1 min read
Microlensing Black Hole

The star-filled sky in this Hubble Space Telescope photo is located in the direction of the Galactic center. The brightness of stars are monitored to see if any change in apparent brightness is made by a foreground object drifting in front of them. The warping of space by the interloper would momentarily brighten the appearance of a background star, due to an effect called gravitational lensing. One such event is shown along the four close-up frames at the bottom. The arrow points to a star that momentarily brightened, as first captured by Hubble beginning in August, 2011. This was caused by a foreground black hole drifting in front of the star, along our line-of-sight. The star brightened and then subsequently faded back to its normal brightness as the black hole passed by. Because a black hole doesn't emit or reflect light, it cannot be directly observed. But its unique thumbprint on the fabric of space can be measured through these so-called microlensing events. Though an estimated 100 million isolated black holes roam our galaxy, finding the telltale signature of one is a needle-in-haystack search for Hubble astronomers.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.17:51:41.9
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-29:37:27.2
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ophiuchus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.5,000 light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.8 Aug. 2011, 31 Oct. 2011, 9 Sept. 2012 and 29 Aug. 2017
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F606W and F814W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.OGLE-2011-BLG-462
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Microlensing black hole
- Release DateJune 10, 2022
- Science ReleaseHubble Determines Mass of Isolated Black Hole Roaming Our Milky Way Galaxy
- CreditNASA, ESA, Kailash Sahu (STScI); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)

These images are a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3 instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (greyscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Cyan: F606W Orange: F814W

Related Images & Videos

Illustration of an Isolated Black Hole
This is an illustration of a close-up look at a black hole drifting through our Milky Way galaxy. The black hole is the crushed remnant of a massive star that exploded as a supernova. The surviving core is several times the mass of our Sun. The black hole traps light due to its...
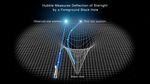
Gravitational Lensing By A Black Hole
This illustration reveals how the gravity of a black hole warps space and bends the light of a distant star behind it. A black hole is the crushed remnant of a massive star that exploded as a supernova. The black hole traps light due to its intense gravitational field, hence it...
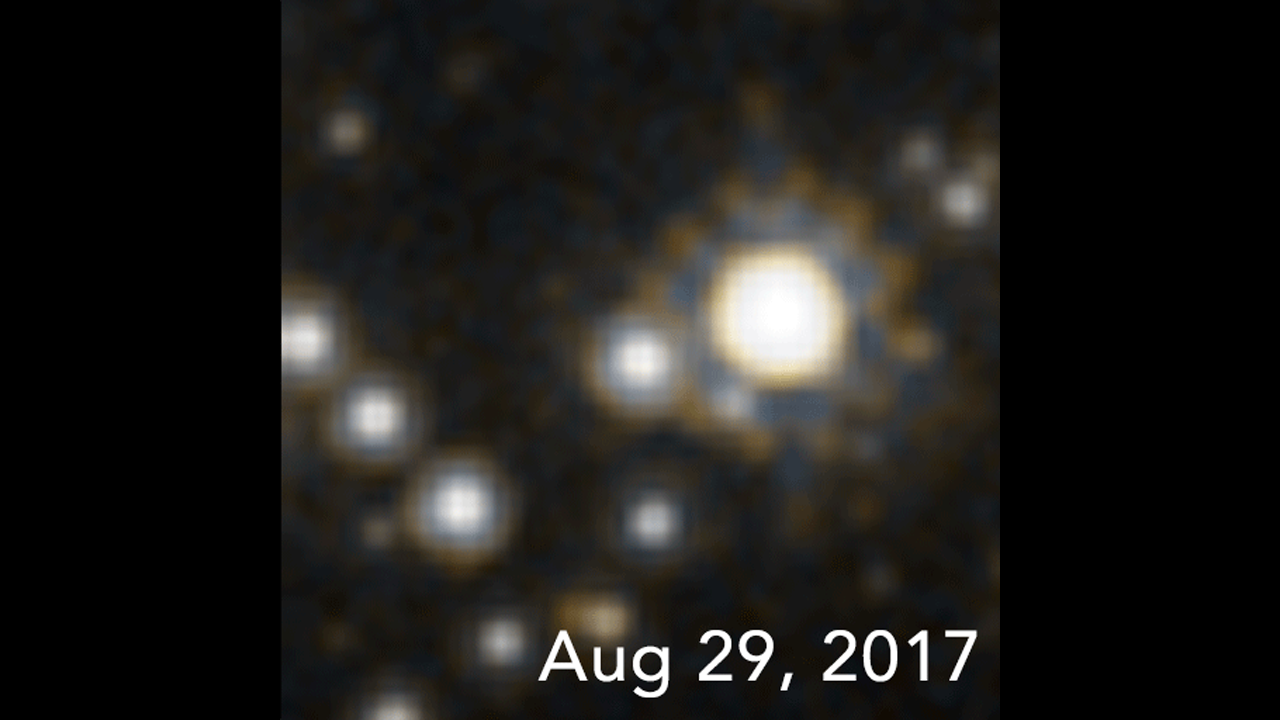
Time-Lapse Look at Microlensing from a Black Hole
This is a time-lapse of a set of four Hubble Space Telescope photos that capture the gravitational effects of an invisible black hole drifting through our galaxy. Because a black hole doesn't emit or reflect light, it cannot be directly observed. But its unique thumbprint on the...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




























