1 min read
Disruption of the Red Supergiant Star Betelgeuse
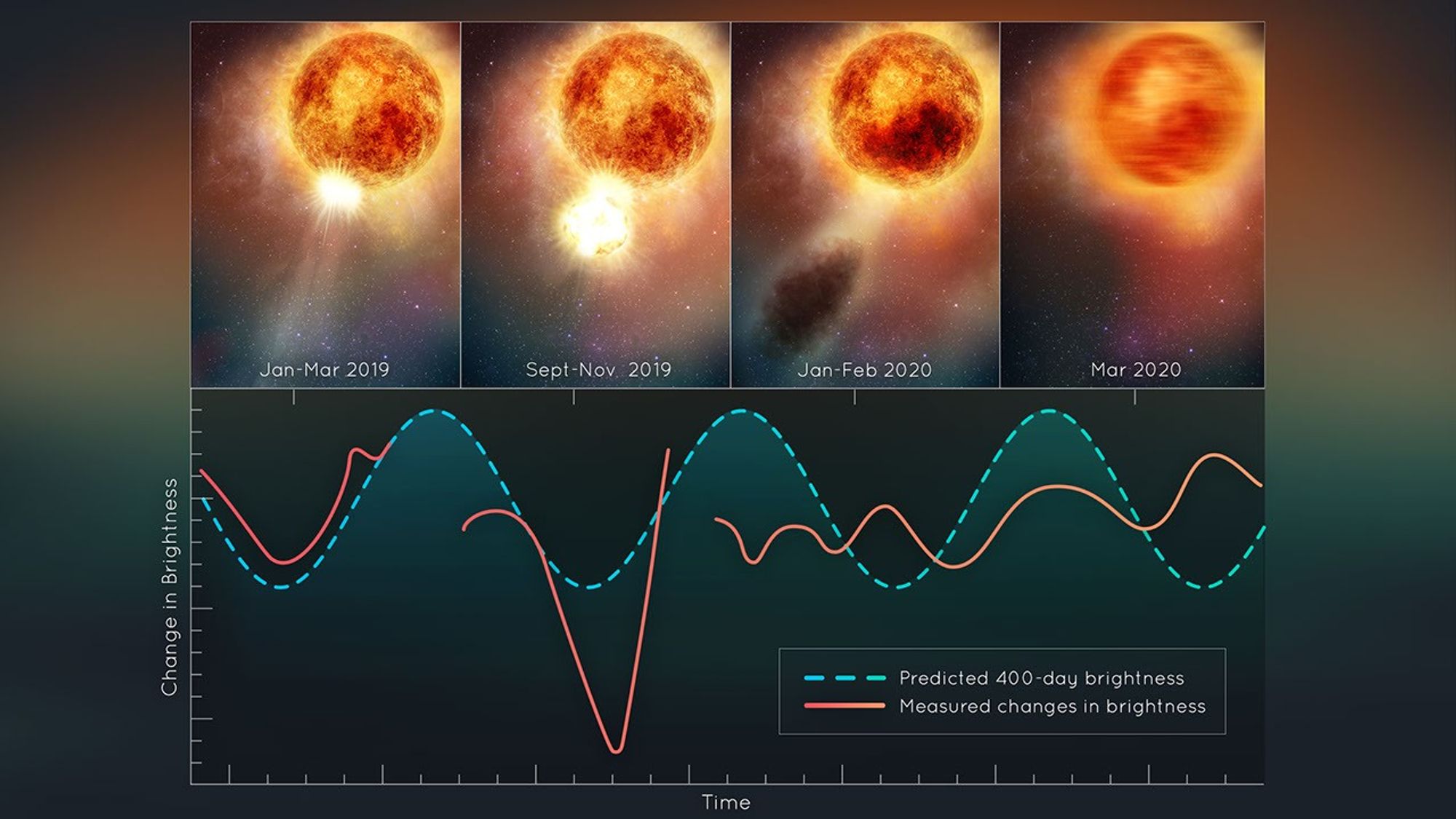
This illustration plots changes in the brightness of the red supergiant star Betelgeuse, following the titanic mass ejection of a large piece of its visible surface. The escaping material cooled to form a cloud of dust that temporarily made the star look dimmer, as seen from Earth. This unprecedented stellar convulsion disrupted the monster star’s 400-day-long oscillation period that astronomers had measured for more than 200 years. The interior may now be jiggling like a plate of gelatin dessert.
- Release DateAugust 11, 2022
- Science ReleaseHubble Sees Red Supergiant Star Betelgeuse Slowly Recovering After Blowing Its Top
- CreditNASA, ESA, Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI)
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov



























