1 min read
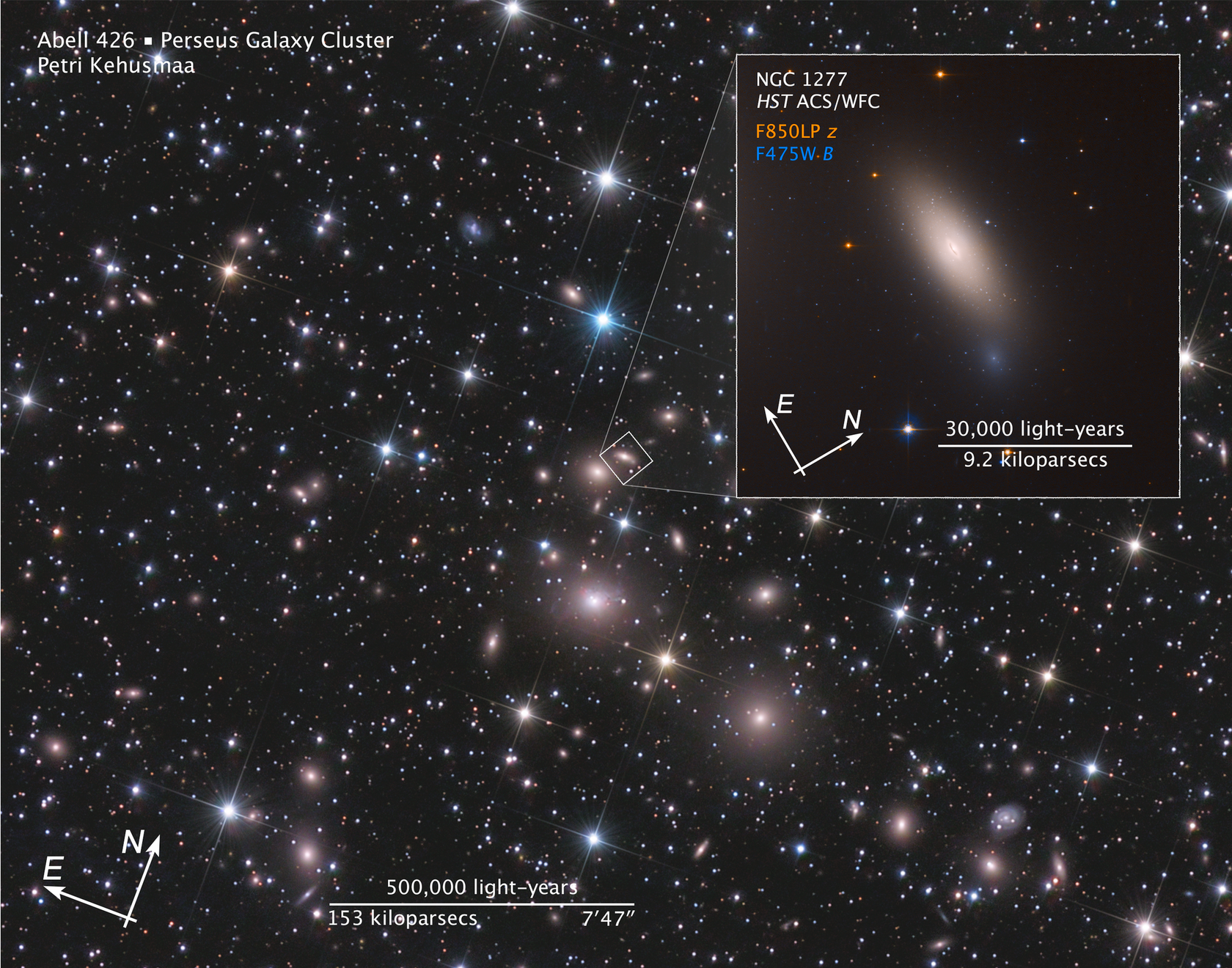
Galaxy NGC 1277

[Upper right] —This is a Hubble Space Telescope image of galaxy NGC 1277. The galaxy is unique in that it is considered a relic of what galaxies were like in the early universe. The galaxy is composed exclusively of aging stars that were born 10 billion years ago. But unlike other galaxies in the local universe, it has not undergone any further star formation. Astronomers nickname such galaxies as "red and dead," because the stars are aging and there aren't any successive generations of younger stars.
The telltale sign of the galaxy's "arrested development" lies in the ancient globular clusters that swarm around it. The reddish clusters are the strongest evidence that the galaxy went out of the star-making business long ago. Otherwise, there would be a lot of blue globular star clusters, which are largely absent. The lack of blue clusters suggests that NGC 1277 never grew further by gobbling up surrounding galaxies.
[Background image] — The galaxy lives near the center of the Perseus cluster of over 1,000 galaxies, located 240 million light-years away from Earth. NGC 1277 is moving so fast through the cluster, at 2 million miles per hour, that it cannot merge with other galaxies to collect stars or pull in gas to fuel star formation. In addition, near the galaxy cluster center, intergalactic gas is so hot it cannot cool to condense and form stars.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03:19:51.482
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+41:34:24.902
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Perseus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The galaxy is located 240 million light-years away from Earth.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Main image is 31 arcmin across (about 2 million light-years); Inset image is 1 arcmin across (about 64,000 light-years).
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST observations include those from program 14215 (I. Trujillo). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.August 28, 2017
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F850LP, F475W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 1277
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Lenticular galaxy with primordial globular clusters
- Release DateMarch 12, 2018
- Science ReleaseArrested Development: Hubble Finds Relic Galaxy Close to Home
- Credit

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the ACS/WFC instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Cyan: F475W Orange: F850LP
Related Images & Videos

NGC 1277 Globular Clusters Comparison
This is a blink comparison that plots the location of the red stars and blue stars that dominate the globular clusters in galaxies NGC 1277 and NGC 1278. It shows that NGC 1277 is dominated by ancient red globular clusters. This is evidence that galaxy NGC 1277 stopped making...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov