Technology Highlights
Innovative Instrument Reveals Hidden Features Deep Inside the Van Allen Radiation Belts
A new instrument is using advanced detection techniques and leveraging an orbit with specific characteristics to increase our understanding of the Van Allen belts—regions surrounding Earth that contain energetic particles that can endanger both robotic and human space missions. Recently,…

Carbon Nanotubes and the Search for Life on Other Planets
A NASA-developed material made of carbon nanotubes will enable our search for exoplanets—some of which might be capable of supporting life. Originally developed in 2007 by a team of researchers led by Innovators of the Year John Hagopian and Stephanie…

Entrepreneurs Challenge Prize Winner Uses Artificial Intelligence to Identify Methane Emissions
The NASA Science Mission Directorate (SMD) instituted the Entrepreneurs Challenge to identify innovative ideas and technologies from small business start-ups with the potential to advance the agency’s science goals. Geolabe—a prize winner in the latest Entrepreneurs Challenge—has developed a way…

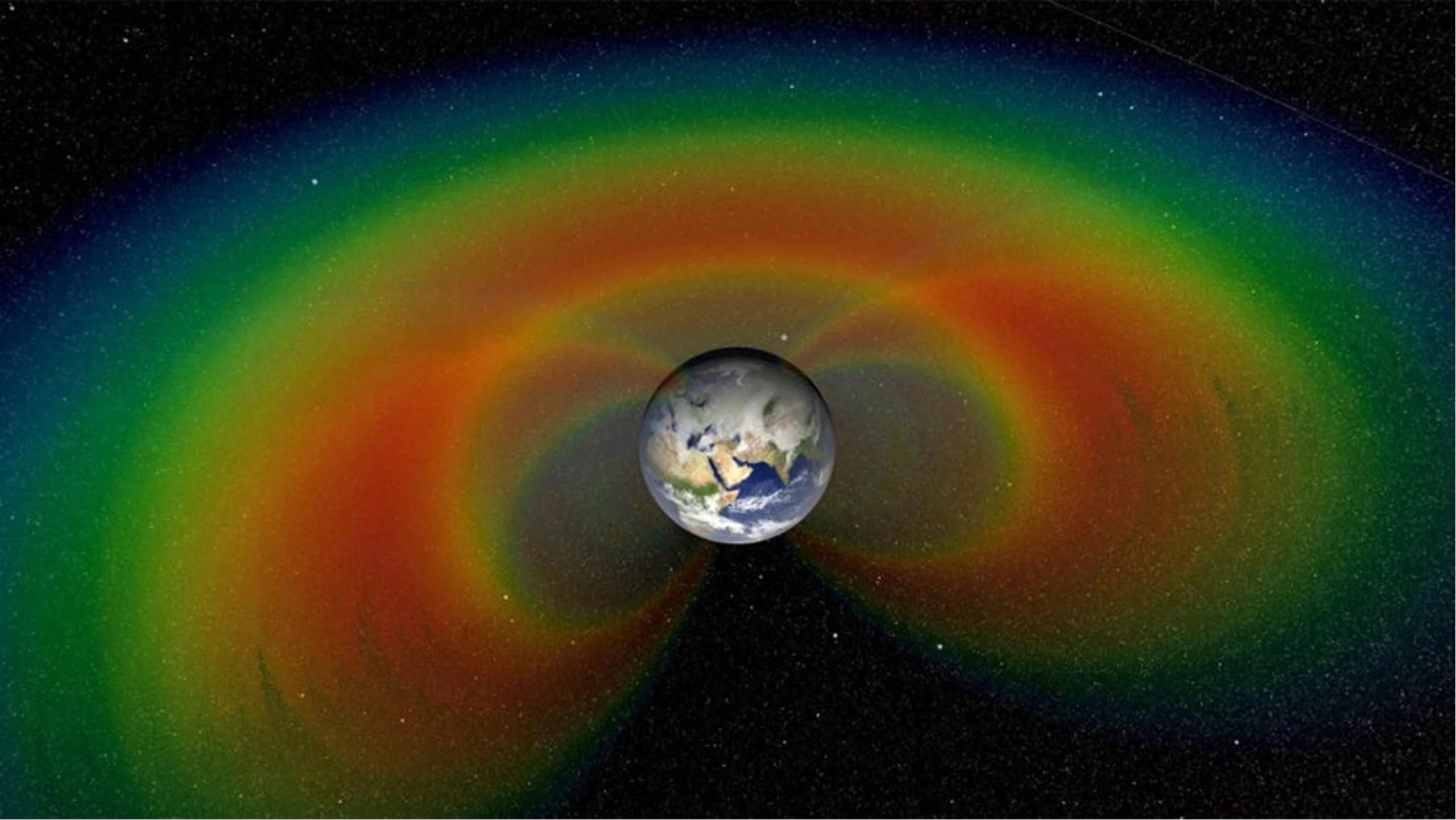
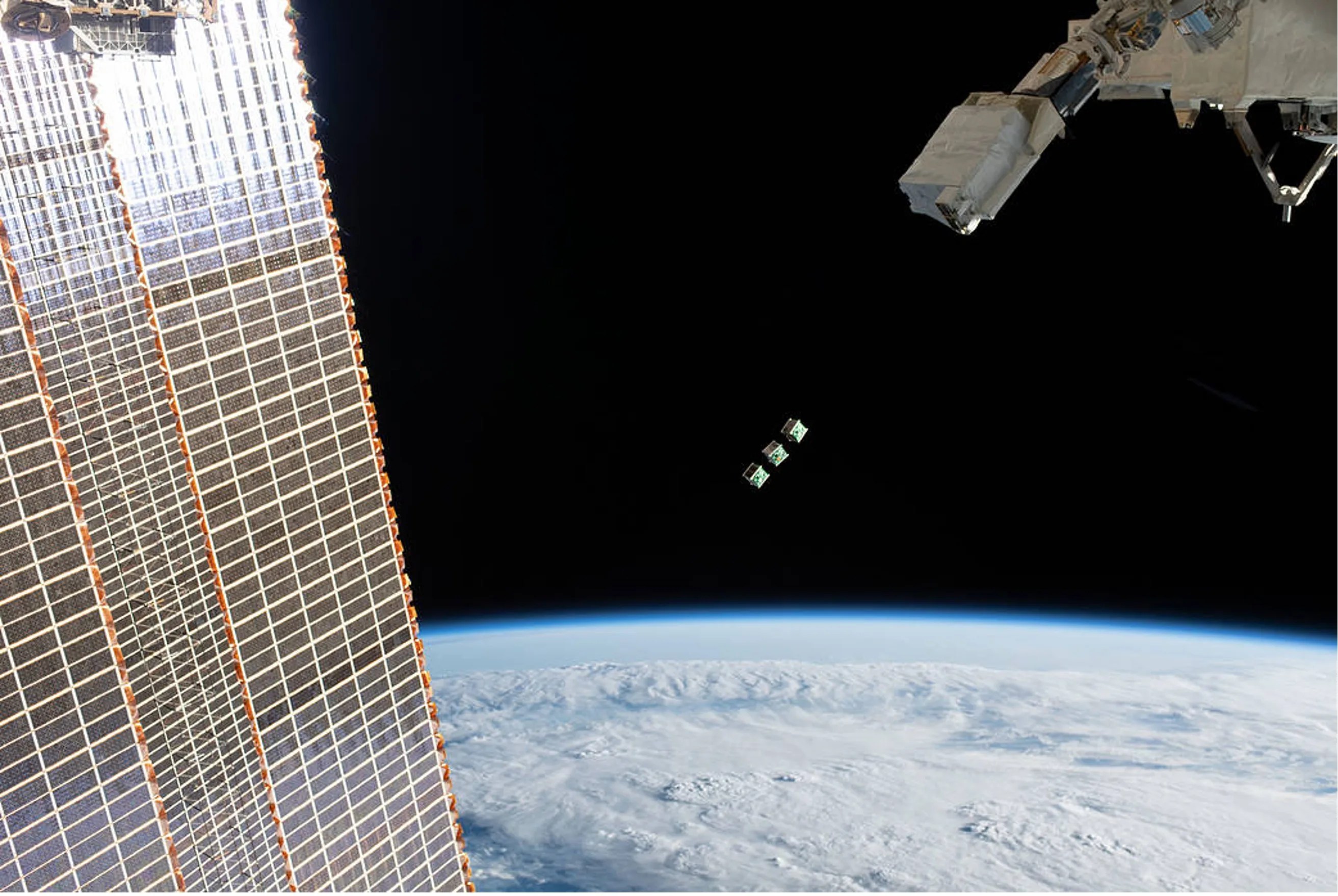
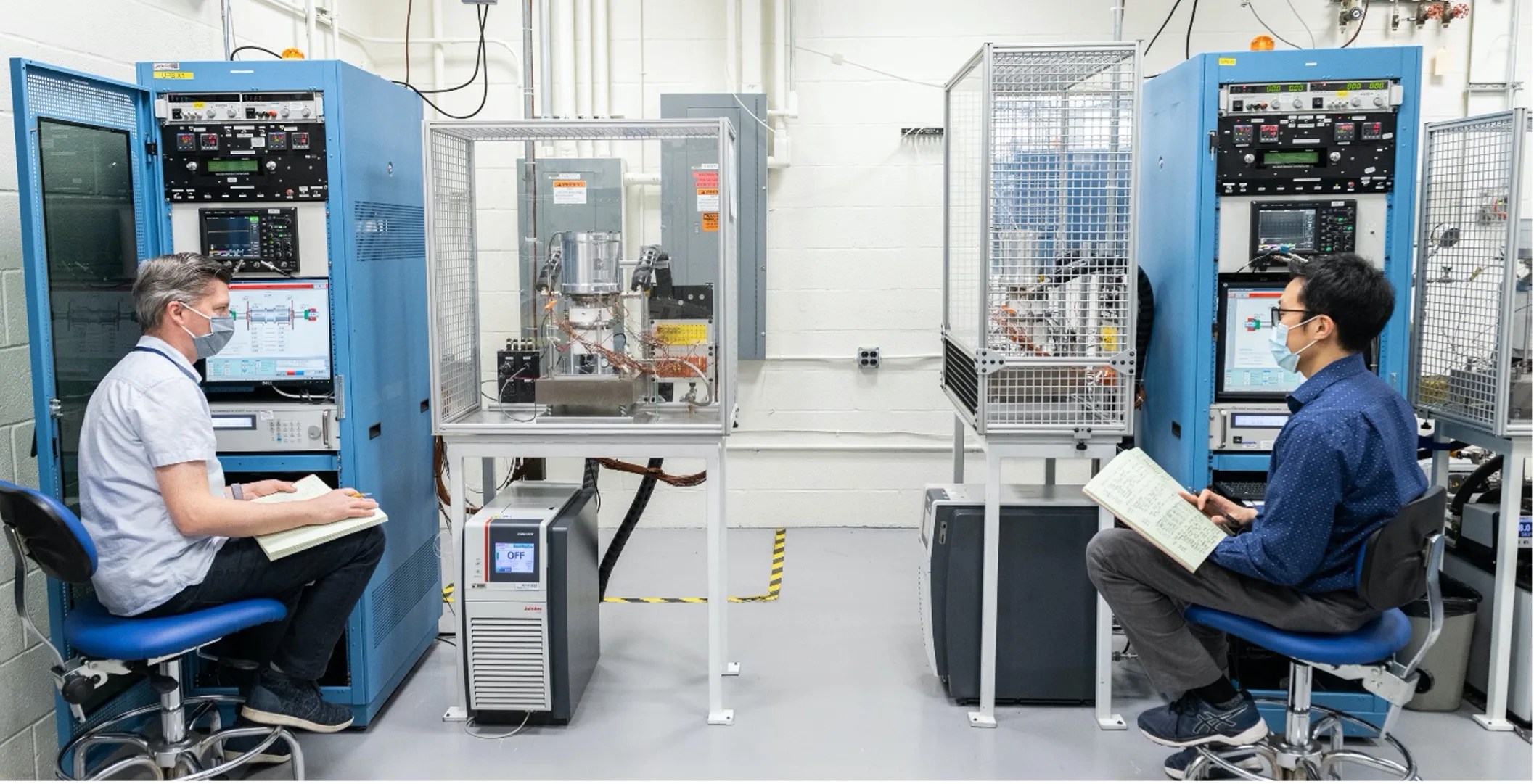
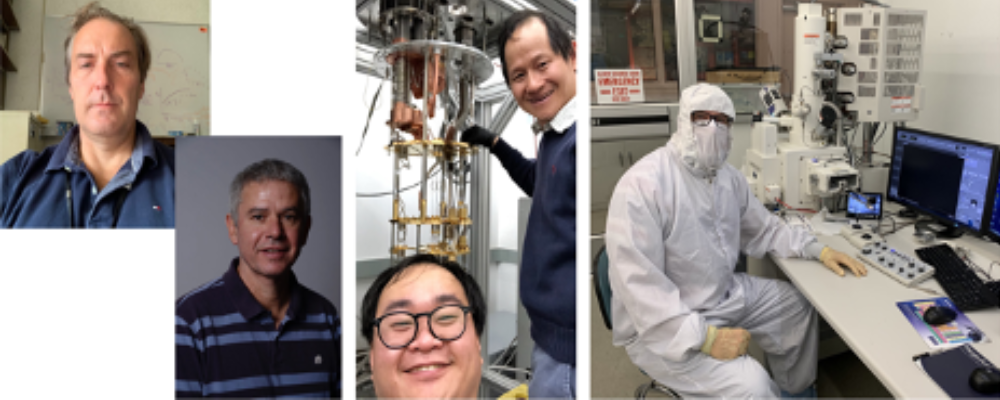
Quantum Scale Sensors used to Measure Planetary Scale Magnetic Fields
Magnetic fields are everywhere in our solar system. They originate from the Sun, planets, and moons, and are carried throughout interplanetary space by solar wind. This is precisely why magnetometers—devices used to measure magnetic fields—are flown on almost all missions…

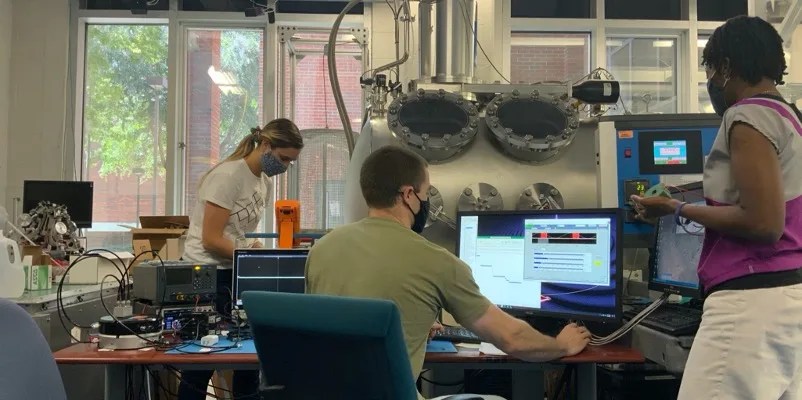
Solid State Quantum Magnetometers—Seeking out water worlds from the quantum world
“Follow the water!” The solar system is full of water in different states, from the Sun’s water vapor to the ice of Pluto and beyond. Water is not only linked to the possibility to sustain life, it is also interesting…

NASA “Wildfire Digital Twin” Pioneers New AI Models and Streaming Data Techniques for Forecasting Fire and Smoke
NASA’s “Wildfire Digital Twin” project will equip firefighters and wildfire managers with a superior tool for monitoring wildfires and predicting harmful air pollution events and help researchers observe global wildfire trends more precisely.
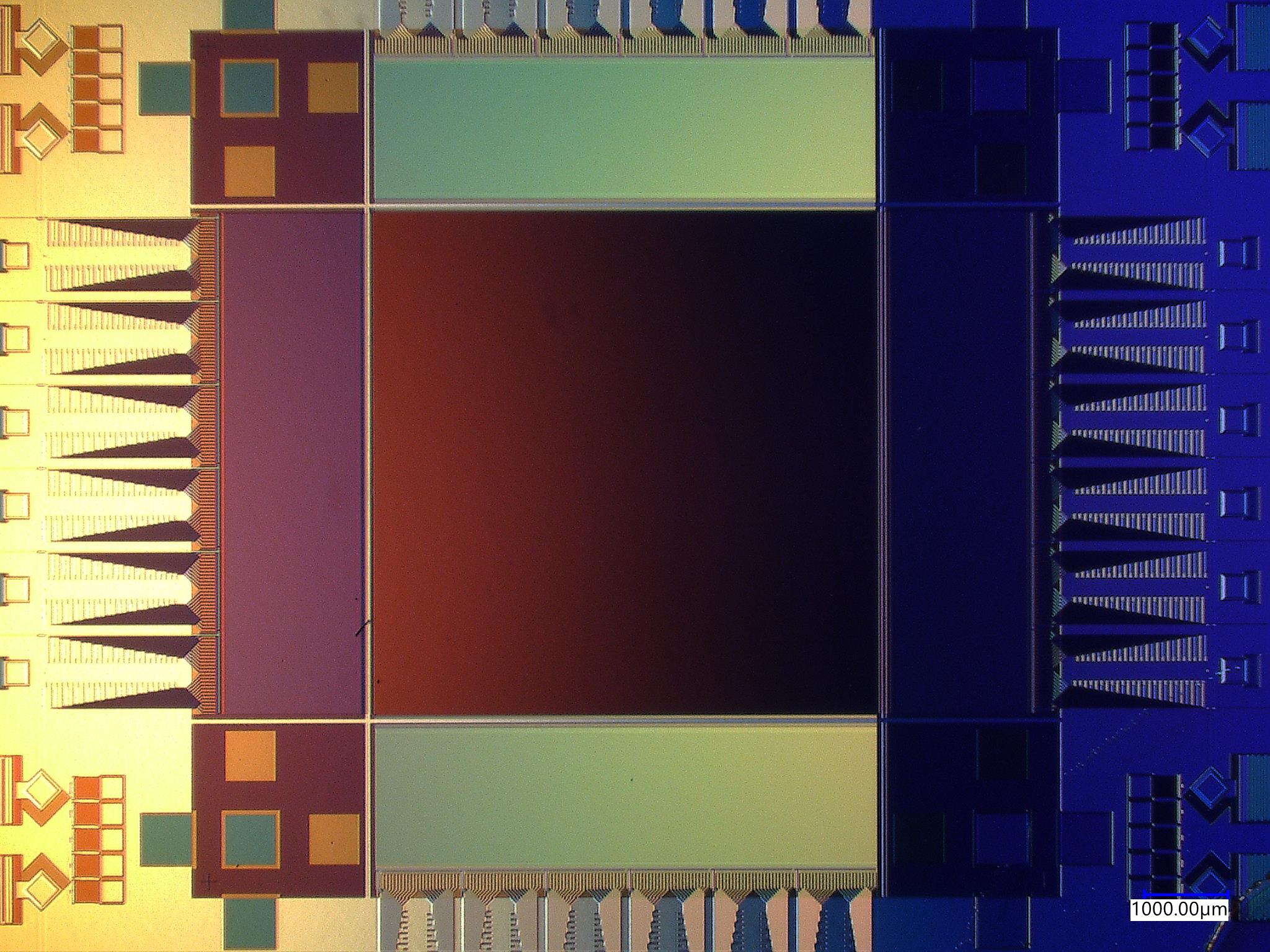
Breaking the Scaling Limits: New Ultralow-noise Superconducting Camera for Exoplanet Searches
When imaging faint objects such as distant stars or exoplanets, capturing every last bit of light is crucial to get the most out of a scientific mission. These cameras must be extremely low-noise, and be able to detect the smallest…
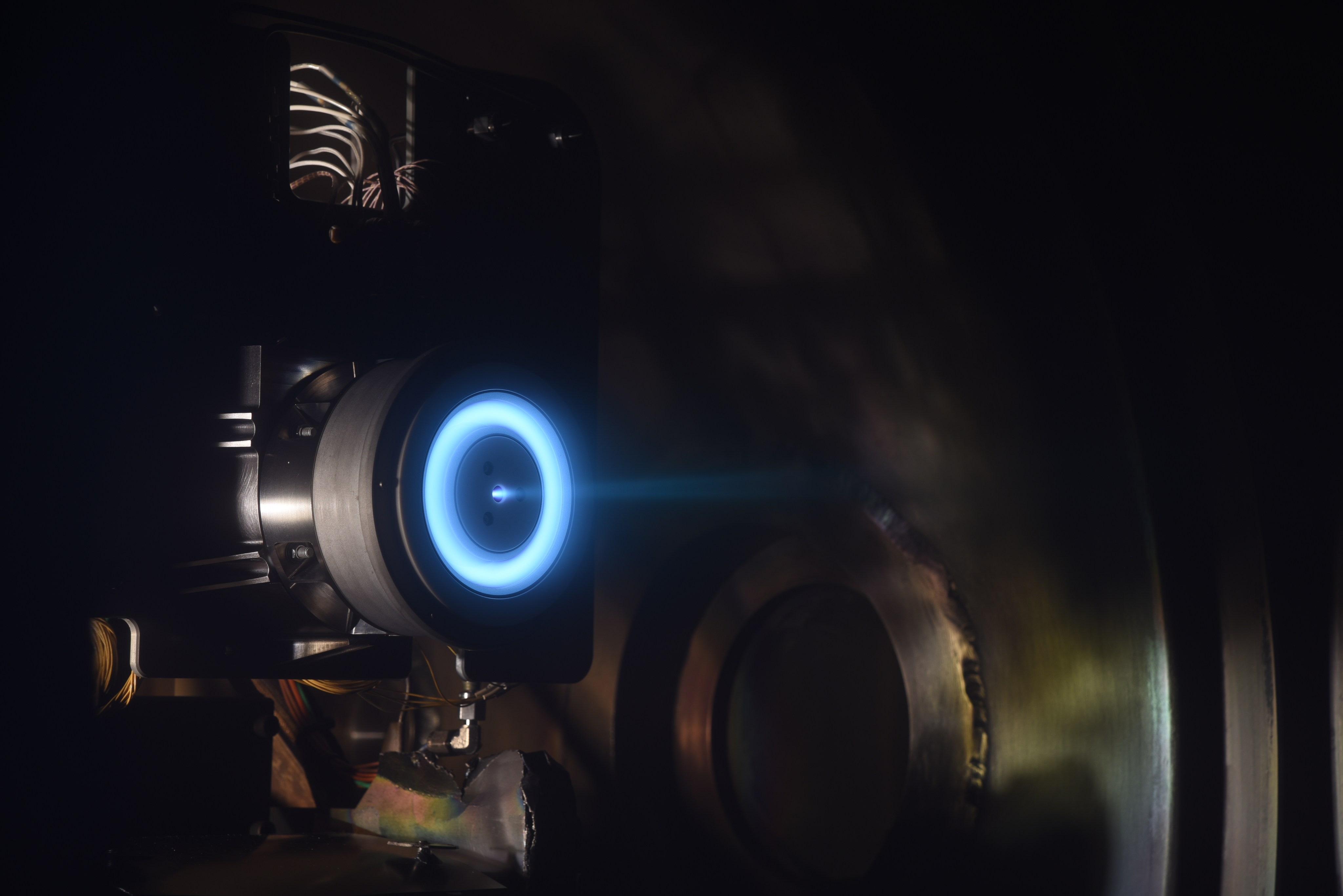

Pushing the Limits of Sub-Kilowatt Electric Propulsion Technology to Enable Planetary Exploration and Commercial Mission Concepts
NASA has developed an advanced propulsion technology to facilitate future planetary exploration missions using small spacecraft. Not only will this technology enable new types of planetary science missions, one of NASA’s commercial partners is already preparing to use it for…
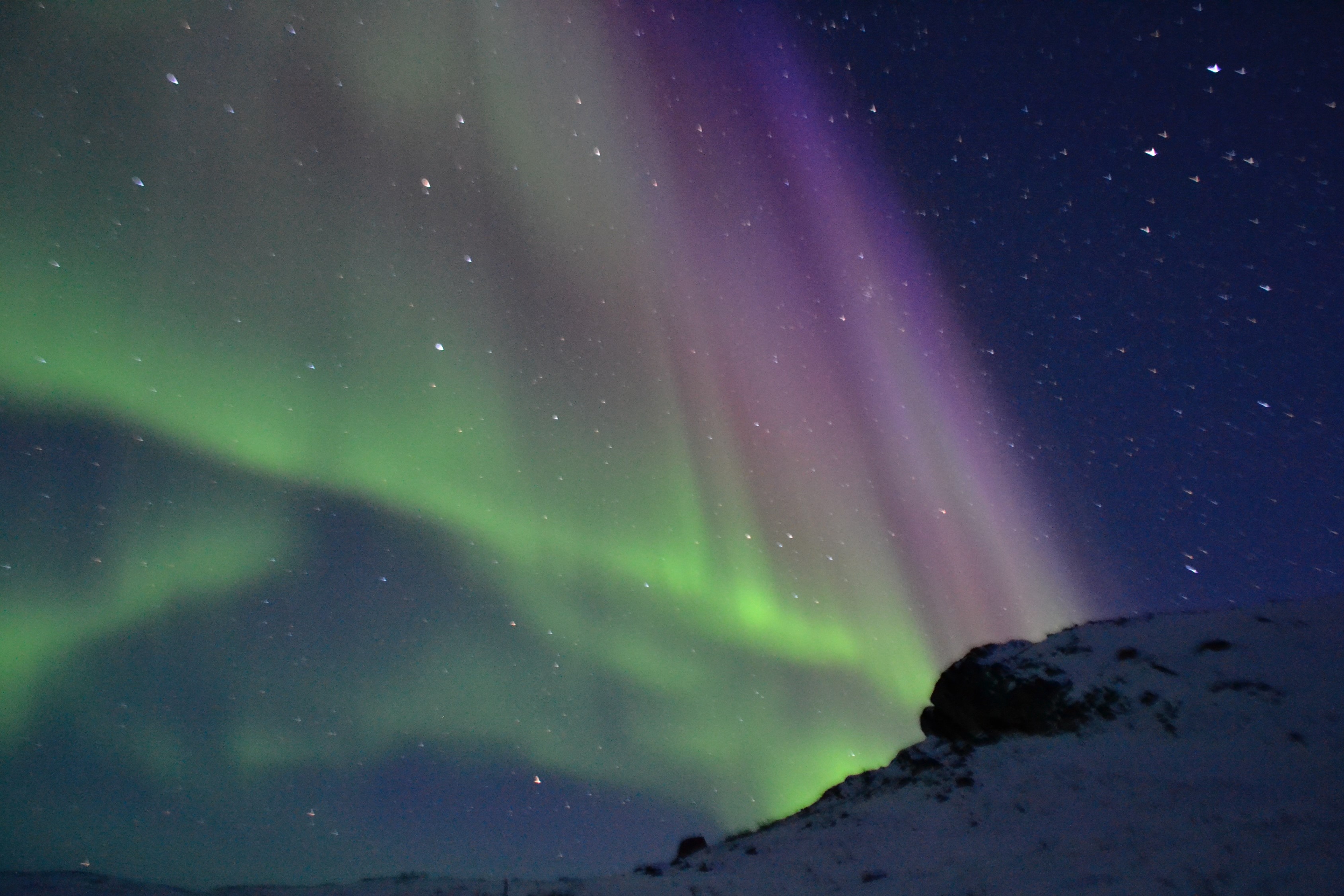

Making Ultra-fast Electron Measurements in Multiple Directions to Reveal the Secrets of the Aurora
The energetic electrons that drive the aurora borealis (the northern lights) have a rich and very dynamic structure that we currently do not fully understand. Much of what we know about these electrons comes from instruments that have fundamental limitations…
New NASA Software Simulates Science Missions for Observing Terrestrial Freshwater
From radar instruments smaller than a shoebox to radiometers the size of a milk carton, there are more tools available to scientists today for observing complex Earth systems than ever before. But this abundance of available sensors creates its own…

Zero-Boil-Off Tank Experiments to Enable Long-Duration Space Exploration
Do we have enough fuel to get to our destination? This is probably one of the first questions that comes to mind whenever your family gets ready to embark on a road trip. If the trip is long, you will…
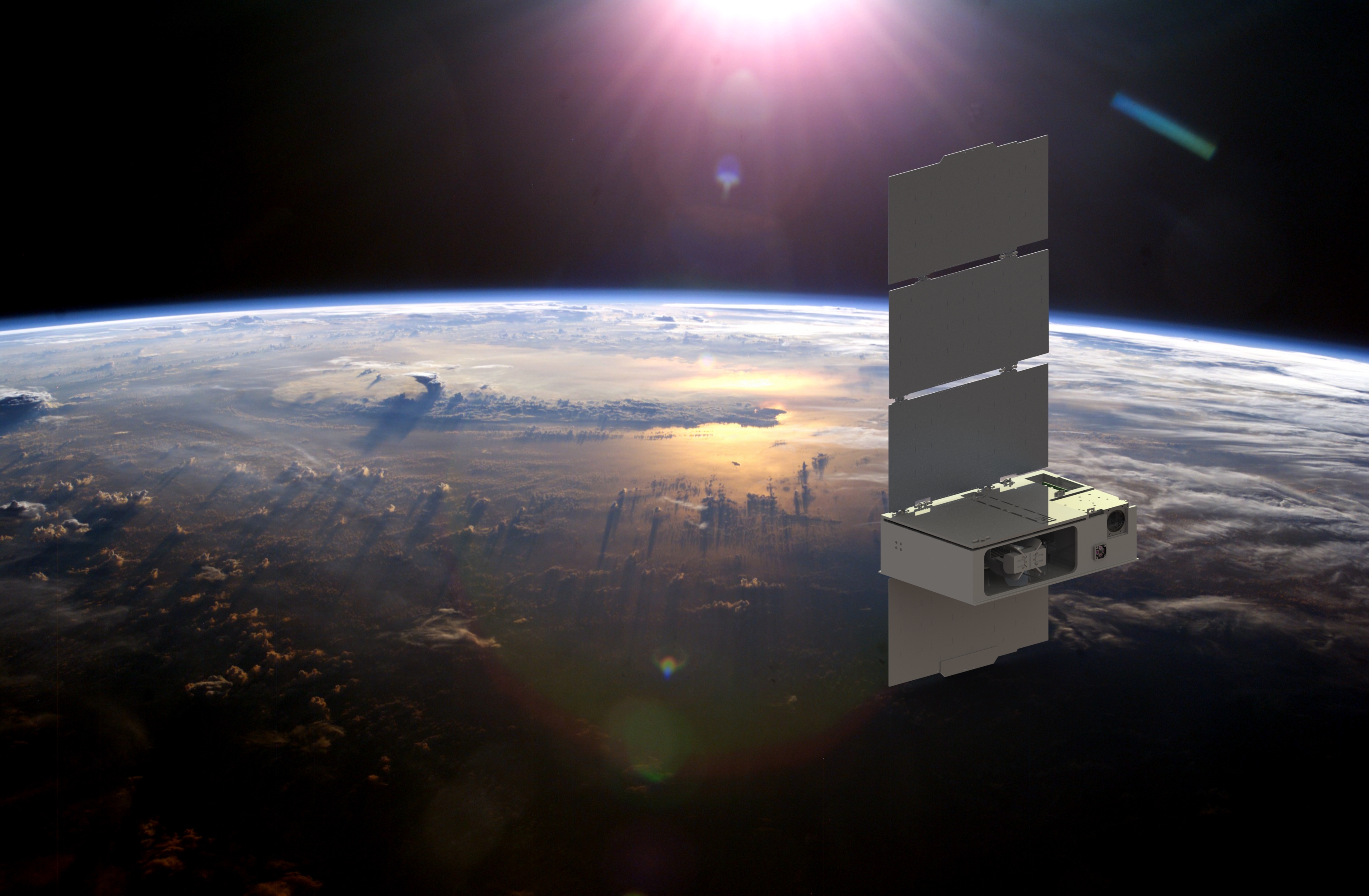

The CUTE Mission: Innovative Design Enables Observations of Extreme Exoplanets from a Small Package
Of the approximately 5,500 exoplanets discovered to date, many have been found to orbit very close to their parent stars. These close-in planets provide a unique opportunity to observe in detail the phenomena critical to the development and evolution of…

Mighty MURI brings the heat to test new longwave infrared radiometer
NASA's new Multiband Uncooled Radiometer Instrument (MURI) features a novel bolometer that detects infrared radiation without a cryogenic cooler, greatly reducing the cost and complexity of dispatching infrared radiometers into low-Earth orbit.
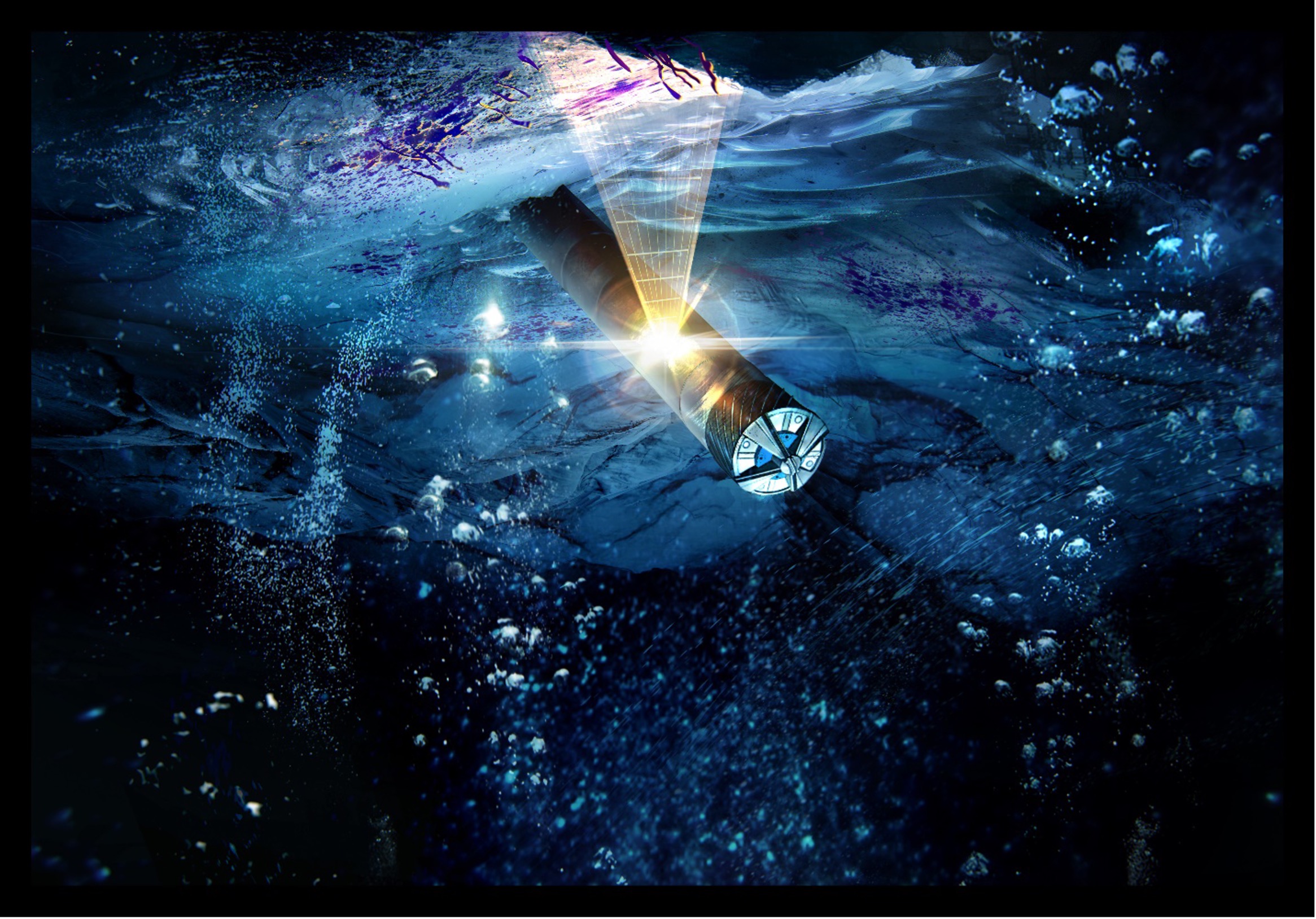

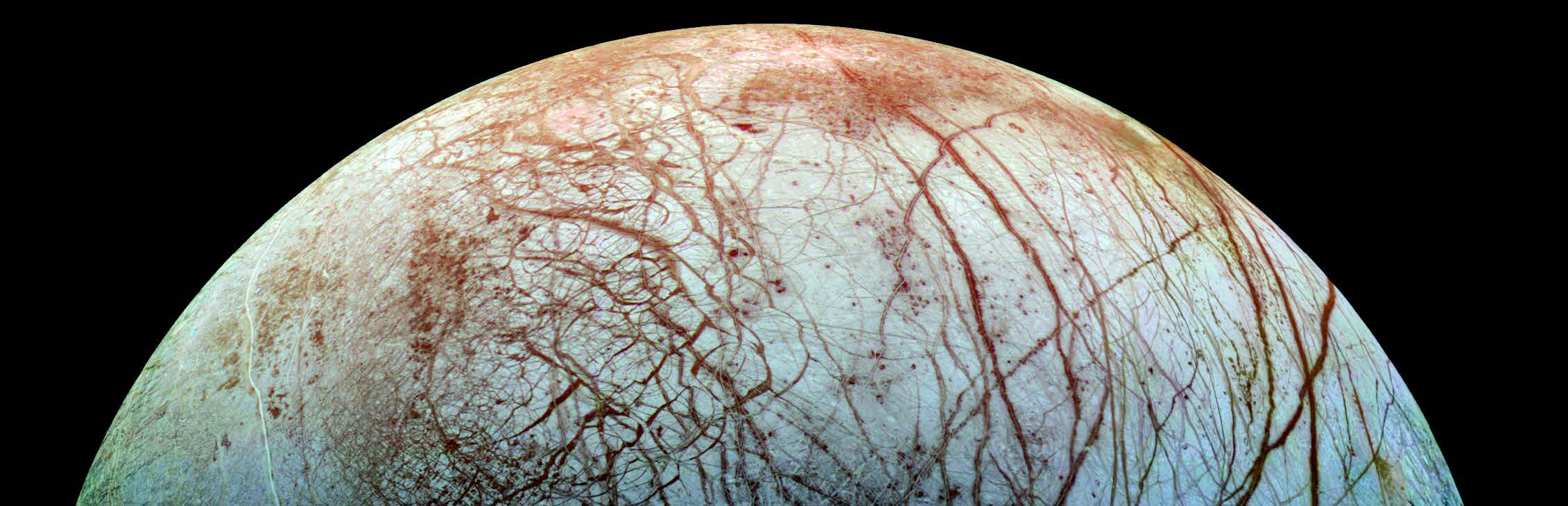
Digging Deeper to Find Life on Ocean Worlds
In February 2023, researchers from around the country gathered at a NASA-sponsored workshop to discuss the latest developments and a roadmap for a cryobot mission concept to drill through the icy crusts of Europa and Enceladus and search for life.
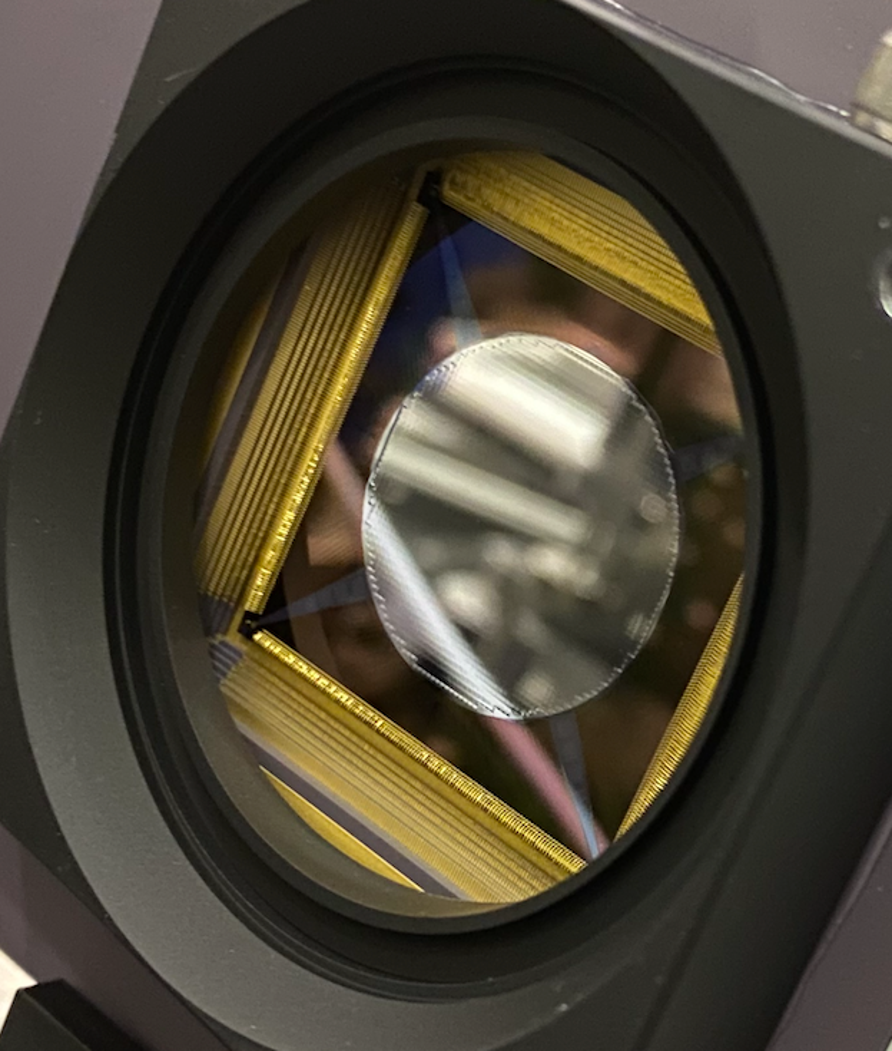

Deformable Mirrors in Space: Key Technology to Directly Image Earth Twins
Finding and studying Earth-like planets orbiting nearby stars is critical to understand whether we are alone in the universe. To study such planets and assess if they can sustain life, it is necessary to directly image them. However, these planets…

Deploying and Demonstrating Navigation Aids on the Lunar Surface
NASA is developing lunar navigation beacons to be deployed on spacecraft or the lunar surface to aid in localization and help future space vehicles determine position, velocity, and time to high accuracy.
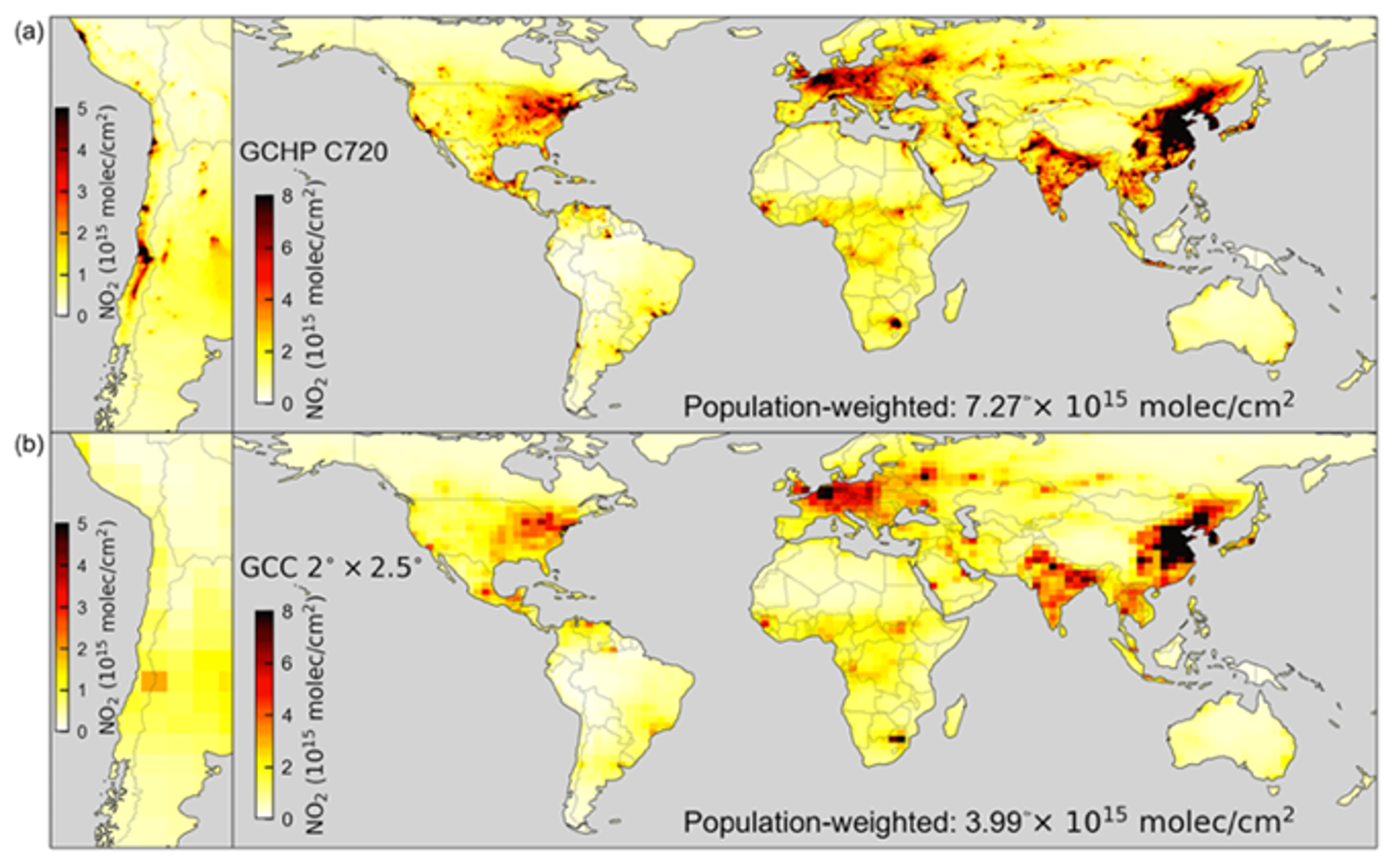
New Software Enables Atmospheric Modeling with Greater Resolution
Next-generation software is making it easier for researchers, policy makers, and citizen scientists to model air quality and greenhouse gases using NASA meteorological data.
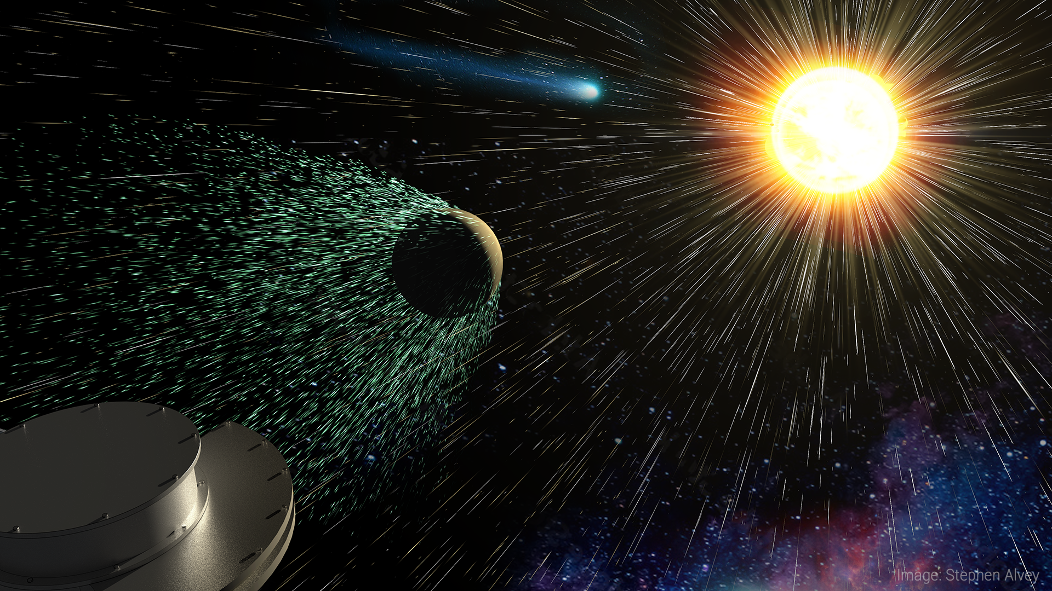

Tracing the Origin and Energization of Plasma in the Heliosphere
PROJECT: Solar Wind Pickup Ion Composition Energy Spectrometer (SPICES) SNAPSHOT: SPICES is a new sensor that will help scientists discover where matter originates and how it is energized throughout the solar system Imagine that you have a secret decoder ring…
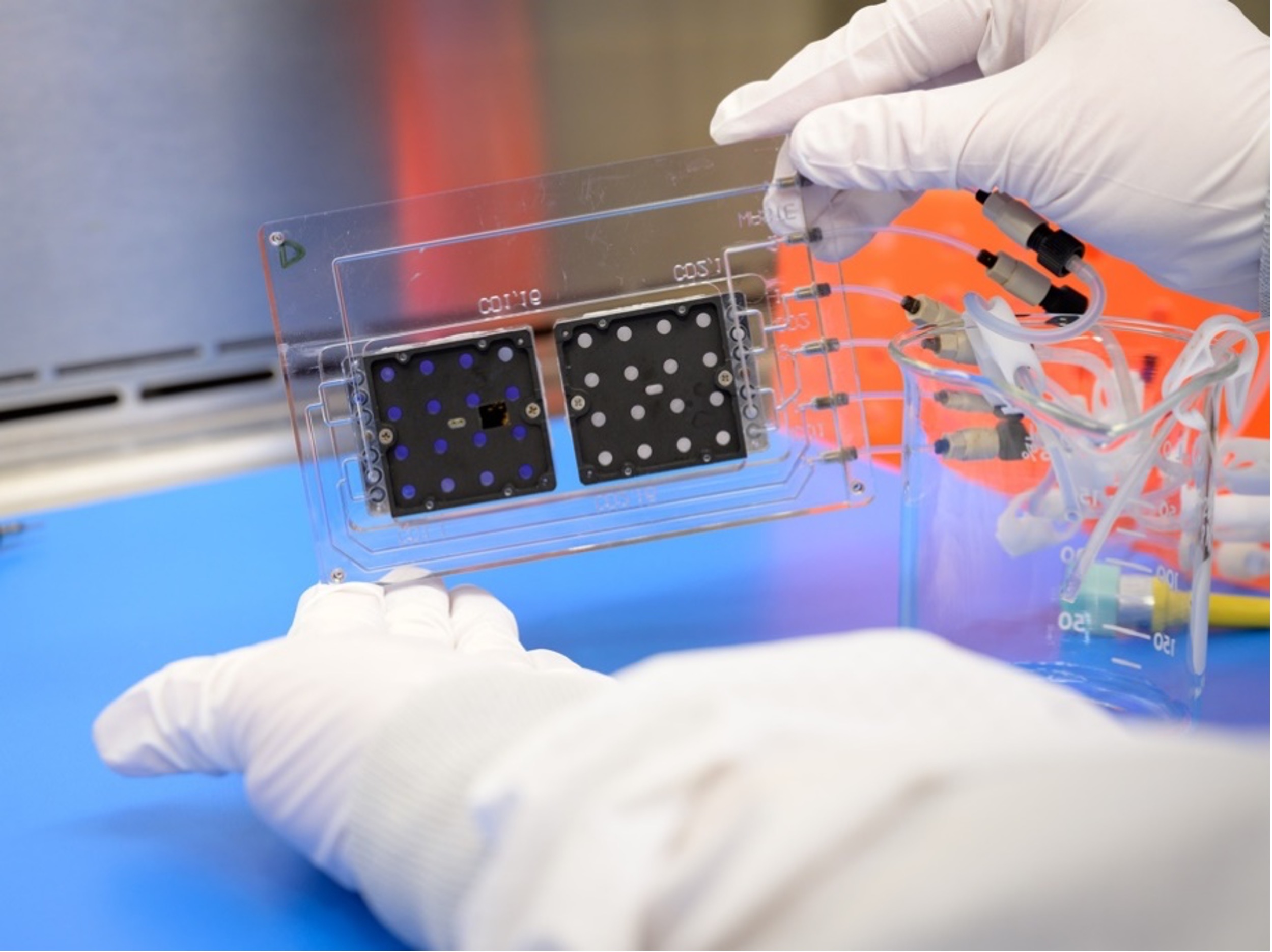
Growing Yeast on the Moon to Study Radiation Risks to Human Explorers
PROJECT: Lunar Explorer Instrument for space biology Applications (LEIA) SNAPSHOT: An autonomous microfluidic culturing system with CubeSat heritage teams up with two state-of-the-art radiation detectors to measure how biology responds to the radiation and reduced gravity environment on the lunar…
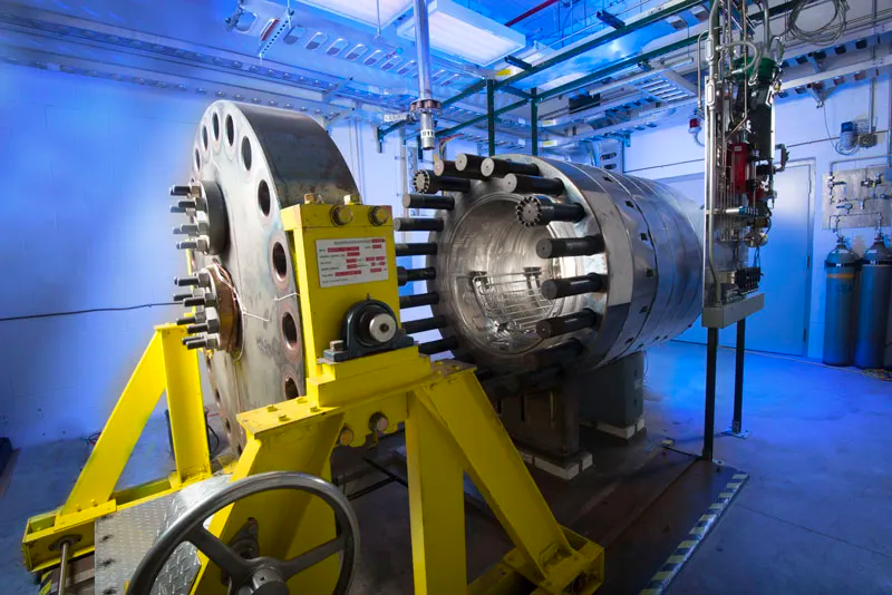
HOTTech Attempts to Tackle Venus
Specialized test rig determines how new technologies fare in extreme conditions PROJECT: Hot Operating Temperature Technology (HOTTech) Program; NASA Glenn Extreme Environment Rig (GEER) SNAPSHOT: Projects in NASA’s HOTTech Program are developing technologies that will operate on the surface of…
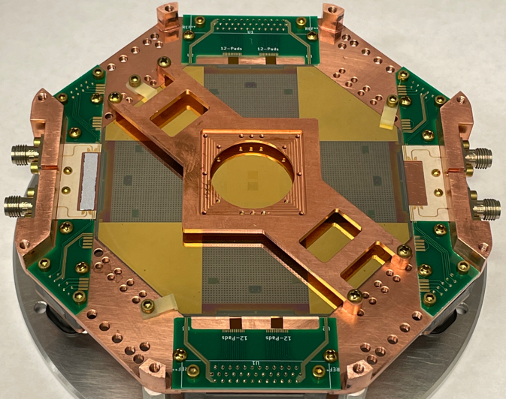
New X-ray Detectors to Provide Unprecedented Vision of the Invisible Universe
PROJECT: Advanced Magnetic Microcalorimeter development SNAPSHOT: A new class of X-ray detector with unprecedented energy resolution and array size could help transform our understanding of the cosmos through unparalleled vision into the otherwise invisible universe. Very detailed information is now…

Sending Signals Through the Ice on Ocean Worlds
PROJECT: Ocean Worlds Signals Through the Ice (STI) SNAPSHOT: The Ocean Worlds Signals Through the Ice (STI) team is developing communication technologies to enable subsurface exploration of ocean worlds where conditions may be conducive to life. Detection of extraterrestrial life…

Coexisting quantum gases in Earth’s orbit
PROJECT Cold Atom Lab (CAL) SNAPSHOT Two species of quantum gases have been created to coexist and interact for the first time in space. Accessing resonant interactions among these gases will allow scientists to explore few-body physics, quantum chemistry, and…
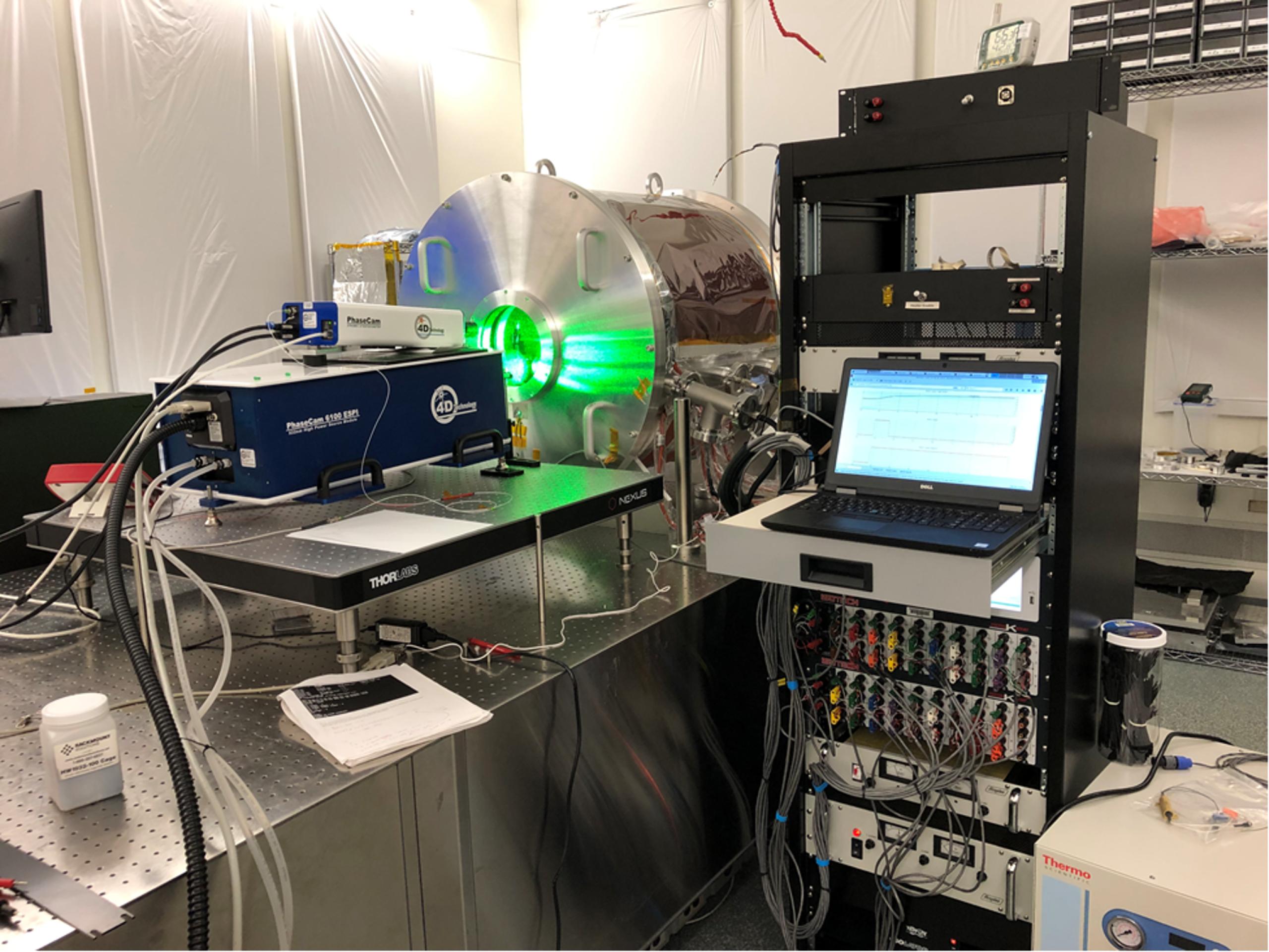
Developing an Ultra-stable Testbed to Enable Future Great Observatory Missions
PROJECT Ultra-stable Telescope Testbed project SNAPSHOT A NASA team has developed a laboratory to enable the design and development of large ultra-stable telescopes—the kind of telescope needed to detect and characterize Earth-like planets around distant stars. “Are we alone in…
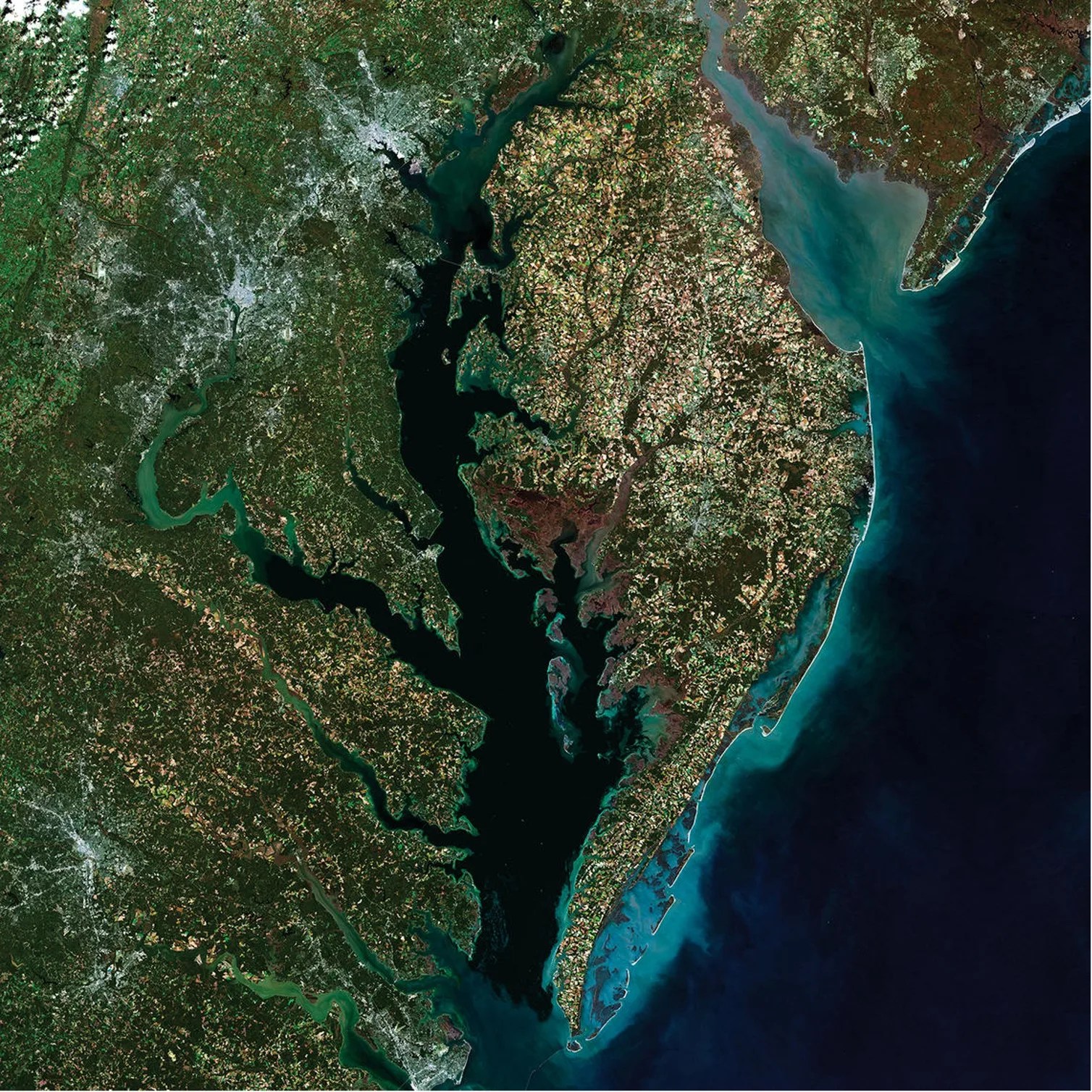

New NASA software could help predict water quality problems in the Chesapeake Bay
PROJECT Supporting Shellfish Aquaculture in the Chesapeake Using Artificial Intelligence SNAPSHOT A NASA team is training and verifying machine learning algorithms that will be used to identify areas of poor water quality in satellite images—starting with the Chesapeake Bay. Excess…

New Superconducting Sensor Arrays Will Enable Future Far-Infrared Space Missions
PROJECT Development of a Robust, Efficient Process to Produce Scalable, Superconducting Kilopixel Far-IR Detector Arrays SNAPSHOT An SMD-sponsored team has taken major steps towards providing the new detector arrays needed for future far-infrared space missions. In the Decadal Survey on…

Cooling Technique Developed for Space Use Makes Charging Electric Cars on Earth Quicker and Easier
PROJECT Flow Boiling and Condensation Experiment (FBCE) SNAPSHOT An advanced temperature control technique developed for future NASA missions can also make charging electric vehicles easier and faster—potentially paving the way for increased adoption of electric cars. Numerous future NASA space…
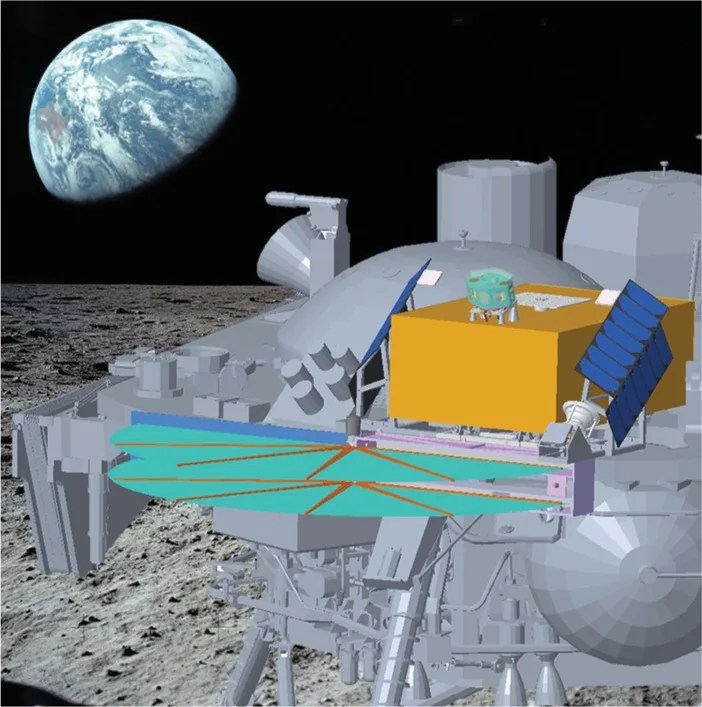
Space-age buoys for long-duration monitoring of the Moon
PROJECT The Lunar Environment Monitoring Station (LEMS) SNAPSHOT As we embark on an era of renewed exploration of our closest cosmic neighbor—the Moon—a need arises for a new generation of surface instruments that can operate autonomously for very long durations…

How did Black Holes Shape the Cosmos? Fast, Low-noise X-ray Sensors May Provide the Answer
PROJECT Extremely Low-noise, High Frame-rate X-ray Image Sensors for Strategic Astrophysics Missions SNAPSHOT New imaging technology will help enable future large X-ray telescopes to trace the origin and growth of black holes and the ways they’ve shaped the cosmos. How…
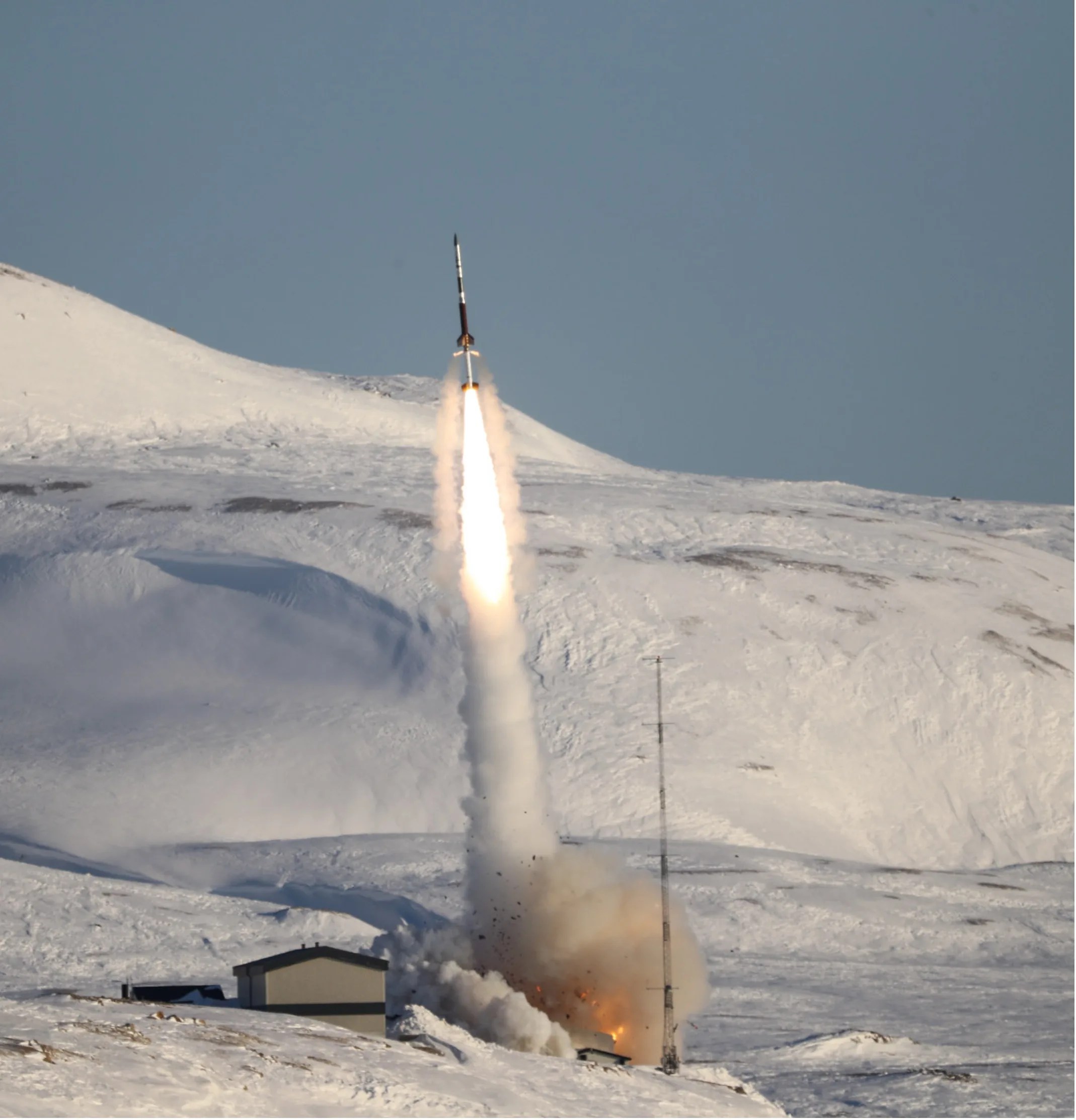

New Plasma Analyzer Flies on Rocketship Endurance
PROJECT NASA Sounding Rocket Endurance SNAPSHOT Endurance carried a new type of space plasma analyzer with extremely fine energy resolution to make the first measurements of Earth’s electrical potential. This technology could also enable new tools to measure plasmas in…
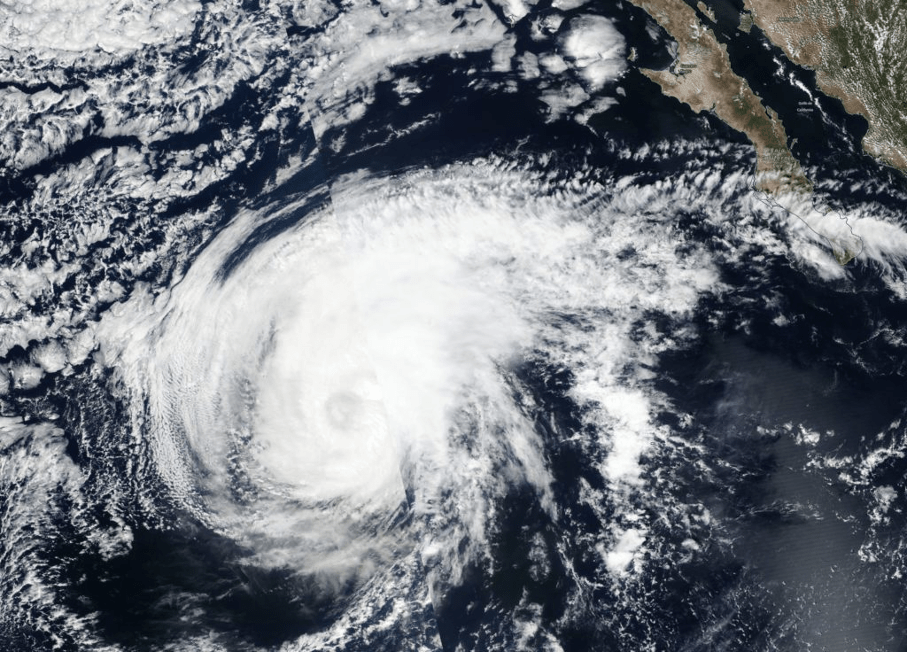
Next-generation Radar Receiver Set to Supply Scientists with Improved Weather Data
PROJECT Global Navigation Satellite System bistatic radar receiver (NGRx) SNAPSHOT An SMD-sponsored team is developing a new radar receiver that will enable future spaceborne instruments to process more signals and produce data at much higher resolution—greatly enhancing scientists’ ability to…

Taking the Pulse of NASA’s Robotic Explorers
PROJECT Model-based Off-Nominal State Identification and Detection (MONSID) software SNAPSHOT Keeping NASA’s robotic explorers healthy takes smart software, especially in remote and harsh environments. An initial investment by NASA’s Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Program led to development of a…
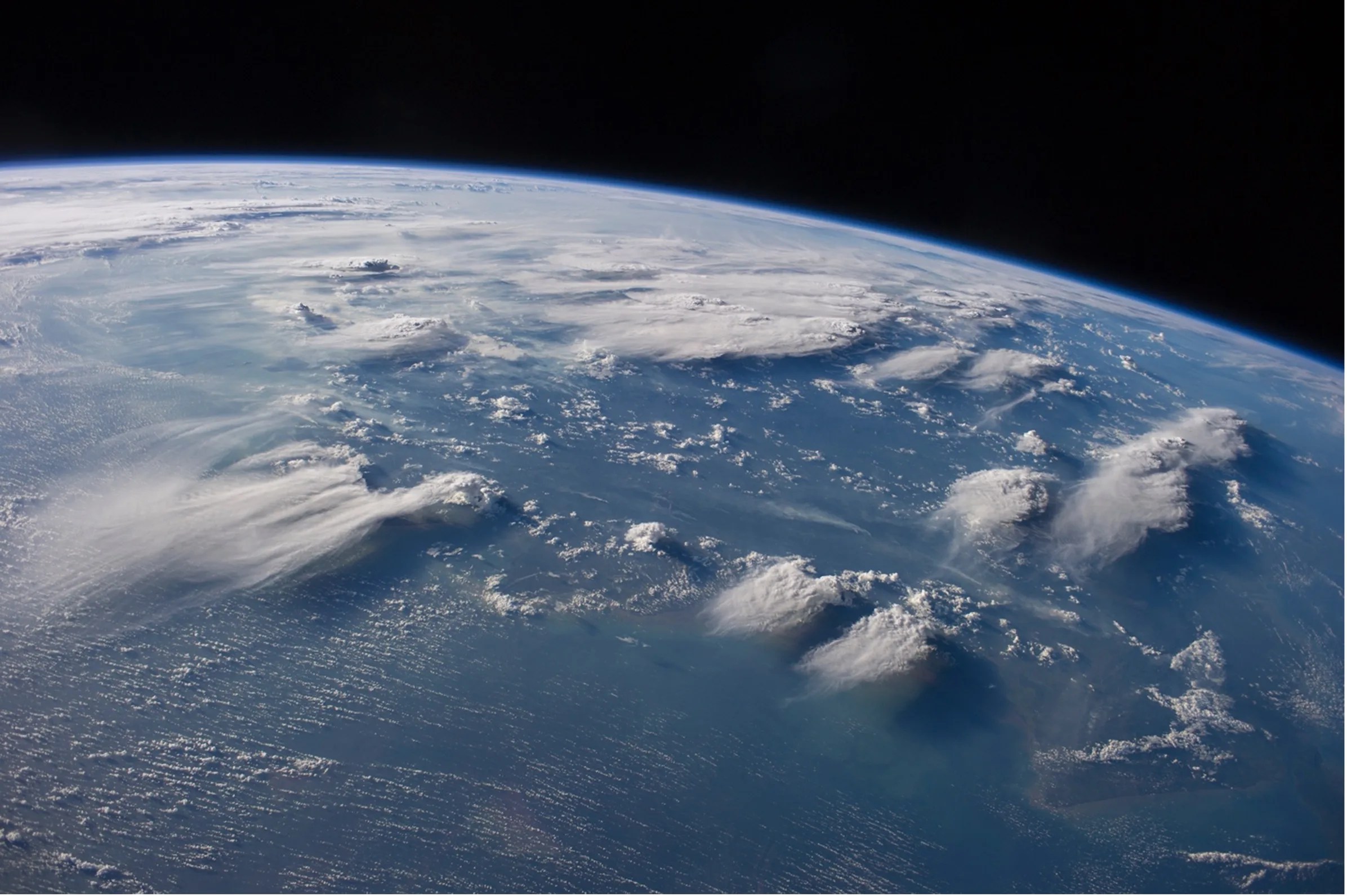

Advanced Satellite System Sets its Sights on Ice Clouds to Improve Weather and Climate Modeling
PROJECT Smart Ice Cloud Sensing (SMICES) SNAPSHOT With support from NASA’s Earth Science Technology Office (ESTO), a team of researchers is developing a new instrument that will help scientists better understand the impact high-altitude ice clouds have on weather and…

Protecting Future Planetary Missions from Extreme Heat
PROJECT Phenolic Impregnated Carbon Ablator – Domestic (PICA-D) Development and PICA Capability Sustainment (PCS) SNAPSHOT To ensure the availability of Phenolic Impregnated Carbon Ablator (PICA) thermal protection systems (TPS) for NASA missions, the agency is developing PICA-D – an updated…
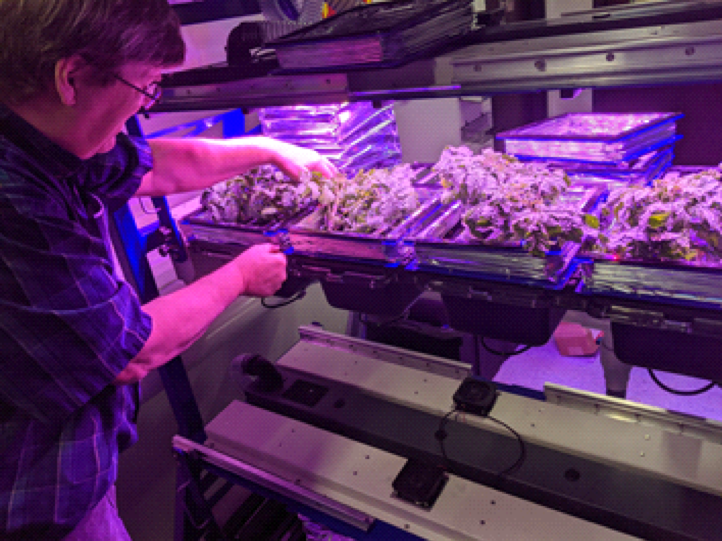

A Novel Approach to Growing Gardens in Space
PROJECT eXposed Root On-Orbit Test System (XROOTS) SNAPSHOT To investigate techniques that can be scaled for crop production in microgravity, a NASA-sponsored Sierra Space team is developing soilless nutrient delivery and recovery technologies that will be demonstrated via plant tests…

NEID: A New, Ultra-Precise Window into Nearby Worlds
PROJECT The NEID Doppler Spectrometer SNAPSHOT A collaborative partnership between NASA and the National Science Foundation (NSF) has produced the NEID spectrometer, which makes extremely precise measurements of the wobbles of stars caused by the planets that orbit them. NEID…
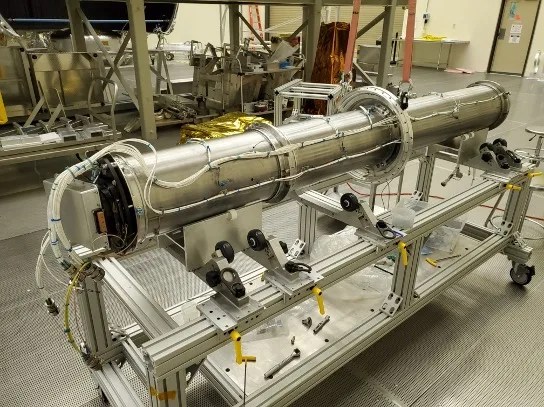

Unlocking the Sun’s X-rays
PROJECT Marshall Grazing Incidence X-ray Spectrometer (MaGIXS) SNAPSHOT NASA has developed a new type of instrument that can provide key information to predict and understand solar flares. X-ray spectroscopy provides unique capabilities for answering fundamental questions in solar physics and…

New Instrument Brings Next-generation Molecular Analysis of Mars into Sharp Focus
PROJECT Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometer (LITMS) SNAPSHOT To address the growing need for in situ molecular analysis of Mars samples at fine spatial scales, NASA is developing the miniature LITMS instrument, which combines a laser and gas chromatograph mass…
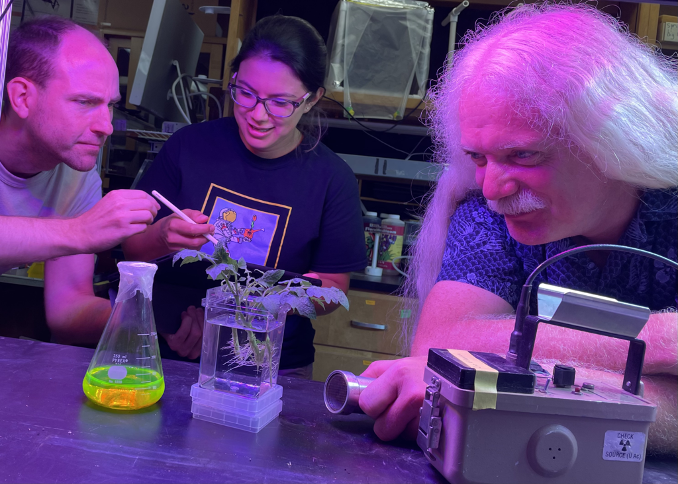

Exploring How Radiation Exposure Will Affect Life Forms on the Way to Mars
PROJECT Rad-Bio-App SNAPSHOT A NASA-sponsored team has developed a discovery environment that enables researchers to explore information on radiation exposure from numerous spaceflight experiments and extend our understanding of how radiation affects life forms in space. Spaceflight significantly increases exposure…

SMARTIE Computer Tiles Could Provide Satellites with Advanced Data Processing Power
PROJECT Stacked Miniaturized and Radiation Tolerant Intelligent Electronics (SMARTIE) SNAPSHOT Using a grant from NASA’s Earth Science Technology Office (ESTO), a team of researchers is working on a novel computer-tile technology that could help space-based remote sensors process data more…

Bracewell Nulling Interferometry Enables Astronomers to See the Glow of Alien Stardust
PROJECT Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer (LBTI) SNAPSHOT The search for and characterization of extra-solar planets (‘exoplanets’) that might host life is one of NASA’s highest ambitions. But observing exoplanets and distinguishing them from the scattered light coming from the stars…

Surviving the Lunar Night: DRPS Could Enable the Power to Explore
PROJECT Dynamic Radioisotope Power Systems Project SNAPSHOT Dynamic Radioisotope Power Systems (DRPS) may enable lunar science payloads to survive and thrive during the harsh lunar night. New robust DRPS have been built and delivered by industry and are in the…
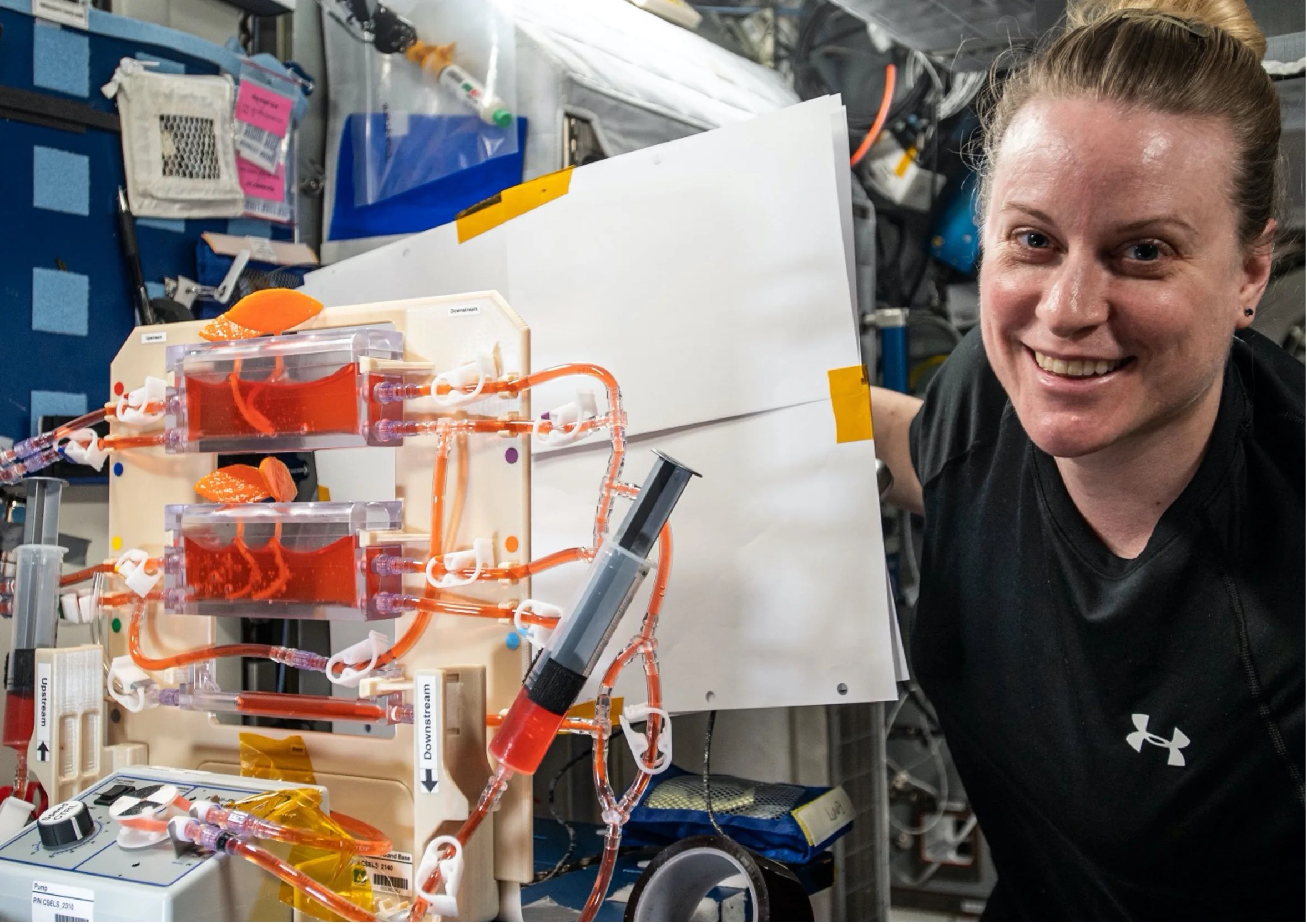
Q: How Do You Water Plants in Space? A: Omni-Gravitational Hydroponics
PROJECT Plant Water Management (PWM) SNAPSHOT NASA is demonstrating that even without the help of gravity, hydroponic plant watering methods can enable plant habitats aboard crewed or robotic space missions. On Earth, plants draw water upwards through the roots against…

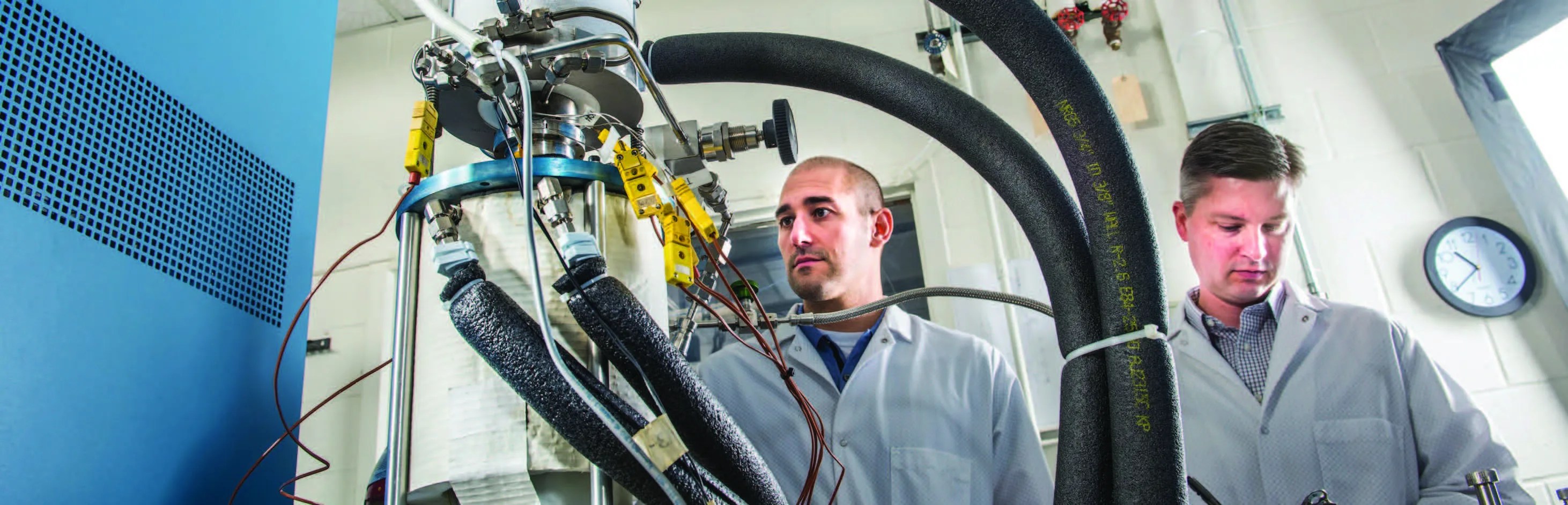
Using Ultraviolet Light to Suppress Electrostatic Noise in Gravitational Wave Observatories
PROJECT LISA Charge Management Device (CMD) SNAPSHOT With support from NASA, the University of Florida and industrial partner Fibertek, Inc. are developing a precisely controlled ultraviolet light source that will prevent electrostatic noise from obscuring gravitational wave signals measured by…
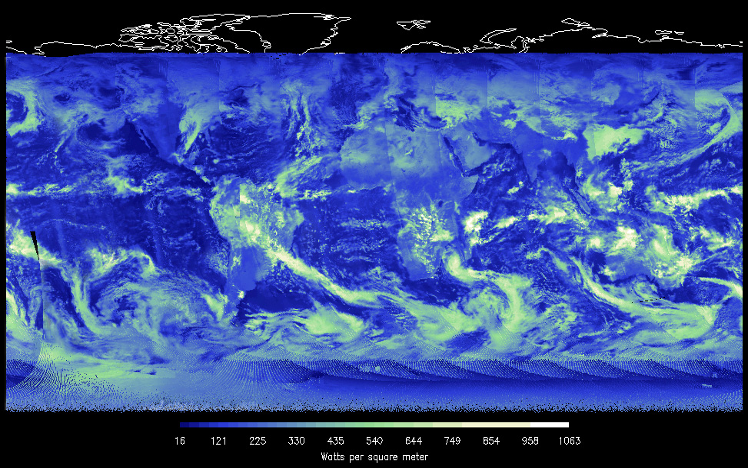
Small Sensor Could Provide Big Insights into Earth’s Radiant Energy
PROJECT DEMonstrating the Emerging Technology for Measuring the Earth’s Radiation Budget (DEMETER) SNAPSHOT A team at NASA’s Langley Research Center is developing a new state-of-the-art sensor and satellite platform to enable continued monitoring of Earth’s radiant energy system. The small,…

Frosty: A Micro-fabricated Optical Seismometer to Measure Minute Forces in a Mighty Environment
PROJECT “Frosty” micro-fabricated optical seismometer SNAPSHOT To characterize ice sheets and mantle on icy worlds, NASA is developing a new type of seismometer that is ultra-small, easy to manufacture, immune to radiation damage, and operates with low power consumption. Icy…
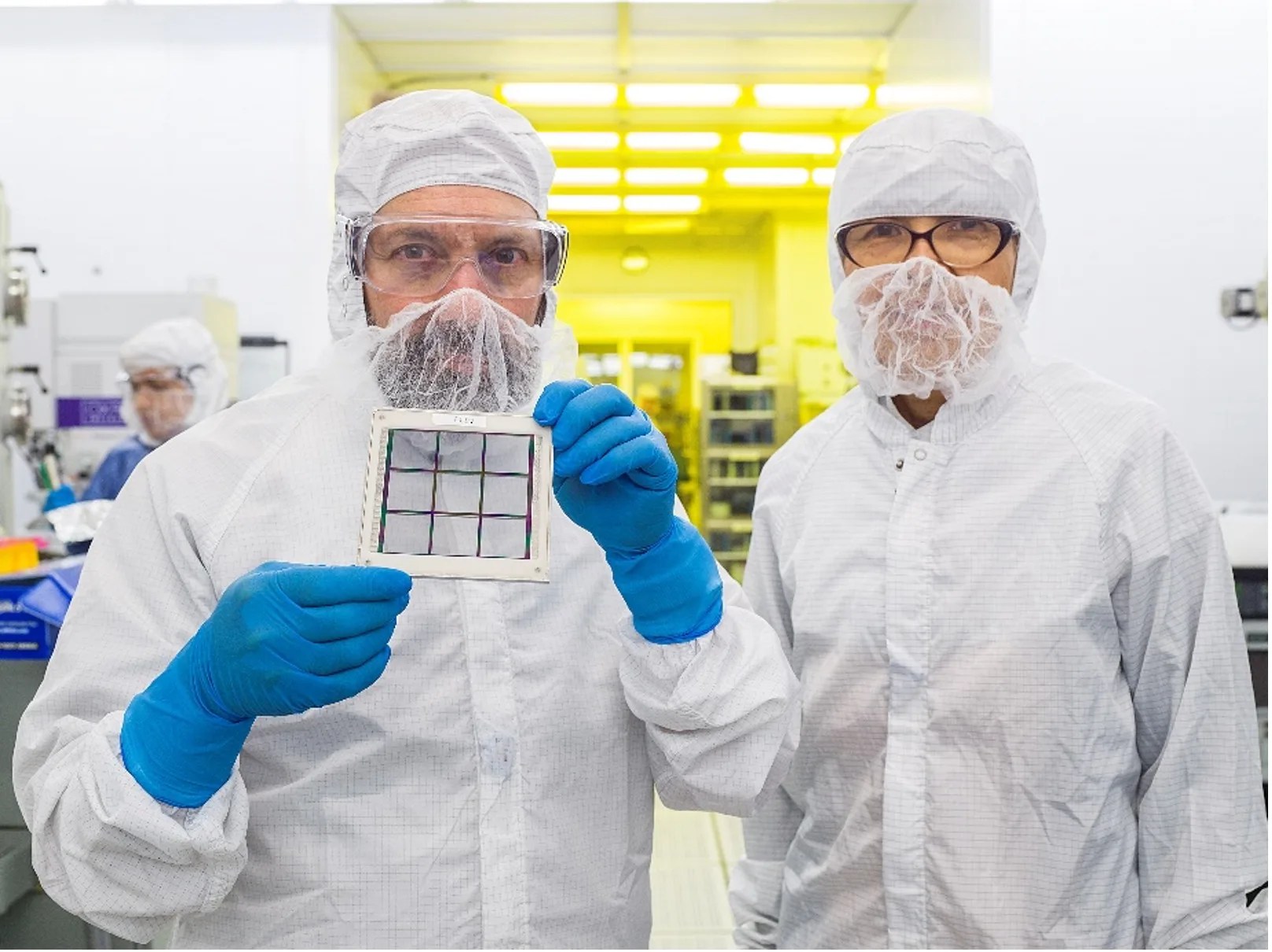

Developing Tiny Micro-Shutter Arrays to Answer Big Questions
PROJECT NexGen Micro-Shutter Array (NGMSA) SNAPSHOT Advanced technology micro-shutters enable NASA to study galaxy evolution across cosmic time. How did the first stars and galaxies form after the big bang? How did they evolve to produce the chemical elements that…
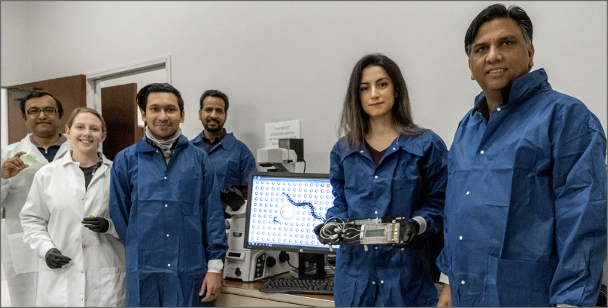
Innovative Technology Measures Muscle Strength of Worms in Space to Prepare Astronauts for Future Missions
PROJECT Determining Muscle Strength in Space-flown C. elegans SNAPSHOT Loss of muscle mass and strength in astronauts remains an issue for space exploration. Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a nematode species that is 1 mm long, shares common traits with humans…
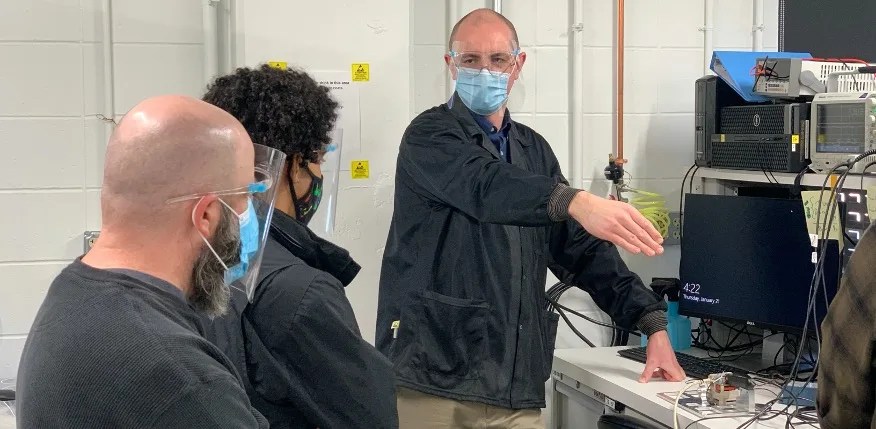

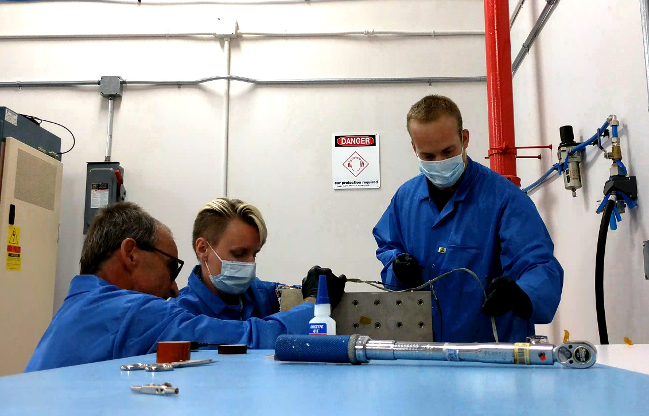
Rediscovering the Lost Art of Fluxgate Magnetometer Cores
PROJECT MAGnetometers for Innovation and Capability (MAGIC) SNAPSHOT A NASA-sponsored team at the University of Iowa is rediscovering and improving lost techniques to develop high-fidelity instruments needed to make the magnetic field measurements that enable many of the nation’s space…
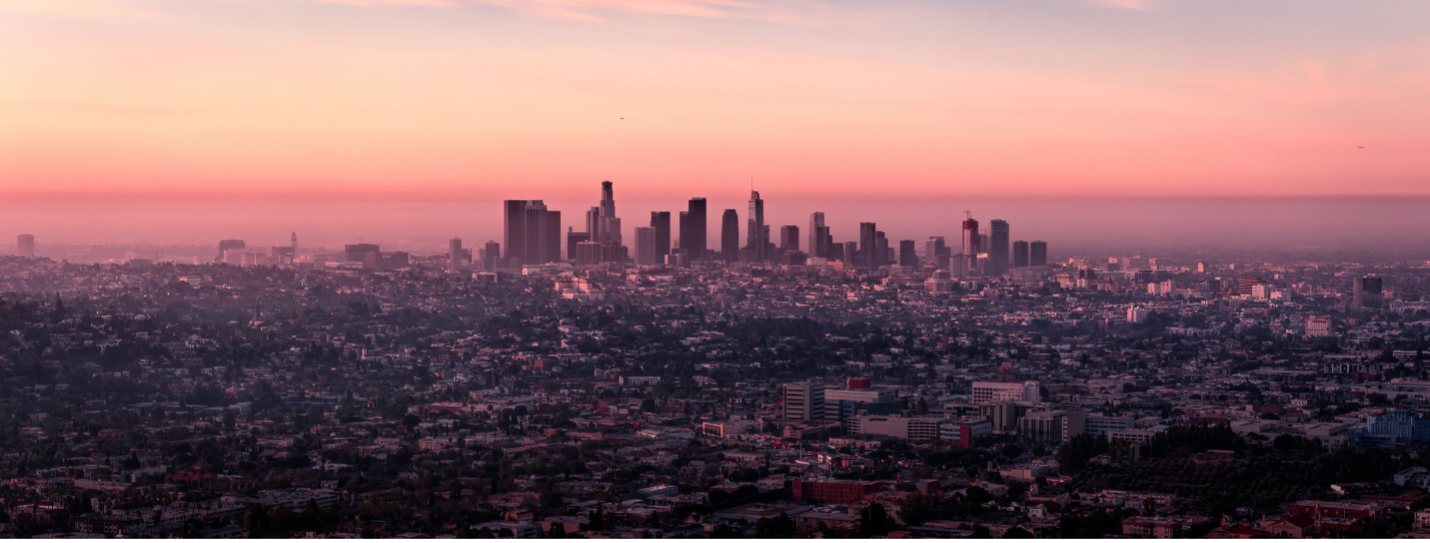

Novel Algorithms Merge Ground- and Space-based Data to Forecast Air Pollution Events
PROJECT Predicting What We Breathe (PWWB) SNAPSHOT A NASA-sponsored research team is developing new machine-learning software that uses data from satellites and ground-based sensors to forecast air pollution events in Los Angeles. Soon, this software will become publicly available, potentially…

Controlling the Temperature of Telescope Mirrors to Search for Earth-like Planets
PROJECT Predictive Thermal Control (PTC) project SNAPSHOT Active thermal control technology helps enable large ultra-stable telescopes needed to detect and characterize Earth-like planets around other stars. “Are we alone in the universe?” may be one of the most compelling questions…

New “Moon Duster” Will Help Clean NASA Assets in Space
PROJECT Lunar Dust Research and Mitigation SNAPSHOT To help protect future space assets and astronauts from dangerous effects that arise from Moon/Mars dust exposure, NASA is developing a new technology that will utilize electron beams/ultraviolet light to remove dust. The…
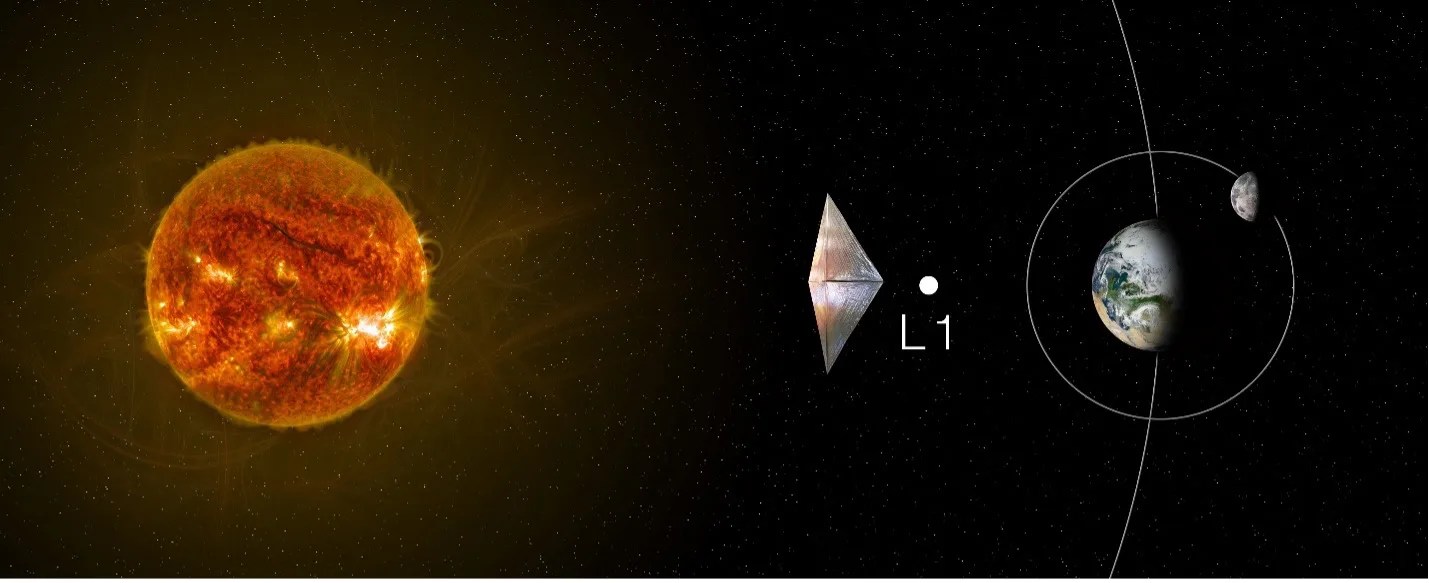
Solar Sail Propulsion: Enabling New Destinations for Science Missions
NASA’s Science Mission Directorate Program Management Council met on June 28, 2022, to evaluate whether the Solar Cruiser project was ready to proceed to the building phase – known as Phase C — of its life cycle. It was determined…

The ‘Bird’ with an Eagle Eye…for Infrared
PROJECT Mid-Wavelength and Long-Wavelength Infrared Focal Plane Arrays for Earth Science Applications SNAPSHOT NASA is sponsoring development of high-performance infrared sensors with reduced requirements for cooling onboard satellites; these new sensors could potentially be flown on small satellite platforms like…
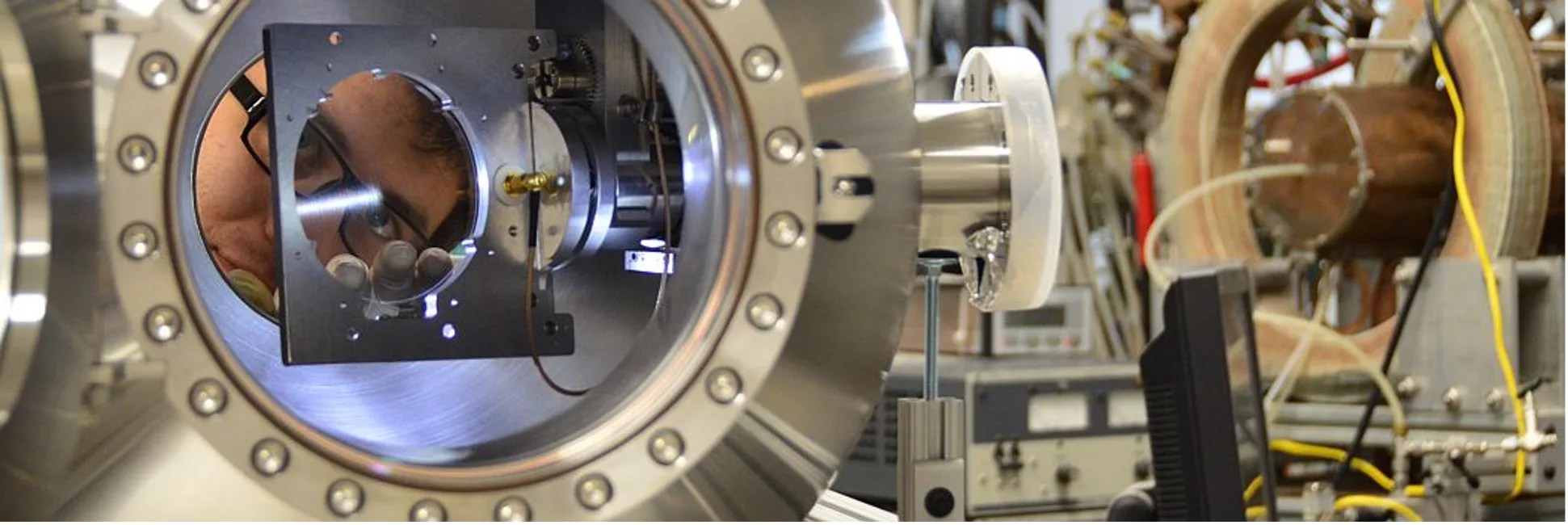
Nanofabricated Mirrors and Gratings Will Enable More Powerful Space Telescopes
PROJECT Sub-arcsecond X-ray telescope optics and high-resolution, high-efficiency X-ray transmission grating spectrometers SNAPSHOT A NASA-sponsored team at the MIT Space Nanotechnology Lab is developing high-performance space instrumentation for more powerful future X-ray telescopes that will study the dynamics of the…
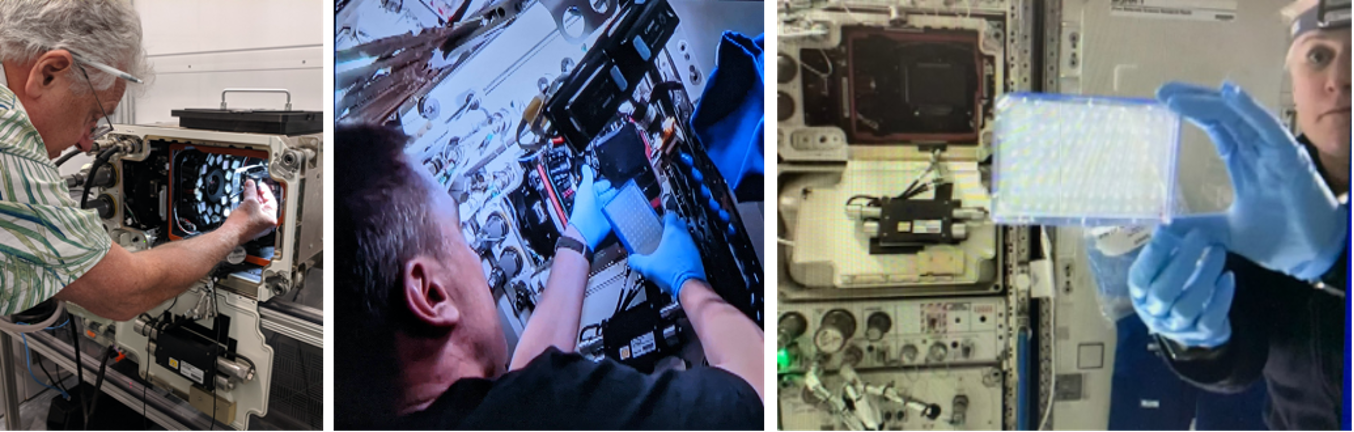
Multi-Spectral Fluorescence Imaging System for Studying Gene Expression on ISS
PROJECT Multi-Spectral Fluorescence Imaging System (Spectrum) SNAPSHOT NASA seeks to understand the impact of the spaceflight environment on organisms in preparation for long-duration missions. Spectrum was developed to undertake these types of studies using model organisms on ISS. All organisms…
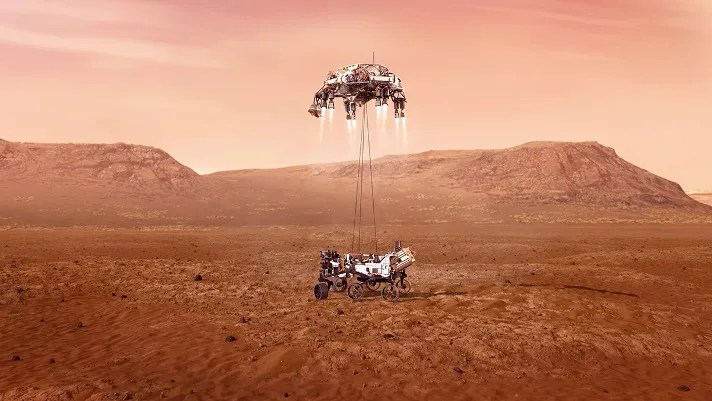

Terrain Relative Navigation: Landing Between the Hazards
PROJECT Terrain Relative Navigation (TRN) SNAPSHOT To land accurately and avoid hazardous terrain, NASA has developed an autonomous, vision-based system for landmark recognition, spacecraft position estimation, and spacecraft retargeting, which will be used on Mars 2020 and potentially other future…

CubeSat Platform Enabled an Inexpensive Space Telescope
PROJECT HaloSat – A CubeSat that studied the hot Galactic halo SNAPSHOT To enable lower cost space-based astronomical observatories, NASA is promoting use of miniature satellites known as CubeSats and instruments built from commercial off-the-shelf components. Space telescopes have historically…
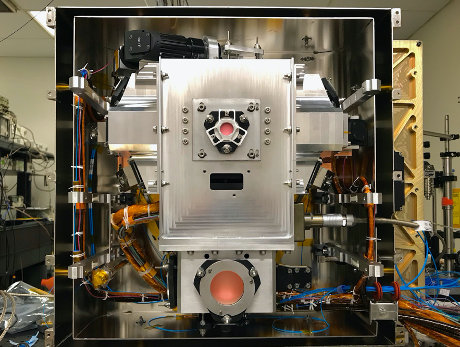
Quantum Technologies Take Flight
PROJECT Cold Atom Lab (CAL) SNAPSHOT Interferometry of atomic matter-waves has been demonstrated for the first time in orbit, opening the door for precision quantum sensing for both fundamental and applied physics applications ranging from tests of general relativity to…

Far-Infrared Detectors: Superconductivity Enables New Astrophysical Discoveries
PROJECT Ultrasensitive Far-Infrared Bolometers for Space Astrophysics SNAPSHOT The far-IR is a powerful but relatively unexplored spectral band that can enable study of the birth and infancy of galaxies. NASA missions with super-cooled telescopes have the potential for orders of…

A Small Satellite With Planetary Ambitions
PROJECT CubeSat Particle Aggregation and Collision Experiment, or Q-PACE SNAPSHOT Q-PACE will capture video of thousands of gentle collisions between particles in microgravity to understand the earliest steps in planet formation. A NASA-sponsored team at the University of Central Florida…

Prototype Ozone Monitoring Instrument Gets Its First Look at The Sun
PROJECT Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) IV Pathfinder SNAPSHOT The miniaturized SAGE IV Pathfinder instrument may one day enable a constellation of small satellites to continue and enhance atmospheric ozone monitoring. The SAGE IV Pathfinder makes measurements of ozone…

New Radar to Monitor Volcanoes and Earthquakes from Space
PROJECT CubeSat Imaging Radar for Earth Sciences (CIRES) SNAPSHOT To help monitor ground deformation from space, NASA developed a new technology equipped with an S-band Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) for a small satellite platform. A global map detailing land…
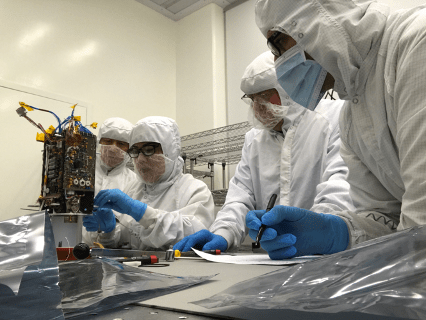
Surface and Exosphere Alterations by Landers (SEAL): NASA’s Next Lunar Payload?
PROJECT Surface and Exosphere Alterations by Landers (SEAL) SNAPSHOT SEAL will provide valuable in situ lunar data to give scientists insight into how a spacecraft landing might affect the composition of nearby regolith samples. When a space vehicle lands on…
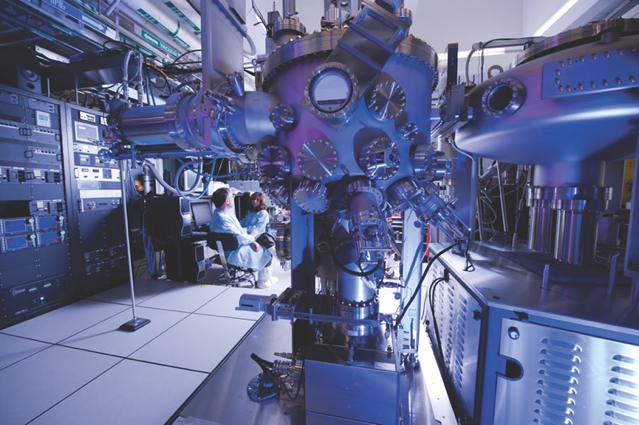
Crafting Detectors Atomic Layer by Atomic Layer has a High Impact on Ultraviolet Astrophysics Missions
PROJECT Advanced FUV/UV/Visible Photon Counting and Ultralow Noise Detectors SNAPSHOT Researchers have developed methods to alter the surface properties of ultraviolet detectors and produce instruments with unprecedented sensitivity and performance. The ultraviolet (UV) spectral range is rich with information about…
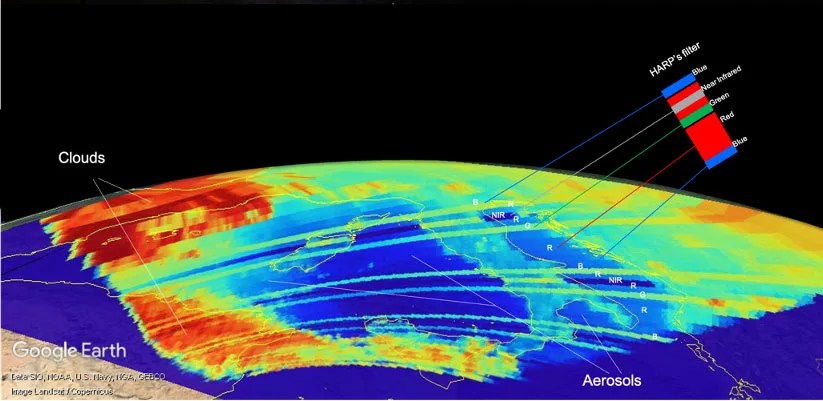
New CubeSat’s First Light Shows Clouds and Aerosols
PROJECT Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter (HARP) SNAPSHOT HARP aims to help identify air pollution, aerosols and clouds. The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter’s measurements help us better understand how clouds and aerosols impact weather, climate, and air quality. The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter (HARP)…
Exploring a New Approach for Measuring Water Vapor on Earth and Mars
PROJECT Vapor Inside-cloud Profiling Radar (VIPR) and WAter Sounding Short-range Radar (WASSR) SNAPSHOT NASA researchers are exploring a new radar-based method to map water vapor both in Earth’s atmosphere and near the surface of Mars. Mapping water vapor is a…

Enhanced Mirror Coatings Will Enable Future NASA Observatory
PROJECT Broadband Mirror Coatings for Future NASA Observatory SNAPSHOT A team at GSFC is investigating techniques for creating highly reflective aluminum mirrors sensitive to the far-ultraviolet in addition to the infrared, optical, and visible wavelengths. The more reflective a telescope…

Lightweight Mirrors Enhance Power Generation Near Gas Giants
PROJECT Extreme Environments Solar Power (EESP) Project demonstration of Transformational Array elements on DART SNAPSHOT The EESP Project is developing advanced solar cell and concentrator technology that will be flight-tested on the upcoming DART mission. The Transformational Array containing this…

Taking Earth’s Temperature from a Tiny Satellite
PROJECT Compact Infrared Radiometer in Space (CIRiS) instrument on a CubeSat SNAPSHOT To demonstrate for the first time from a small satellite the ability to collect, process and calibrate infrared images of Earth. A new miniature sensor, in conjunction with…

In-Space Telescope Assembly: When is it worth it?
PROJECT In Space Assembled Telescope (iSAT) Study SNAPSHOT NASA conducted a detailed study to understand when it is worth assembling telescopes in space rather than folding them into a single rocket and deploying them in space. The conventional approach of…

Balloon-borne Investigation Provides First Simultaneous Measurements of Crucial Coronal Parameters
PROJECT Balloon-borne Investigation of Temperature and Speed of Electrons in the corona (BITSE) SNAPSHOT New technology demonstrated on BITSE has simultaneously detected the 2D density, temperature, and speed of electrons in the solar corona for the first time. An observational…
Playing Lacrosse on Titan
PROJECT Integrated Sampling System (ISS) for Ocean Worlds SNAPSHOT Honeybee Robotics has developed a pneumatic based sample acquisition and transfer system that is self-metering, gravity agnostic, works with sticky materials, and is flexible in terms of delivery location. The system…
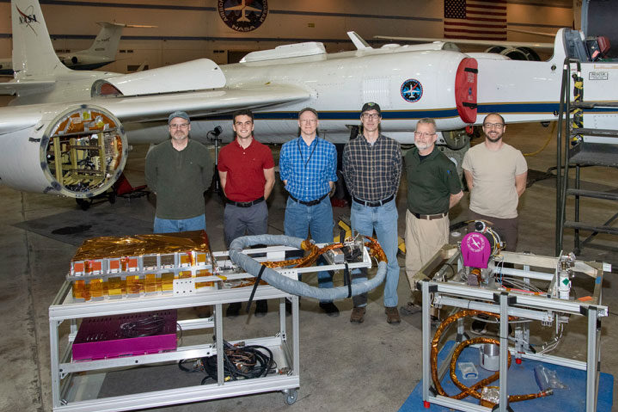

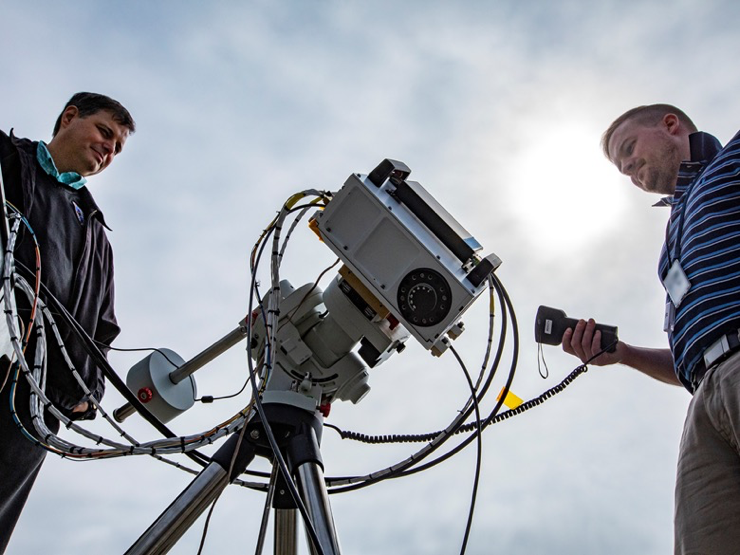
High-flying Moon Sensor Will Help Improve Earth Observations
PROJECT Airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance Instrument (air-LUSI) SNAPSHOT A new instrument flew aboard a high-altitude NASA plane to measure the Moon’s brightness and help Earth observing sensors make more accurate measurements. A new instrument flew aboard NASA’s ER-2 airplane to…
Advanced Magnetic Cooling for Sub-Kelvin Instruments
PROJECT High-Efficiency Continuous Cooling for Cryogenic Instruments SNAPSHOT To cool proposed future science instruments to operating temperatures well below one Kelvin, NASA is developing an advanced spaceflight magnetic refrigeration system. Several proposed future space-science instruments will operate at temperatures well…
Planetary Exploration Science Technology Office
This blog post originated in the 2018 Science Mission Directorate Science and Technology Report. PROJECT Planetary Exploration Science Technology Office (PESTO) KEY POINTS A new office has been created to manage the development of scientific instruments, space vehicle technologies, and…

Big Weather Data from a Tiny CubeSat
This blog post originated in the 2018 Science Mission Directorate Science and Technology Report. PROJECT Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration (TEMPEST-D) KEY POINTS The TEMPEST-D CubeSat demonstrated low-cost, lowrisk, millimeter wave radiometer technology that will enable constellations…

Balloon-bourne Imaging Captures Turbulence Sources Revealed in Polar Mesospheric Clouds
This blog post originated in the 2018 Science Mission Directorate Science and Technology Report. PROJECT Polar Mesospheric Cloud Turbulence experiment (PMC Turbo) KEY POINTS The balloon-borne PMC Turbo experiment successfully provided information about small-scale instabilities and turbulence in the mesosphere…
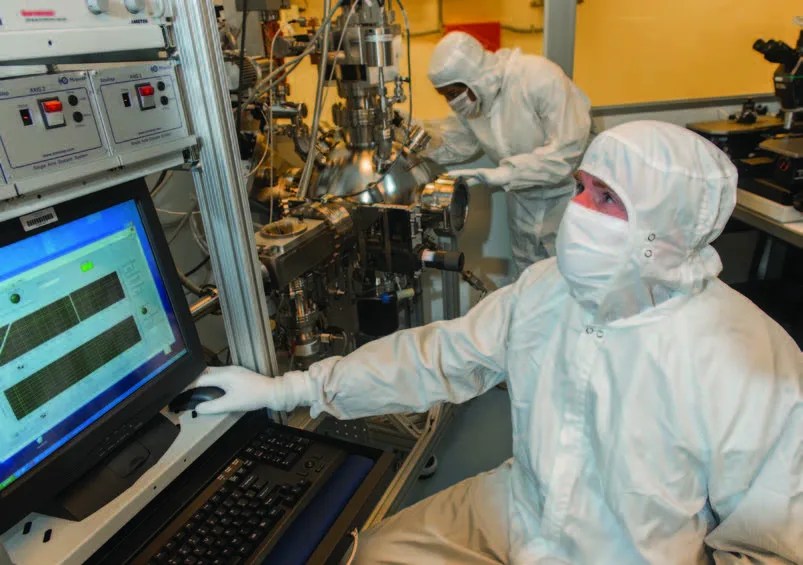

Integrated Circuits to Enable Exploration of the Harshest Environments in the Solar System
PROJECT High Temperature Memory Electronics for Long-Lived Venus Missions KEY POINTS Newly developed silicon carbide electronics have operated in ovens for over a year at 500°C and for 60 days in simulated Venus surface conditions. This technology is key to…

FOXSI’s X-ray Optics and Detectors Put the Sun in Focus
PROJECT Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager (FOXSI) sounding rocket KEY POINTS This third flight of the FOXSI experiment featured direct-focusing X-ray optics, 3D-printed collimating devices for limiting background, and high-resolution X-ray detectors. This technology will enable high-fidelity X-ray imaging in…
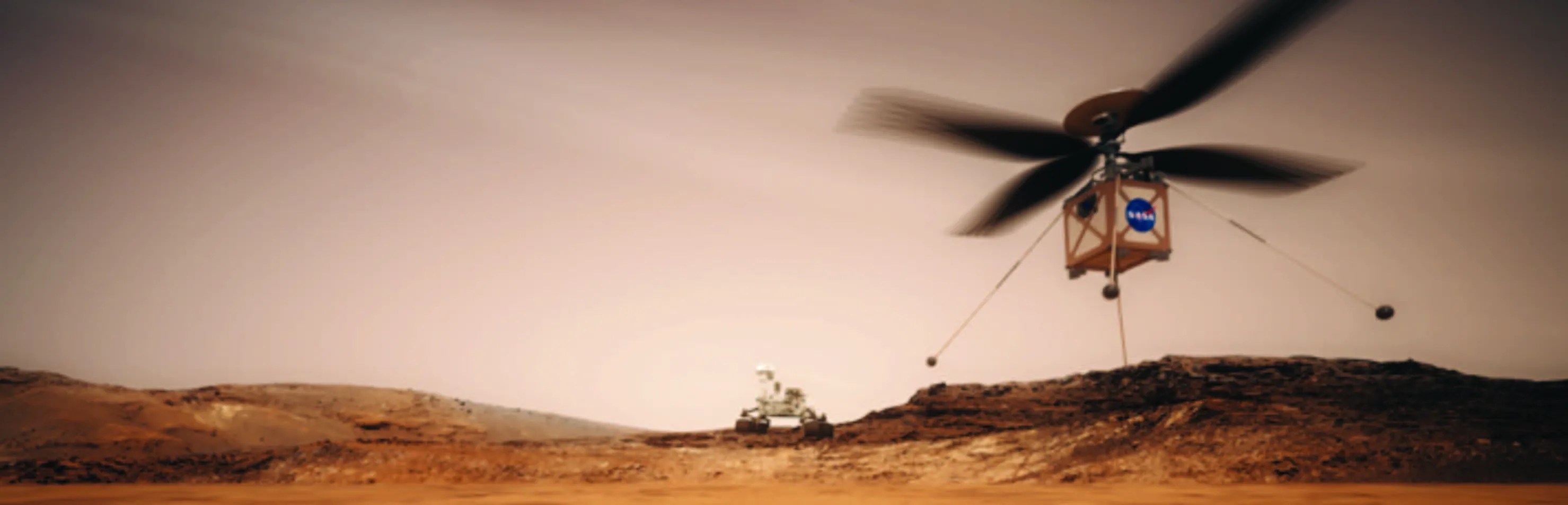

Mars Helicopter is Ready for Extraterrestrial Flight
PROJECT Mars Helicopter KEY POINTS The Mars Helicopter is a technology demonstration for the Mars 2020 rover mission, intended to show the feasibility and utility of using helicopters for Mars exploration. This technology may enable future missions to perform reconnaissance…
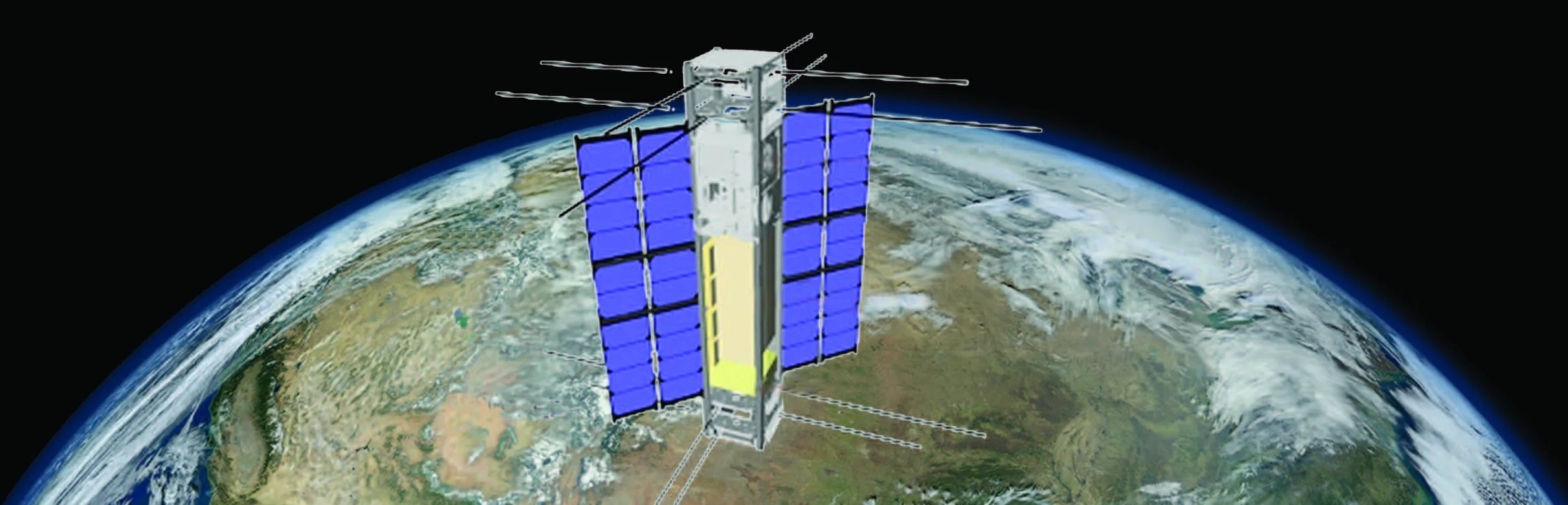
CubeSat to Demonstrate Innovative Method for Mapping Soil Moisture and Snow from Space
PROJECT Signals of Opportunity Airborne Demonstrator (SoOp-AD) and SigNals of Opportunity: P-band Investigation (SNoOPI) KEY POINTS The SoOP-AD project successfully demonstrated, from aircraft, a new instrument prototype for remote sensing of soil moisture. The SNoOPI project will continue this development…
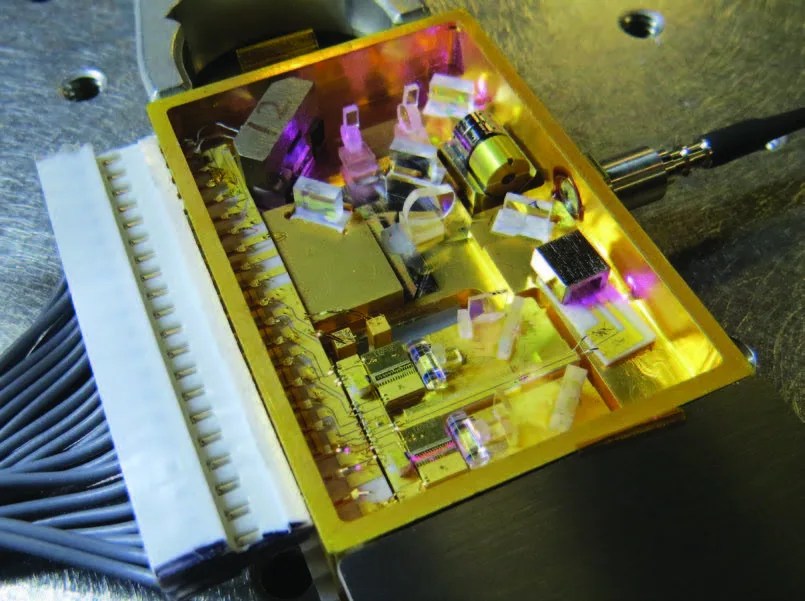

New Laser Transmitter to Enable International Gravitational Wave Observatory
PROJECT Laser Transmitter for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) Mission KEY POINTS A highly stable and robust laser design is a key subsystem required for the LISA observatory. By leveraging lessons learned from previous missions and the latest technologies…
New Compact Remote Sensor to Image Ionospheric Current’s Spatial Structure from Space
PROJECT The Microwave Electrojet Magnetogram (MEM) KEY POINTS The low SWaP MEM sensor enables cost-effective implementation of future high-impact ionospheric current investigations on resource-limited missions, including CubeSat constellations. Understanding the interaction and coupling processes within Earth’s atmosphere, ionosphere, and magnetosphere…

Surveying the Building Blocks of the Solar System
PROJECT High-Performance In Situ Dust Analyzer (Hyperdust) KEY POINTS Hyperdust’s unique ion optics design combines the ability to provide high-performance composition measurements with the aperture that is needed to detect a statistically significant number of particles in space over a…
RainCube Demonstrates Miniature Radar Technology to Measure Storms
PROJECT RainCube (Radar in a CubeSat) KEY POINTS RainCube successfully demonstrated Ka-band precipitation radar technology on a low-cost, quick-turnaround platform. This new technology will enable constellations of small spacecraft that can track storms and provide data about how the storms…

Super Cloud Library Enhances Cloud Process Studies
PROJECT Super Cloud Library KEY POINTS The Super Cloud Library—a big data analysis and visualization tool for Earth science applications—has been infused into the Data Analytics and Storage System (DASS) at the NASA Center for Climate Simulation and is producing…
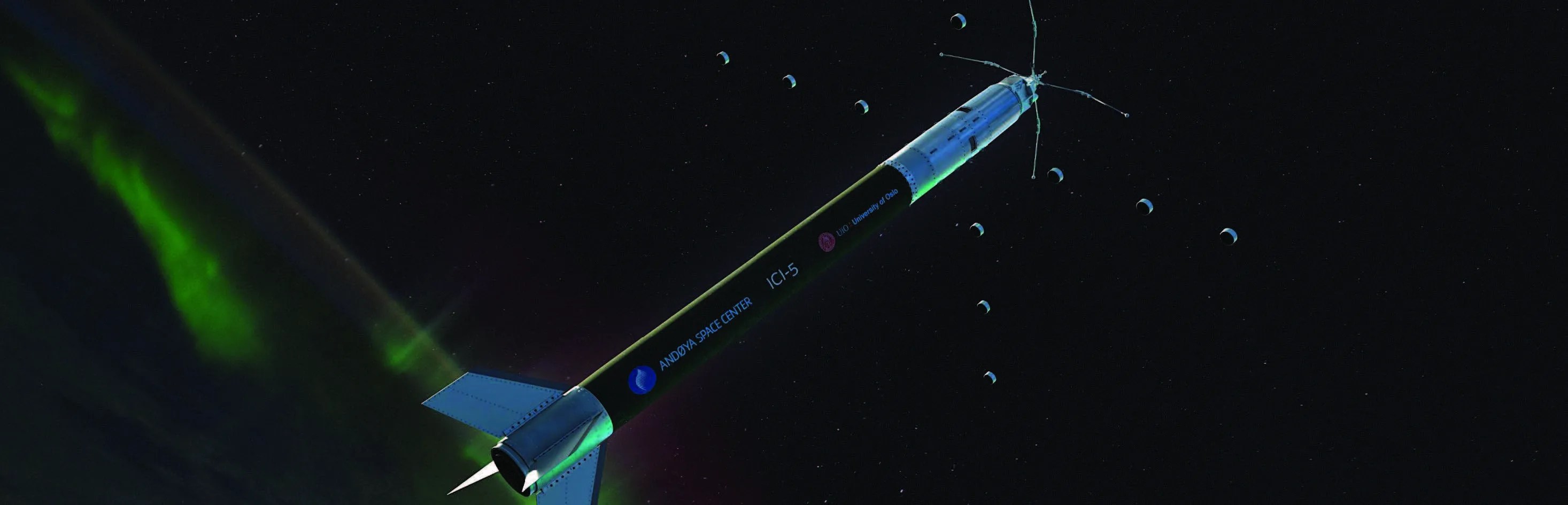
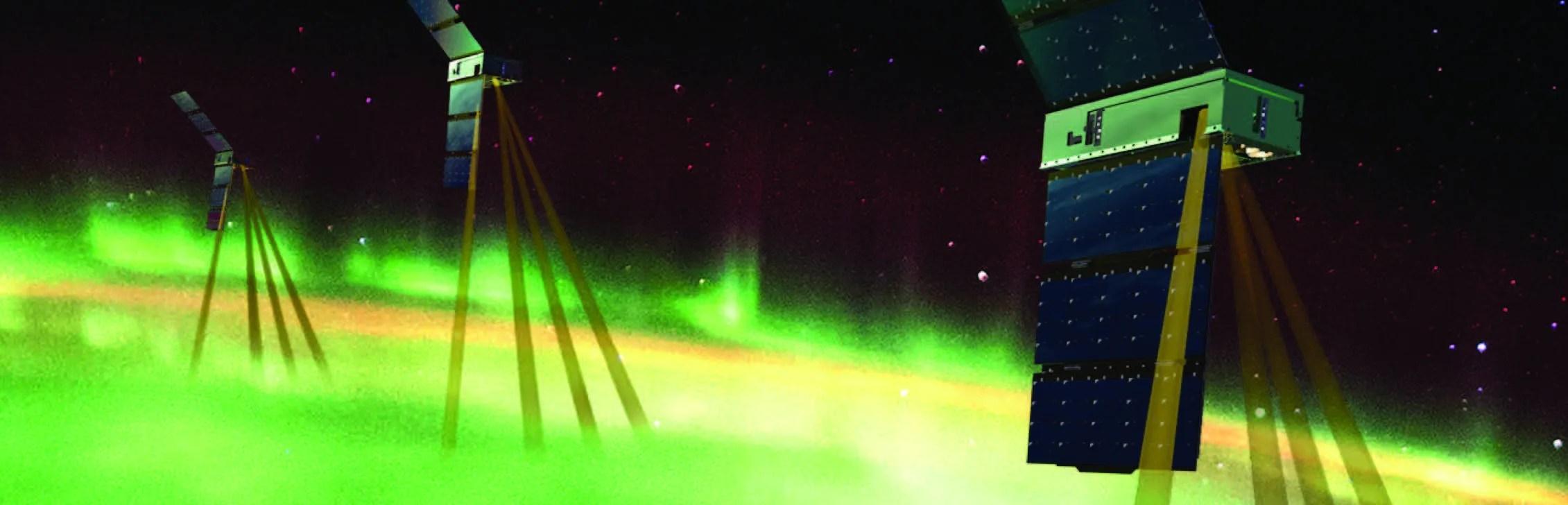
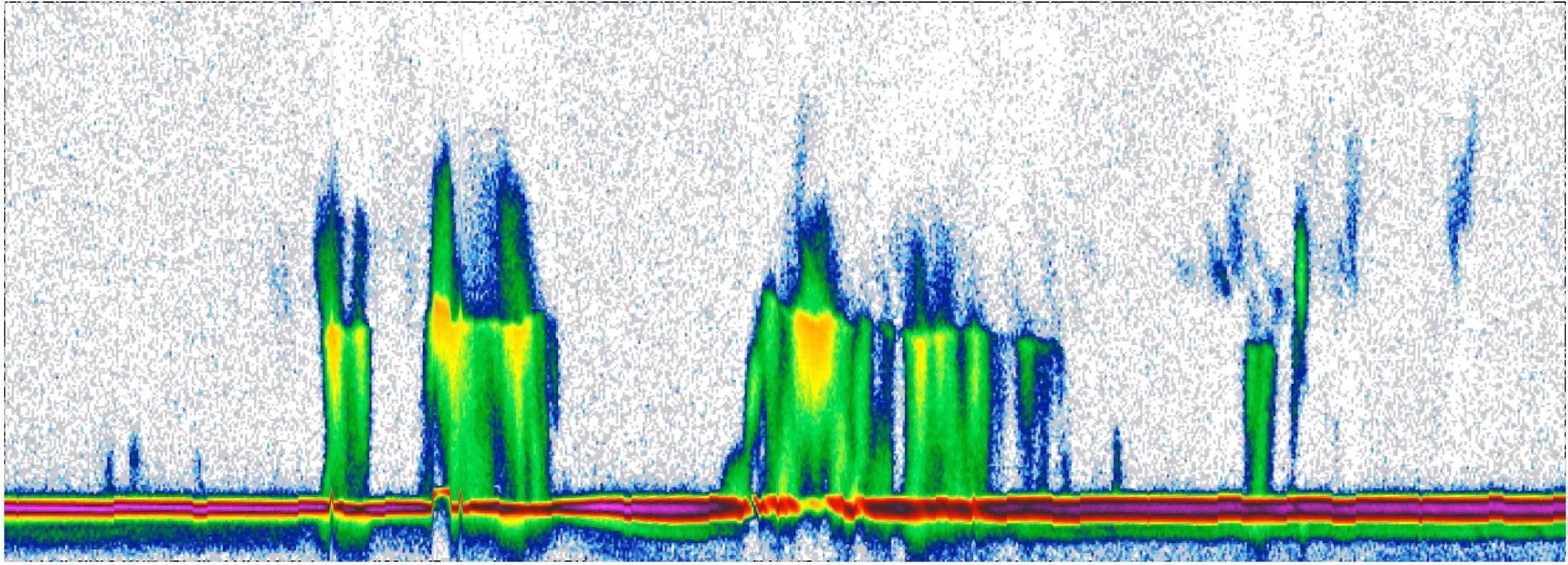
Bifocal Electron Sensor Flight of Opportunity on the Investigation of Cusp Irregularities-5 Mission
Project ICI-5 Bifocal Flight Opportunity Key Points Developed by a team at the University of Iowa, the Bifocal sensor is a next-generation electron instrument with very high angular resolution. The Bifocal sensor will be demonstrated on the ICI-5 sounding rocket…

Record Setting Power System Disassembled and Analyzed: Proves Viability of Power Technology
Project Dynamic Radioisotope Power Key Points Understanding potential failure modes can lead to improved designs that will enable Dynamic RPS to provide highly reliable power to planetary science missions for up to 17 years of operational life. Future NASA missions…
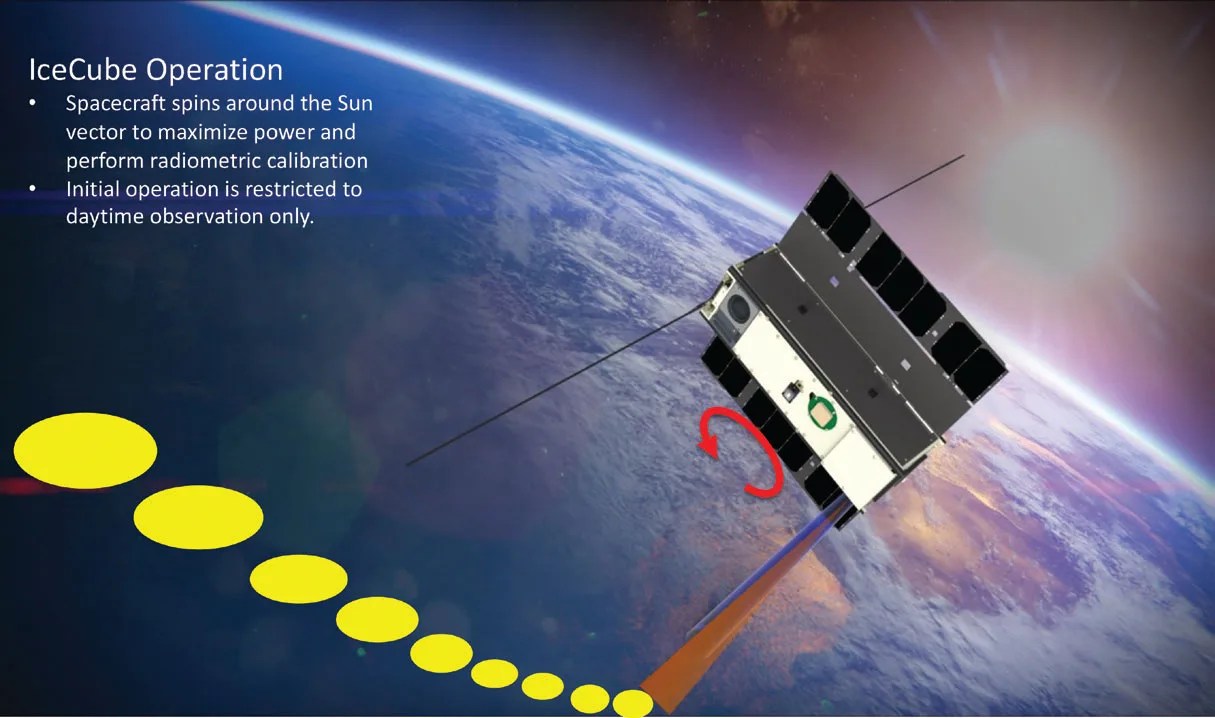
IceCube Demonstrates New Capability to Measure Cloud Ice from Space
Technology Infusion IceCube—a tiny, bread loaf-sized satellite—has produced the world’s first map of the global distribution of atmospheric ice in the 883-Gigahertz (GHz) band. Information about cloud ice enables researchers to better understand Earth’s weather and changing climate. Sensing atmospheric…
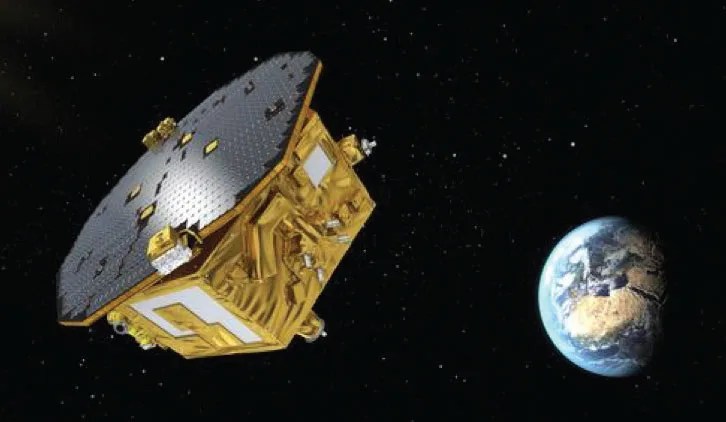

Colloid Microthrusters Demonstrated on LISA Pathfinder
Technology Infusion A colloid microthruster provides electric micropropulsion for drag-free and fine pointing applications. It uses an electrospray (electrostatically generated and accelerated charged droplets) to provide spacecraft control at tens of micronewtons of thrust (about the weight of a mosquito!)…
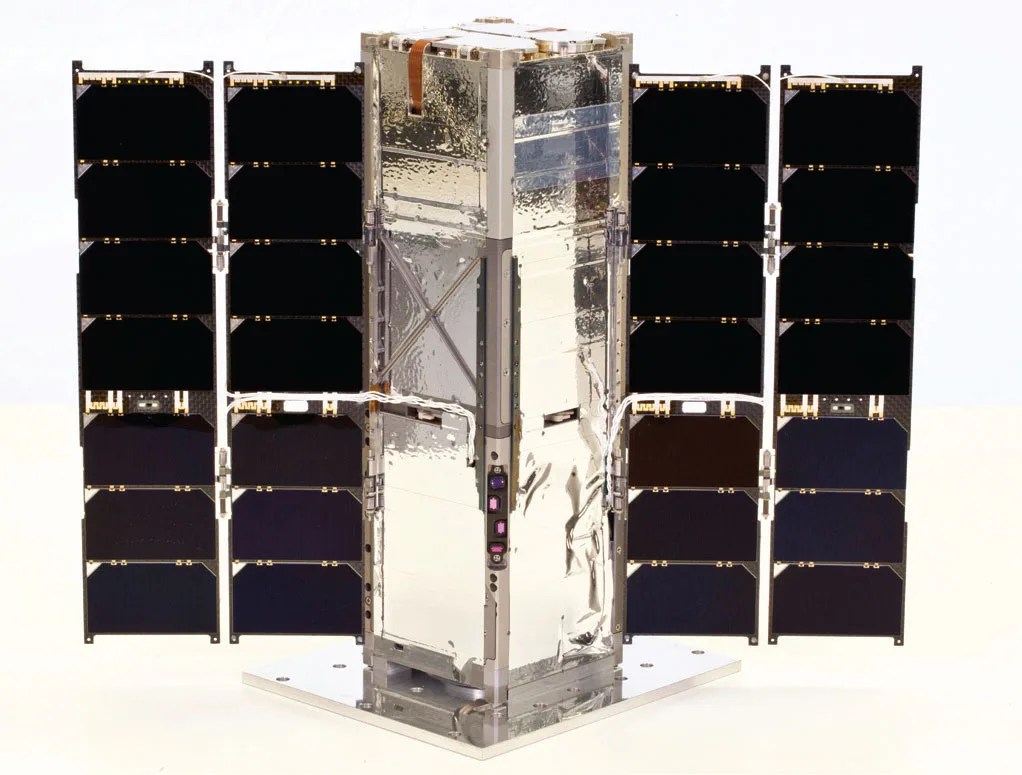

RAVAN CubeSat Successfully Demonstrates Two Radiation Measurement Technologies
Technology Infusion The Radiometer Assessment using Vertically Aligned Nanotubes (RAVAN) CubeSat has met its goal of validating two new technologies to measure Earth’s radiation imbalance—the difference between the amount of energy from the Sun that reaches Earth and the amount…

Gemini Plus Enables Next-Generation Planetary Composition Measurements
Technology Infusion NASA has funded the development of a new high-purity germanium gamma-ray detector—the GeMini Plus—for use in upcoming planetary exploration missions. High-purity germanium detectors provide superior performance compared to other gamma-ray detectors. This development is being carried out jointly…

DopplerScatt’s Simultaneous Ocean Wind and Current Measurements Employed in Two Studies
Technology Development A NASA-developed airborne instrument called DopplerScatt participated in two large-scale oceanographic experiments in April and May of 2017. A Ka-band Doppler scatterometer, DopplerScatt’s ability to take simultaneous measurements of ocean surface winds and water currents is a new…
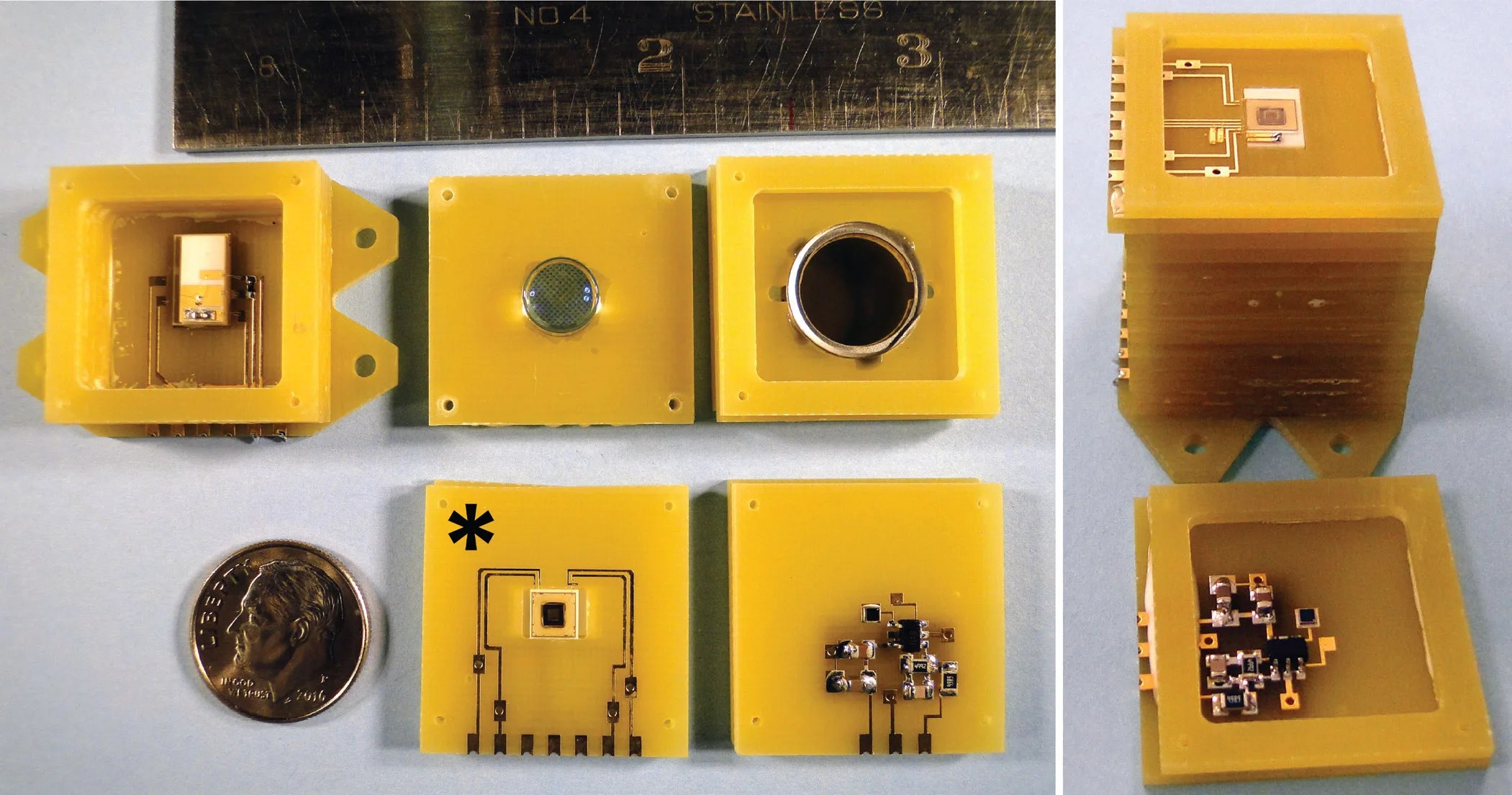
Miniature Magnetometer Will Enable Space Exploration on Resource-Constrained Platforms
Technology Development NASA is sponsoring a joint effort by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to develop a novel miniature absolute scalar magnetometer based on a micro-fabricated alkali-metal…

Wireless Networks Gather Soil Moisture Data in the Arctic
Technology Development Accurate measurement of soil moisture is important to numerous fields including agriculture, weather prediction, and the study of climate change. An SMD-sponsored project—the Soil moisture Sensing Controller And oPtimal Estimator (SoilSCAPE)—is helping scientists monitor soil moisture at several…
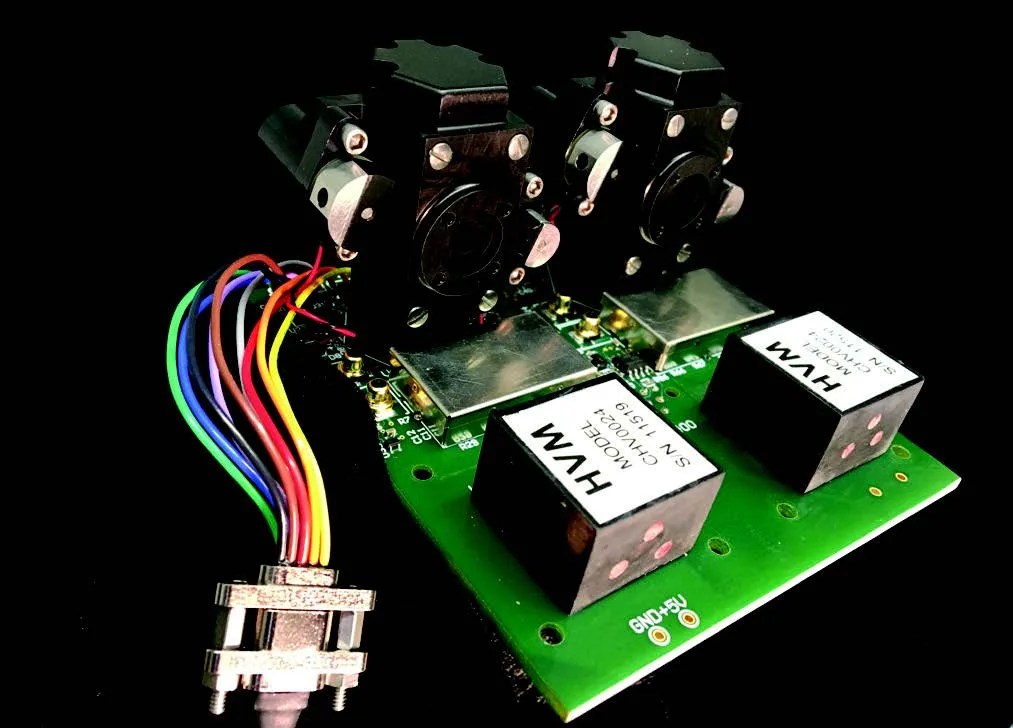
Development of a Compact Multi-spectral Photometer for Space Science
Technology Development Earth’s ionosphere is increasingly recognized as a region of space that directly impacts the development and use of space assets for modern society. For example, changing conditions in the ionosphere can adversely affect radio communications and space-based navigation…
Aerocapture Technologies are Ready for Future Mission Use
Technology Development Aerocapture technologies have the potential to enable orbital missions to the outer planets and their satellites by the judicious use of aerodynamic forces in a planetary atmosphere. These forces can be used to guide a spacecraft from an…
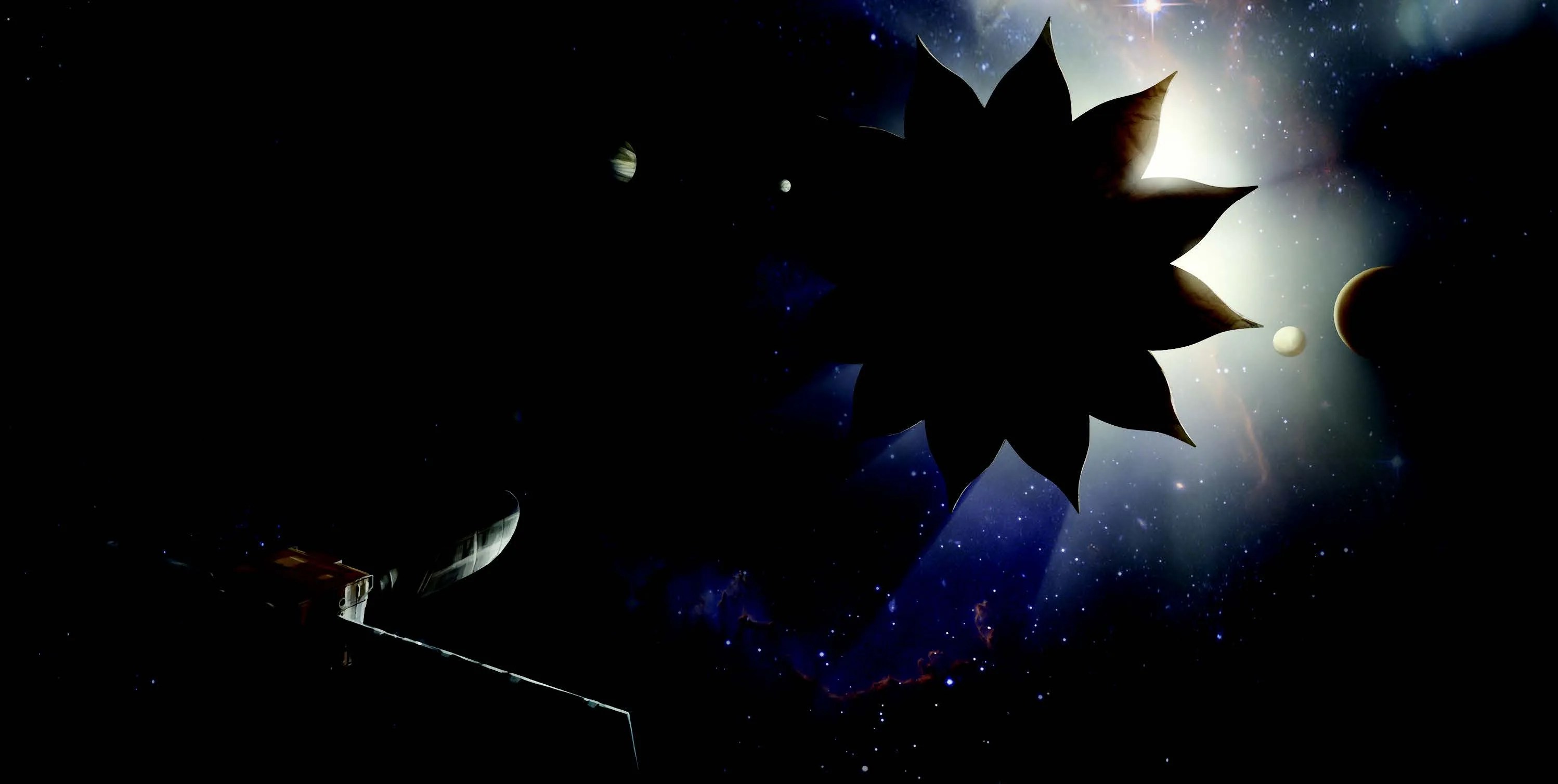

Developing Starshade Technology to Image Earth-sized Exoplanets Around Neighboring Stars
Technology Development Acquiring images and spectra from planets around our neighboring stars could give us a sense of their atmospheres and habitability—but only if we can block out the star’s light. The light reflected off an Earth-sized planet around a…
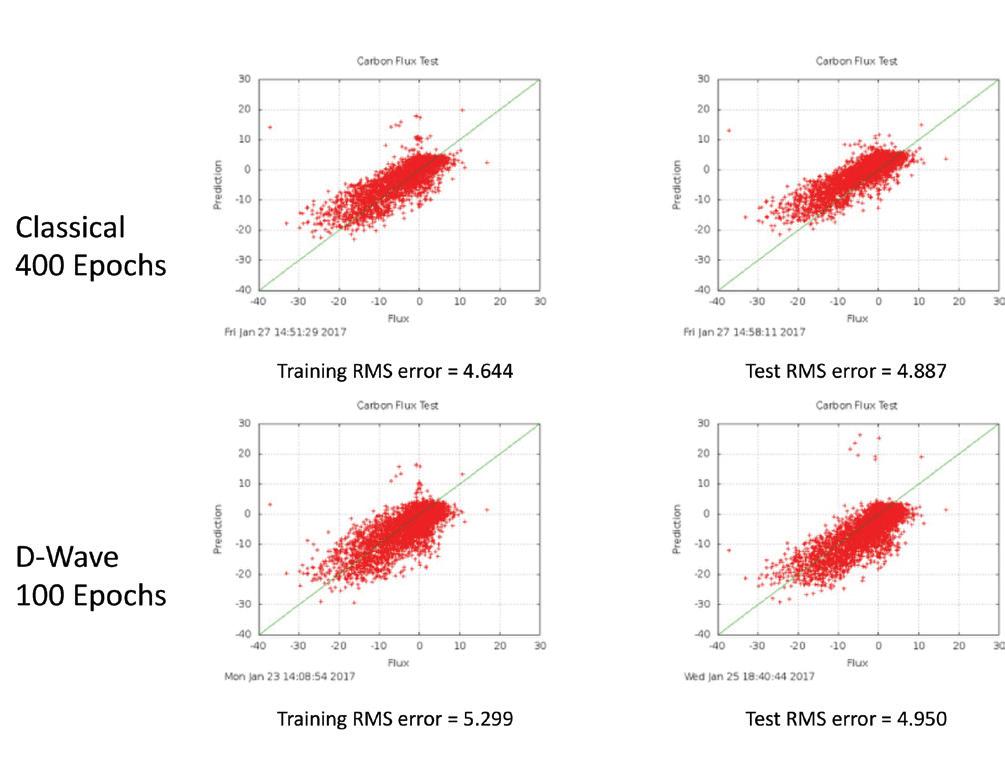
Estimating Carbon Flux with Quantum Computing
Technology Development A NASA-funded team has been exploring the use of quantum annealing computers for a scientifically meaningful application—to estimate the net annual ecosystem carbon flux over land using satellite data. Carbon flux is the exchange process of carbon dioxide…

