1 min read
Webb View of Dimorphos Ejecta (NIRCam)

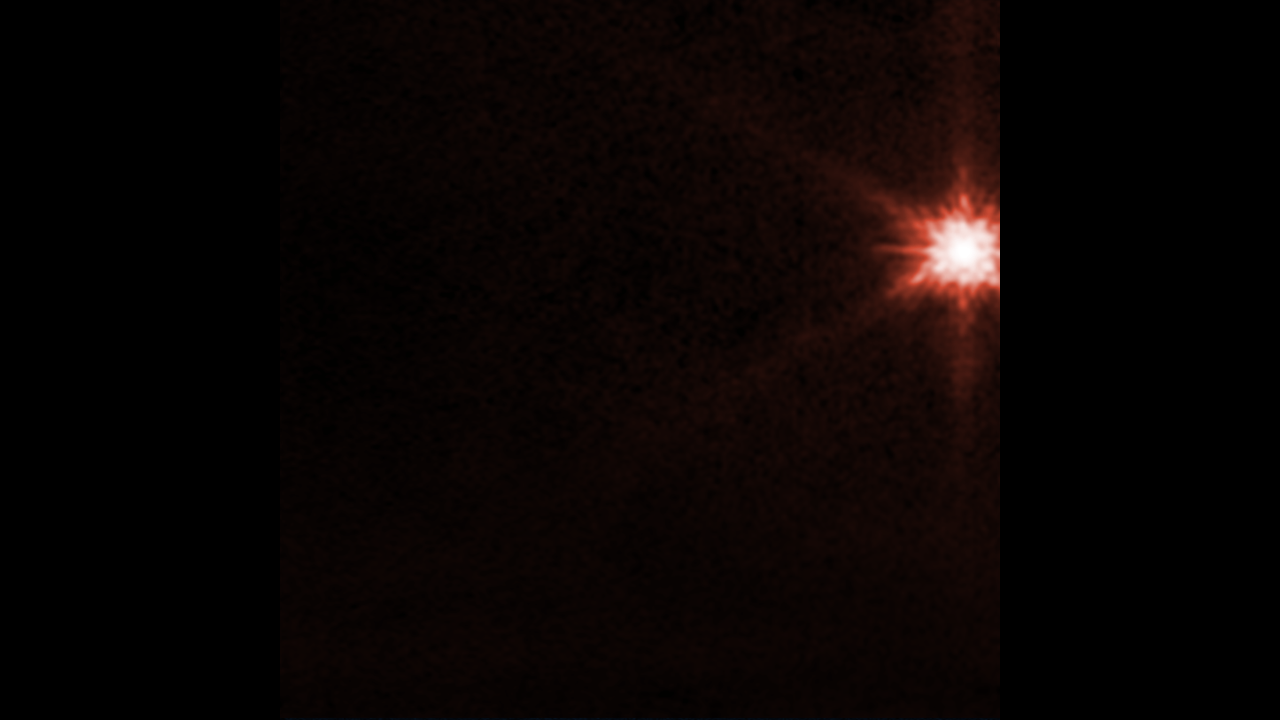
This image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) instrument shows Dimorphos, the asteroid moonlet in the double-asteroid system of Didymos, about 4 hours after NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) made impact. A tight, compact core and plumes of material appearing as wisps streaming away from the center of where the impact took place, are visible in the image. Those sharp points are Webb’s distinctive eight diffraction spikes, an artifact of the telescope’s structure.
These observations, when combined with data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, will allow scientists to gain knowledge about the nature of the surface of Dimorphos, how much material was ejected by the collision, and how fast it was ejected.
In the coming months, scientists will use Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) and Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) to observe ejecta from Dimorphos further. Spectroscopic data will also provide researchers with insight into the asteroid’s chemical composition.
The observations shown here were conducted in the filter F070W (0.7 microns) and assigned the color red.
NIRCam was built by a team at the University of Arizona and Lockheed Martin’s Advanced Technology Center.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from JWST data from proposal: 1245 (C. Thomas)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.JWST>NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.26-27 Sept 2022
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.JWST>F070W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Dimorphos
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) on asteroid Dimorphos
- Release DateSeptember 29, 2022
- Science ReleaseWebb, Hubble Capture Detailed Views of DART Impact
- CreditNASA, ESA, CSA, Cristina Thomas (Northern Arizona University), Ian Wong (NASA-GSFC); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)

The image is a single exposure acquired by the NIRCam instrument on the James Webb Space Telescope. The color results from assigning a red hue to a monochromatic (grayscale) image. Red: JWST>F070W
Related Images & Videos

Hubble Views of Dimorphos Ejecta
These images from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope, taken 22 minutes, 5 hours, and 8.2 hours after NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) intentionally impacted Dimorphos, show expanding plumes of ejecta from the asteroid’s body. This event was the world’s first test of the...

Hubble/Webb Side-by-Side of Dimorphos Ejecta
For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and Hubble Space Telescope have taken simultaneous observations of the same target. These images, Hubble on left and Webb on the right, show observations of the Didymos-Dimorphos system several hours after NASA’s Double...

Hubble/Webb Side-by-Side (WFC3/NIRCam Compass Image)
Image is two columns, the column on the left is a photo with a black background and a bright blue spot at the center, labeled as Hubble. There is a bright haze around the dot, which is the Didymos-Dimorphos system, along with 5 diffraction spikes extending outward. The photo on...

Hubble Time-Lapse of Dimorphos Ejecta
This animated gif combines three of the images NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured after NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) intentionally impacted Dimorphos, a moonlet asteroid in the double asteroid system of Didymos. The animation spans from 22 minutes after...
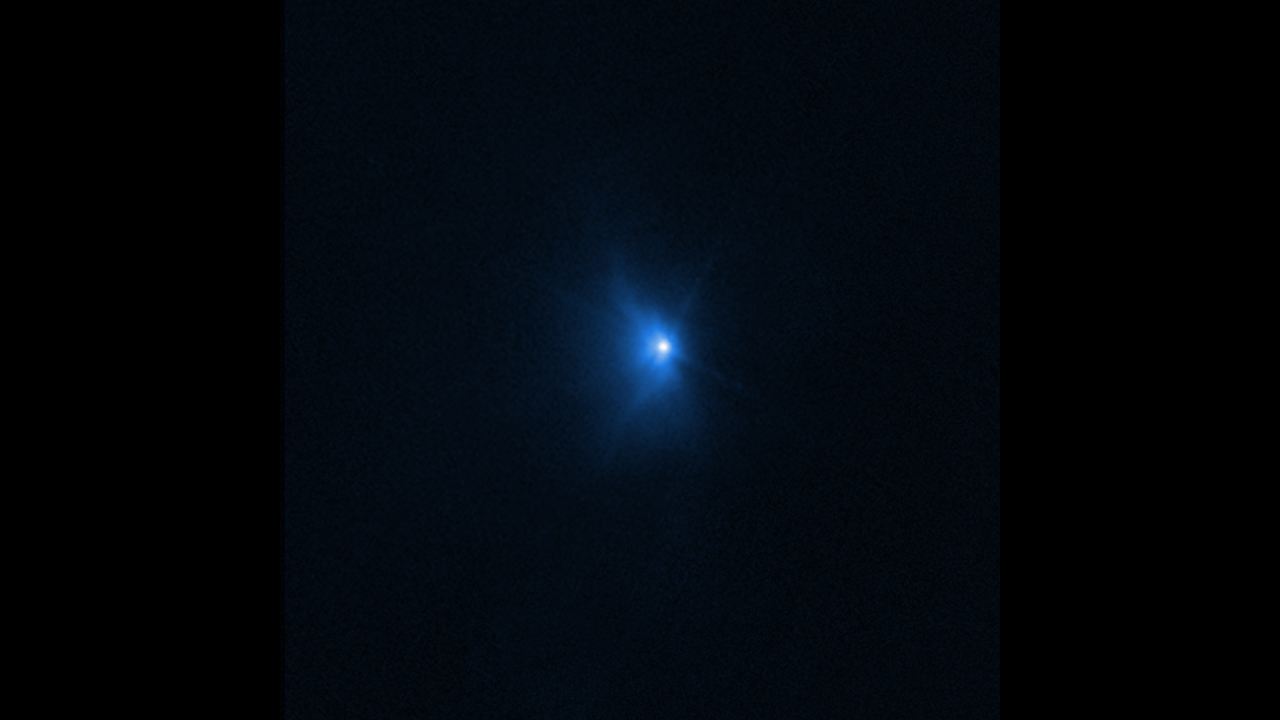
Webb Time-Lapse of Dimorphos Ejecta
This animation features a time-lapse of images from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope showing the aftermath of NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) intentionally slamming into the moonlet asteroid Dimorphos. This animation covers the time spanning just before impact at...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
































