1 min read
Galactic Black Hole with Optical Jet
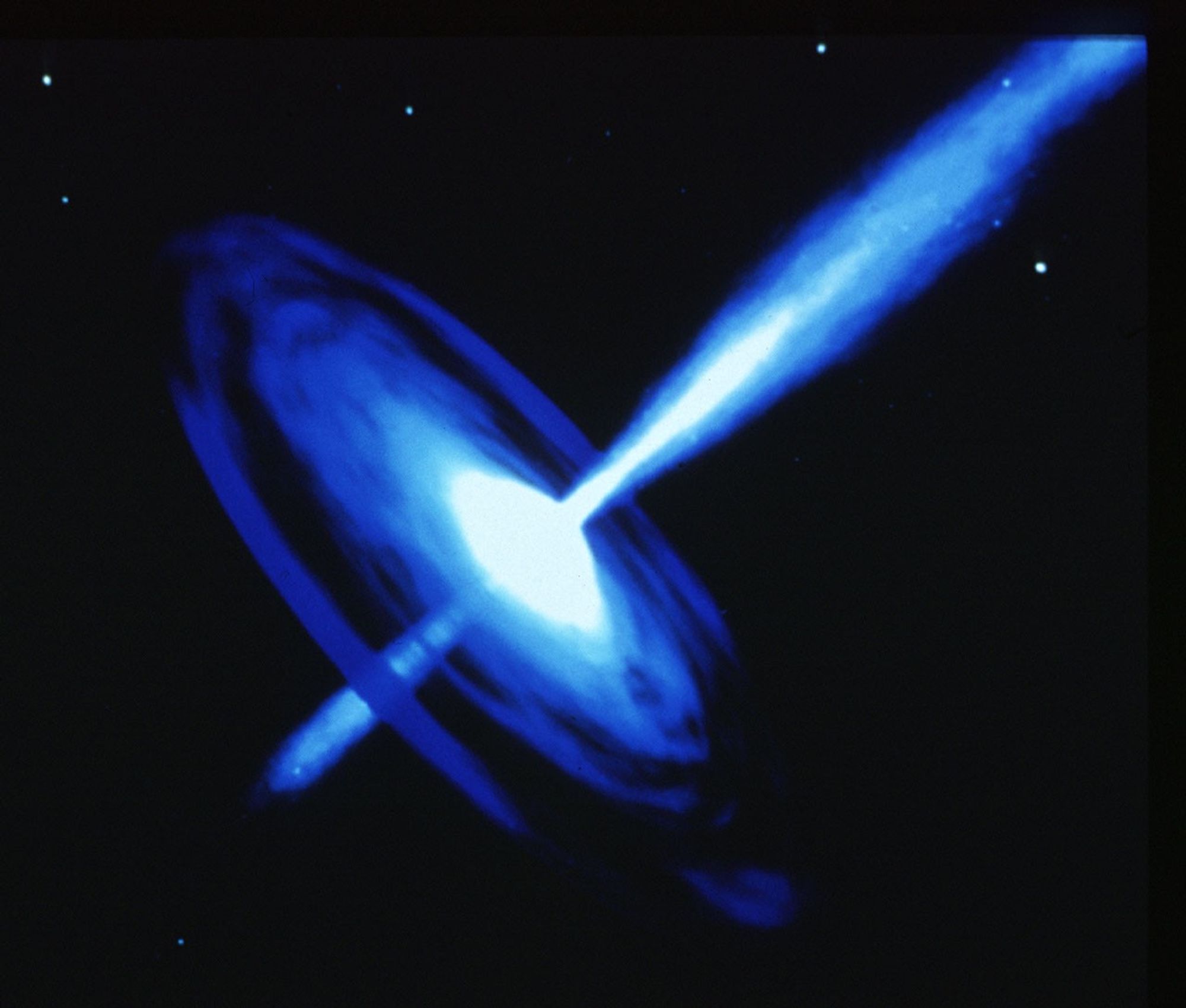

The energy source needed to create and maintain the galactic let in galaxy PKS 0521-36 is generated deep within the core of the galaxy, and is far too small to resolved. The favored mechanism behind these cosmic fireworks is a spinning, massive black hole. The hole is fueled by a continual in-fall of nearby gas and stars. This gravitational accretion process is far more efficient at converting mass to energy than thermonuclear fusion processes which power individual stars. The extraordinary high pressure and temperature generated near the hole would cause some of the in-falling gas to be ejected along the direction of the black hole's spinning axis to create the galactic let.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 22m 57.98s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-36° 27' 30.85"
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.PKS 0521-36
- Release DateOctober 4, 1990
- Science ReleaseGalactic Black Hole with Optical Jet
- Credit
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov