1 min read
I Zwicky 18: Possibly the Youngest Galaxy Ever Seen
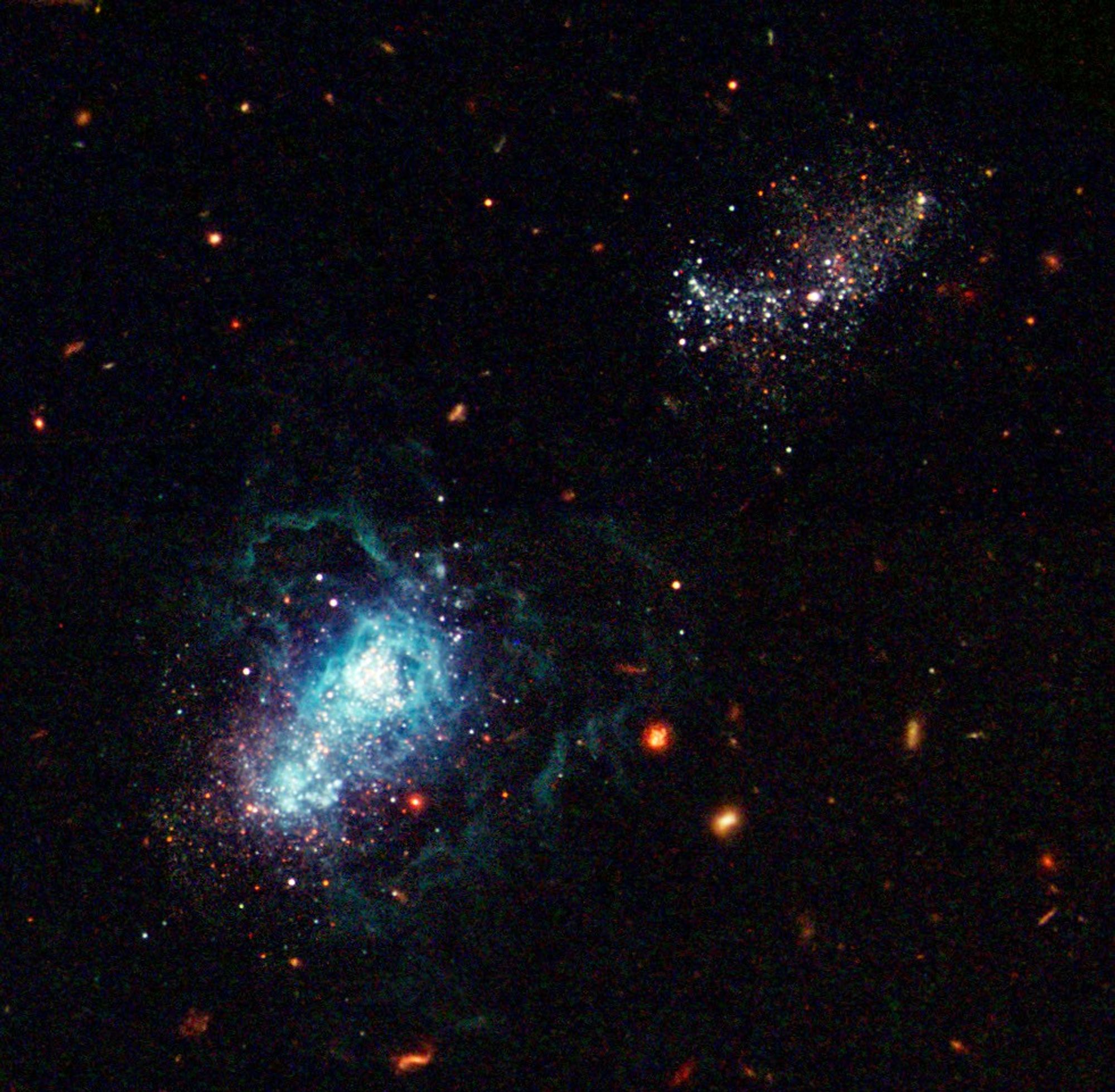

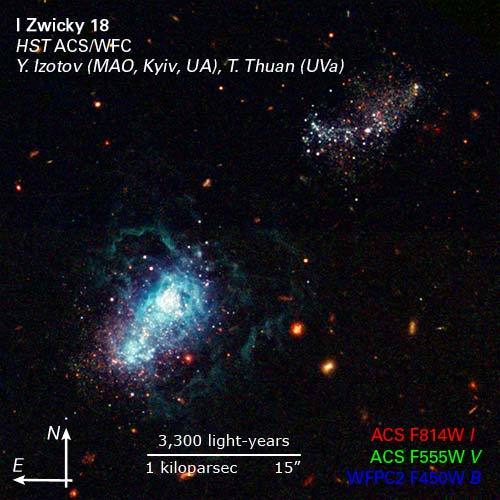
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope snapped a view of what may be the youngest galaxy ever seen. This "late bloomer" may not have begun active star formation until about 13 billion years after the Big Bang. Called I Zwicky 18 [below, left], the galaxy may be as young as 500 million years old. This youngster has gone though several sudden bursts of star formation - the first only some 500 million years ago and the latest only 4 million years ago. This galaxy is typical of the kinds of galaxies that inhabited the early universe. The galaxy is classified as a dwarf irregular galaxy and is much smaller than our Milky Way.
The two major starburst regions are the concentrated bluish-white knots embedded in the heart of the galaxy. The wispy blue filaments surrounding the central starburst region are bubbles of gas that have been heated by stellar winds and intense ultraviolet radiation unleashed by hot, young stars. The redder stars are slightly older stars and star clusters, but they are still less than 1 billion years old. A companion galaxy lies just above and to the right of the dwarf galaxy. The companion may be interacting with the dwarf galaxy and may have triggered that galaxy's recent star formation. The red blobs surrounding the dwarf galaxy are the dim glow from ancient fully formed galaxies.
This image was taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in 2003.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.09h 34m 0.9s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.55° 14' 34.19"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Major
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.45 million light-years (14 Megaparsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.This image is 50 arcseconds (11,000 light-years or 3.3 kiloparsecs) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble image was created from HST data from proposal 9400: T. Thuan (Univ. of Virginia) and Y. Izotov (Main Astronomical Observatory, Kyiv, UA). The Hubble NICMOS data are from the following HST proposals: 7461 and 7880: G. Ostlin (Stockholm Univ.), N. Bergvall, A. Hidalgo Gamez, and K. Olofsson (Uppsala Astronomical Observatory), and J. Rönnback (Uppsala Univ.). The science team is comprised of G. Ostlin of (Stockholm Observatory) and M. Mouhcine (Univ. of Nottingham). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC and HST>NICMOS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.May 26 – June 6, 2003, Exposure Time: 19 hours (ACS); December 28, 1997; Feb 15/22, 1998, Exposure Time: 12 hours (NICMOS)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS: F555W (V) and F814W (I) NICMOS: F110W (J) F160W (H), F205W (K), F171M (1.68-1.76 µm) and F180M (1.76-1.83 µm)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.I Zwicky 18, I Zw 18
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Irregular Dwarf Galaxy
- Release DateDecember 1, 2004
- Science ReleaseHubble Uncovers a Baby Galaxy in a Grown-Up Universe
- Credit

Blue: WFPC2 F450W (B) Green: ACS F555W (V) Red: ACS F814W (I)
Related Images & Videos
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




























