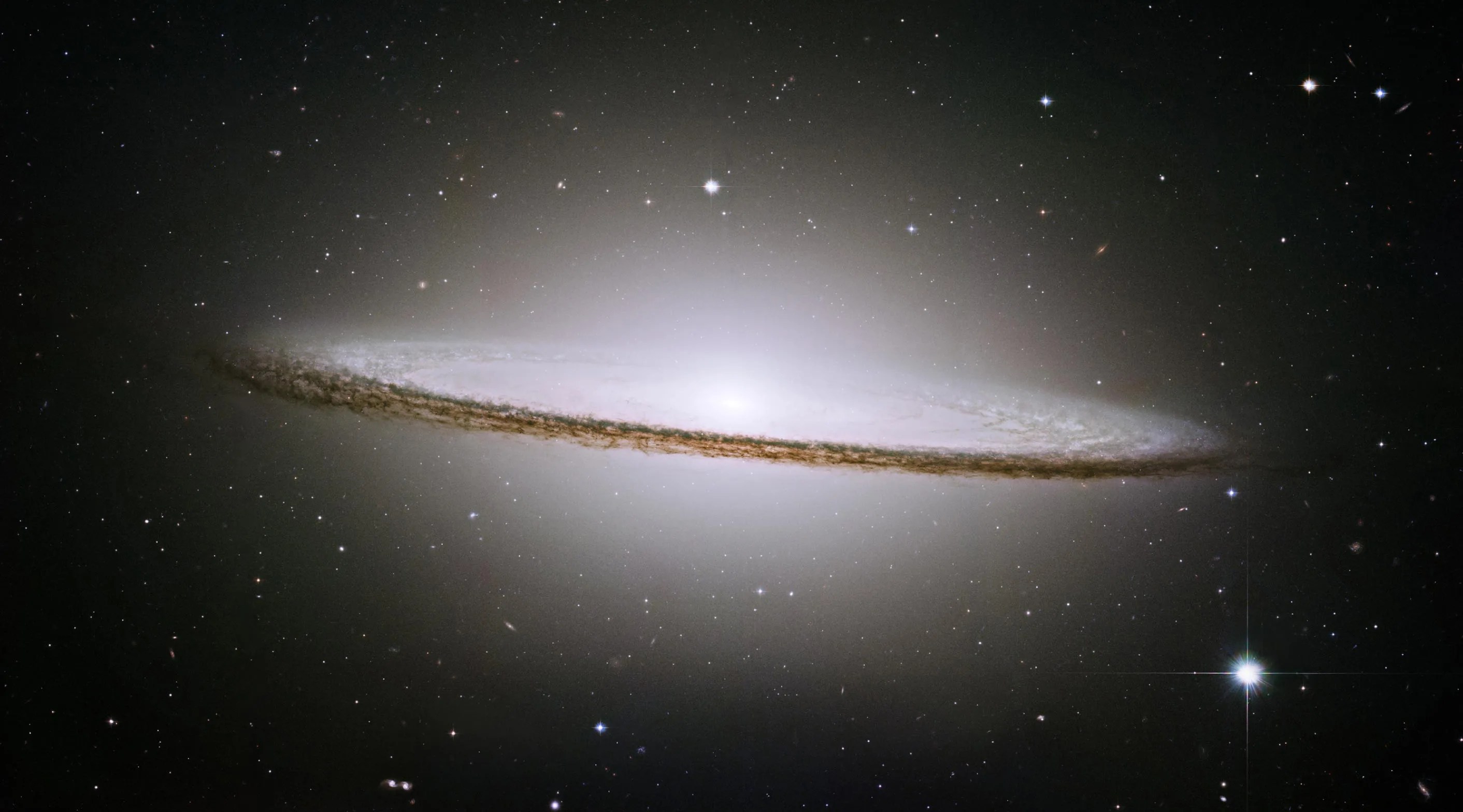
Astronomer Edwin Hubble pioneered the study of galaxies based simply on their appearance and categorized them according to three basic shapes: spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Some 60 years later, the sharp vision of the space telescope named in his honor began seeing unprecedented details in galaxies, revealing intricate, dark dust lanes and glowing knots of star formation. Hubble helped uncover the supermassive black holes that power the bright centers of massive galaxies, and revealed the interdependent relationship black holes have with their host galaxy.
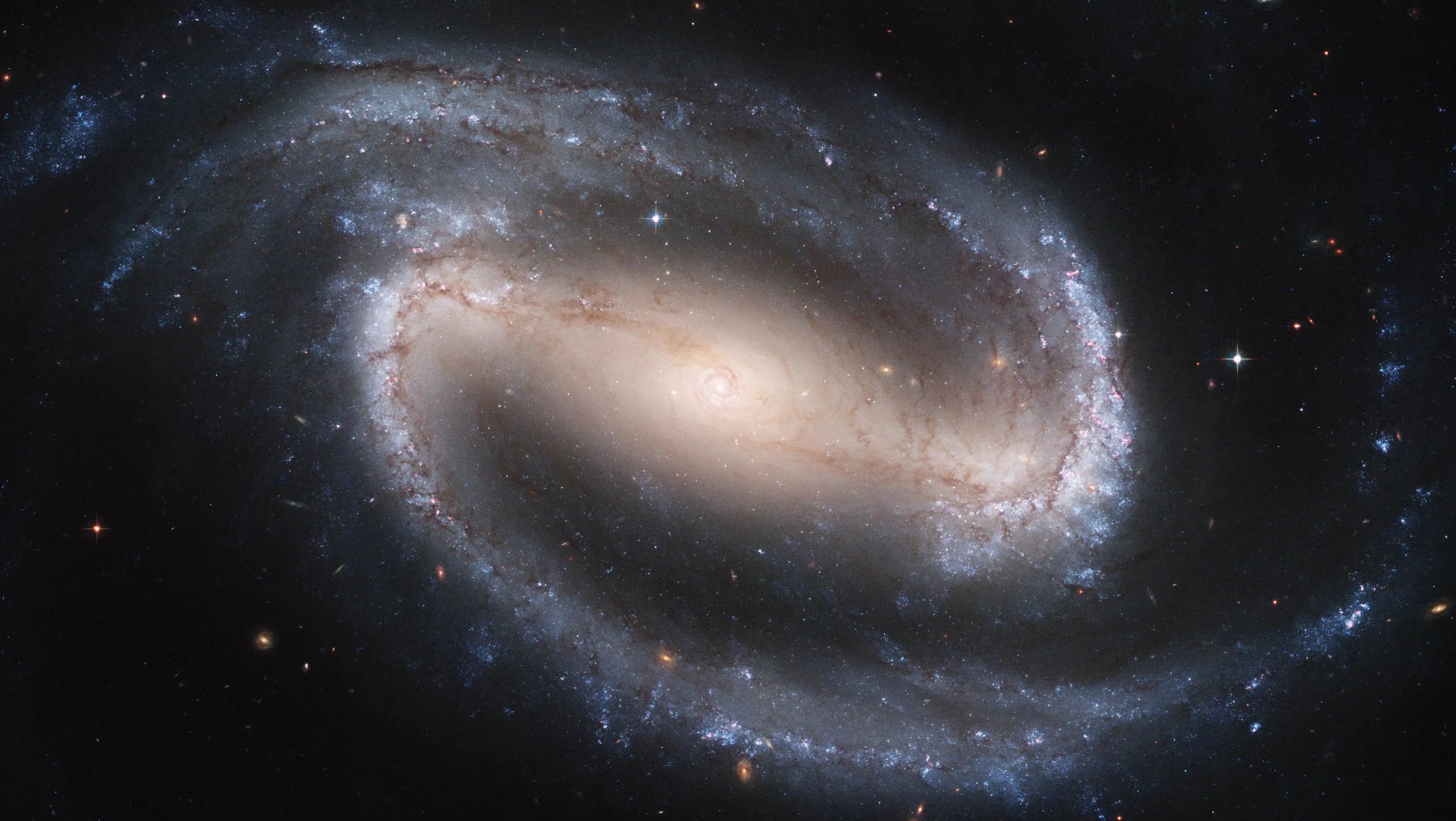

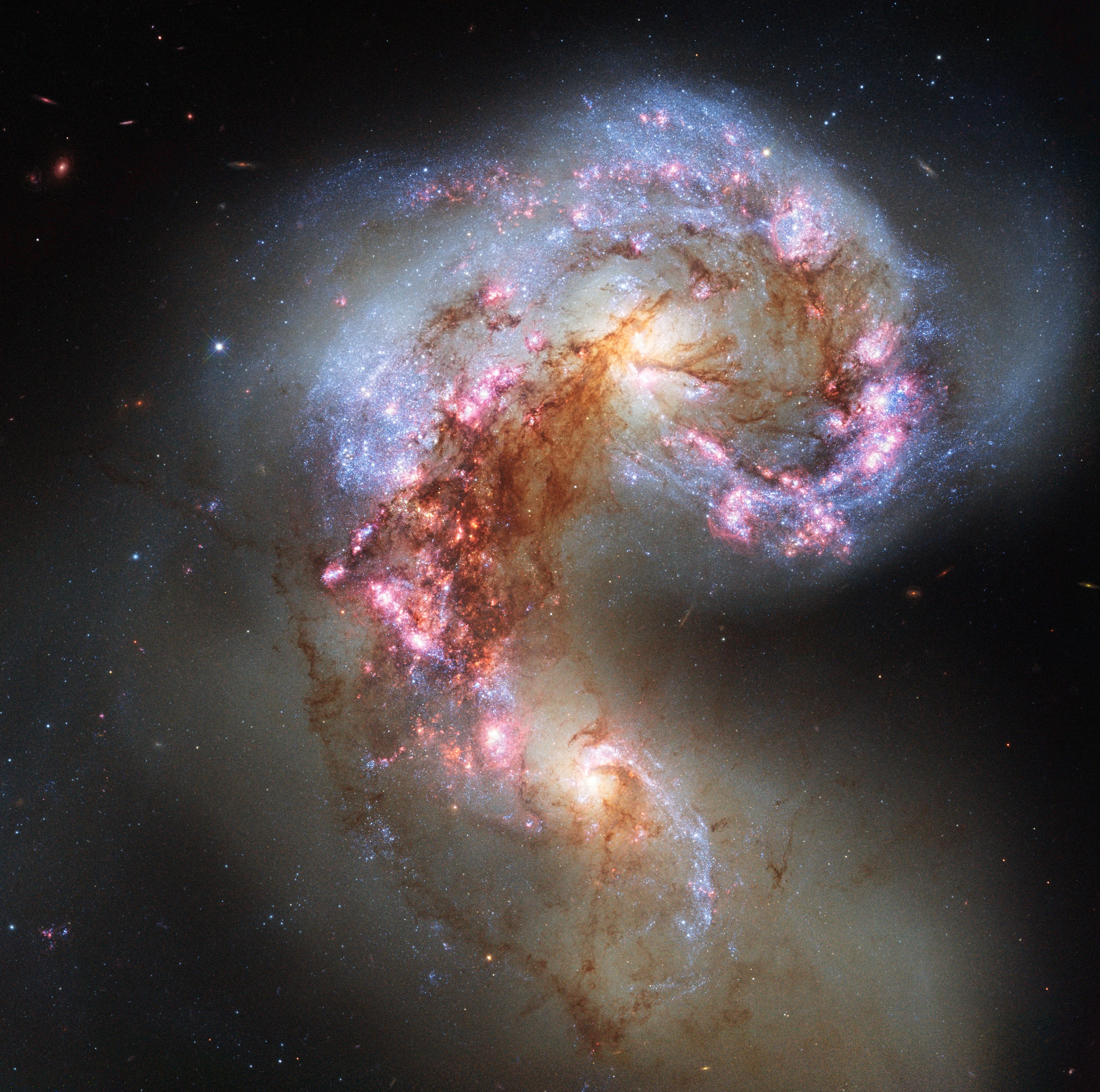
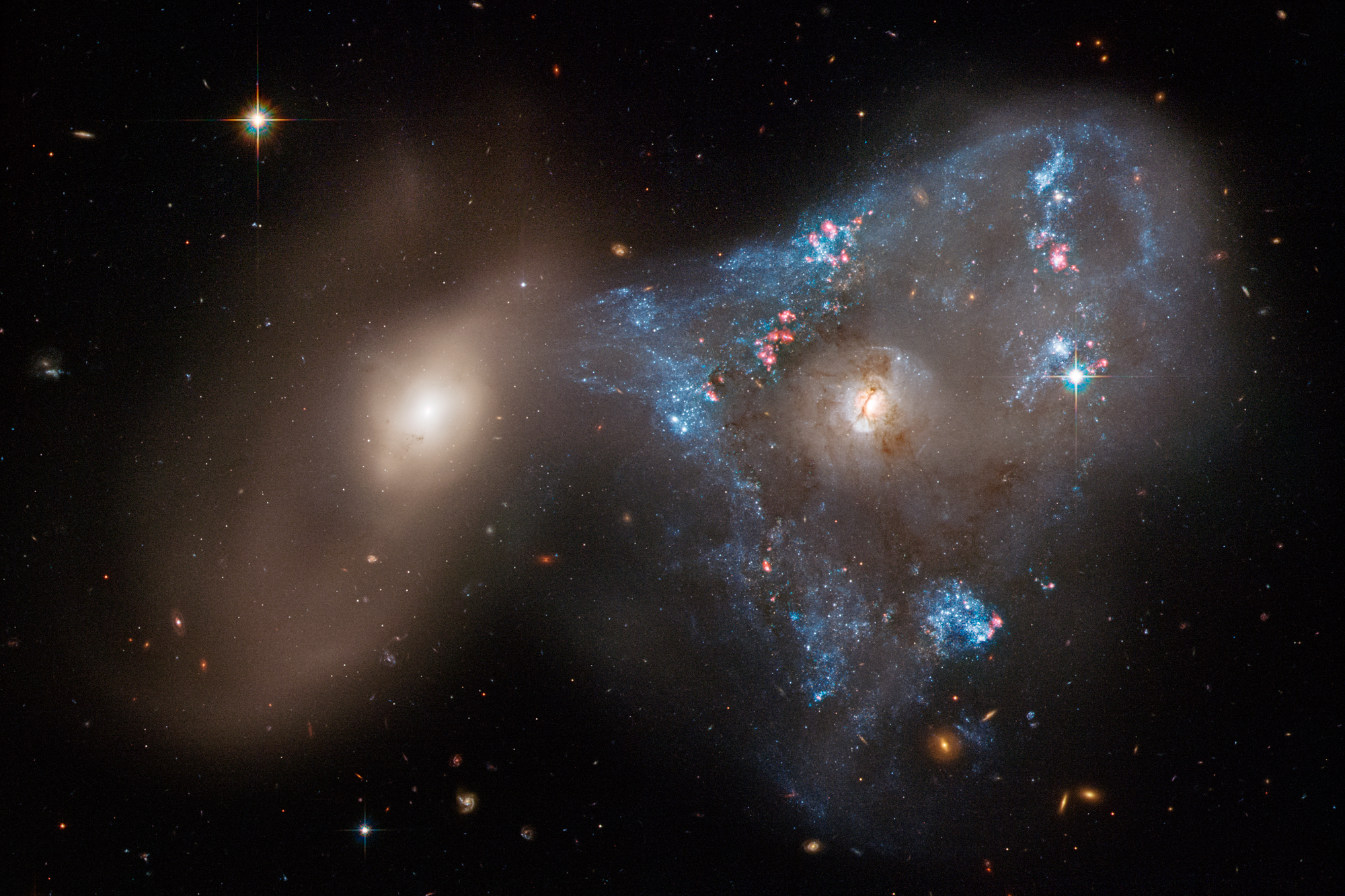
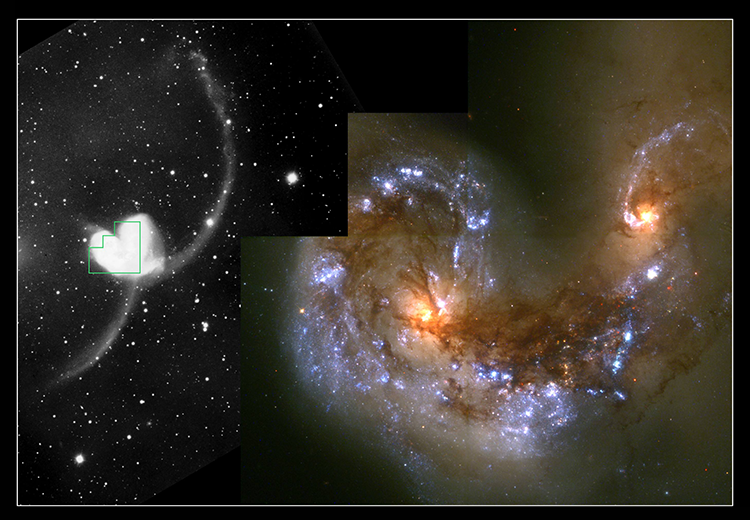
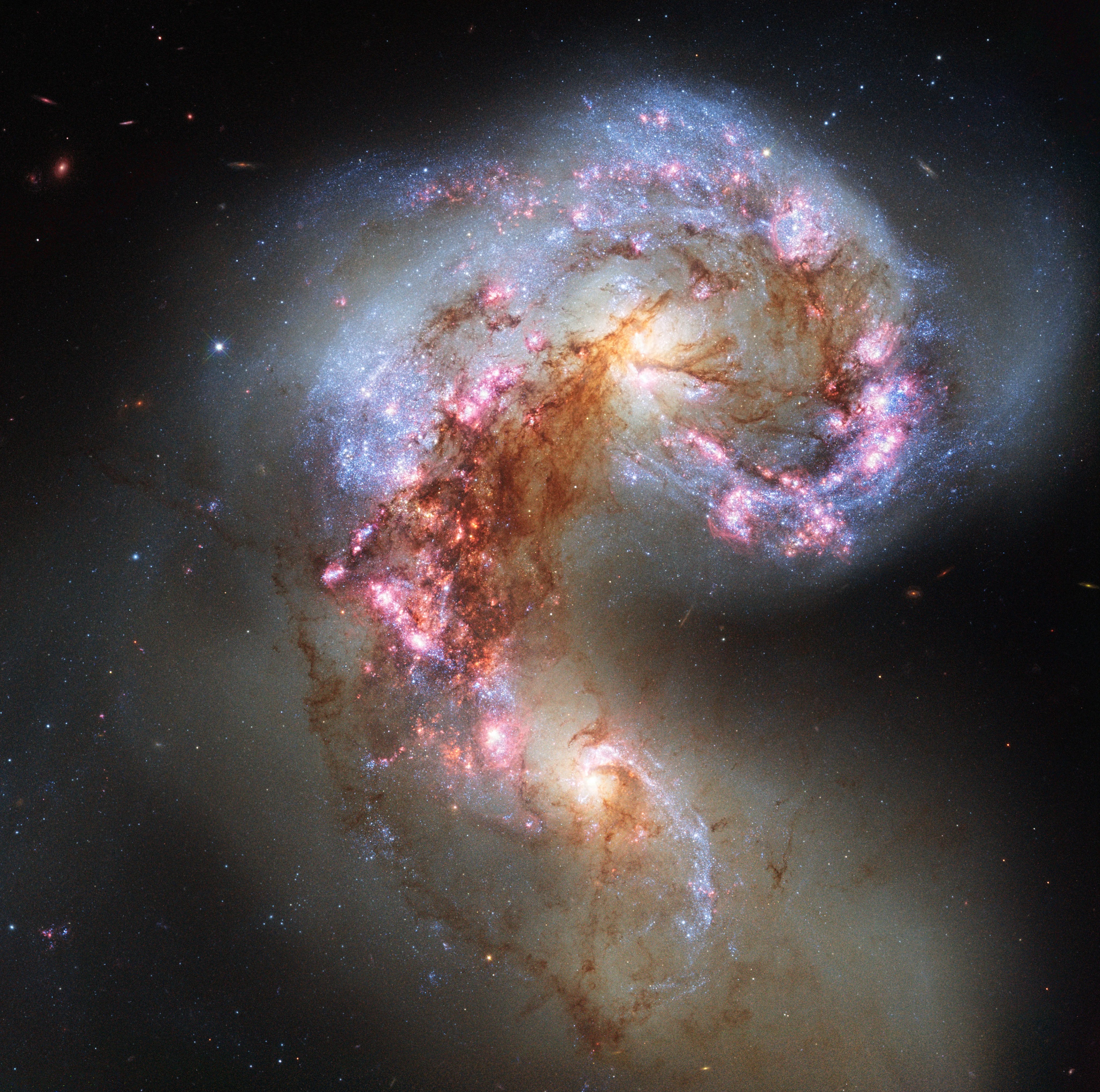
Hubble has also captured merging galaxies that look like a “Great Pumpkin,” a “Space Triangle,” “Antennae,” and “Mice.” For all their violence, galactic collisions take place at a snail’s pace – over timescales that span several hundred million years. Hubble captures a mere snapshot of these mergers.

Josh Barnes (University of Hawaii) and John Hibbard (National Radio Astronomy Observatory)
Hubble images of the “tadpole-like” Antennae and Mice galaxies reveal the gravitational turbulence these galaxies endure. The interacting duo called Arp 143 (the “Space Triangle”) holds a pair of distorted, star-forming spiral galaxies. Astronomers think the pair passed through each other, igniting a triangular firestorm of new stars.
Mergers like this preview the coming collision between our own Milky Way and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy 4 billion years from now.

Learn More
Hubble Science Highlights
Discover the breadth and depth of Hubble's exciting discoveries!
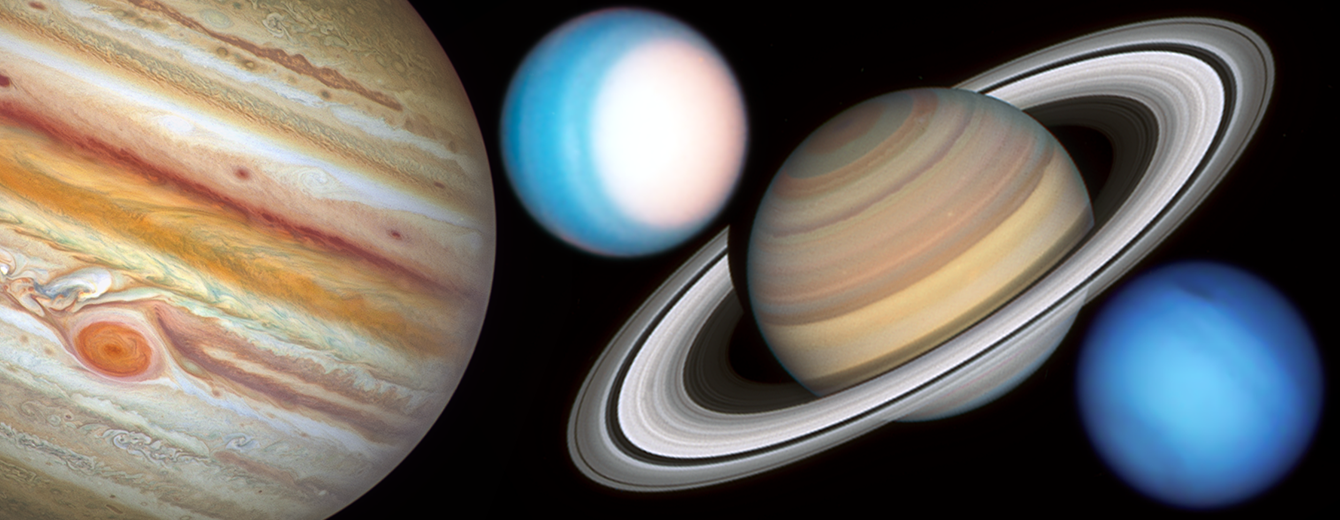
Studying the Planets and Moons
Hubble’s systematic observations chart the ever-changing environments of our solar system's planets and their moons.

Tracking Evolution in the Asteroid Belt
These conglomerates of rock and ice may hold clues to the early solar system.
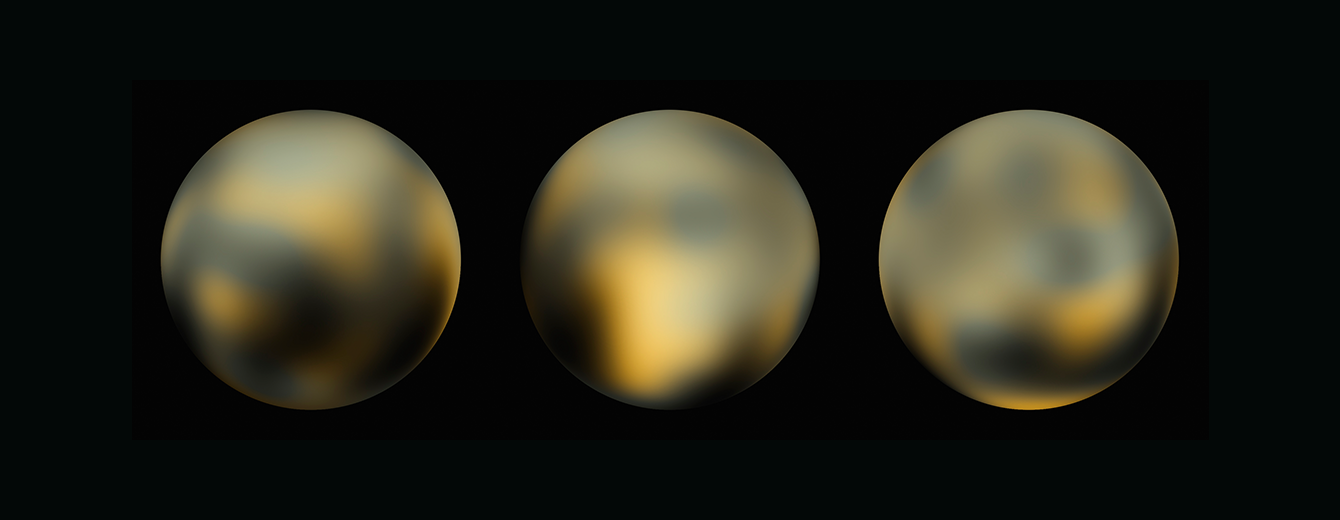
Uncovering Icy Objects in the Kuiper Belt
Hubble’s discoveries helped NASA plan the New Horizon spacecraft’s flyby of Pluto and beyond.
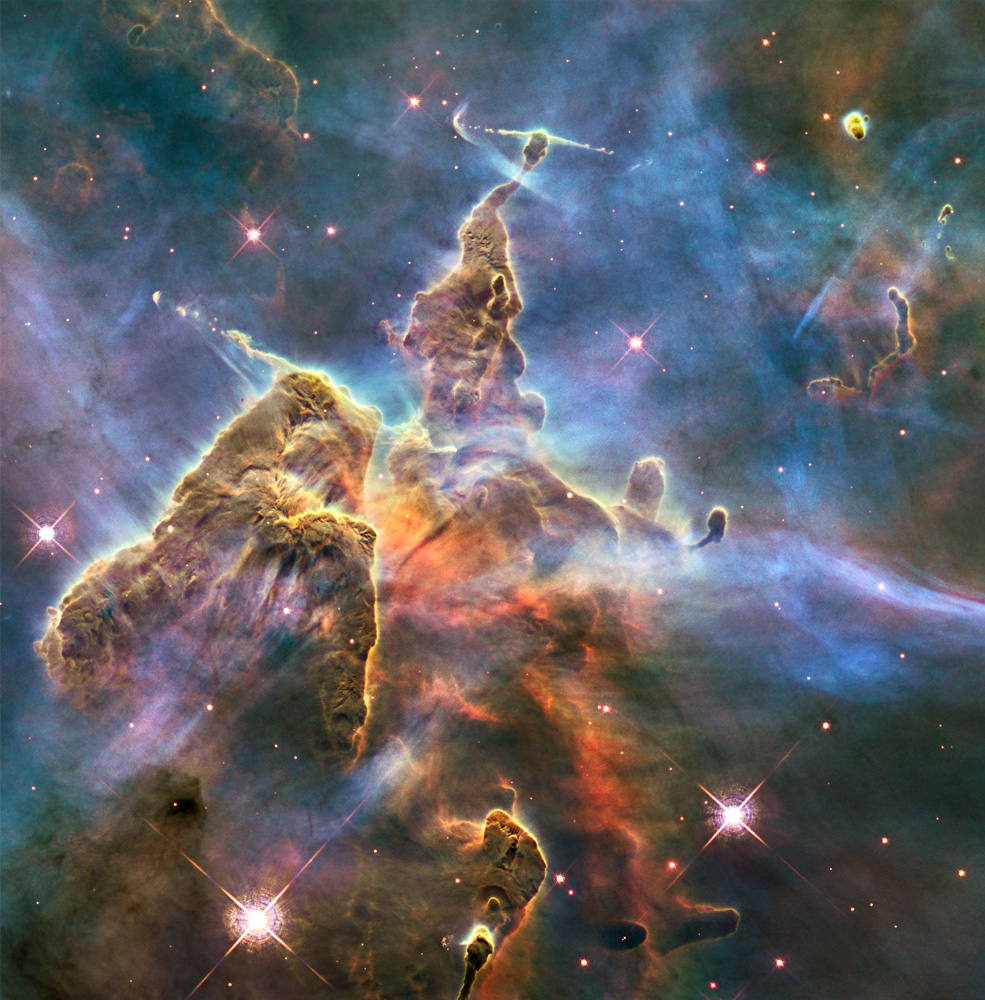

Exploring the Birth of Stars
Seeing ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light helps Hubble uncover the mysteries of star formation.
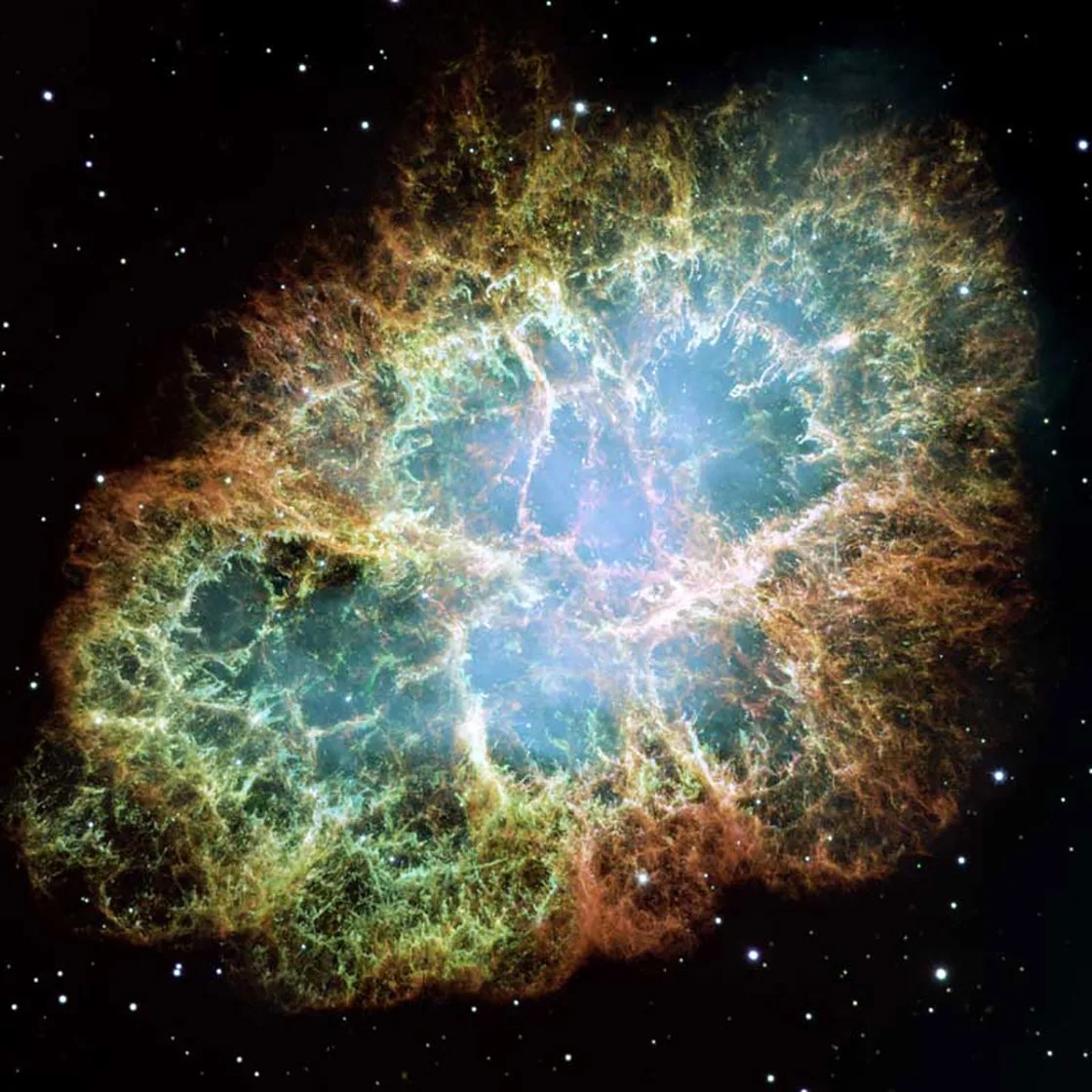

The Death Throes of Stars
When stars die, they throw off their outer layers, creating the clouds that birth new stars.
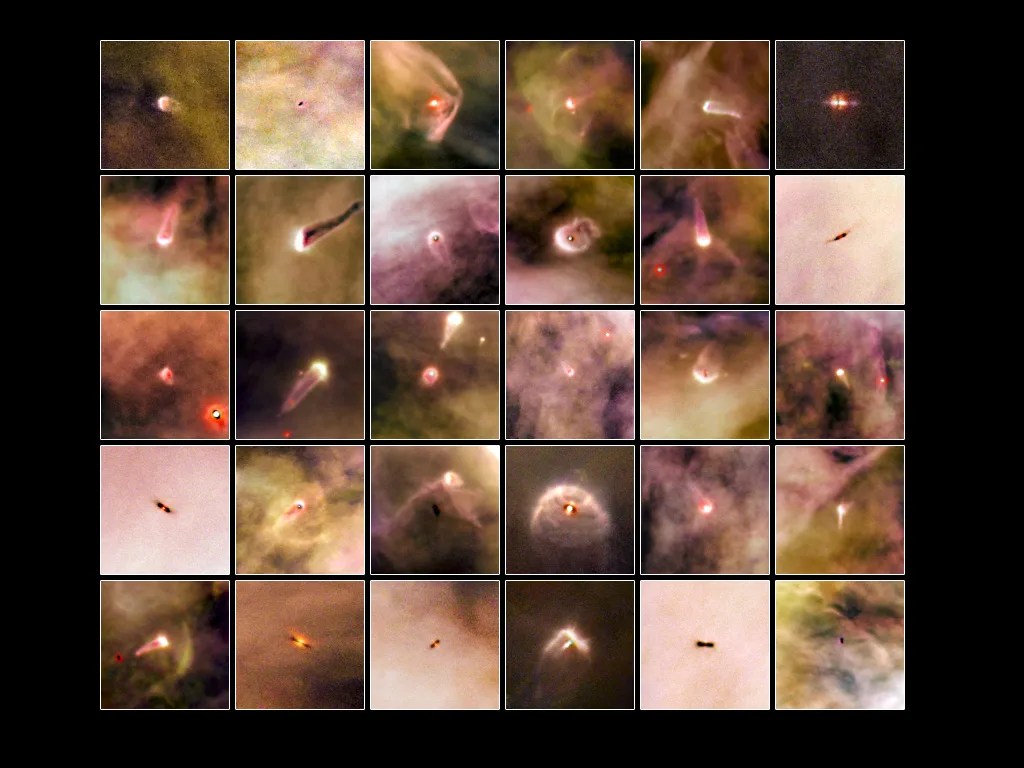

Finding Planetary Construction Zones
Hubble’s sensitivity uncovers the seeds of planets in enormous disks of gas and dust around stars.
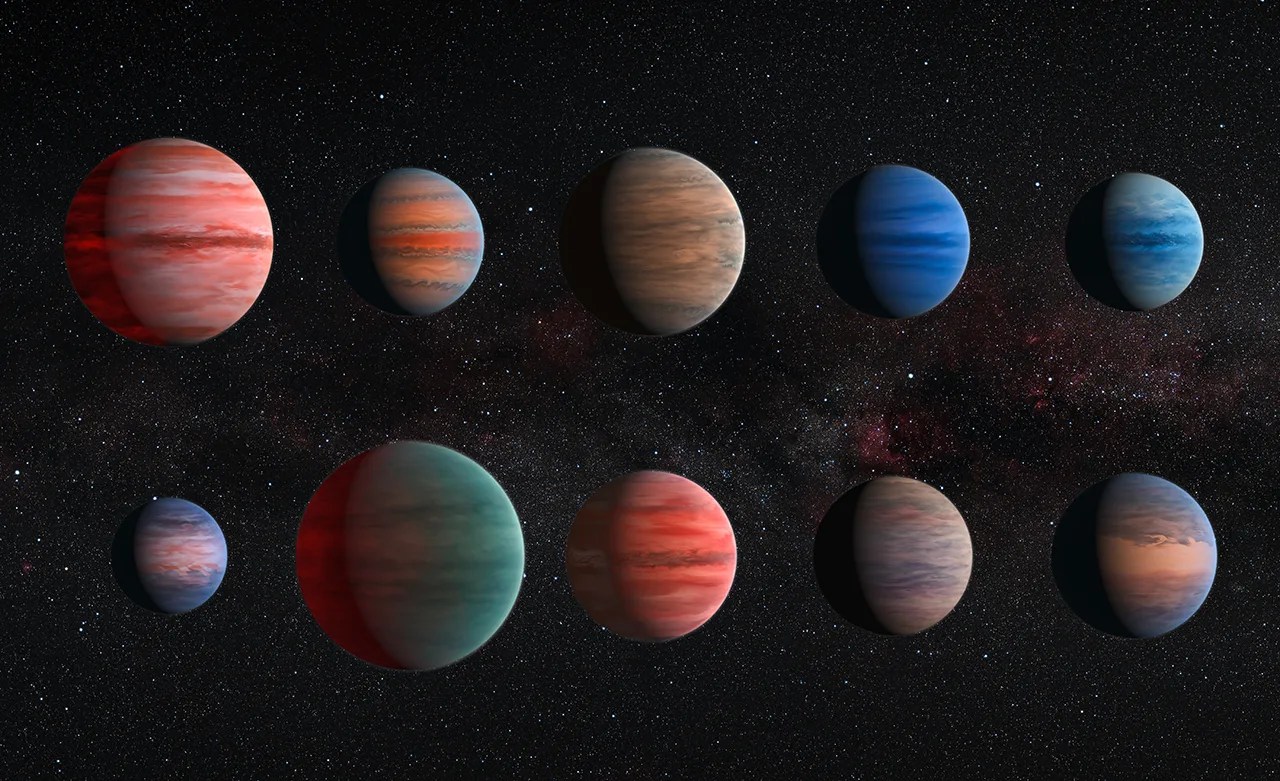

Recognizing Worlds Beyond Our Sun
Hubble can detect and measure the basic organic components for life on planets orbiting other stars.
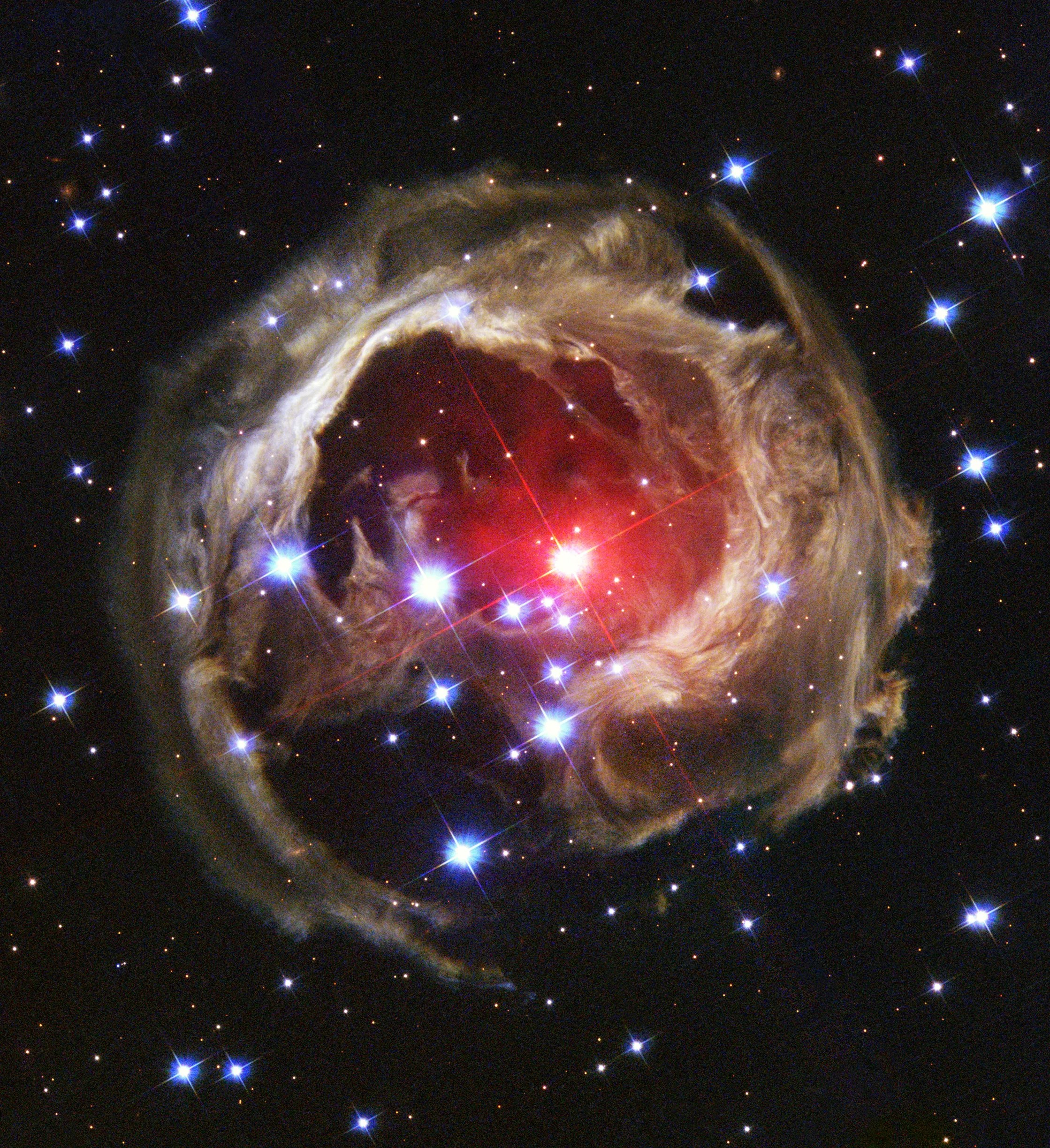

Seeing Light Echoes
Like ripples on a pond, pulses of light reverberate through cosmic clouds forming echoes of light.
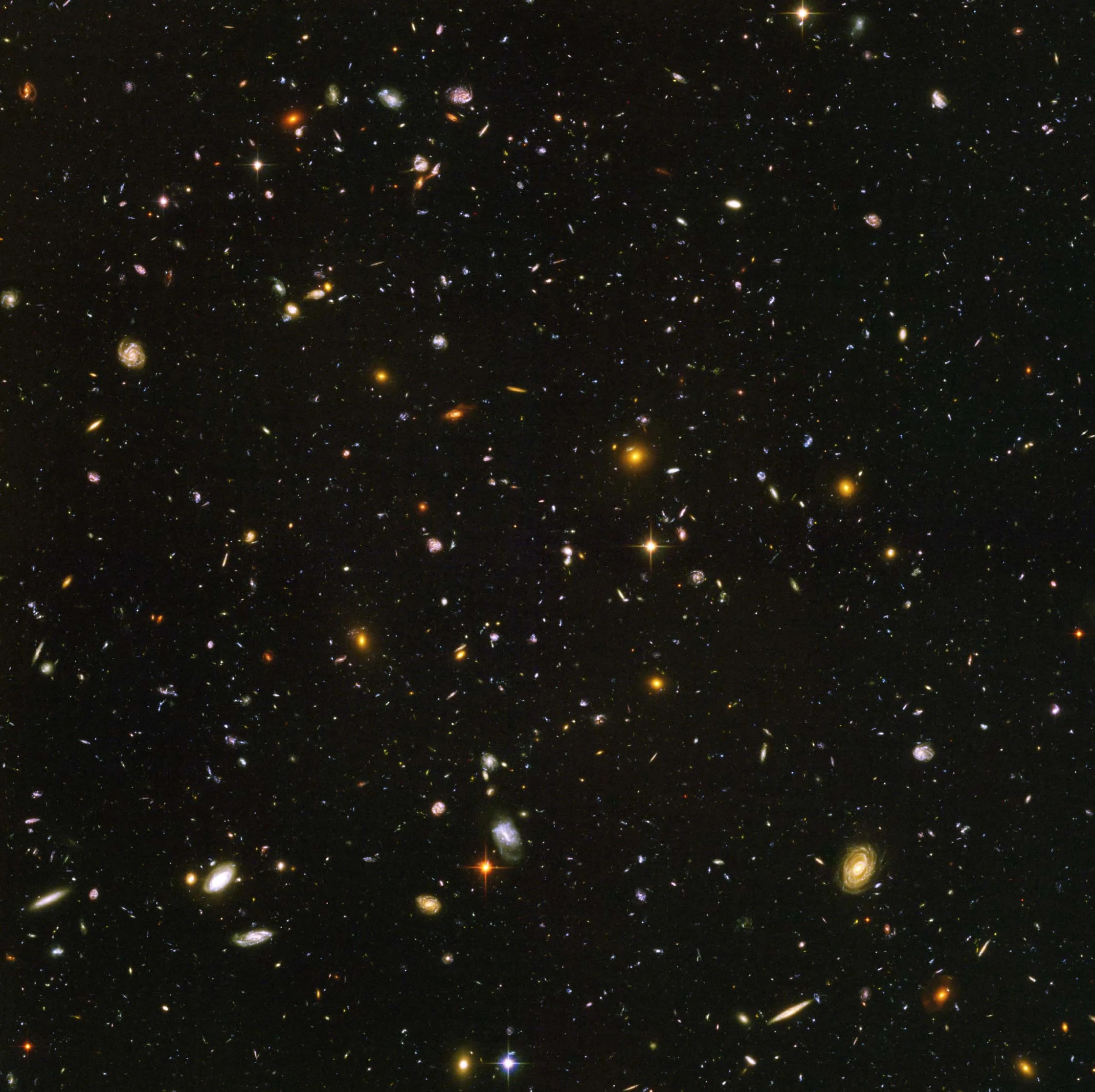

Tracing the Growth of Galaxies
Hubble's Deep Field observations are instrumental in tracing the growth of galaxies.
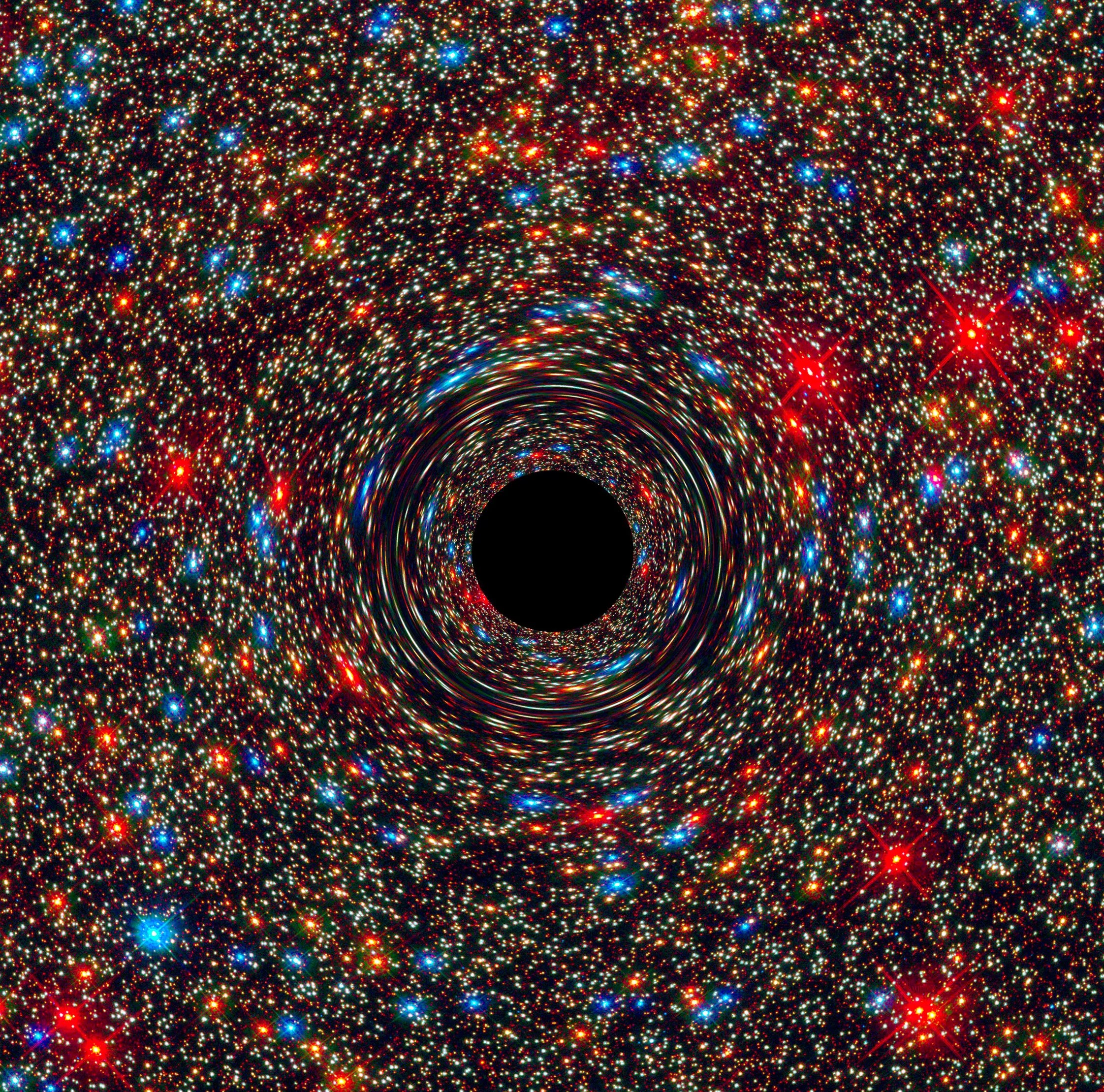

Monster Black Holes are Everywhere
Supermassive black holes lie at the heart of nearly every galaxy.

Homing in on Cosmic Explosions
Hubble helps astronomers better understand and define some of the largest explosions in the universe.
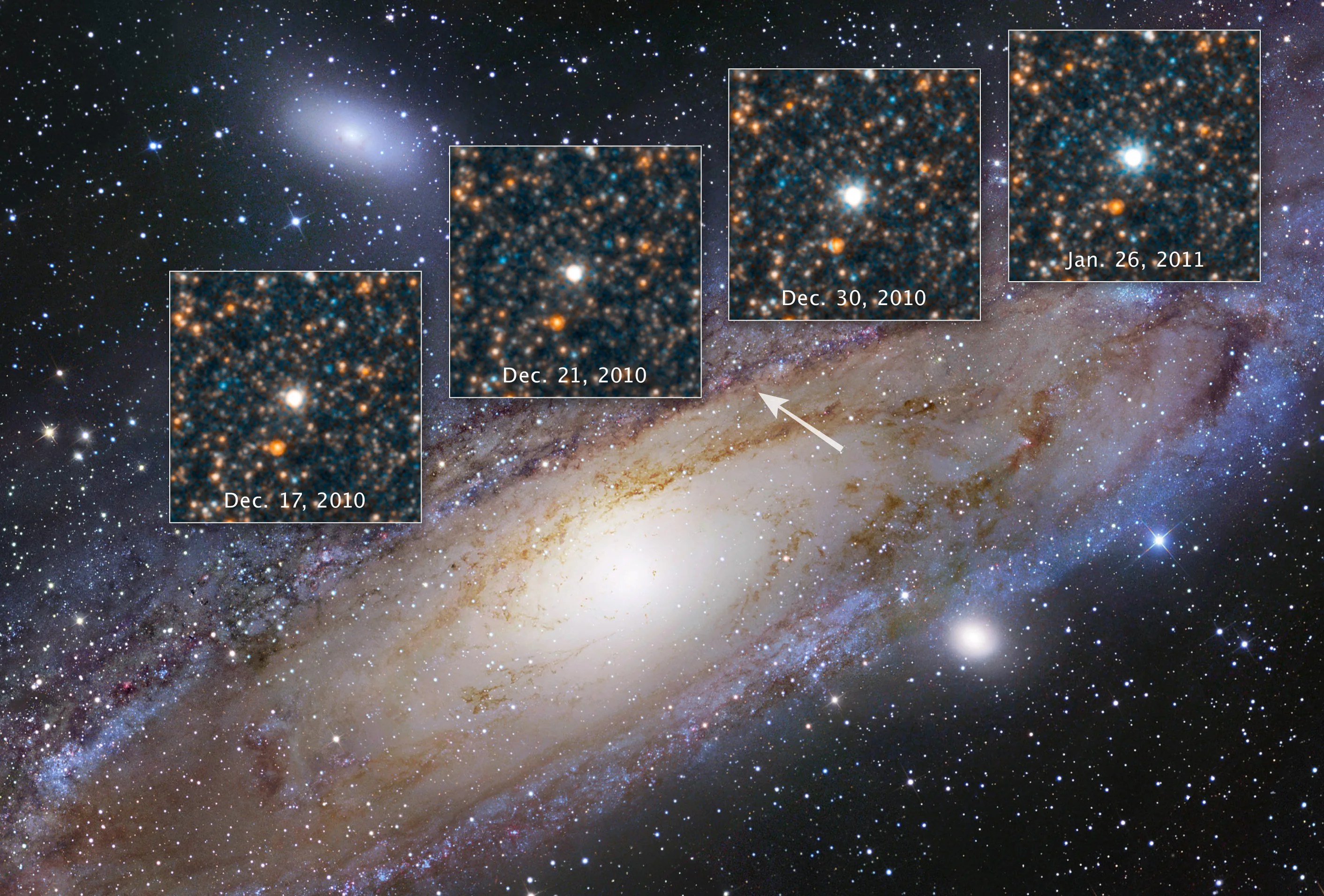

Discovering the Runaway Universe
Our cosmos is growing, and that expansion rate is accelerating.

Focusing in on Gravitational Lenses
Gravitational lenses are 'Nature's Boost', expanding our view deeper into space and farther back in time.
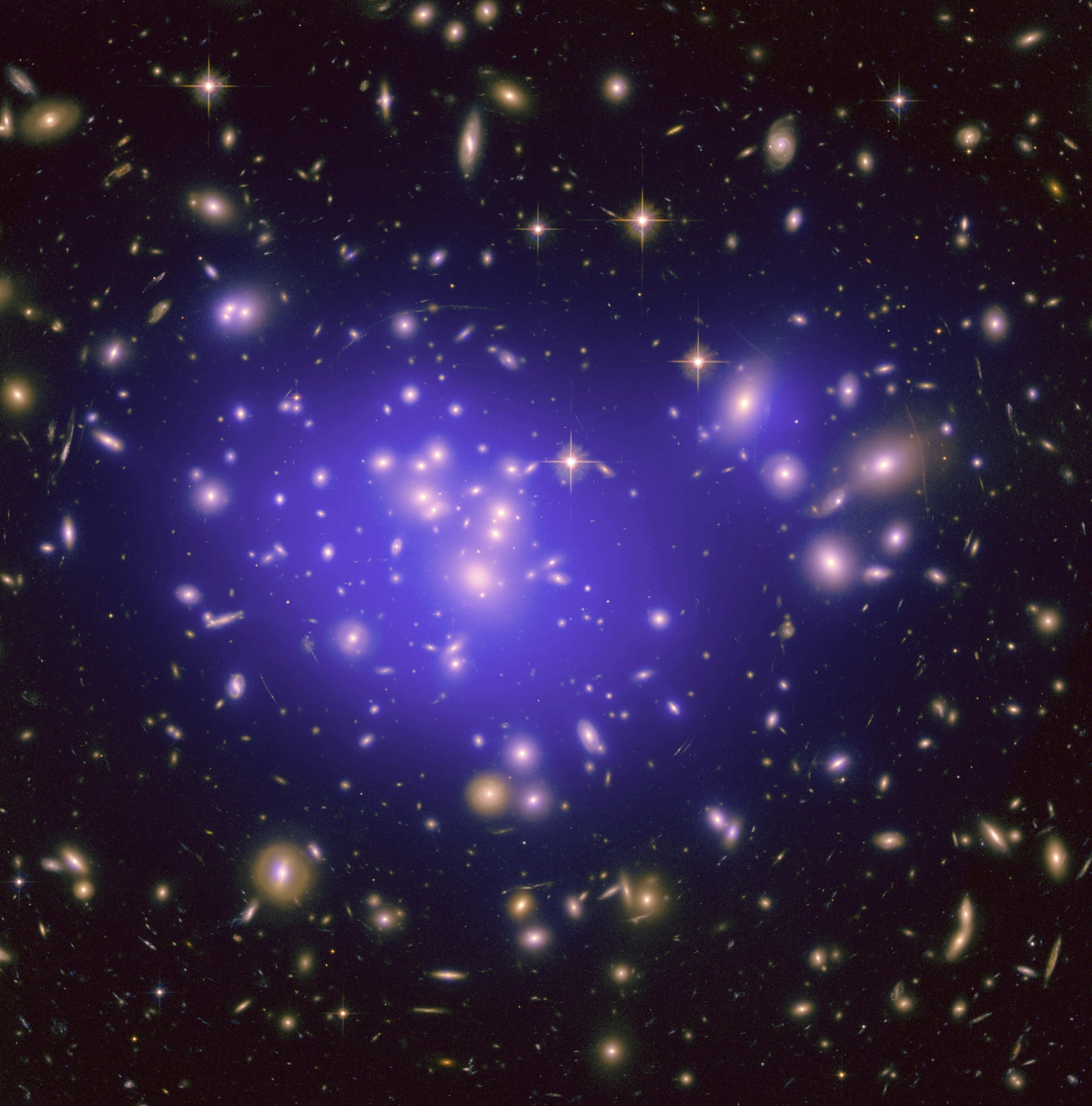

Shining a Light on Dark Matter
The gravitational pull of dark matter guides the formation of everything we can see in the universe.

Mapping the Cosmic Web
Filaments and sheets of matter create an interconnected web that forms the large-scale structure of the universe.




