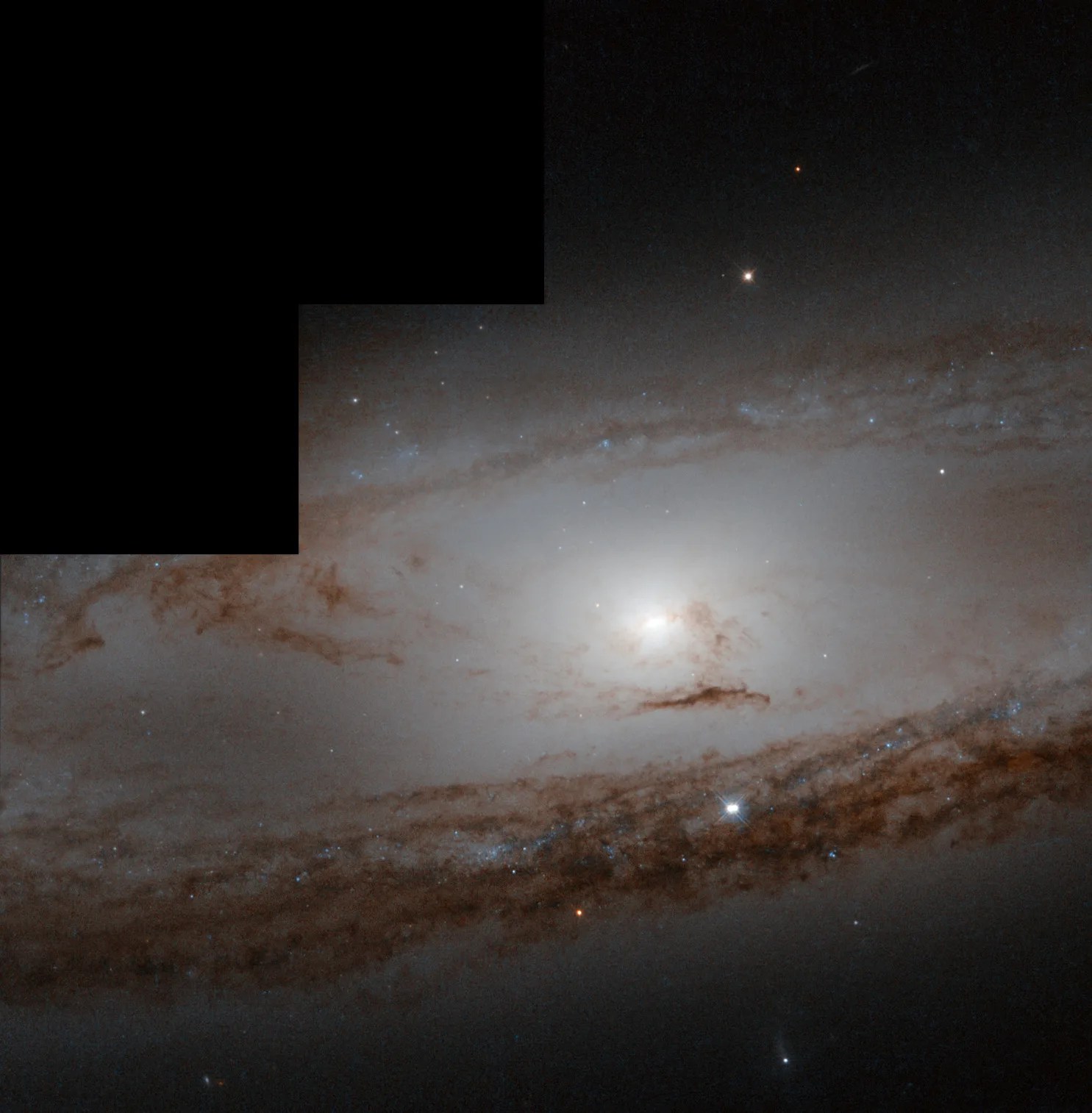
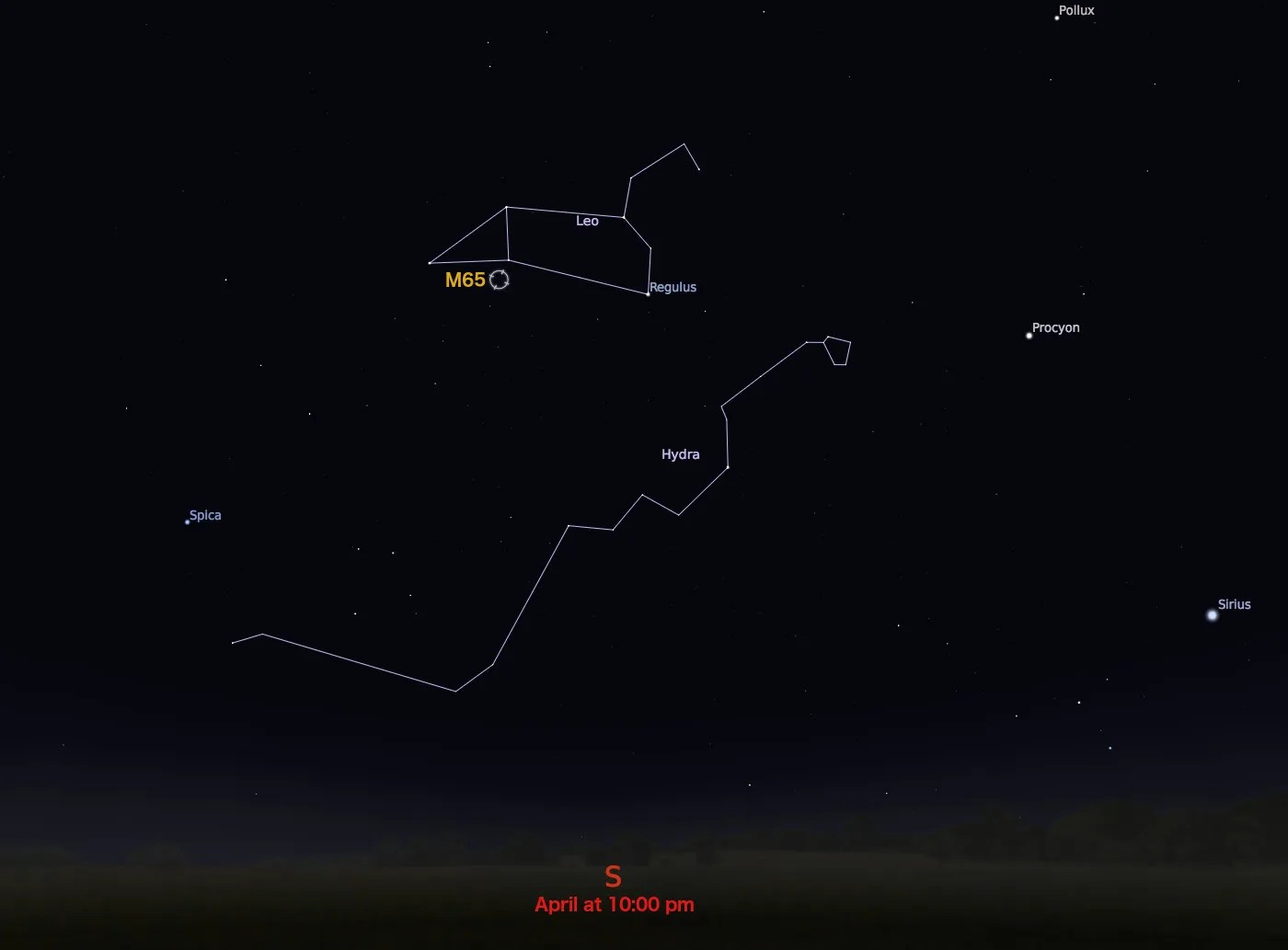
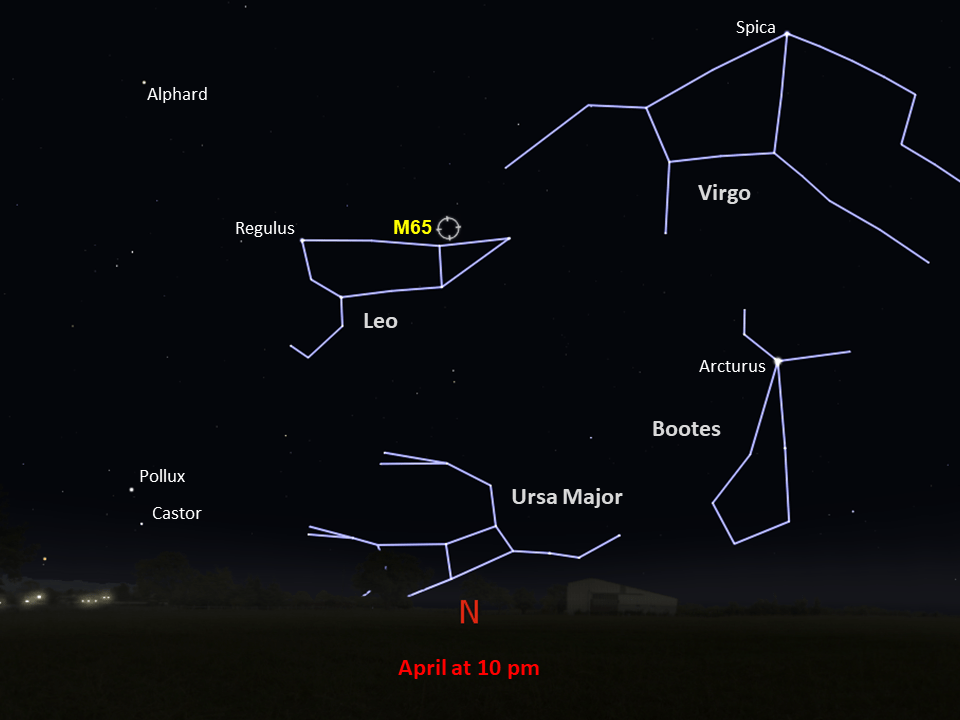
Messier 65
Messier 65 is a member of the Leo Triplet of galaxies.
Distance
35 million light-years
Apparent Magnitude
10.3
constellation
Leo
object type
Spiral Galaxy
M65 is a spiral galaxy with an apparent magnitude of 10.3. Charles Messier discovered it and its neighbor M66 on the same night in 1780. Located roughly 35 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Leo, M65 is a member of the Leo Triplet of galaxies. It can be spotted with a small telescope in the same field of view as the other members of the triplet (M66 and NGC 3628). The best time to observe M65 is in April.
This image of M65’s center is a composite created using exposures taken with Hubble at both visible and infrared wavelengths. Its stair-step appearance results from the design of the camera used to take the exposures. The camera consisted of four light detectors, one of which provided a higher resolution but had a smaller field of view than the other three. Because the detector with the higher resolution did not cover as much area as the others, black regions remain when the images from all four detectors are combined into one picture.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M65, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.