1 min read
Globular Cluster NGC 1846
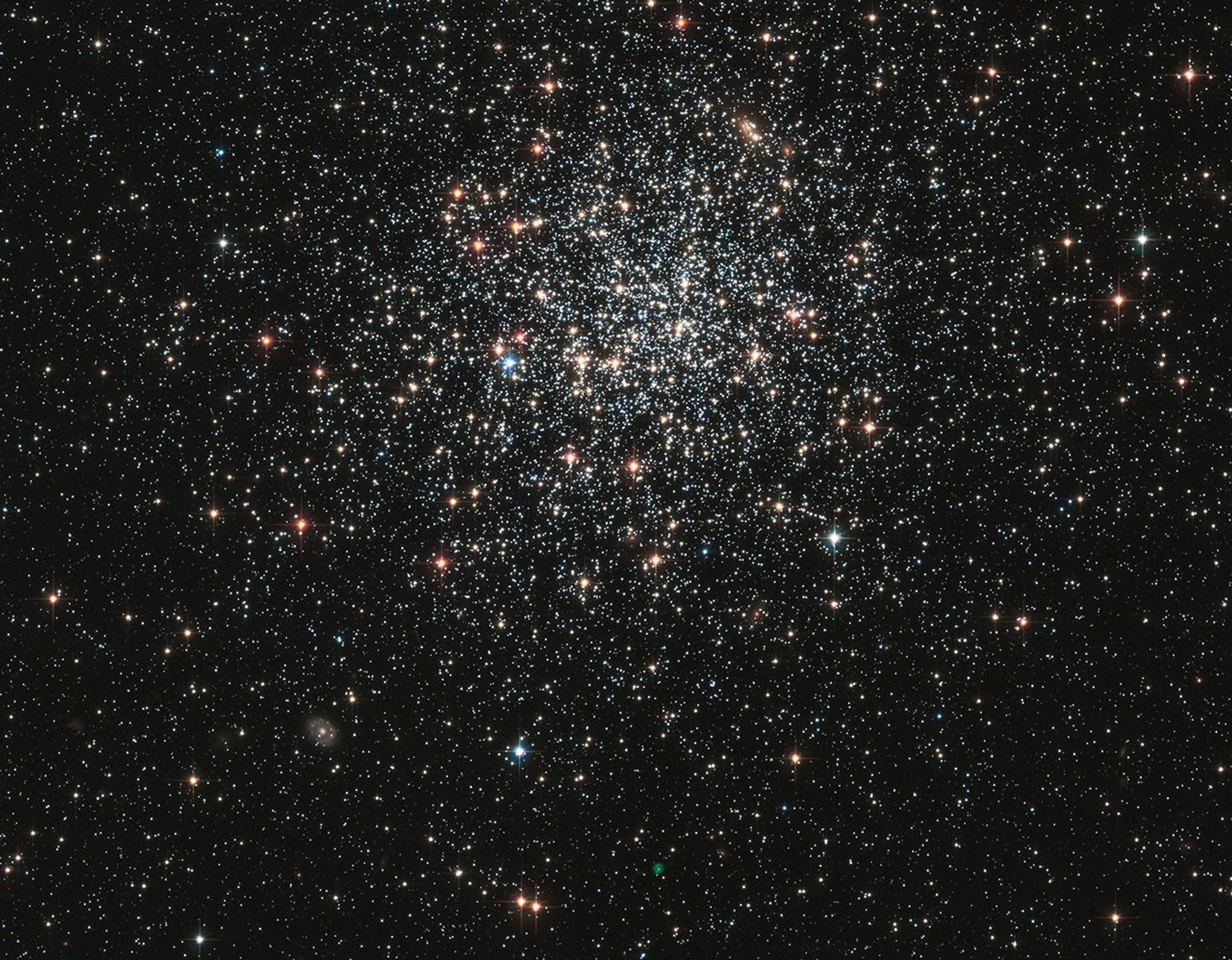

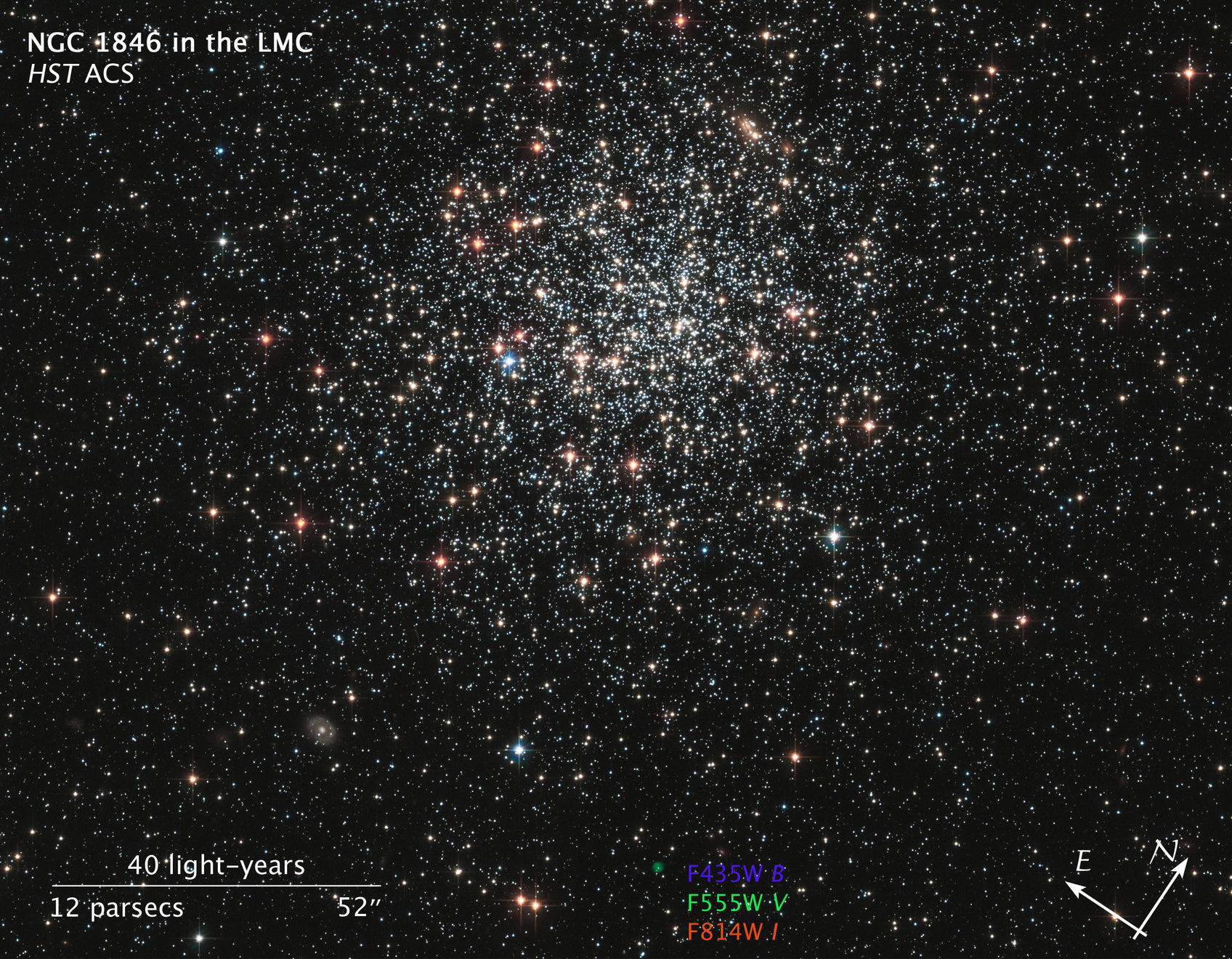
A new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image shows globular cluster NGC 1846, a spherical collection of hundreds of thousands of stars in the outer halo of the Large Magellanic Cloud, a neighboring dwarf galaxy of the Milky Way that can be seen from the southern hemisphere.
Aging bright stars in the cluster glow in intense shades of red and blue. The majority of middle-aged stars, several billions of years old, are whitish in color. A myriad of far distant background galaxies of varying shapes and structure are scattered around the image.
The most intriguing object, however, doesn't seem to belong in the cluster. It is a faint green bubble near the bottom center of the image. This so-called 'planetary nebula' is the aftermath of the death of a star. The burned-out central star can be seen inside the bubble. It is uncertain whether the planetary nebula is a member of NGC 1846, or simply lies along the line of sight to the cluster. Measurements of the motion of the cluster stars and the planetary nebula's central star suggest it might be a cluster member.
This Hubble image was taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys in January of 2006. The cluster was observed in filters that isolate blue, green, and infrared starlight. As a member of the Large Magellanic Cloud, NGC 1846 is located roughly 160,000 light-years away in the direction of the constellation Doradus.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 7m 33.93s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-67° 27' 41.29"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Dorado
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.160,000 light-years (49,000 parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposal 10595: P. Goudfrooij (STScI), F. De Angeli (University of Cambridge), V. Kozhurina-Platais (STScI), R. Chandar (University of Toledo), T. Puzia (Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile), and T. Brown (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.January 12, 2006, Exposure Time: 34 minutes
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F555W (V), and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 1846
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Globular Cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud
- Release DateNovember 22, 2011
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Finds Stellar Life and Death in a Globular Cluster
- Credit

This image is a composite of many separate exposures made by the ACS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope using three broadband filters. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F435W (B) Green: F555W (V) Red: F814W (I)
Related Images & Videos

NASA's Hubble Finds Stellar Life and Death in a Globular Cluster
A new NASA Hubble Space Telescope image shows globular cluster NGC 1846, a spherical collection of hundreds of thousands of stars in the outer halo of the Large Magellanic Cloud, a neighboring dwarf galaxy of the Milky Way that can be seen from the southern hemisphere. Aging...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov





























