1 min read
Kilonova and Host Galaxy

A team of scientists has used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to observe an exceptionally bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and its associated kilonova. Kilonovas—an explosion produced by a neutron star merging with either a black hole or with another neutron star—are extremely rare, making it difficult to observe these events. The highly sensitive infrared capabilities of Webb helped scientists identify the home address of the two neutron stars that created the kilonova.
This image from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) instrument highlights GRB 230307A’s kilonova and its former home galaxy among their local environment of other galaxies and foreground stars. The neutron stars were kicked out of their home galaxy and traveled the distance of about 120,000 light-years, approximately the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy, before finally merging several hundred million years later.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.04:03:26.01
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-75:22:42.78
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Mensa
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is approximately 1.3 arcminutes across
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Webb observations include those from program: 4434 (A. Levan)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.NIRCam
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.05 April 2023, 08 May 2023
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F115W, F150W, F277W, F356W, F444W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GRB 230307A
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Gamma ray burst from two colliding neutron stars
- Release DateOctober 25, 2023
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Makes First Detection of Heavy Element from Star Merger
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Andrew Levan (IMAPP, Warw)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F115W + F150W Green: F277W Red: F356W + F444W

Related Images & Videos

Kilonova Emission Spectrum
This graphic presentation compares the spectral data of GRB 230307A’s kilonova as observed by the James Webb Space Telescope and a kilonova model. Both show a distinct peak in the region of the spectrum associated with tellurium, with the area shaded in red. The detection of...
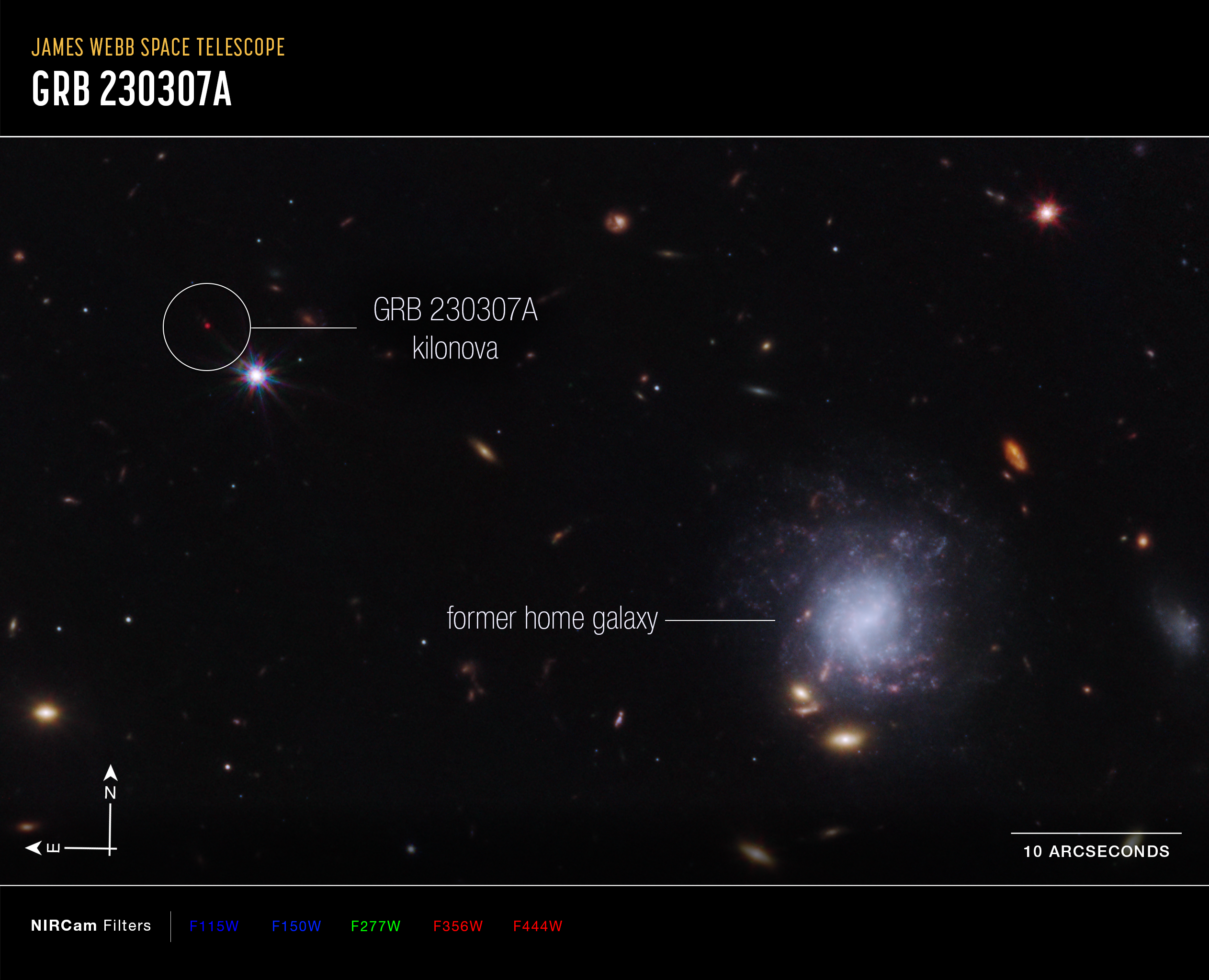
Kilonova and Host Galaxy (Compass Image)
An image of the GRB 230307A kilonova and the former home galaxy of the neutron stars captured by Webb's NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera), with compass arrows, a scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky....
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Andrew Levan (IMAPP, Warw)




























