1 min read
Survey of Andromeda’s Satellite Galaxies
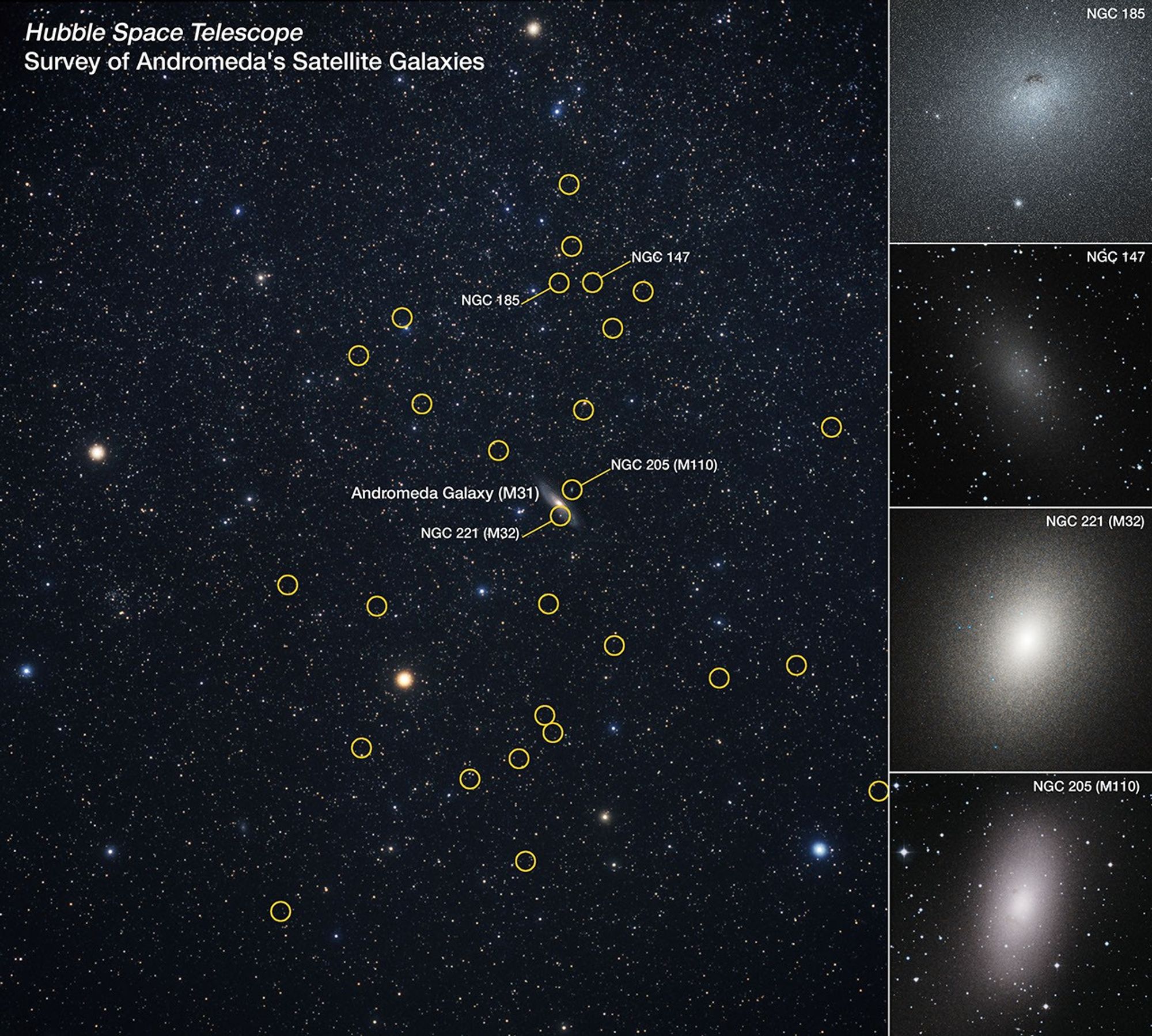
This is a wide-angle view of the distribution of known satellite galaxies orbiting the large Andromeda galaxy (M31), located 2.5 million light-years away. The Hubble Space Telescope was used to study the entire population of 36 mini-galaxies circled in yellow. Andromeda is the bright spindle-shaped object at image center. All the dwarf galaxies seem to be confined to a plane, all orbiting in the same direction. The wide view is from ground-based photography. Hubble's optical stability, clarity, and efficiency made this ambitious survey possible. Hubble close up snapshots of four dwarf galaxies are on image right. The most prominent dwarf galaxy is M32 (NGC 221), a compact ellipsoidal galaxy that might be the remnant core of a larger galaxy that collided with Andromeda a few billion years ago.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.00:42:44
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+41:16:09
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Andromeda
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.2.537 million light-years
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The pullout image of NGC 185 was created from Hubble data from proposal 15336 (A. Ferguson).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NGC 185: WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.NGC 185: September 2019
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F606W, F814W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Andromeda Galaxy and surroundings
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Spiral Galaxy
- Release DateFebruary 27, 2025
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Provides Bird’s-Eye View of Andromeda Galaxy’s Ecosystem
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, DSS2, Alessandro Savino (UC Berkeley), Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Akira Fujii

These images were acquired by the WFC3 instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to a monochromatic (grayscale) image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Cyan: F606W, Orange: F814W.
Related Images & Videos

The Distribution of Satellite Galaxies around M31
This animation begins with a view of the neighboring Andromeda galaxy. We zoom through a scattering of foreground stars and enter the inky blackness of intergalactic space. We cross 2.5 million light-years to reach the Andromeda system, consisting of 36 dwarf satellite galaxies...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, DSS2, Alessandro Savino (UC Berkeley), Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Akira Fujii




























