1 min read
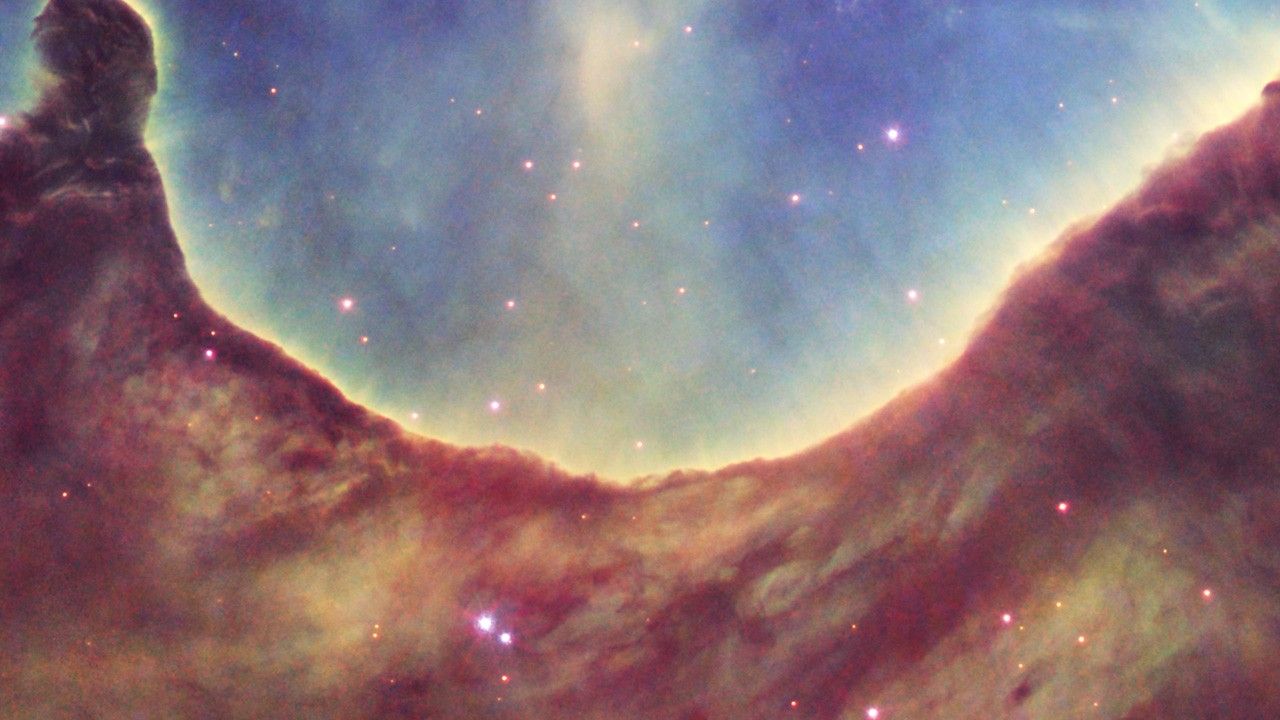
Hubble Image of NGC 3324

The landmark 10th anniversary of the Hubble Space Telescope's Hubble Heritage Project is being celebrated with a 'landscape' image from the cosmos. Cutting across a nearby star-forming region are the "hills and valleys" of gas and dust displayed in intricate detail. Set amid a backdrop of soft, glowing blue light are wispy tendrils of gas as well as dark trunks of dust that are light-years in height.
The Hubble Heritage Project, which began in October 1998, has released nearly 130 images mined from the Hubble data archive as well as a number of observations taken specifically for the project. By releasing a new, previously unseen Hubble image every month, the team's intent was to showcase some of the most attractive images ever taken by the Hubble telescope, and share them with a wide audience. The Heritage team continues to create aesthetic images that present the universe from an artistic perspective.
This month's three-dimensional-looking Hubble image shows the edge of the giant gaseous cavity within the star-forming region called NGC 3324. The glowing nebula has been carved out by intense ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from several hot, young stars. A cluster of extremely massive stars, located well outside this image in the center of the nebula, is responsible for the ionization of the nebula and excavation of the cavity.
The image also reveals dramatic dark towers of cool gas and dust that rise above the glowing wall of gas. The dense gas at the top resists the blistering ultraviolet radiation from the central stars, and creates a tower that points in the direction of the energy flow. The high-energy radiation blazing out from the hot, young stars in NGC 3324 is sculpting the wall of the nebula by slowly eroding it away.
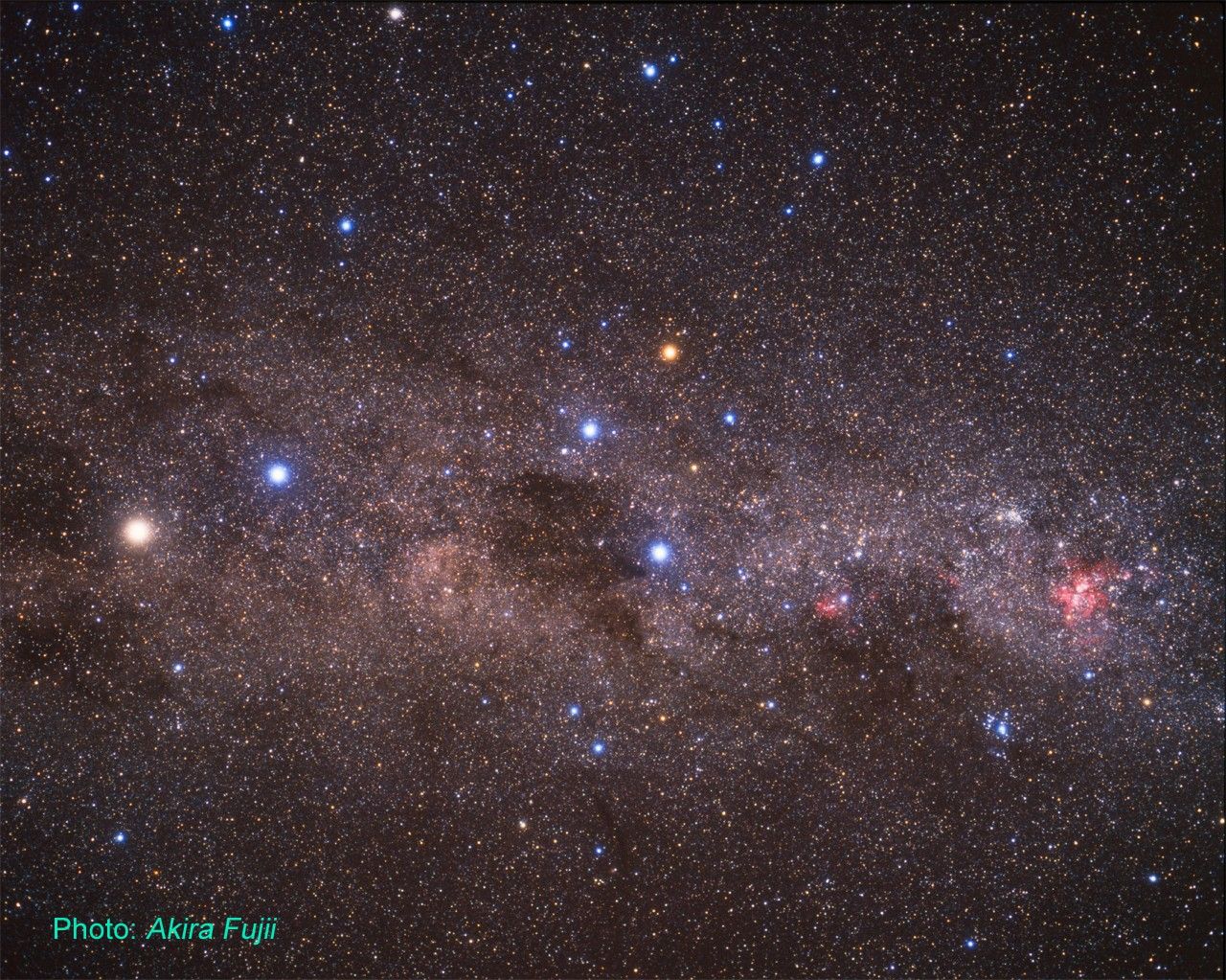
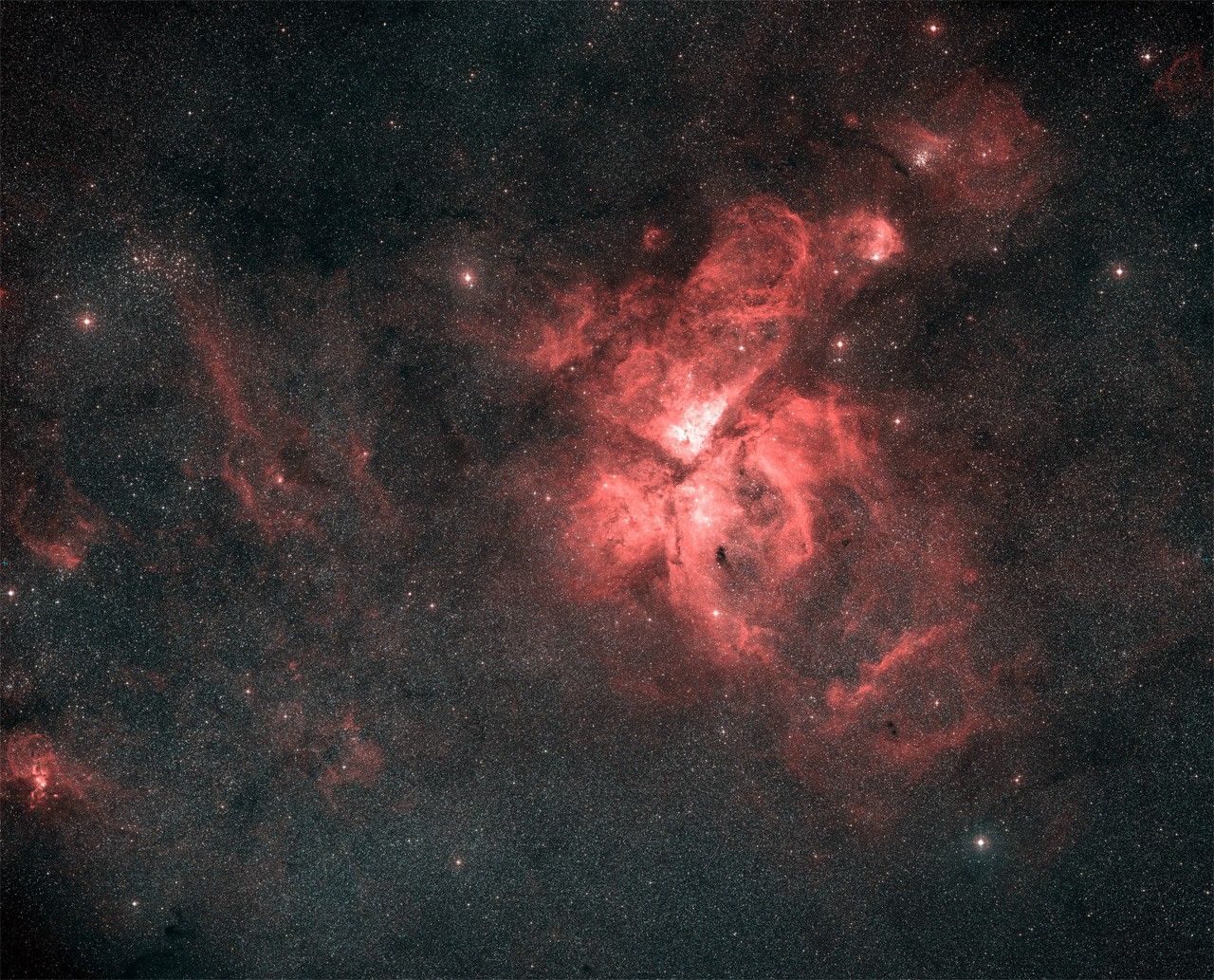
Located in the Southern Hemisphere, NGC 3324 is at the northwest corner of the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), home of the Keyhole Nebula and the active, outbursting star Eta Carinae. The entire Carina Nebula complex is located at a distance of roughly 7,200 light-years, and lies in the constellation Carina.
This image is a composite of data taken with two of Hubble's science instruments. Data taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) in 2006 isolated light emitted by hydrogen. More recent data, taken in 2008 with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2), isolated light emitted by sulfur and oxygen gas. To create a color composite, the data from the sulfur filter are represented by red, from the oxygen filter by blue, and from the hydrogen filter by green.
The Heritage project has released images using several of Hubble's optical cameras: the Wide Field Planetary Camera (WF/PC), which was installed when the telescope was first deployed in 1990; WFPC2, which replaced WFPC in 1993 and is still in service today; and ACS, which was added in 2002. After the Hubble Servicing Mission in early 2009, the Hubble Heritage team hopes to continue using ACS as well as the newest of the optical cameras, Wide Field Camera 3.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10h 36m 59.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-58° 37' 0.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Carina
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.7,200 light-years (2.2 kiloparsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.This image is roughly 6.5 arcminutes (13.4 light-years or 4.1 parsecs) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.HST Proposal: 10475 N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley), J. Bally University of Colorado, Boulder), N. Walborn (STScI), and J. Morse (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center) and 11800: K. Noll, H. Bond, C. Christian, L. Frattare, F. Hamilton, Z. Levay, M. Mutchler, and W. Januszewski (Hubble Heritage Team/STScI), A. Bowers (Baltimore, MD) and N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC and HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.March 2006 and July 2008, Exposure Time: 2 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS: F658N (H-alpha+[N II]) WFPC2: F502N ([O III]) and F673N ([S II])
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 3324
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Star-Forming Region in the Carina Nebula
- Release DateOctober 2, 2008
- Science ReleaseA Celestial Landscape in Celebration of 10 Years of Stunning Hubble Heritage Images
- CreditNASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA); Acknowledgment: N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley)

The image is a composite of separate exposures made by the ACS and WFPC2 instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope. Three filters were used to sample narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F502N ([O III]) Green: F658N (H-alpha+[N II]) Red: F673N ([S II])

Related Images & Videos

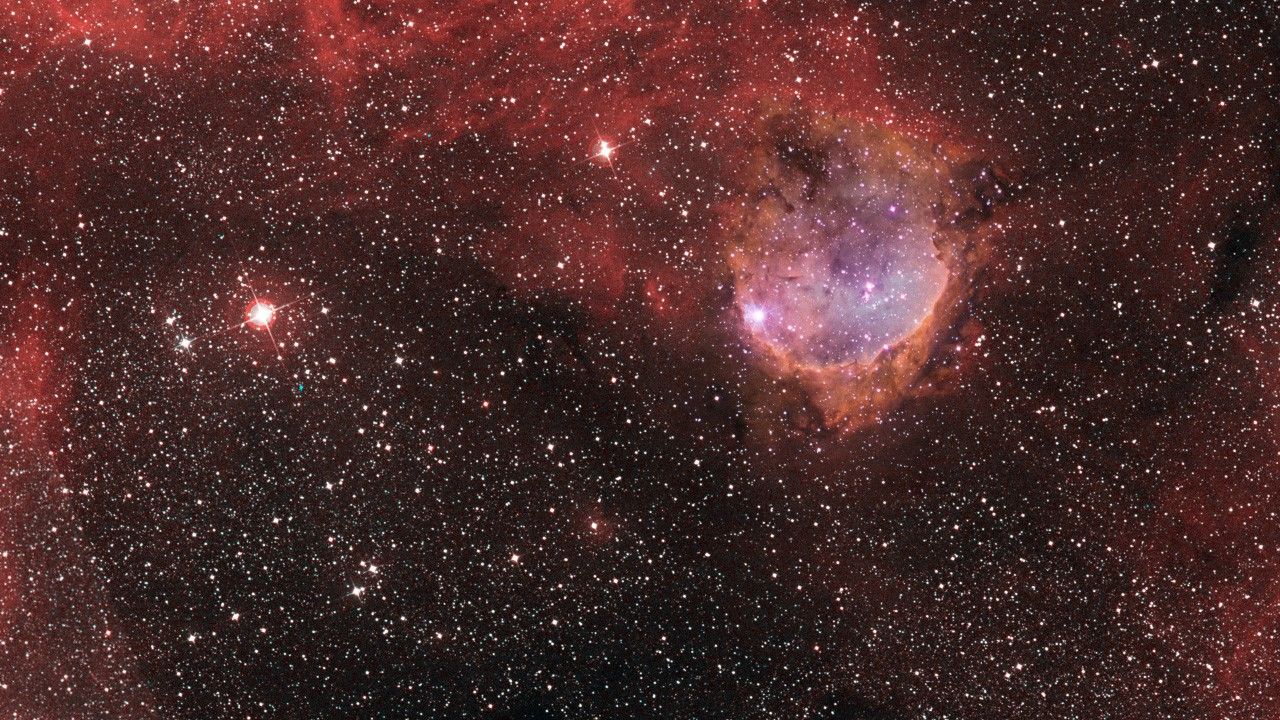
Pan Across Star-Forming Region NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula
Panning across this star-forming region, dramatic dark towers of cool gas and dust are seen rising above a glowing wall of gas. The high-energy radiation blazing out from the hot, young stars in NGC 3324 is sculpting the wall of the nebula by slowly eroding it away. This image...

Zoom into Star-Forming Region NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula
This zoom into the Carina Nebula starts from a photograph from the Akira Fujii collection then transitions to a Digitized Sky Survey image. A picture taken by amateur astronomer Brad Moore in Australia precedes a final image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov