1 min read
Compass and Scale Image for HCG 31
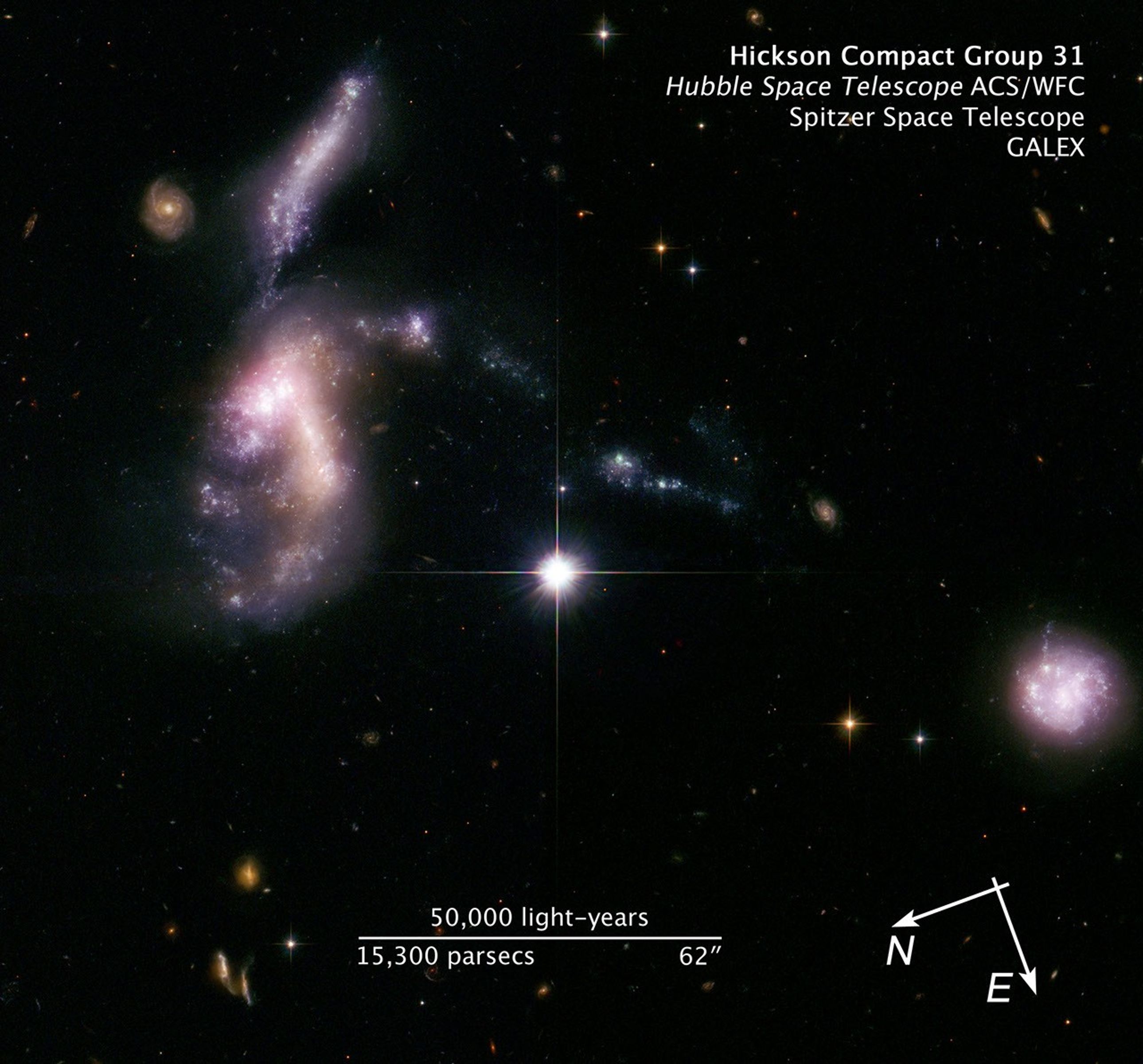

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 1m 38.74s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-4° 15' 34.1"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Eridanus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.166 million light-years (51 million parsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.This image is 3.2 arcminutes (156,000 light-years or 48,000 parsecs) wide.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposal 10787: J. Charlton (Pennsylvania State University), A. Zabludoff (University of Arizona), M. de Oliveira (University of São Paulo, Brazil), J. Hibbard (AURA/NRAO), S. Zonak (University of Maryland), A. Hornschemeier (NASA/GSFC), P. Hickson (University of British Columbia), J. Mulchaey (Carnegie Institution of Washington), K. Johnson (University of Virginia), A. Maybhate (STScI), R. Chandar (University of Toledo), S. Gallagher (The University of Western Ontario), C. Palma, S. Hunsberger, N. Brandt, and M. Eracleous (Pennsylvania State University), P. Durrell (Youngstown State University), J. English (University of Manitoba), B. Whitmore (STScI), D. Elmegreen (Vassar College), and K. Knierman (Arizona State University). The science team comprises: S. Gallagher (The University of Western Ontario), P. Durrell (Youngstown State University), D. Elmegreen (Vassar College), R. Chandar (University of Toledo), J. English (University of Manitoba), J. Charlton, C. Gronwall, and J. Young (Pennsylvania State University), P. Tzanavaris (NASA/GSFC), K. Johnson (University of Virginia/NRAO), M. de Oliveira (University of São Paulo, Brazil), B. Whitmore (STScI), A. Hornschemeier (NASA/GSFC), et al. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC, HST>WFPC2, Spitzer>IRAC, and GALEX
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.August 8, 2006, Exposure Time: 1.1 hours (HST), February 22, 2005 (Spitzer), and December 27, 2004 (GALEX)
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.HST>ACS: F435W (B), F606W (V), and F814W (I) HST>WFPC2: F439W (B), F555W (V), F675W (R), and F814W (I) Spitzer>IRAC: 8 micron GALEX: NUV Imaging Channel
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Hickson Compact Group 31, HCG 31
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Galaxy Group
- Release DateFebruary 18, 2010
- Science ReleaseJurassic Space: Ancient Galaxies Come Together After Billions of Years
- Credit

Note: Spitzer and GALEX data were combined with the Hubble data to create the composite image. The Spitzer data were taken February 22, 2005 (PI: K. Johnson, University of Virginia/NRAO). The GALEX data were taken December 27, 2004 (archival data). A small amount of WFPC2 data (proposal 5900, PI: P. Conti) taken on October 7, 1995, was used to fill in a portion of the ACS/WFC chip gap in this composite image of HCG 31. This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by three separate space telescopes. Exposures in the optical range of the spectrum were acquired with ACS and WFPC2 instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The near-ultraviolet light was acquired by the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), while near-infrared emission was captured by the IRAC instrument on the Spitzer Space Telescope (SST). Several filters were used to sample these wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Red: ACS F814W (I) + WFPC2 F814W (I) Yellow/green: ACS F606W (V) + WFPC2 F555W (V) + WFPC2 F675W (R) Blue: ACS F435W (B) + WFPC2 F439W (B) Orange: IRAC 8 micron Purple: GALEX NUV Imaging Channel

Related Images & Videos

Hickson Compact Group 31: Interacting Galaxies Aglow with Millions of Young Stars
These four dwarf galaxies waited billions of years to come together, setting off a fireworks show as thousands of new star clusters come to life. The distorted galaxies are quickly producing massive, hot, young stars that are pumping out ultraviolet radiation, heating up...

Hubble's View of Hickson Compact Group 31
These four dwarf galaxies waited billions of years to come together, setting off a fireworks show as thousands of new star clusters come to life. The distorted galaxies are quickly producing massive, hot, young stars that are pumping out ultraviolet radiation, heating up...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov