Why Have a Telescope in Space?
Hubble's unique characteristics – like its broad wavelength coverage, its position beyond Earth's atmosphere, and its assortment of science instruments – have made it one of astronomy's most important tools.
Quick Facts

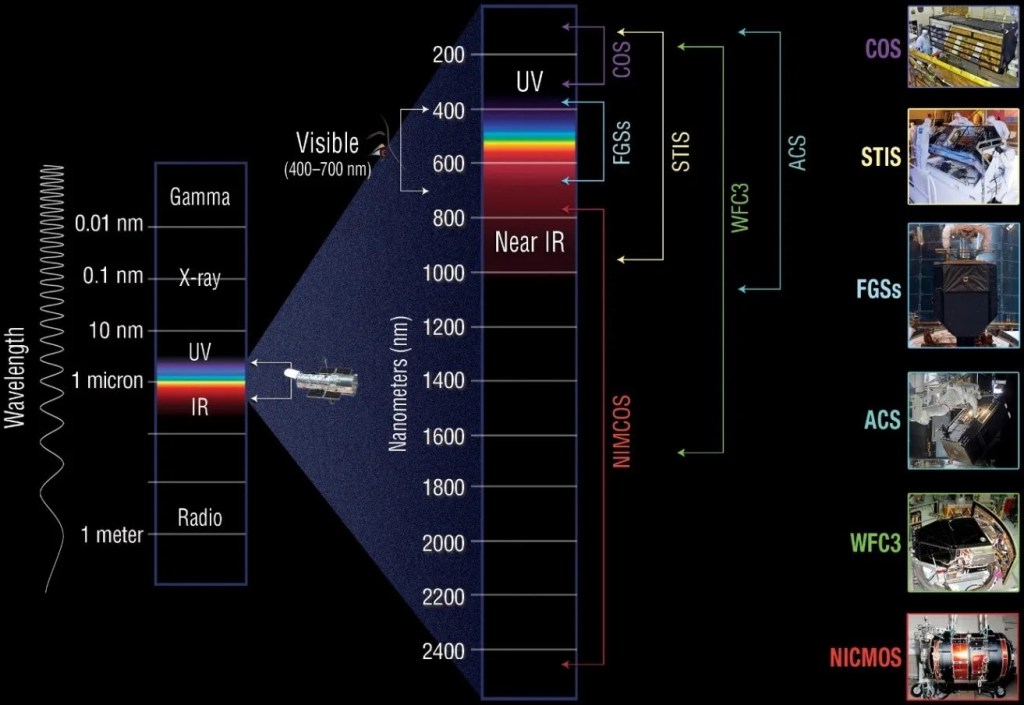
Hubble was designed as a general purpose observatory, meant to explore the universe in visible, ultraviolet, and infrared wavelengths. To date, the telescope has studied a vast array of cosmic objects, providing views that astronomers were unable to capture from the ground.
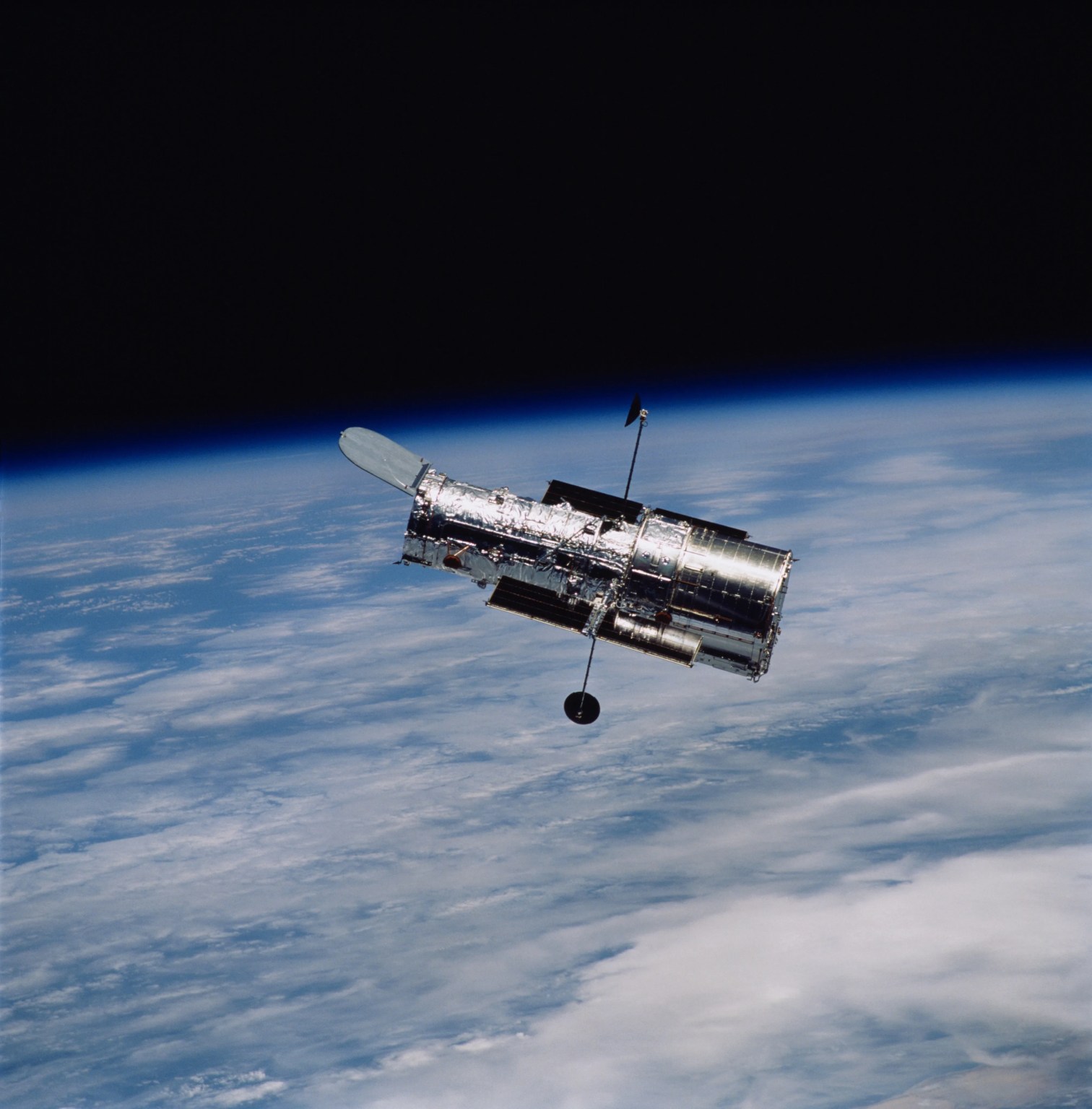
In addition to blocking certain wavelengths of light altogether, Earth’s atmosphere is made up of shifting pockets of air that cause the twinkling appearance of stars in the night sky. This motion blurs images captured by telescopes on the ground. Hubble was placed into orbit above the atmosphere to avoid these effects.
As the telescope orbits Earth, its mirror gathers light from the cosmos, collecting images and data. For some of deepest images, the telescope has stared at the same point in the sky for days to capture the dim glow of the distant universe.
Hubble Advantages
01
Distortion-Free
When you look up at the stars in the sky, they seem to twinkle. That’s because shifting pockets of air in Earth’s atmosphere distort your view, even on the clearest nights. When astronomers try to take a picture of a cosmic object from the ground, that picture ends up blurry. Hubble’s position above the atmosphere lets it observe steady, unwavering light from cosmic objects and thus achieve higher resolution.

02
More Wavelengths
Earth’s atmosphere stops certain wavelengths of light. This is good for life on our planet, since it keeps away some dangerous radiation, but it also blinds us to some of the light emitted by cosmic objects. Hubble is designed to view some ultraviolet and infrared wavelengths, which are blocked or partially blocked by the atmosphere, as well as visible light. Hubble’s perceptiveness to this broad range of wavelengths captures details that would otherwise be invisible, revealing a wealth of information about cosmic objects.

03
Resolution
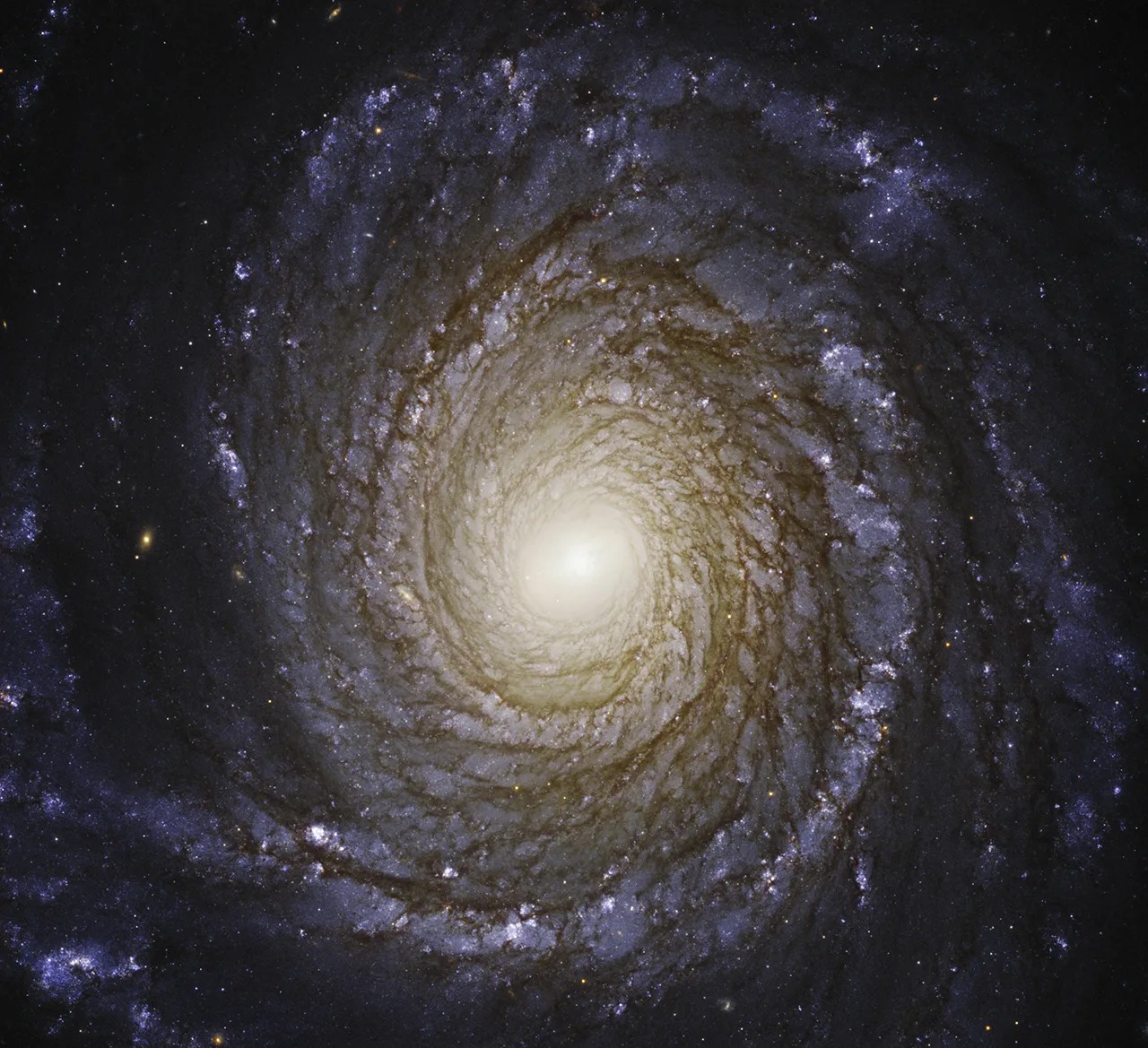
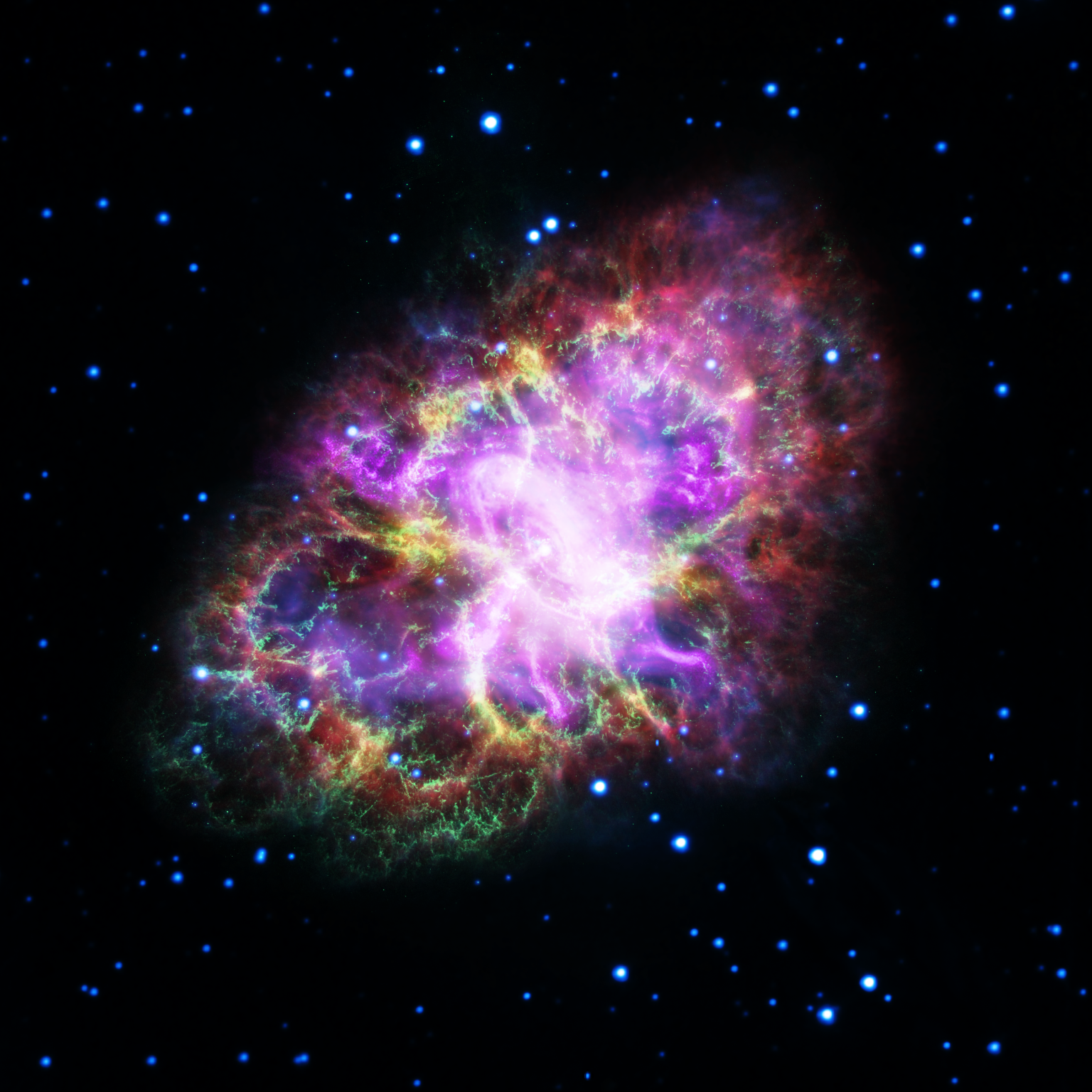
Hubble has extremely high angular resolution, or ability to distinguish between two objects that are very close together. If your eyes had Hubble’s resolution, you could read the date on a dime two miles away. For Hubble, this means it can see fine details in star-forming nebulae, galaxies, and other cosmic objects.

04
Dark Skies
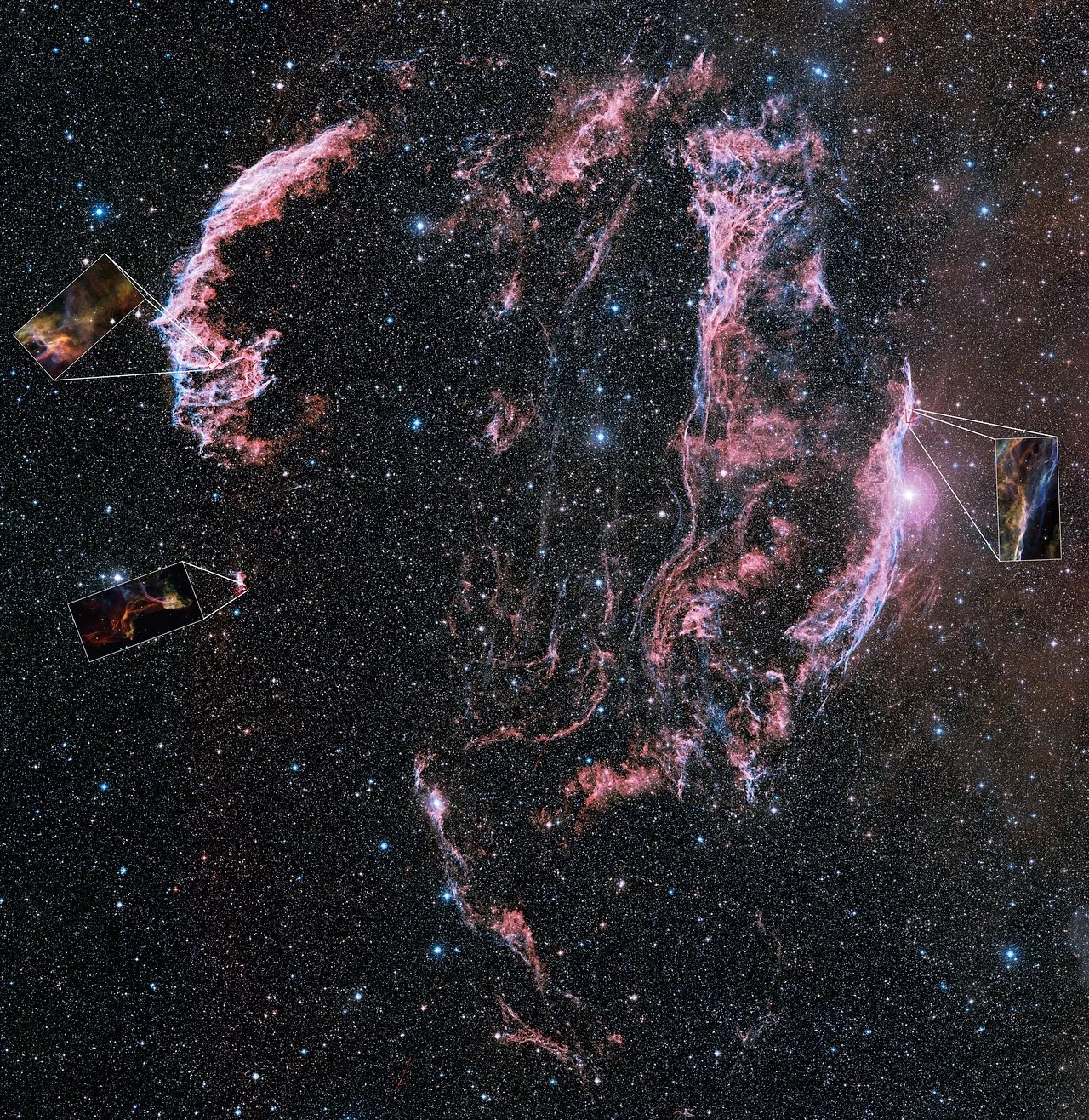
Orbiting 300 miles (483 km) above the surface, Hubble doesn’t have to contend with any form of light pollution or weather conditions. This gives it a permanent, clear dark sky, which, combined with its sharp vision, allows it to see objects 10 times fainter than those that can be observed from Earth even by the largest telescopes.

05
Serviceability
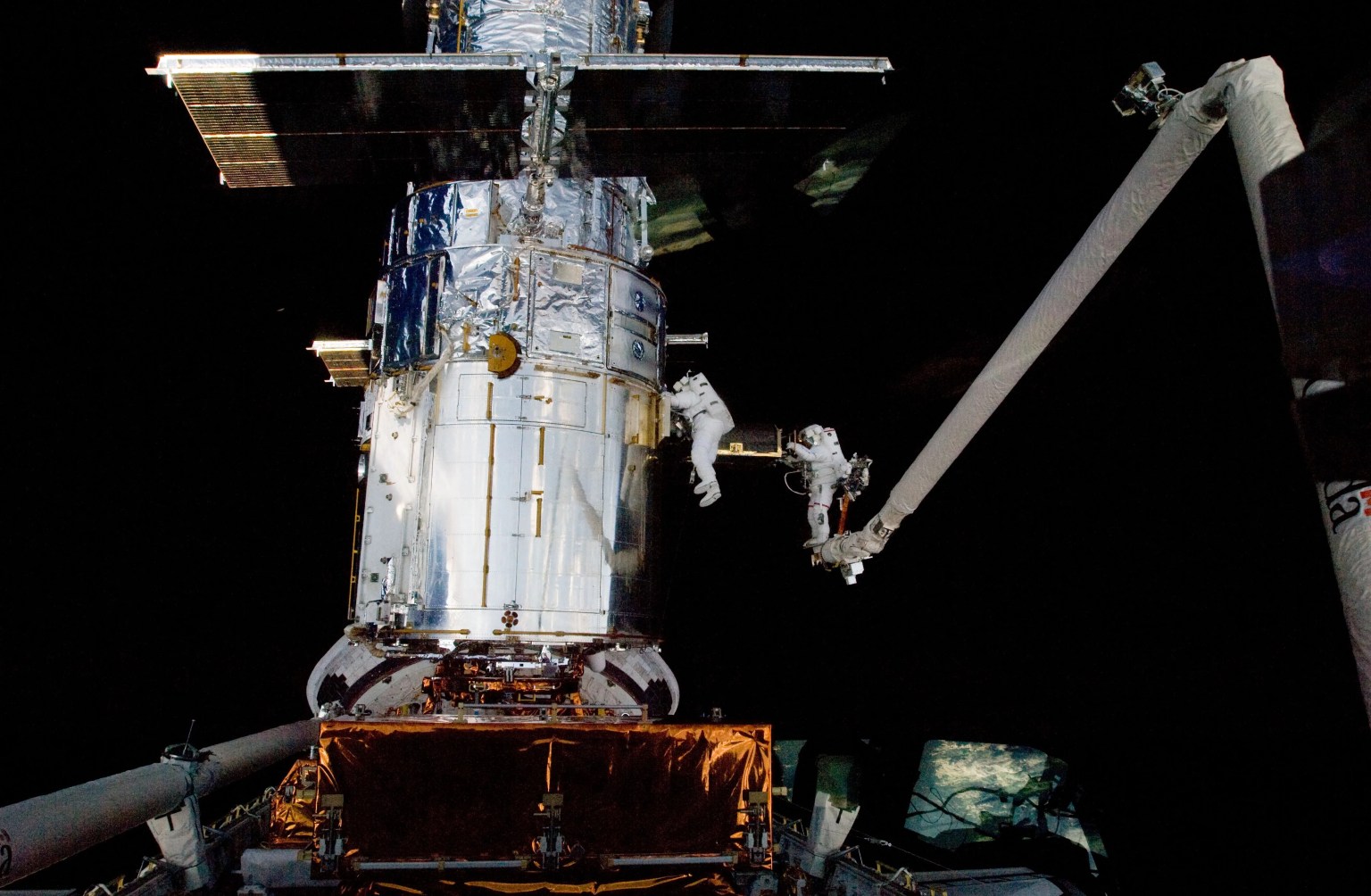
Hubble was positioned just above Earth’s atmosphere, in what’s called a low-Earth orbit, so it would be unaffected by Earth’s atmosphere. That position only hundreds of miles above the surface also meant that Hubble could be repaired and upgraded by astronauts, enabling the repair of its original mirror flaw, keeping the telescope in orbit for more than three decades and continuously renewing it with the newest technology.
06
Diversity
Hubble has multiple science instruments dedicated to probing the universe in unique ways. Hubble’s cameras observe the universe in a variety of wavelengths, including those invisible to the human eye. Its spectrometers dissect light into its component colors, exposing details like chemical composition and temperature. Its interferometers are used for aiming the telescope but can also measure the relative positions and brightnesses of stars.