers)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Principal Astronomers: M. Brown and C. Trujillo (Caltech) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.DSS (left), ACS/HRC (top right), and HST>ACS (bottom right)
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.July 5, 2002 (HRC), July 5, 2002 and August 1, 2002 (ACS)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.2002 LM60, Quaoar
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Kuiper Belt Object
- Release DateOctober 7, 2002
- Science ReleaseHubble Spots an Icy World Far Beyond Pluto
- CreditNASA and Michael Brown (Caltech, Pasadena, CA)
Related Images & Videos

Artist's View of Kuiper Belt Object "Quaoar"
This is an artist's impression of the icy Kuiper belt object 2002 LM60, dubbed "Quaoar" by its discoverers. With the help of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have determined that Quaoar (pronounced kwa-whar) is the largest body found in the solar system since the...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov