1 min read
The Carina Nebula: Star Birth in the Extreme

In celebration of the 17th anniversary of the launch and deployment of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, a team of astronomers is releasing one of the largest panoramic images ever taken with Hubble's cameras. It is a 50-light-year-wide view of the central region of the Carina Nebula where a maelstrom of star birth - and death - is taking place.
Hubble's view of the nebula shows star birth in a new level of detail. The fantasy-like landscape of the nebula is sculpted by the action of outflowing winds and scorching ultraviolet radiation from the monster stars that inhabit this inferno. In the process, these stars are shredding the surrounding material that is the last vestige of the giant cloud from which the stars were born.
The immense nebula contains at least a dozen brilliant stars that are roughly estimated to be at least 50 to 100 times the mass of our Sun. The most unique and opulent inhabitant is the star Eta Carinae, at far left. Eta Carinae is in the final stages of its brief and eruptive lifespan, as evidenced by two billowing lobes of gas and dust that presage its upcoming explosion as a titanic supernova.
The fireworks in the Carina region started three million years ago when the nebula's first generation of newborn stars condensed and ignited in the middle of a huge cloud of cold molecular hydrogen. Radiation from these stars carved out an expanding bubble of hot gas. The island-like clumps of dark clouds scattered across the nebula are nodules of dust and gas that are resisting being eaten away by photoionization.
The hurricane blast of stellar winds and blistering ultraviolet radiation within the cavity is now compressing the surrounding walls of cold hydrogen. This is triggering a second stage of new star formation.
Our Sun and our solar system may have been born inside such a cosmic crucible 4.6 billion years ago. In looking at the Carina Nebula we are seeing the genesis of star making as it commonly occurs along the dense spiral arms of a galaxy.
The immense nebula is an estimated 7,500 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina the Keel (of the old southern constellation Argo Navis, the ship of Jason and the Argonauts, from Greek mythology).
This image is a mosaic of the Carina Nebula assembled from 48 frames taken with Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys. The Hubble images were taken in the light of neutral hydrogen. Color information was added with data taken at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile. Red corresponds to sulfur, green to hydrogen, and blue to oxygen emission.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10h 43m 59.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-59° 52' 59.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Carina
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Approximately 7,500 light-years (2,300 parsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.This image is roughy 25 arcminutes (53 light-years or 16 parsecs) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This color image combines many exposures from Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS)* and NOAO/AURA/NSF Cerro-Tololo Interamerican Observatory's (CTIO) 4m Blanco Telescope and MOSAIC2 camera.
The ACS data was from the HST proposal 10241: N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley), J. Bally (University of Colorado at Boulder), N. Walborn (STScI), and J. Morse (NASA/GSFC).
*A small area of the Hubble ACS image that was saturated around the brightest star in the field, Eta Carinae, was replaced with images from previous shorter exposures from Hubble's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2.
The CTIO observing team includes: N. Smith (University of California, Berkeley), J. Bally (University of Colorado at Boulder), and J. Walawender (Institute for Astronomy/University of Hawaii).
*A small area of the Hubble ACS image that was saturated around the brightest star in the field, Eta Carinae, was replaced with images from previous shorter exposures from Hubble's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS, CTIO>4m Blanco Telescope and CTIO>MOSAIC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.March - July 2005 (HST), December 2001 - March 2003 (CTIO)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS: F658N (H-alpha+[N II])CTIO: ([O III] 501nm), (H-alpha+[N II] 658nm) and ([S II] 672+673nm)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Carina Nebula, NGC 3372
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Emission Nebula in the Milky Way Galaxy
- Release DateApril 24, 2007
- Science ReleaseThe Carina Nebula: Star Birth in the Extreme
- Credit

This image is a composite of many separate exposures made by the ACS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope along with ground-based observations. In total, three filters were used to sample narrow wavelength emission. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are:Luminosity*: F658N (H-alpha+[N II])Blue: CTIO ([O III] 501nm)Green: CTIO (H-alpha+[N II] 658nm)Red: CTIO ([S II] 672+673nm)*The higher resolution, black & white Hubble image and the lower resolution, color CTIO images were combined using a technique that takes luminosity (brightness) information from the black and white ACS image and color information from the composite CTIO image. This preserves all of the higher-resolution detail from the Hubble data while rendering a color image representing the physical processes in this active region of space.

Related Images & Videos

Grayscale Image of the Carina Nebula: Star Birth in the Extreme
In celebration of the 17th anniversary of the launch and deployment of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, a team of astronomers is releasing one of the largest panoramic images ever taken with Hubble's cameras. It is a 50-light-year-wide view of the central region of the Carina...
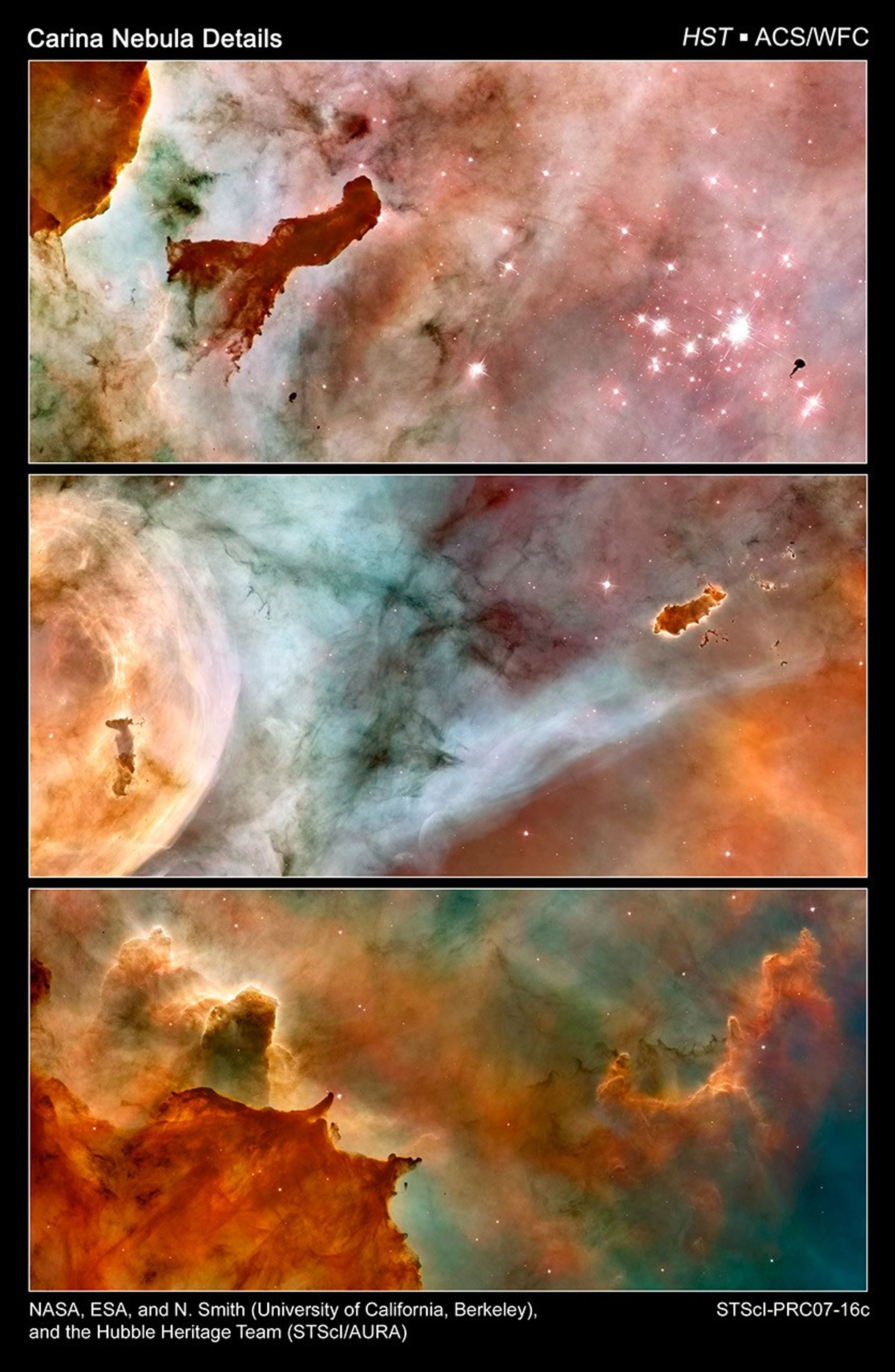

Carina Nebula Details
This Hubble Space Telescope view of the central region of the Carina Nebula reveals a violent maelstrom of star birth. The fantasy-like landscape of the nebula is sculpted by the intense pressure of starlight from monster stars and their accompanying star clusters, as well as...

Carina Nebula Details: Pillar
An approximately one-light-year tall "pillar" of cold hydrogen towers above the wall of the molecular cloud. The 2.5-million-year-old star cluster called Trumpler 14 appears at the right side of the image. A small nugget of cold molecular hydrogen, called a Bok globule, is...

Carina Nebula Details: The Caterpillar
A Bok globule nicknamed the "caterpillar" appears at the right. Its glowing edge indicates that it is being photoionized by the hottest stars in the cluster. It has been hypothesized that stars may form inside such dusty cocoons. The top of the Keyhole Nebula, the most prominent...

Carina Nebula Details: Great Clouds
These great clouds of cold hydrogen resemble summer afternoon thunderheads. They tower above the surface of a molecular cloud on the edge of the nebula. So-called "elephant trunk" pillars resist being heated and eaten away by blistering ultraviolet radiation from the nebula's...

Star-Forming Region in the Carina Nebula
[Left] - A towering "mountain" of cold hydrogen gas laced with dust is the site of new star formation in the Carina Nebula. The great gas pillar is being eroded by the ultraviolet radiation from the hottest newborn stars in the nebula. [Right] - A close-up look at the peak of...

Star-Forming Region in the Carina Nebula: Detail 2
A close-up look at the peak of one of these "pillars of creation" reveals unequivocal evidence that stars are being born inside the columns. A pencil-like streamer of gas shoots out in both directions from the pillar and plows into surrounding gas like a fire hose hitting a wall...

Dark Globule and Stellar Jet in the Carina Nebula
The tadpole-looking feature in the center of this image is a nodule of cold hydrogen gas laced with dust. The image offers circumstantial evidence that a young star is being born inside the placental cloud. The diagonal feature may be caused by twin jets of gas blasting away...
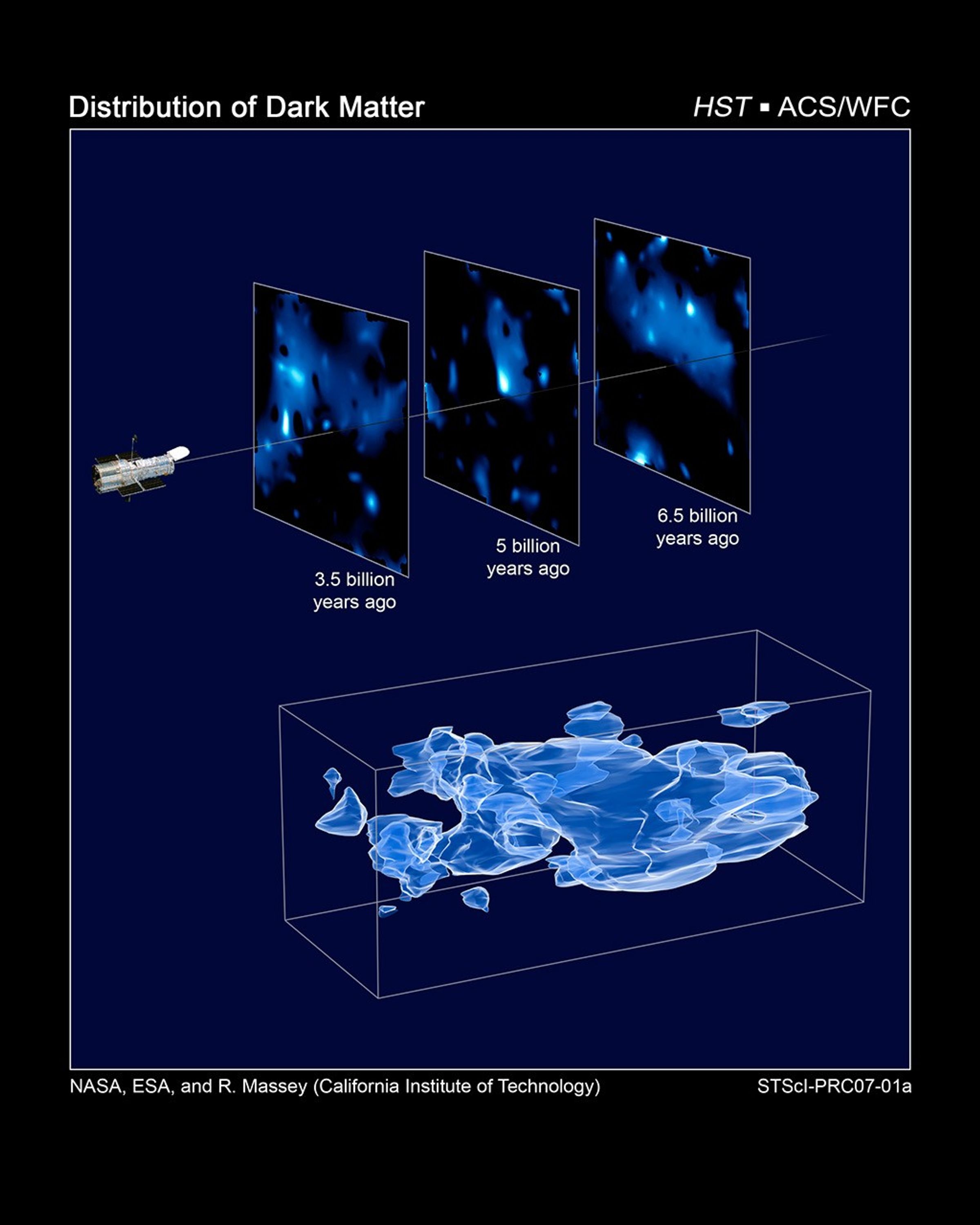
Three-Dimensional Distribution of Dark Matter in the Universe (with 3 slices of time)
This three-dimensional map offers a first look at the web-like large-scale distribution of dark matter, an invisible form of matter that accounts for most of the universe's mass. This milestone takes astronomers from inference to direct observation of dark matter's influence in...

Artist's Impression of a Transiting Exoplanet
This is an artist's impression of a Jupiter-sized planet passing in front of its parent star. Such events are called transits. When the planet transits the star, the star's apparent brightness drops by a few percent for a short period. Through this technique, astronomers can use...

A Gallery of 'Tadpole Galaxies'
These postage-stamp-size images reveal 36 young galaxies caught in the act of merging with other galaxies. These galaxies appear as they existed many billions of years ago. Astronomers have dubbed them "tadpole galaxies" because of their distinct knot-and-tail shapes, which...
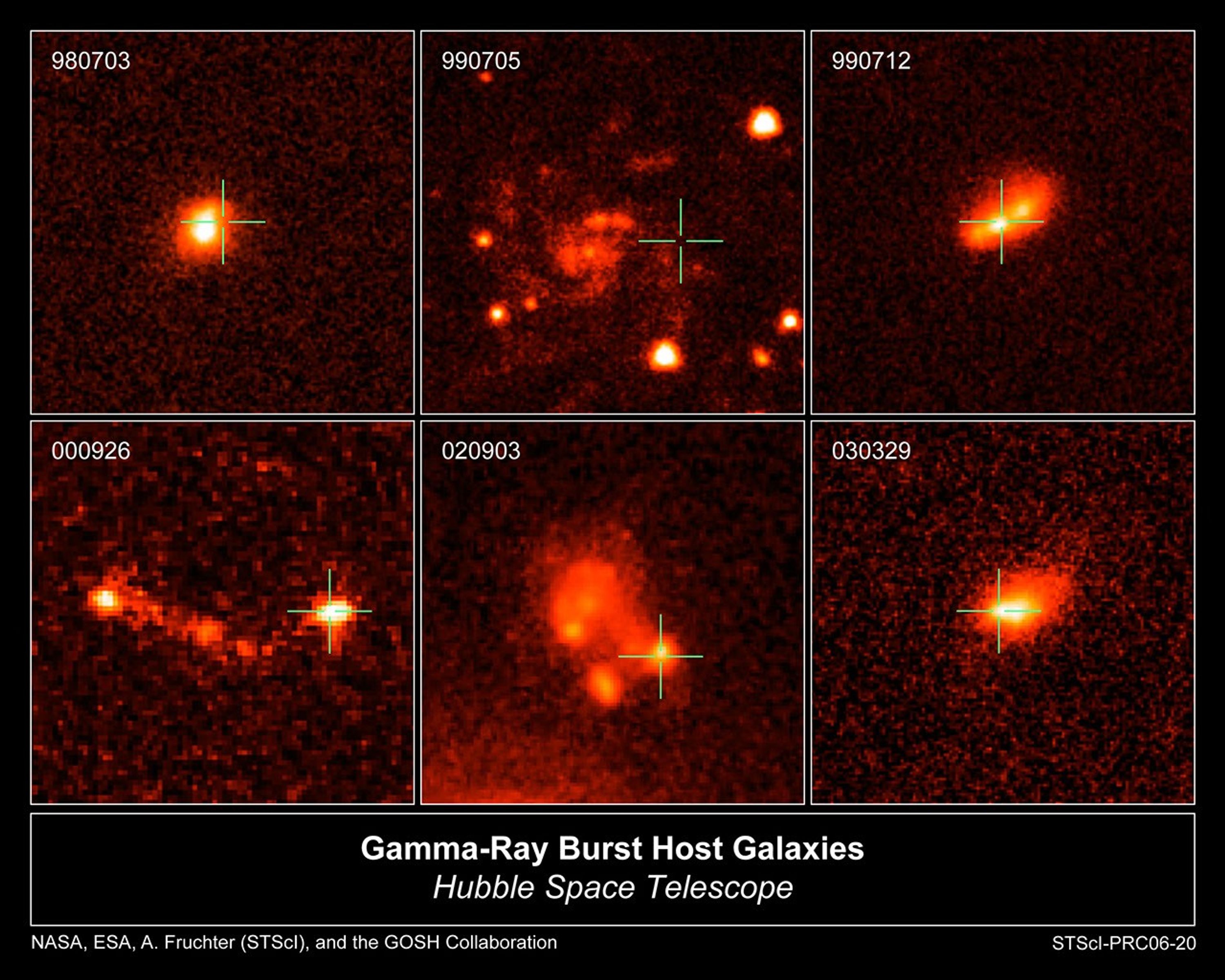
The Host Galaxies of Gamma-ray Bursts
This is a sampling of the host galaxies of long-duration gamma-ray bursts taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Gamma-ray bursts are powerful flashes of high-energy radiation that arise from some supernovae, the explosive deaths of extremely massive stars. Long-duration bursts...

Artist's Concept of Nearest Exoplanet to Our Solar System
This is an artist's concept of a Jupiter-mass planet orbiting the nearby star Epsilon Eridani. Located 10.5 light-years away, it is the closest known exoplanet to our solar system. The planet is in an elliptical orbit that carries it as close to the star as Earth is from the...

A String of 'Cosmic Pearls' Surrounds an Exploding Star
Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. Since that first sighting, the doomed star, called Supernova 1987A, has continued to fascinate astronomers with its spectacular light show. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is one of...

Looking 'Underneath' Quasar HE0450-2958
This image shows the quasar HE0450-2958 after advanced image processing known as MCS-deconvolution. Thanks to this technique, it is possible to remove the brilliant glare from the quasar itself. The most interesting feature in the image is the nearly total absence of starlight...

Photo Illustration of Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy 9 and Planet Jupiter
This is a composite photo, assembled from separate images of Jupiter and Comet P/Shoemaker-Levy 9, as imaged by the Wide Field & Planetary Camera-2 (WFPC-2), aboard. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Jupiter was imaged on May 18, 1 994, when the giant planet was at a distance...

Pluto and Its Moons: Charon, Nix, and Hydra
A pair of small moons that NASA's Hubble Space Telescope discovered orbiting Pluto now have official names: Nix and Hydra. Photographed by Hubble in 2005, Nix and Hydra are roughly 5,000 times fainter than Pluto and are about two to three times farther from Pluto than its large...
Carina Nebula: Star Birth in the Extreme (Color)
In celebration of the 17th anniversary of the launch and deployment of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, a team of astronomers is releasing one of the largest panoramic images ever taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. It is a 50-light-year- wide view of the central...

Carina Nebula: Star Birth in the Extreme (Black and White)
In celebration of the 17th anniversary of the launch and deployment of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, a team of astronomers is releasing one of the largest panoramic images ever taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. It is a 50-light-year- wide view of the central...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov