1 min read
Chance Alignment Between Galaxies Mimics a Cosmic Collision

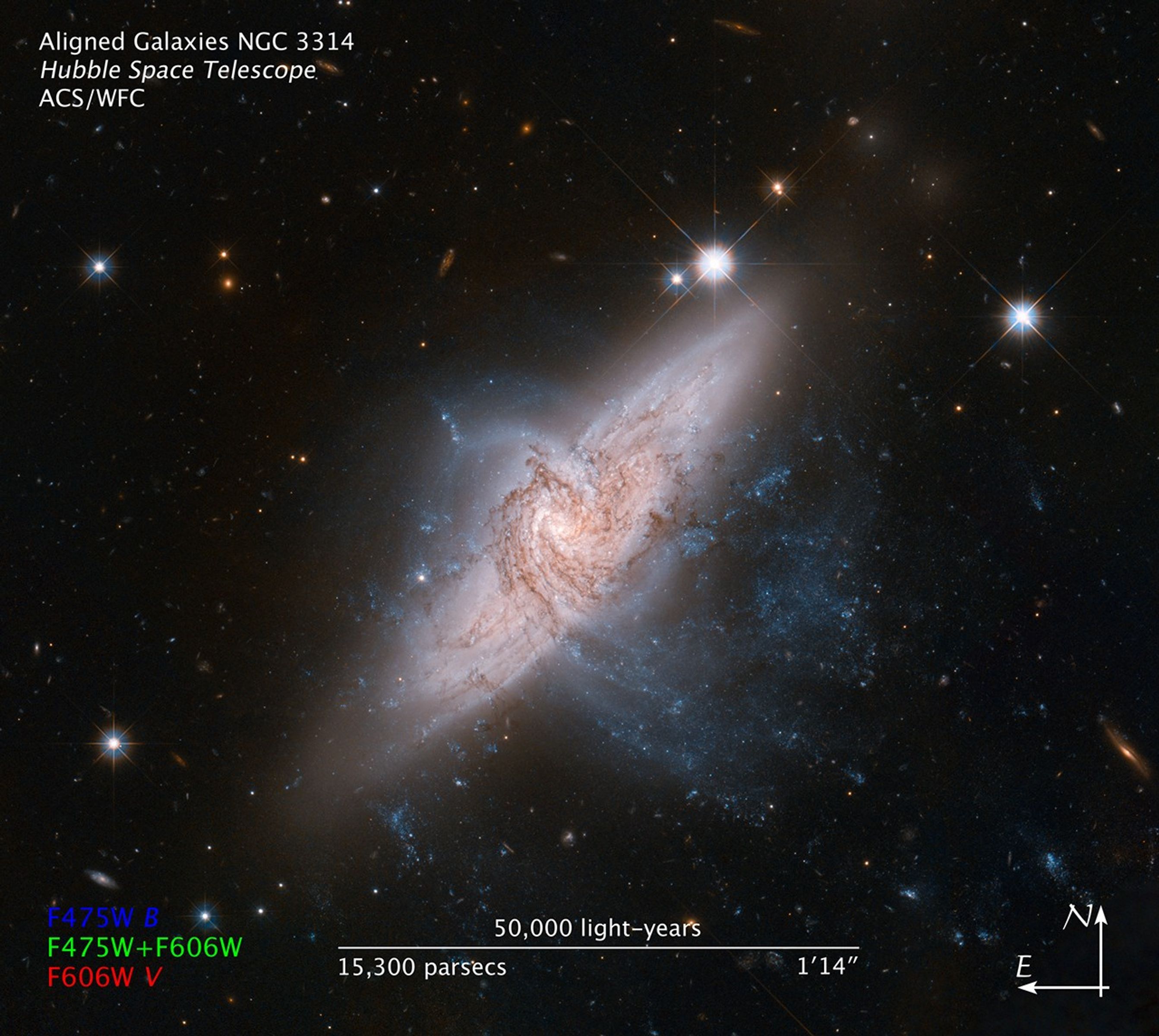
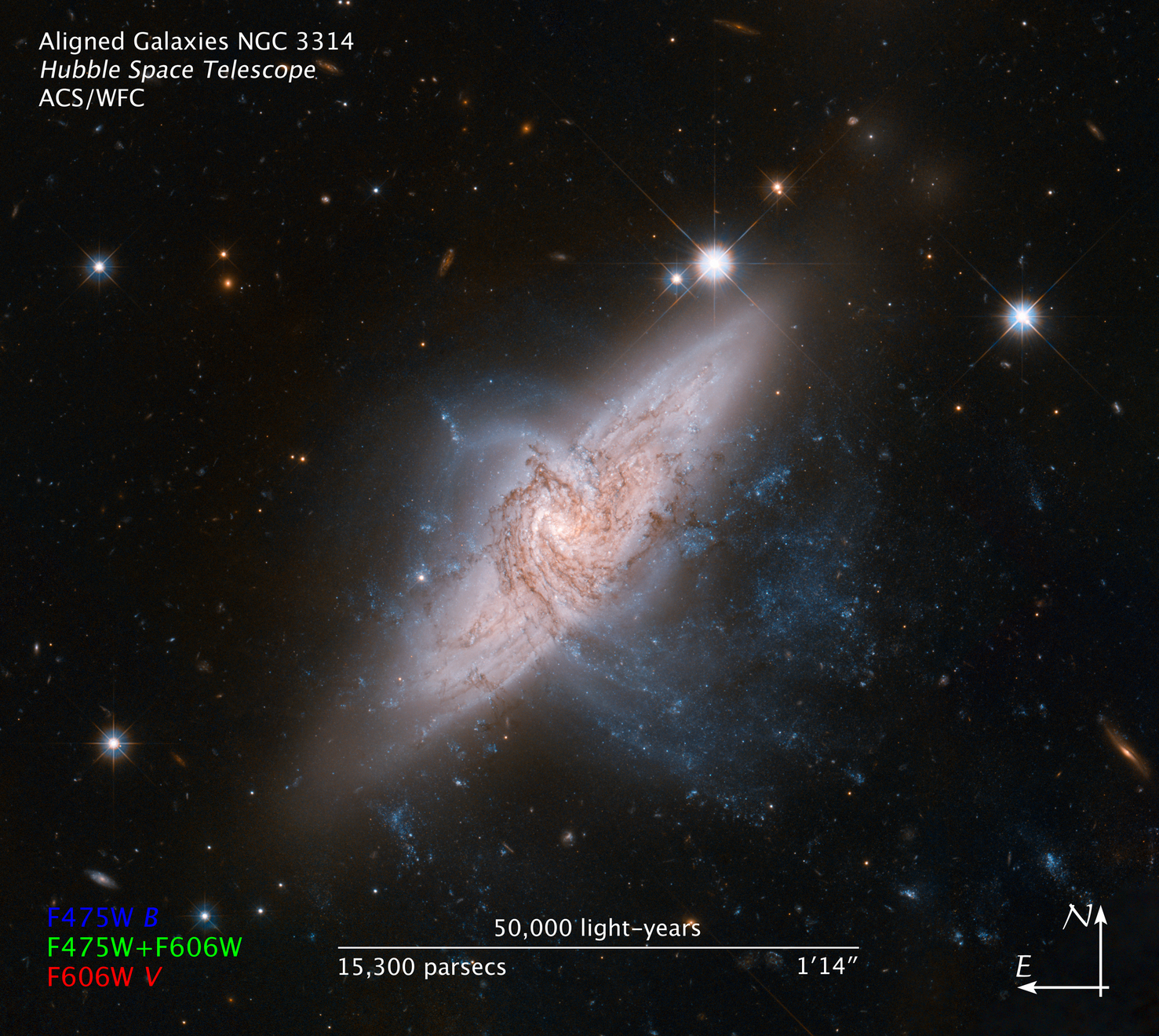
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows a rare view of a pair of overlapping galaxies, called NGC 3314. The two galaxies look as if they are colliding, but they are actually separated by tens of millions of light-years, or about ten times the distance between our Milky Way and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy. The chance alignment of the two galaxies, as seen from Earth, gives a unique look at the silhouetted spiral arms in the closer face-on spiral, NGC 3314A.
The motion of the two galaxies indicates that they are both relatively undisturbed and that they are moving in markedly different directions. This indicates they are not on any collision course. NGC 3314A's warped shape is likely due to an encounter with another nearby galaxy, perhaps the large spiral galaxy NGC 3312 (located outside the Hubble image).
Because of the alignment, NGC 3314B's dust lanes appear lighter than those of NGC 3314A. This is not because that galaxy lacks dust, but rather because its dust lanes are lightened by the bright fog of stars in the foreground. NGC 3314A's dust, in contrast, is backlit by the stars of NGC 3314B, silhouetting them against the bright background.
The color composite was produced from exposures taken in blue and red light with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. The pair of galaxies lie roughly 140 million light-years from Earth, in the direction of the southern hemisphere constellation Hydra.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10h 37m 13.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27° 41' 4.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Hydra
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The distance to NGC 3314A is roughly 117 million light-years (35 Mpc).The distance to NGC 3314B is roughly 140 million light-years (42 Mpc).
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.2002 - 2004, Exposure Time: 14 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F475W (B) and F606W (V)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 3314, NGC 3314A, NGC 3314B
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Aligned Galaxies
- Release DateJune 14, 2012
- Science ReleaseChance Alignment Between Galaxies Mimics a Cosmic Collision
- CreditNASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration, and W. Keel (University of Alabama)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the ACS instrument. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F475W (B) Green: F475W (B) + F606W (V) F606W (V)

Related Images & Videos

NGC 3314 Zoom Sequence (with Music)
This video begins with an image of the whole night sky, before zooming in to the constellation of Hydra and the curious pair of galaxies catalogued as NGC 3314. These two galaxies are actually separated by around 20 million light years, even if from our vantage point they look...
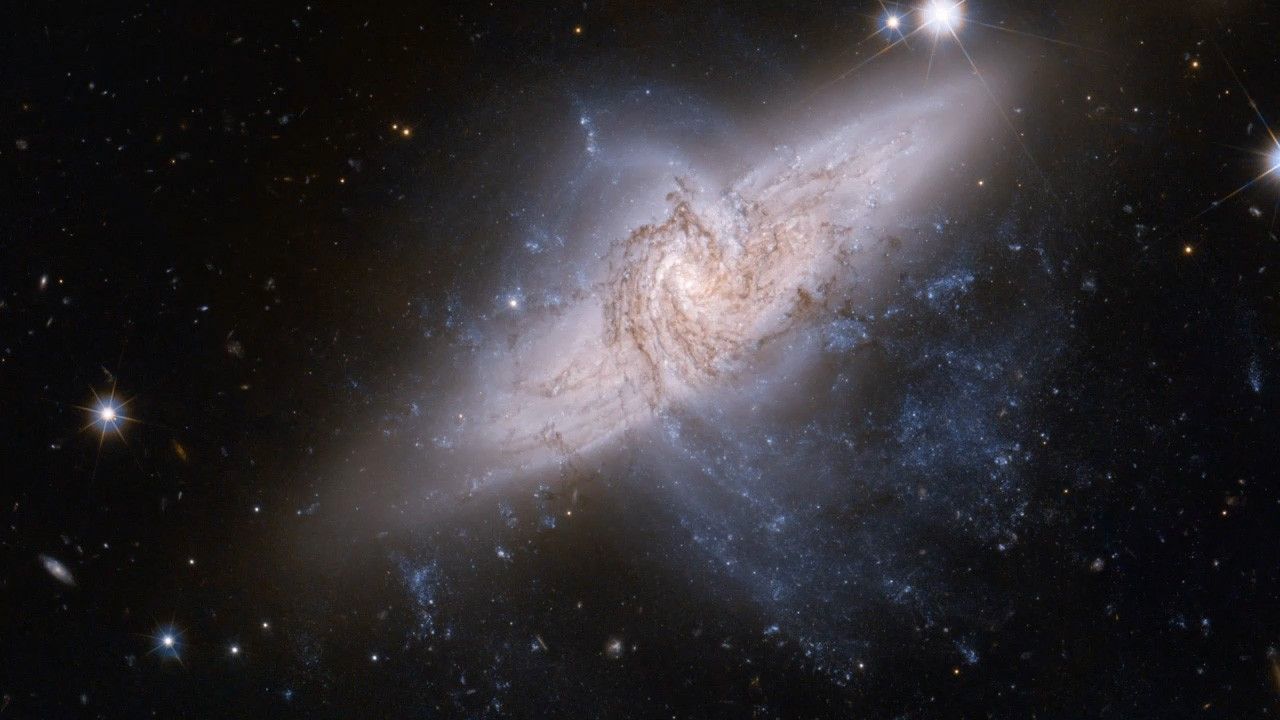

NGC 3314A and NGC 3314B Pan Sequence (with Music)
This video pans across Hubble Space Telescope observations of NGC 3314A and NGC 3314B, a pair of galaxies in the constellation Hydra. While they might look like they are in the midst of a cosmic collision, they are in fact separated by tens of millions of light-years of space.
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov