1 min read
The Helix Nebula: a Gaseous Envelope Expelled By a Dying Star

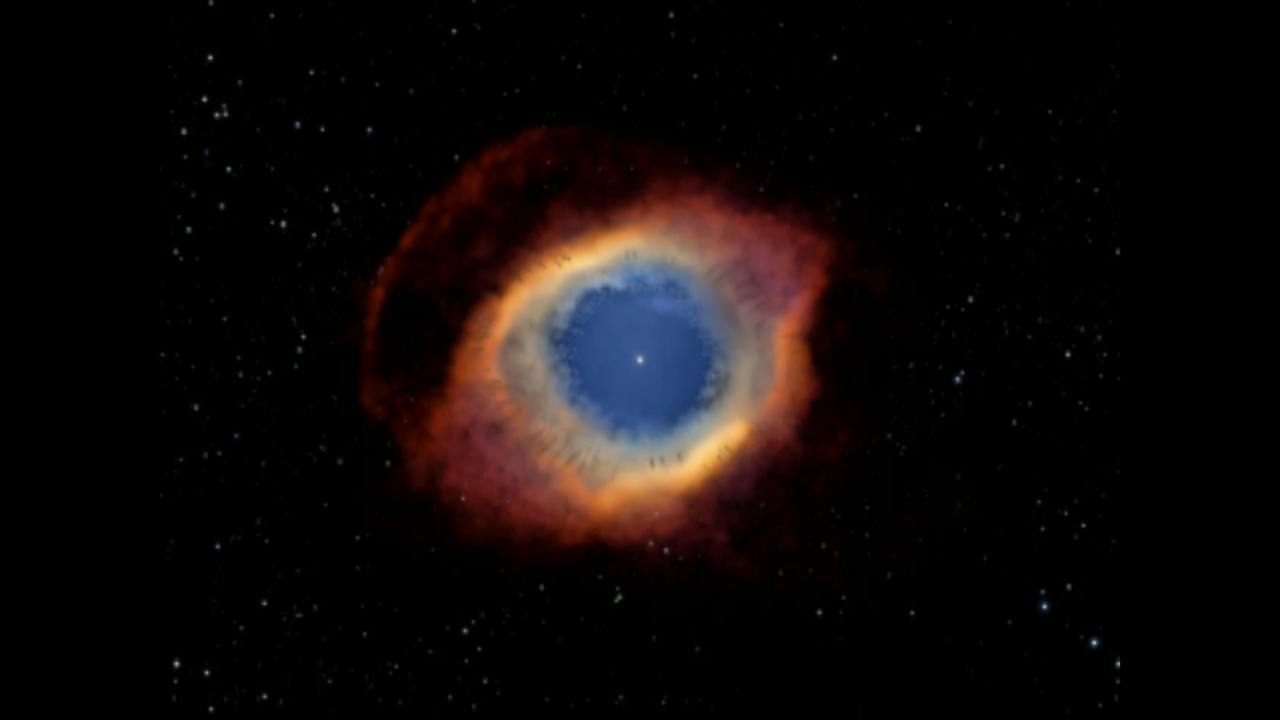
This composite image is a view of the colorful Helix Nebula taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the Mosaic II Camera on the 4-meter telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile. The object is so large that both telescopes were needed to capture a complete view. The Helix is a planetary nebula, the glowing gaseous envelope expelled by a dying, sun-like star. The Helix resembles a simple doughnut as seen from Earth. But looks can be deceiving. New evidence suggests that the Helix consists of two gaseous disks nearly perpendicular to each other.
One possible scenario for the Helix's complex structure is that the dying star has a companion star. One disk may be perpendicular to the dying star's spin axis, while the other may lie in the orbital plane of the two stars. The Helix, located 690 light-years away, is one of the closest planetary nebulas to Earth.
The Hubble images were taken on November 19, 2002; the Cerro Tololo images on Sept. 17-18, 2003.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.22h 29m 48.19s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-20° 49' 25.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Aquarius
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 690 light-years (213 parsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is roughly 287 arcminutes (5.6 light-years or 1.7 parsecs) across.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST data are from proposal 9700. Processed images may be obtained from the Helix MAST web site. The Hubble Helix Team includes: M. Meixner, H.E. Bond, G. Chapman (STScI), Y.-H. Chu (U. Illinois, Urbana-Champaign), P. Cox (Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, France), W. Crothers, L.M. Frattare, R.Gilliland (STScI), M. Guerrero R. Gruendl (U. Illinois, Urbana-Champaign), F. Hamilton, (STScI), R.Hook (STScI/ESO), P. Huggins (New York Univ.), I. Jordan, C.D. Keyes, A. Koekemoer (STScI), K.Kwitter (Williams College), Z.G. Levay, P.R. McCullough, M. Mutchler, K. Noll (STScI), C.R. O'Dell (Vanderbilt University), N. Panagia, M. Reinhart, M. Robberto, K. Sahu, D. Soderblom, L. Stanghellini, C. Tyler, J. Valenti, A. Welty, R. Williams (STScI). The CTIO data were taken by C.R. O'Dell (Vanderbilt University) and L.M. Frattare (STScI). The science team includes C.R. O'Dell (Vanderbilt University), P.R. McCullough and M. Meixner (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS and CTIO>Mosaic II
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.November 19, 2002, Exposure Time: 4.5 hours (ACS); September 17-18, 2003, Exposure Time: 10 minutes (Mosaic II)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.ACS: F502N ([O III]) and F658N (H-alpha) Mosaic II: c6009 (H-alpha) and kc6014 ([O III])
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Helix Nebula, NGC 7293
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planetary Nebula
- Release DateDecember 16, 2004
- Science ReleaseA New Twist on an Old Nebula
- Credit

Blue: F502N ([O III]) Green: c6009 (H-alpha) and kc6014 ([O III]) Red: F658N (H-alpha)

Related Images & Videos
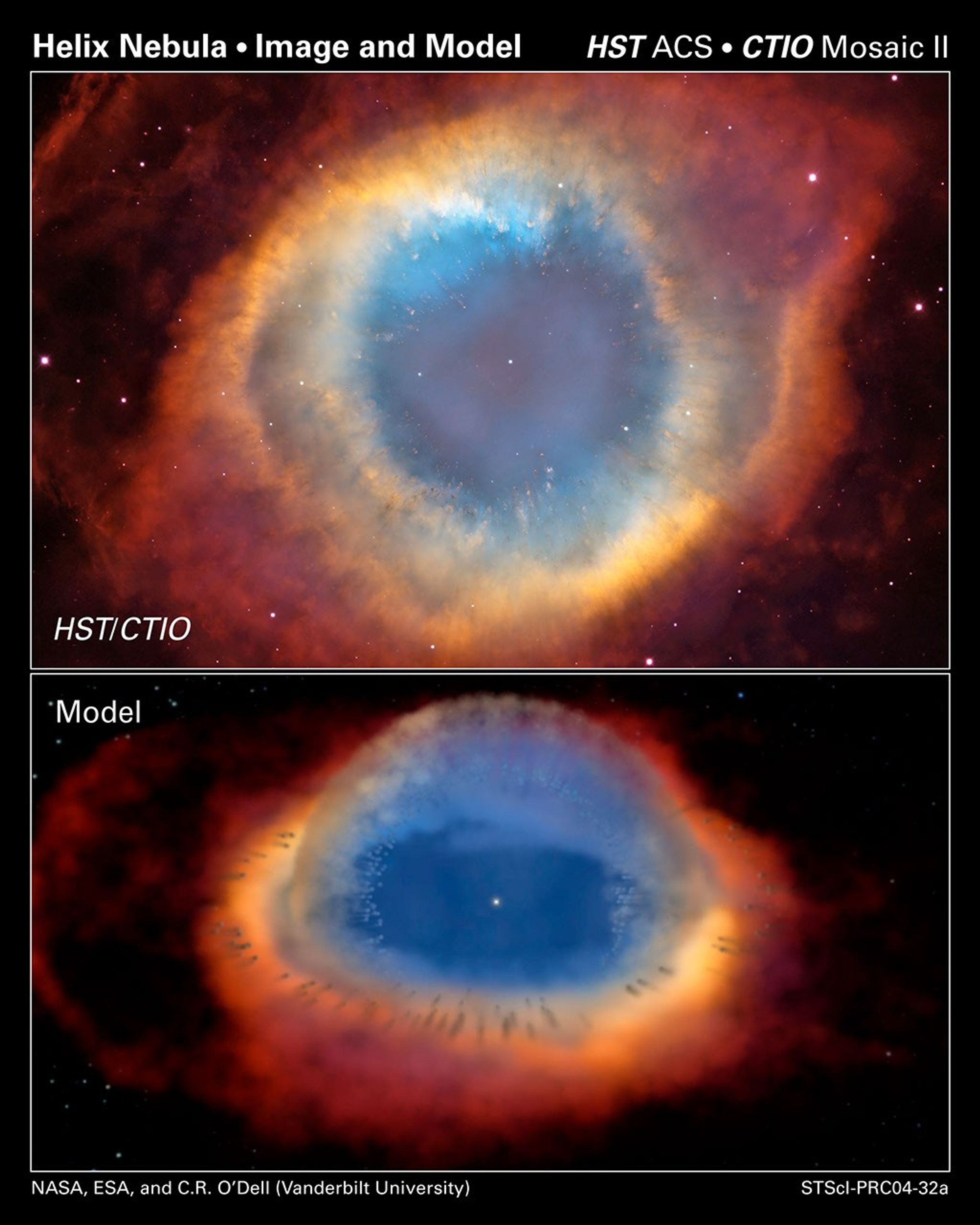
Two Views of a Nebula
The top composite image is a view of the colorful Helix Nebula taken with the Advanced Camera for Surveys aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile. The object is so large that both telescopes were needed to capture a complete...

HubbleMinute - Helix Nebula: A New Twist
A Video News Release explains how the shapes of planetary nebulae are deceiving. Astronomers combined highly detailed images of the Helix Nebula from the Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys, with images from the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile....
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov