1 min read
Spiral Galaxy NGC 4622 Spins “Backwards”

Astronomers have found a spiral galaxy that may be spinning to the beat of a different cosmic drummer.
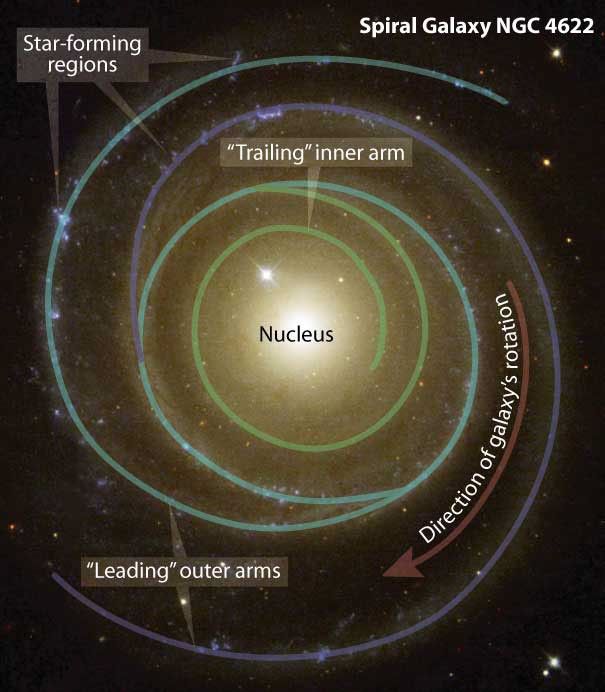
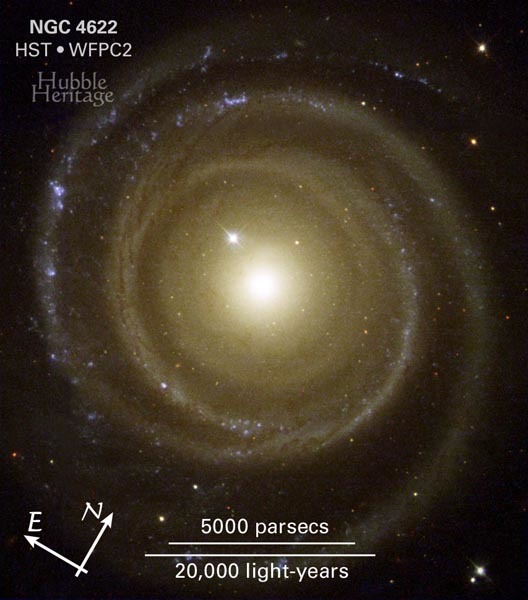
To the surprise of astronomers, the galaxy, called NGC 4622, appears to be rotating in the opposite direction to what they expected. Pictures by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope helped astronomers determine that the galaxy may be spinning clockwise by showing which side of the galaxy is closer to Earth. A Hubble telescope photo of the oddball galaxy is this month's Hubble Heritage offering. The image shows NGC 4622 and its outer pair of winding arms full of new stars [shown in blue].
Astronomers are puzzled by the clockwise rotation because of the direction the outer spiral arms are pointing. Most spiral galaxies have arms of gas and stars that trail behind as they turn. But this galaxy has two "leading" outer arms that point toward the direction of the galaxy's clockwise rotation. To add to the conundrum, NGC 4622 also has a "trailing" inner arm that is wrapped around the galaxy in the opposite direction it is rotating. Based on galaxy simulations, a team of astronomers had expected that the galaxy was turning counterclockwise.
NGC 4622 is a rare example of a spiral galaxy with arms pointing in opposite directions. What caused this galaxy to behave differently from most galaxies? Astronomers suspect that NGC 4622 interacted with another galaxy. Its two outer arms are lopsided, meaning that something disturbed it. The new Hubble image suggests that NGC 4622 consumed a small companion galaxy. The galaxy's core provides new evidence for a merger between NGC 4622 and a smaller galaxy. This information could be the key to understanding the unusual leading arms.
Galaxies, which consist of stars, gas, and dust, rotate very slowly. Our Sun, one of many stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, completes a circuit around the Milky Way every 250 million years.
NGC 4622 resides 111 million light-years away in the constellation Centaurus. The pictures were taken in May 2001 with Hubble's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2.
The science team, consisting of Ron Buta and Gene Byrd from the University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, and Tarsh Freeman of Bevill State Community College in Alabama, observed NGC 4622 in ultraviolet, infrared, and blue and green filters. Their composite image and science findings were presented at the meeting of the American Astronomical Society in January of 2002.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h 42m 37.6s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-40° 44' 35.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Centaurus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 34 million parsecs (111 million light-years)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is roughly 1.6 arcminutes (16 kiloparsecs) across.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Principal Astronomers: R. Buta and G. Byrd (University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa), T. Freeman (Bevill State Community College, AL) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.May 25, 2001, Exposure Time: 1.7 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F336W (U), F439W (B), F555W (V)), F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 4622
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Face-on Spiral Galaxy
- Release DateFebruary 7, 2002
- Science ReleaseHubble Reveals “Backwards” Spiral Galaxy
- CreditNASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA); Acknowledgment: Dr. Ron Buta (U. Alabama), Dr. Gene Byrd (U. Alabama) and Tarsh Freeman (Bevill State Community College)
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov