1 min read
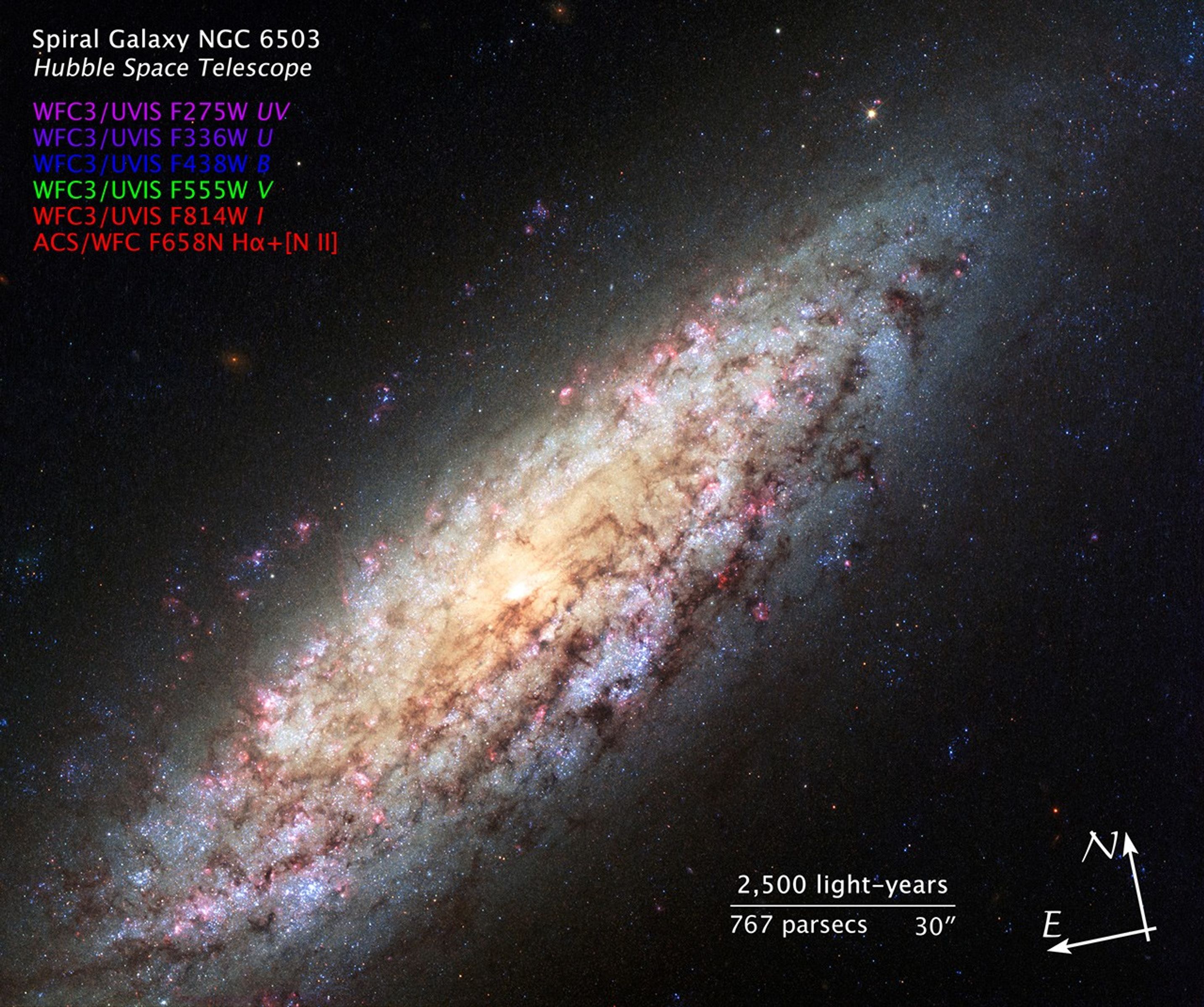
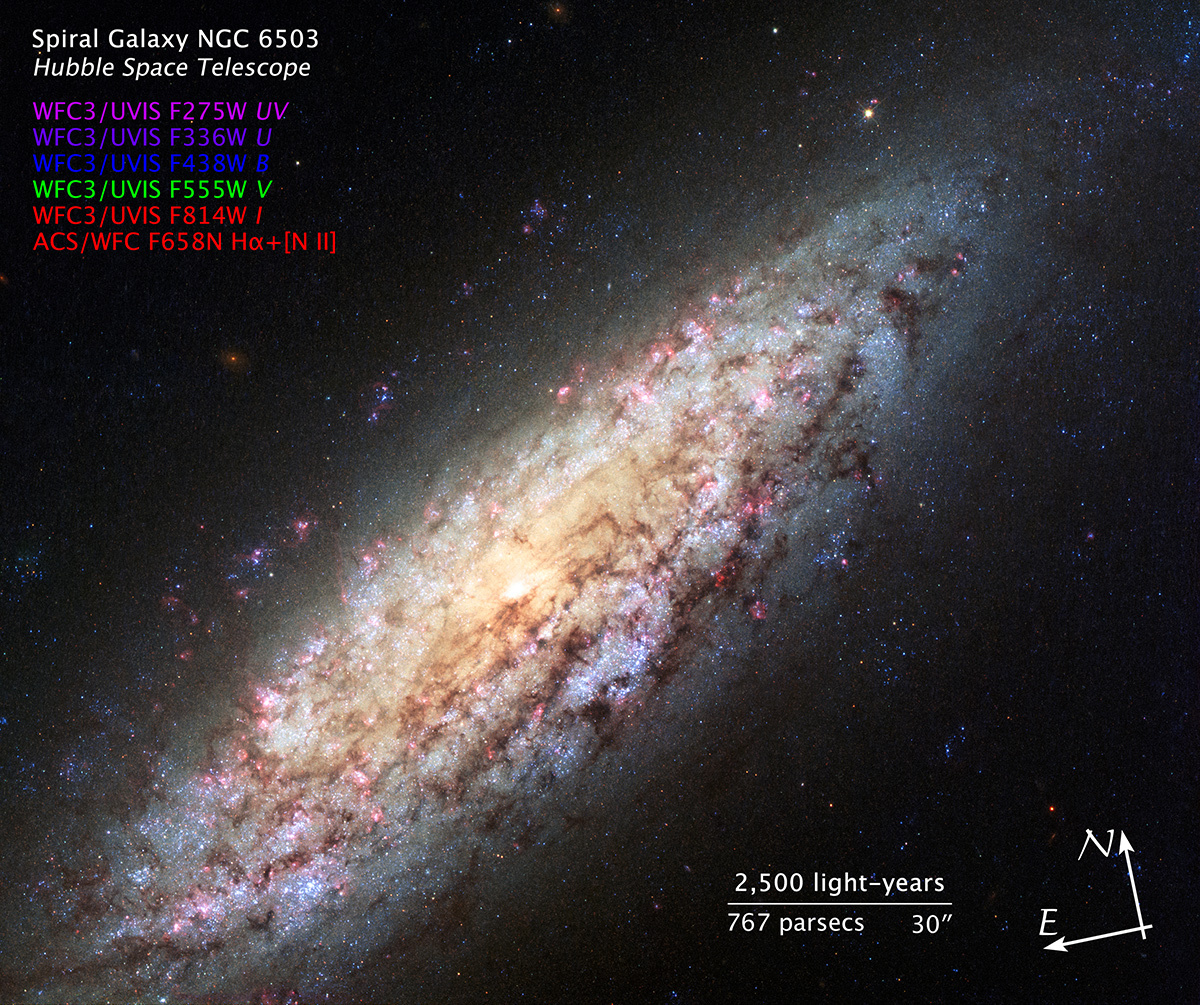
Spiral Galaxy NGC 6503

Most galaxies are clumped together in groups or clusters. A neighboring galaxy is never far away. But this galaxy, known as NGC 6503, has found itself in a lonely position, at the edge of a strangely empty patch of space called the Local Void.
The Local Void is a huge stretch of space that is at least 150 million light-years across. It seems completely empty of stars or galaxies. The galaxy's odd location on the edge of this never-land led stargazer Stephen James O'Meara to dub it the "Lost-In-Space galaxy" in his 2007 book, Hidden Treasures.
NGC 6503 is 18 million light-years away from us in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. NGC 6503 spans some 30,000 light-years, about a third of the size of the Milky Way.
This Hubble Space Telescope image shows NGC 6503 in striking detail and with a rich set of colors. Bright red patches of gas can be seen scattered through its swirling spiral arms, mixed with bright blue regions that contain newly forming stars. Dark brown dust lanes snake across the galaxy's bright arms and center, giving it a mottled appearance.
The Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys data for NGC 6503 were taken in April 2003, and the Wide Field Camera 3 data were taken in August 2013.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.17h 49m 26.42s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.70° 8' 39.73"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Draco
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.18 million light-years (5.5 megaparsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC and HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.April 21, 2003 and August 21, 2013
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F658N (H-alpha+[N II]), F275W (UV), F336W (U), F438W (B), F555W (V), and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 6503
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Spiral Galaxy with Active Star Formation
- Release DateJune 10, 2015
- Science ReleaseLonely Galaxy ‘Lost in Space’
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the ACS/WFC and WFC3/UVIS instruments. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Pink: F275W (UV) Purple: F336W (U) Blue: F438W (B) Green: F555W (V) Red: F814W (I) Red: F658N (H-alpha+[N II])
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov