1 min read
Hubble’s Close Encounter with Mars — August 26, 2003
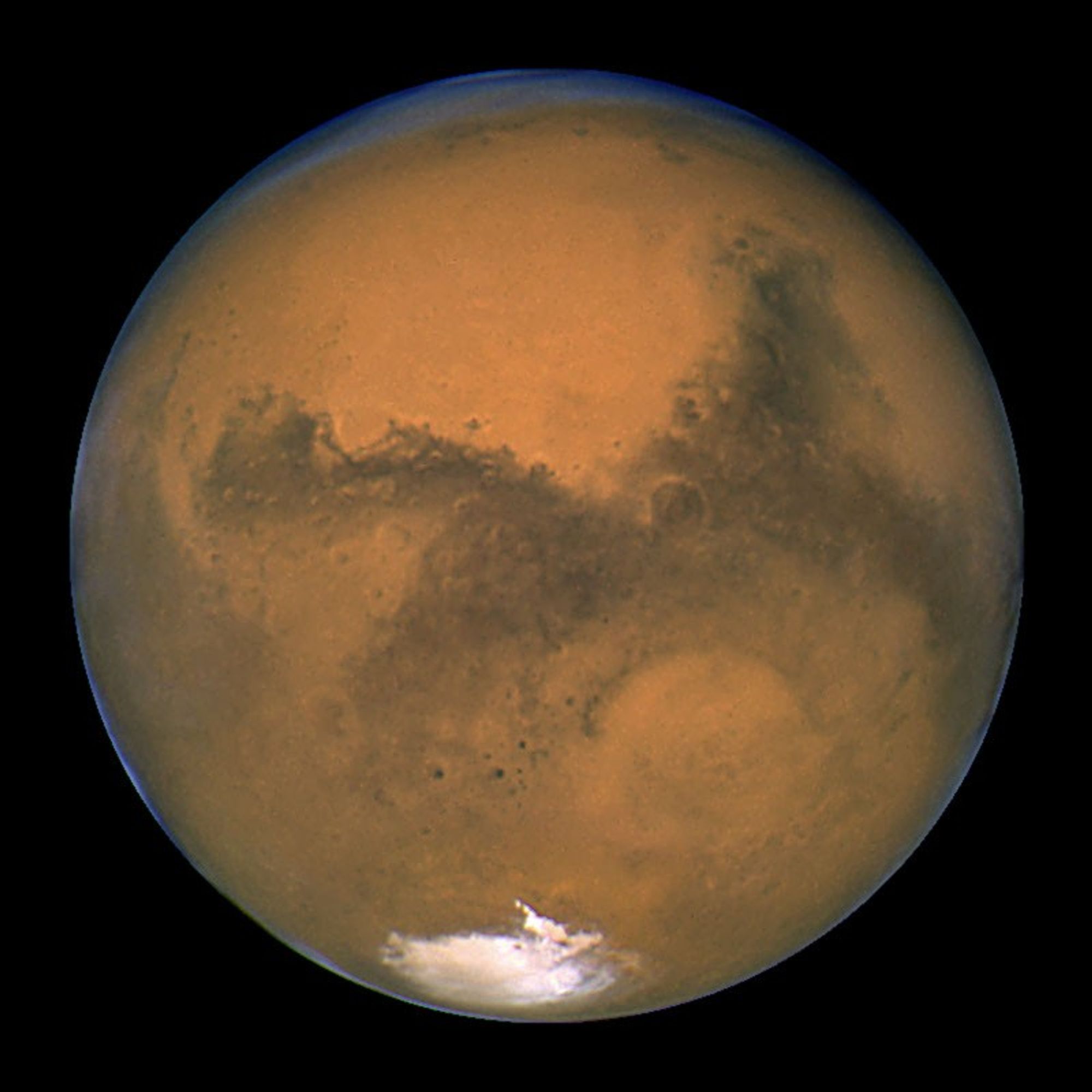

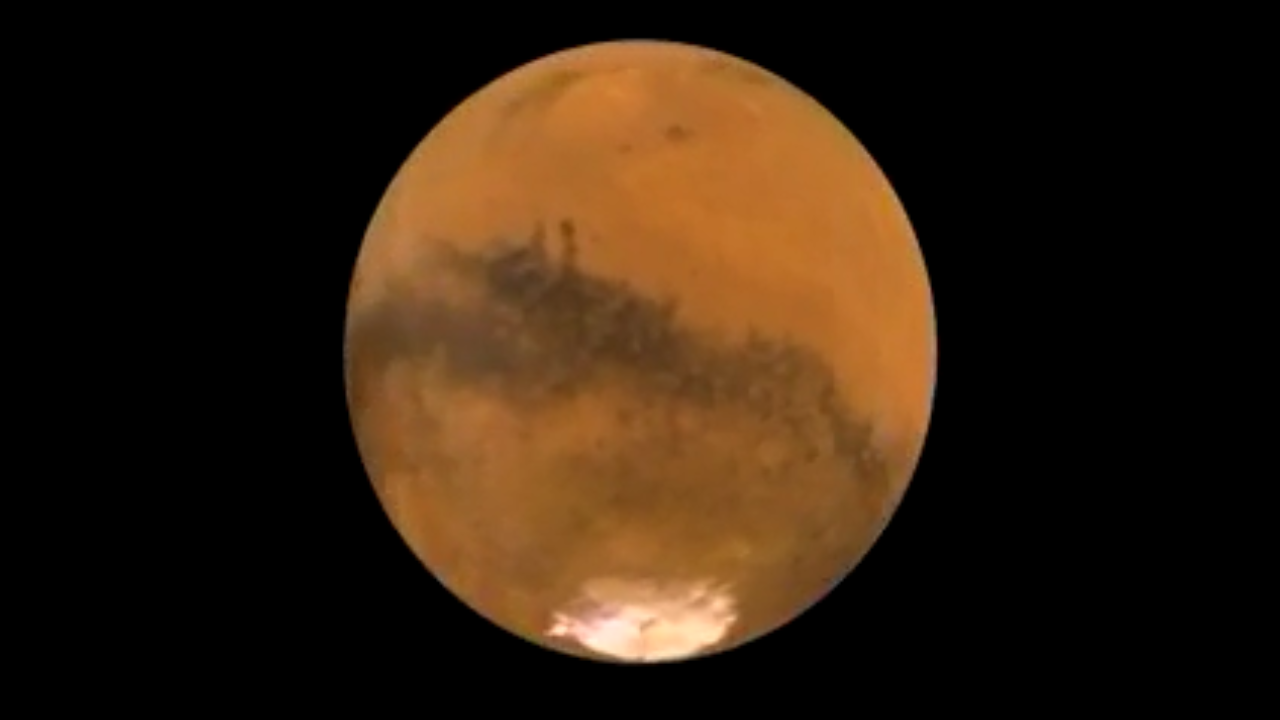
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope took this close-up of the red planet Mars when it was just 34,648,840 miles (55,760,220 km) away. This color image was assembled from a series of exposures taken between 6:20 p.m. and 7:12 p.m. EDT Aug. 26 with Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. The picture was taken just 11 hours before the planet made its closest approach to Earth in 60,000 years.
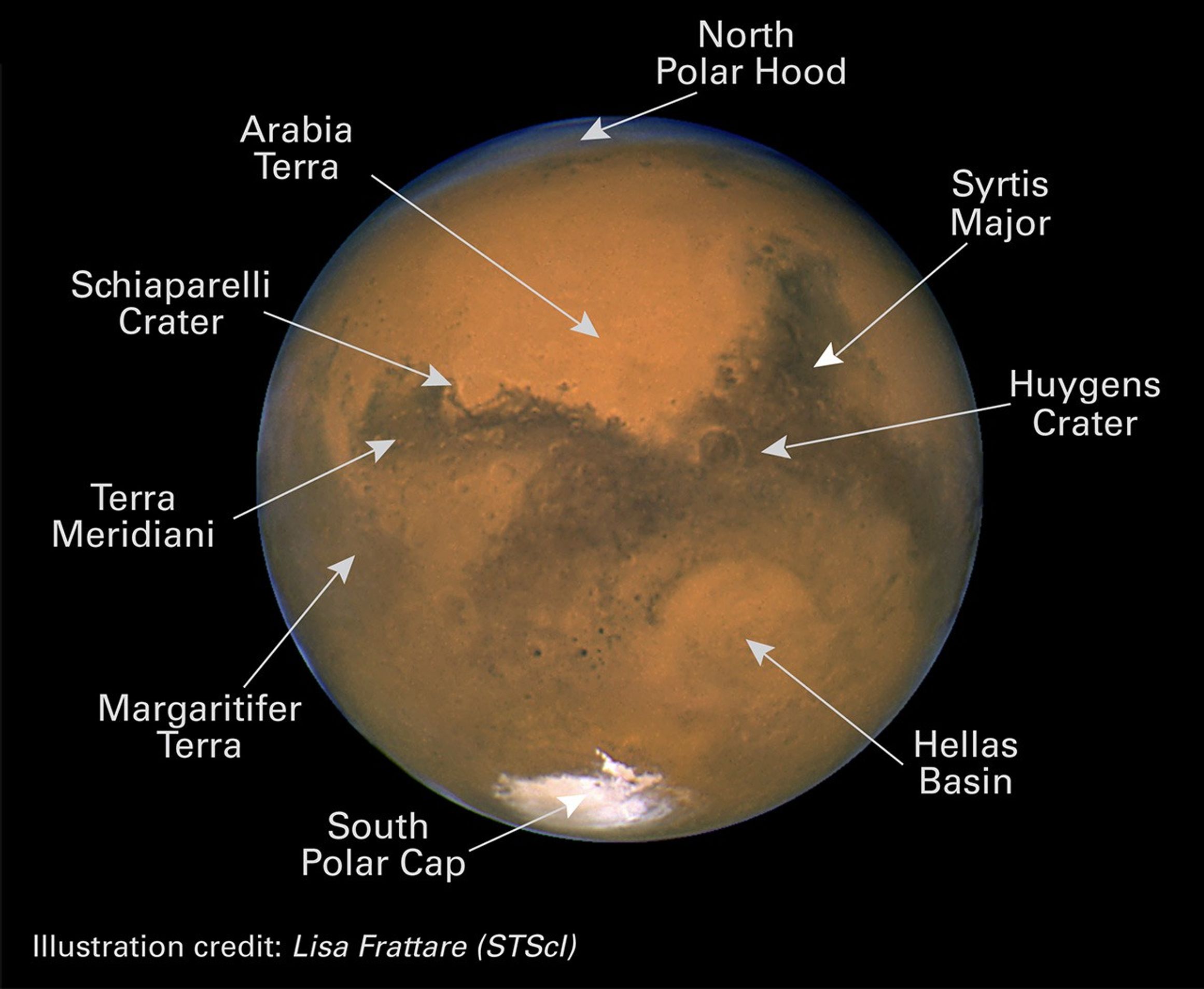
Many small, dark, circular impact craters can be seen, attesting to the Hubble telescope's ability to reveal fine detail on the planet's surface. One of the most striking is the 270-mile- (450-km-) diameter Huygens crater, seen near the centerof the image.
The two dominant dark swatches seen on this part of the planet are classical regions labeled by early Mars observers. The "shark-fin" shape to the right is Syrtis Major. The horizontal lane to the left is Sinus Meridani. One of NASA's Mars Exploration Rovers, named "Opportunity," will land at the western end of this region in January 2004.
The picture shows that it is a relatively warm summer on Mars, as evident in the lack of water-ice clouds at mid-latitude, and the receding southern polar cap. Ice on the rugged topography gives a somewhat ragged, scalloped look. Up north, at the top of the disk where it is Martian winter, a frigid polar hood of clouds covers the northern polar cap and surrounding region.
Even in the relatively balmy Southern Hemisphere, daytime highs are just above freezing in the Hellas impact basin, the circular feature near the image center. Hellas is nearly 5 miles deep (8 km). Hellas is like Death Valley - except that Mars is much drier than even Death Valley. Having a diameter of 1,100 miles (1,760 km), Hellas was formed when an asteroid slammed into Mars billions of years ago. Many summer dust storms originate in this basin, though it is remarkably clear of dust in this Hubble image.
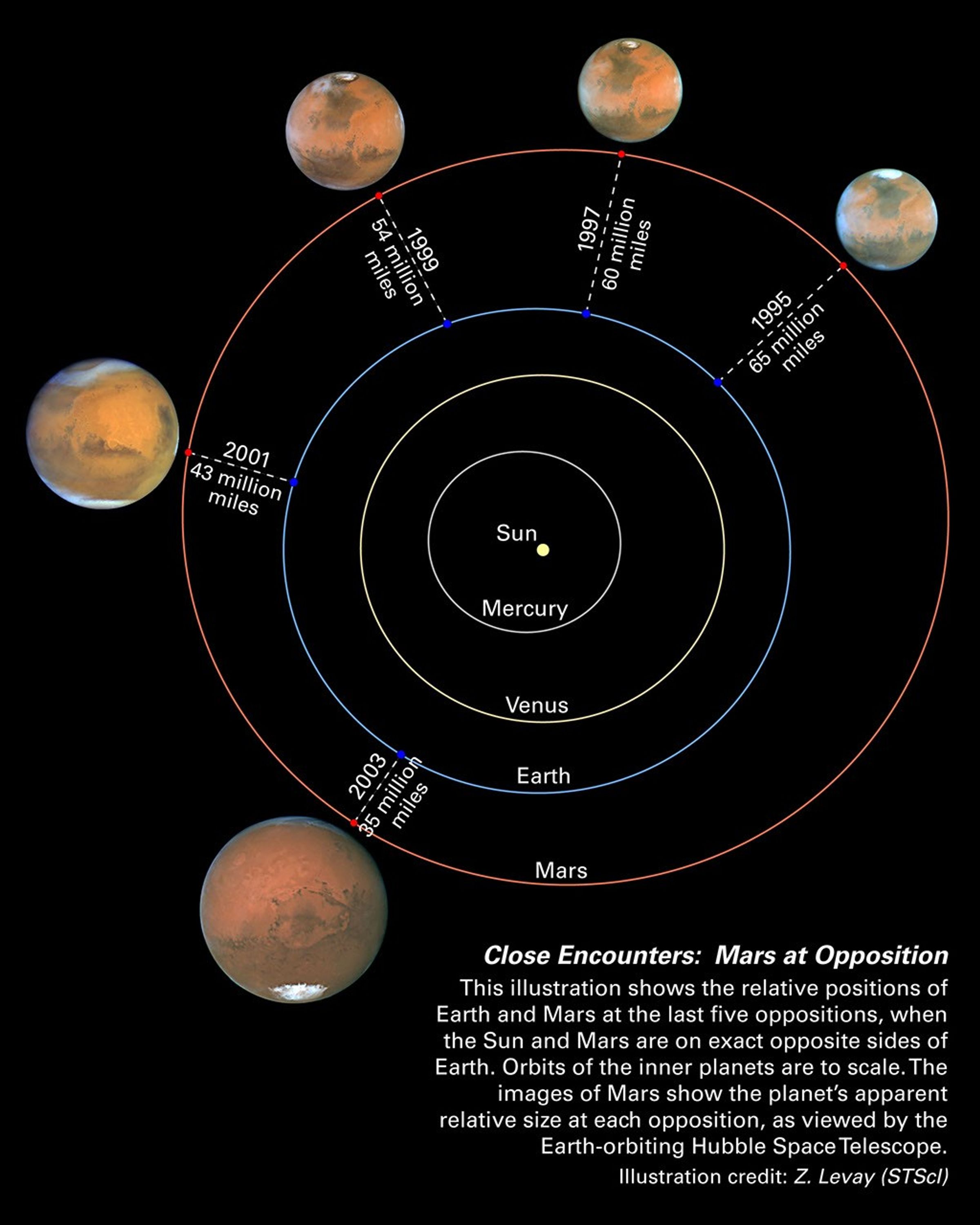
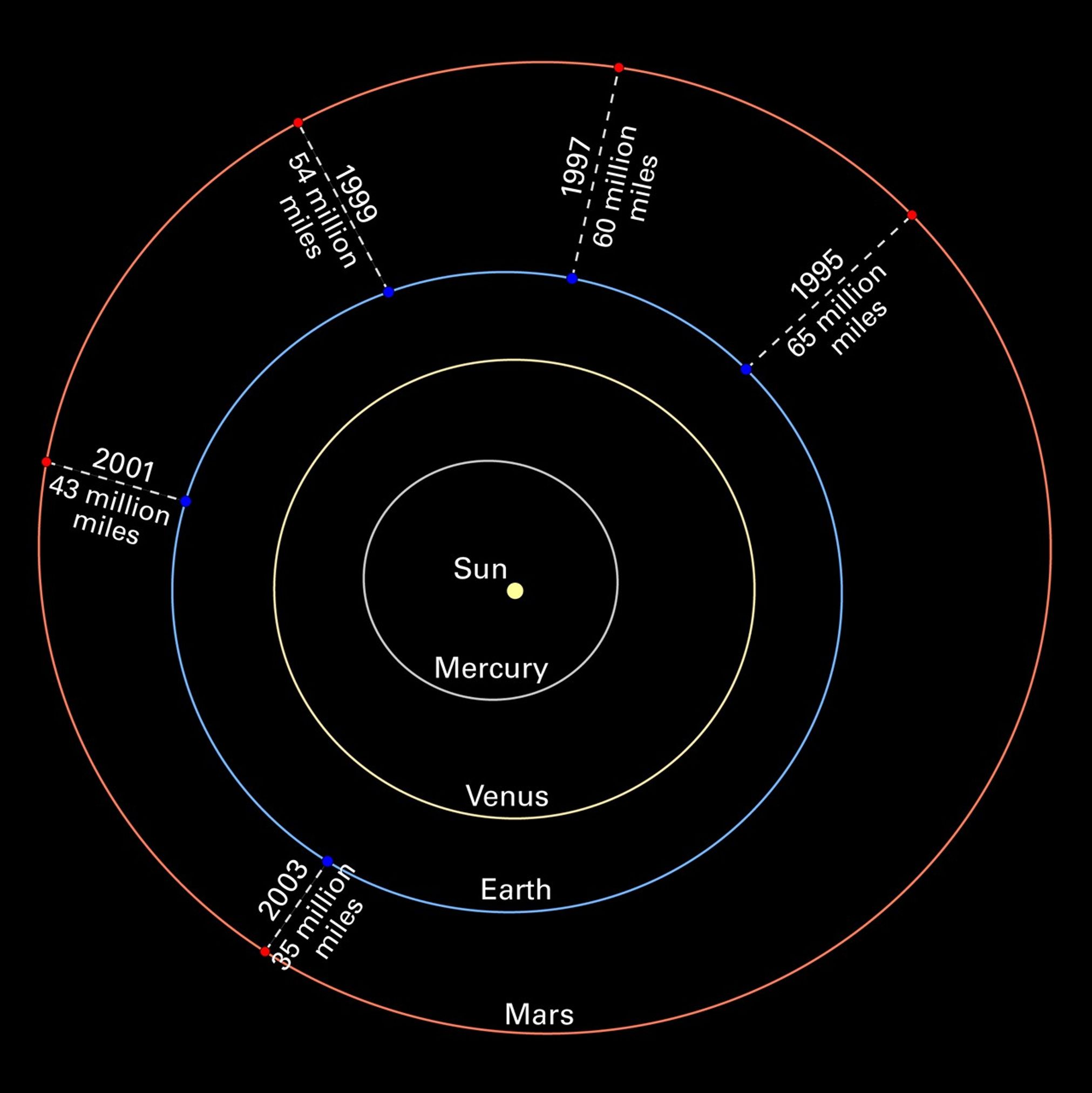
Mars and Earth have a "close encounter" about every 26 months. These periodic encounters are due to the differences in the two planets' orbits. Earth goes around the Sun twice as fast as Mars, lapping the red planet about every two years. Both planets have elliptical orbits, so their close encounters are not always at the same distance. In its close encounter with Earth in 2001, for example, Mars was about 9 million miles farther away. Because Mars will be much closer during this year's close approach, the planet appears 23 percent bigger in the sky.
This photograph is a color composite generated from observations taken with blue, green, and red filters. The resolution is 8 miles (12 km) per pixel.
About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Distance from the Sun: The semi-major axis of Mars' orbit about the sun is 1.52 Astronomical Units (A.U.) or 142 million miles (228 million km); Distance from the Earth: At the 2003 closest approach, Mars was approximately 35 million miles (56 million kilometers) from Earth.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The planet has a diameter of 4,222 miles (6,794 kilometers) at the equator.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.These data are taken from HST proposal 10065 by J. Bell (Cornell U.), M. Wolff (Space Science Institute), A. Lubenow (STScI), and K. Noll (STScI). Additional image processing and analysis support from: K. Noll and A. Lubenow (STScI); M. Hubbard (Cornell U.); R. Morris (NASA/JSC); P. James (U. Toledo); S. Lee (U. Colorado); and T. Clancy, B. Whitney and G. Videen (SSI); and Y. Shkuratov (Kharkov U.). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.August 26, 2003
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F410M (B), F502N (V), and F631N (R)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Mars
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateAugust 27, 2003
- Science ReleaseMars: Closest Encounter
- CreditNASA, J. Bell (Cornell U.) and M. Wolff (SSI); Additional image processing and analysis support from: K. Noll and A. Lubenow (STScI); M. Hubbard (Cornell U.); R. Morris (NASA/JSC); P. James (U. Toledo); S. Lee (U. Colorado); and T. Clancy, B. Whitney and G. Videen (SSI); and Y. Shkuratov (Kharkov U.)
Related Images & Videos

Hubble's Closest View of Mars — August 27, 2003
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope snapped this portrait of Mars within minutes of the planet's closest approach to Earth in nearly 60,000 years. This image was made from a series of exposures taken between 5:35 a.m. and 6:20 a.m. EDT Aug. 27 with Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary...

Hubble's Sharpest View of Mars — August 24, 2003
This view of Mars from the Hubble Space Telescope's new Advanced Camera for Surveys provides the sharpest view of the red planet attainable by the Earth-oribiting observatory. The picture was taken August 24, when Mars was approximately 34.7 million miles from Earth. The central...
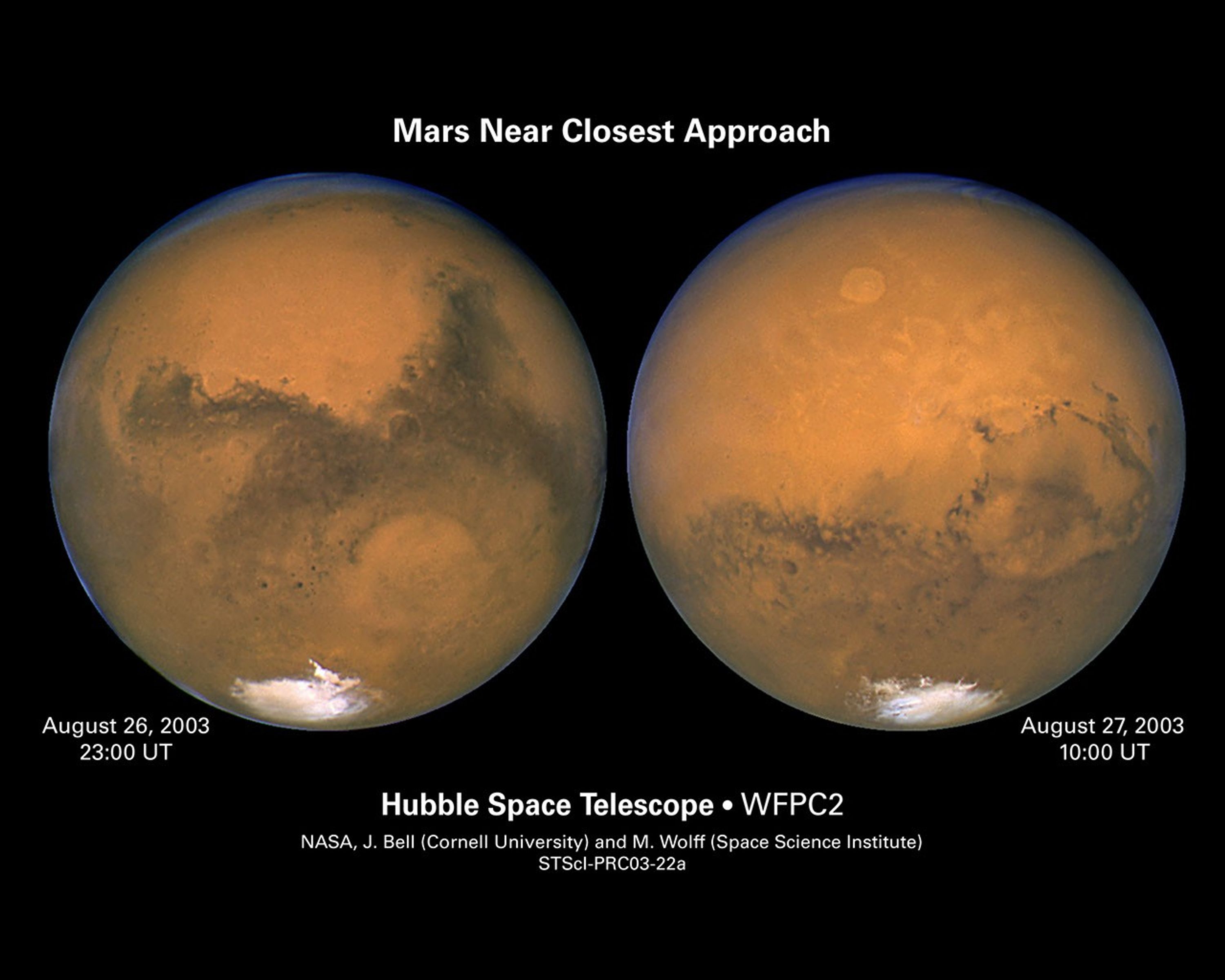
The Two Faces of Mars
These two images, taken 11 hours apart with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, reveal two nearly opposite sides of Mars. Hubble snapped these photos as the red planet was making its closest approach to Earth in almost 60,000 years. Mars completed nearly one half a rotation between...

Sharpest Ever Color View of Mars
This view of Mars, the sharpest photo ever taken from Earth, reveals small craters and other surface markings only about a dozen miles (a few tens of kilometers) across. (The spatial scale is 5 miles, or 8 kilometers per pixel). The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) aboard...

MARS: Closest Encounter
Footage of Astronomers James Bell of Cornell University, Michael Wolff of the Space Science Institute and Keith Noll of Space Telescope Science Institute receiving the Mars image from NASA Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. Footage contains initial reaction...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov