1 min read
Sagittarius B2 (MIRI Image)

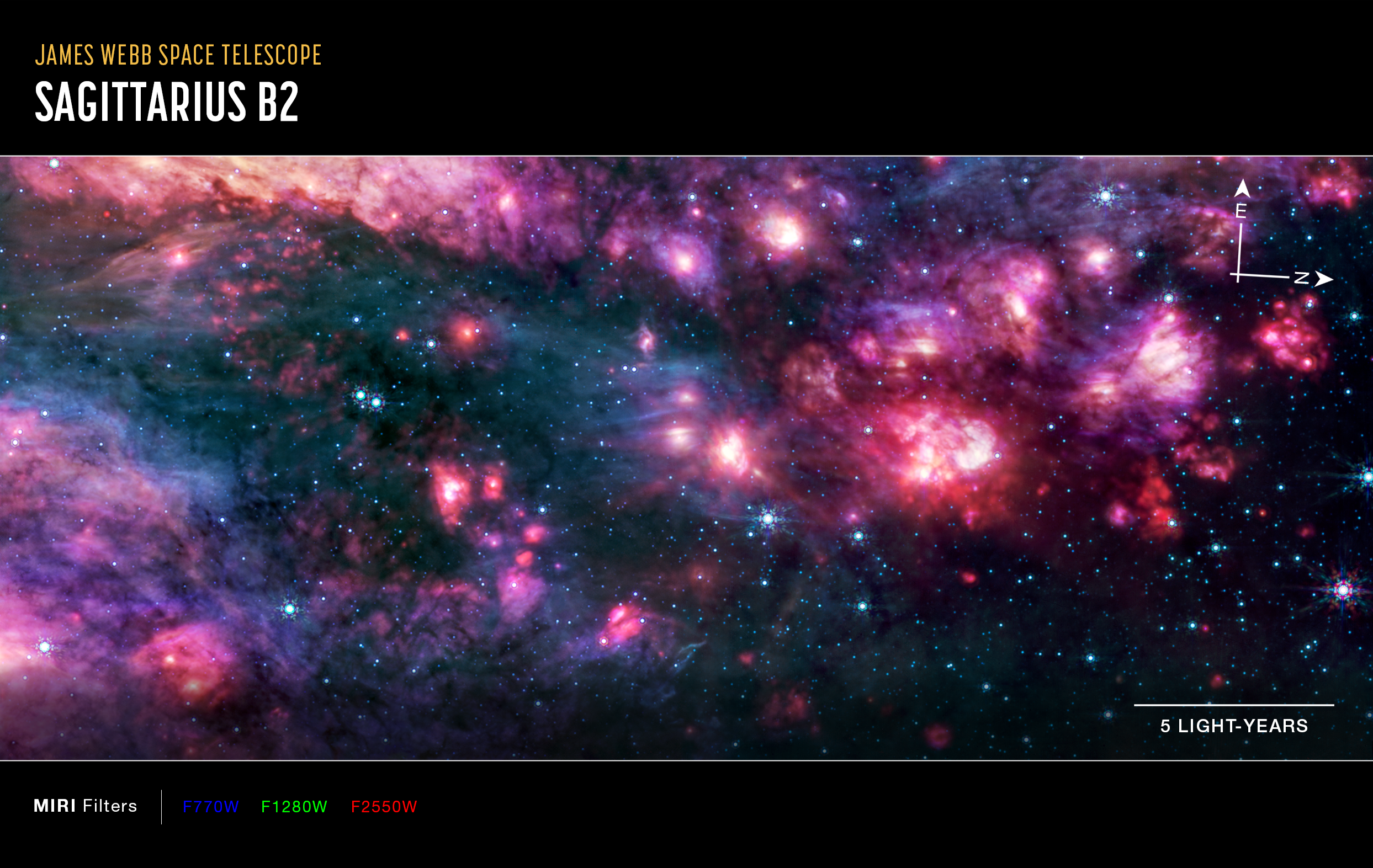
Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) shows the Sagittarius B2 (Sgr B2) region in mid-infrared light, with warm dust glowing brightly. To the right is one clump of clouds that captured astronomers’ attention. It is redder than the rest of the clouds in the image and corresponds to an area that other telescopes have shown to be one of the most molecularly rich regions known. Additional analysis of this intriguing region could yield important insights into why Sgr B2 is so much more productive in making stars than the rest of the galactic center.
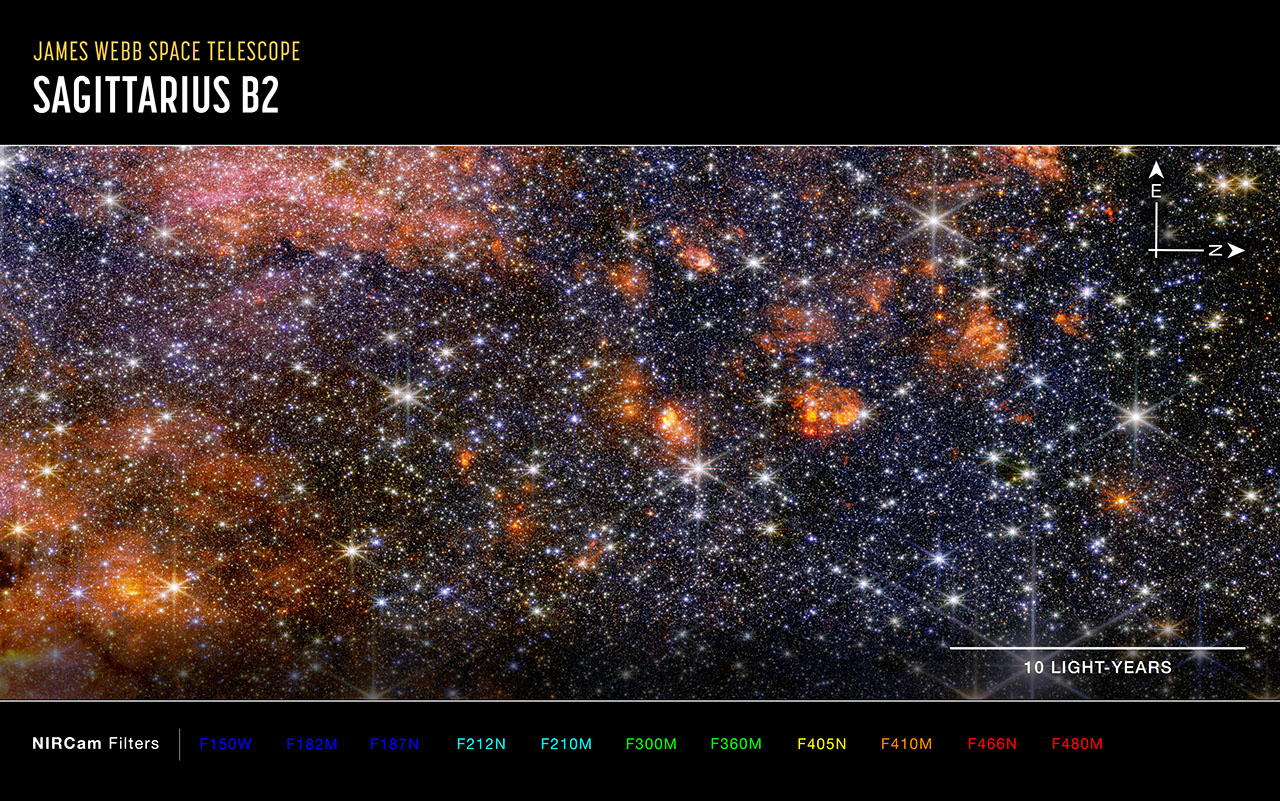
Only the brightest stars in this region emit mid-infrared light that can be picked up by Webb’s MIRI instrument, which is why this image has so many fewer stars than that captured by Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera). The darkest areas of the image are not empty space but areas where cosmic dust and gas are so dense that light cannot penetrate them to reach the telescope.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.17:47:19.98
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-28:23:50.73
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Sagittarius
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 26,000 light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 4.6 arcminutes across (35 light-years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created with Webb data from proposal: 5365 (A. Ginsburg).
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.MIRI
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.15 Sept. 2024
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F770W, F1280W, F1550W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Sagittarius B2, Sgr B2
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Giant molecular cloud at the center of the Milky Way
- Release DateSeptember 24, 2025
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Webb Explores Largest Star-Forming Cloud in Milky Way
- CreditImage: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Adam Ginsburg (University of Florida), Nazar Budaiev (University of Florida), Taehwa Yoo (University of Florida); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the MIRI instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue= F770W, Green= F1280W, Red= F1550W
Related Images & Videos
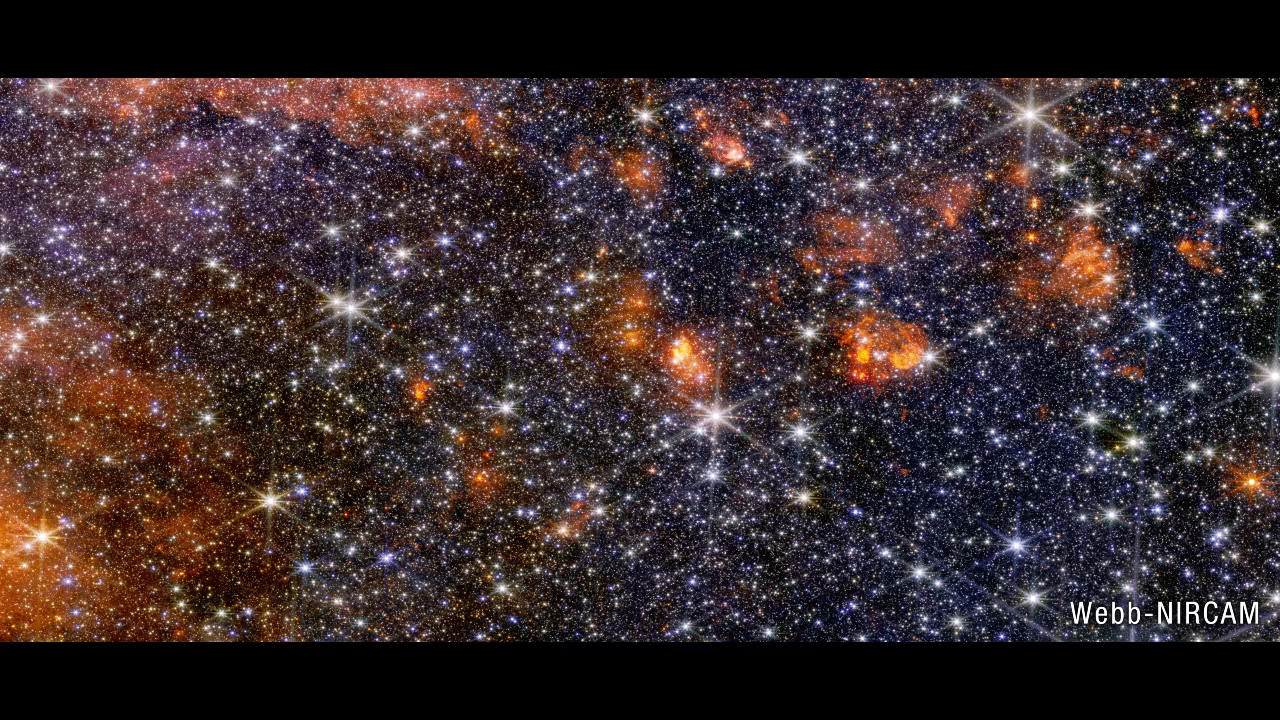

Sagittarius B2 NIRCam to MIRI Fade
See what different wavelengths of infrared light reveal and conceal. Near-infrared light, which is nearest to visible red, comes from some gas and an abundance of colorful stars. The longer wavelengths of mid-infrared light are emitted by warm dust and only the brightest stars....
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov