1 min read
Four-Panel Zoom into the Galactic Center
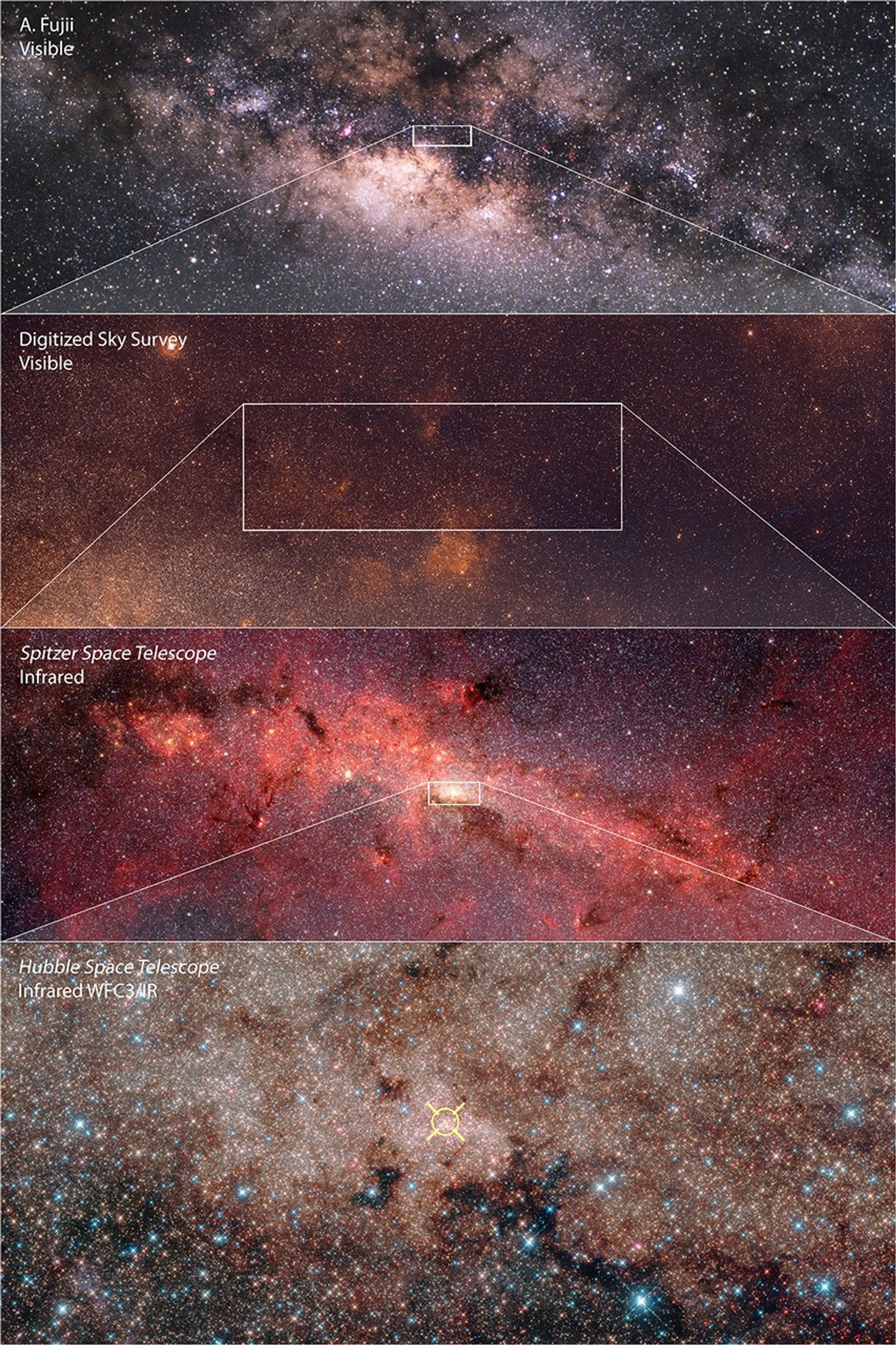

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.17h 45m 36.0s
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Sagittarius
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.27,000 light-years (8,000 parsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.-28° 55' 58.8"
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The HST data were taken from proposals 13049, 12663, and 12182 PI: T. Do (UCLA) and 11671 PI: A. Ghez (UCLA). The science team comprises T. Do, A. Ghez, and M. Morris (UCLA), R. Schodel (Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucia), J. Lu (University of Hawaii), W. Clarkson (University of Michigan), D. Merritt (RIT), B. Hansen and S. Yelda (UCLA), J. Bullock (University of California, Irvine), J. Anderson (STScI), L. Meyer, E. Mills, and N. McCrady (UCLA), and J.-U. Pott (Max Planck Insititue for Astronomy, Heidelberg).
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Milky Way Center
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Center of the Milky Way Galaxy
- Release DateMarch 31, 2016
- Science ReleaseHubble’s Journey to the Center of Our Galaxy
- Credit
Related Images & Videos

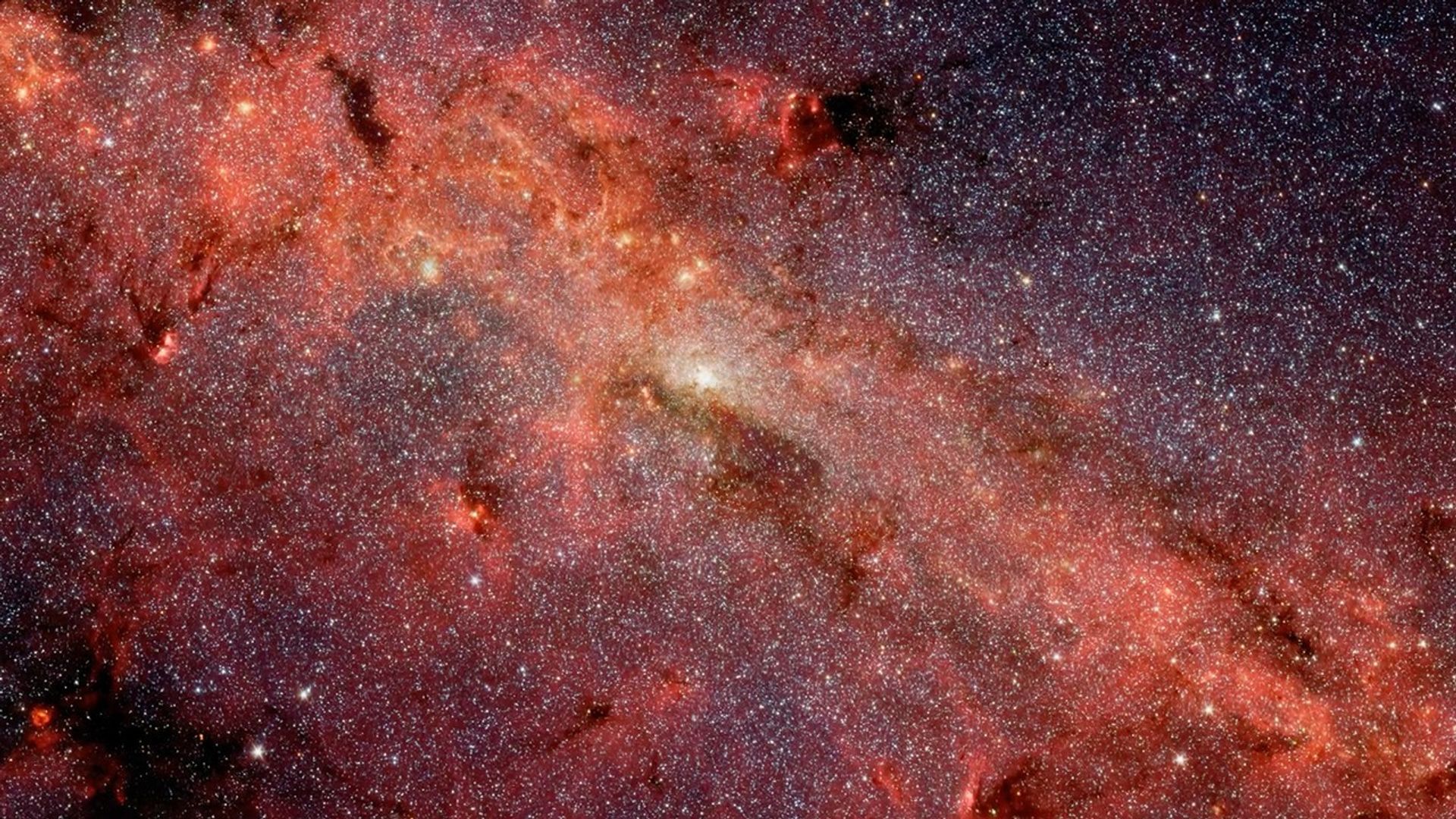
Milky Way Nuclear Star Cluster
Peering deep into the heart of our Milky Way galaxy, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reveals a rich tapestry of more than half a million stars. Except for a few blue, foreground stars, the stars are part of the Milky Way's nuclear star cluster, the most massive and densest star...
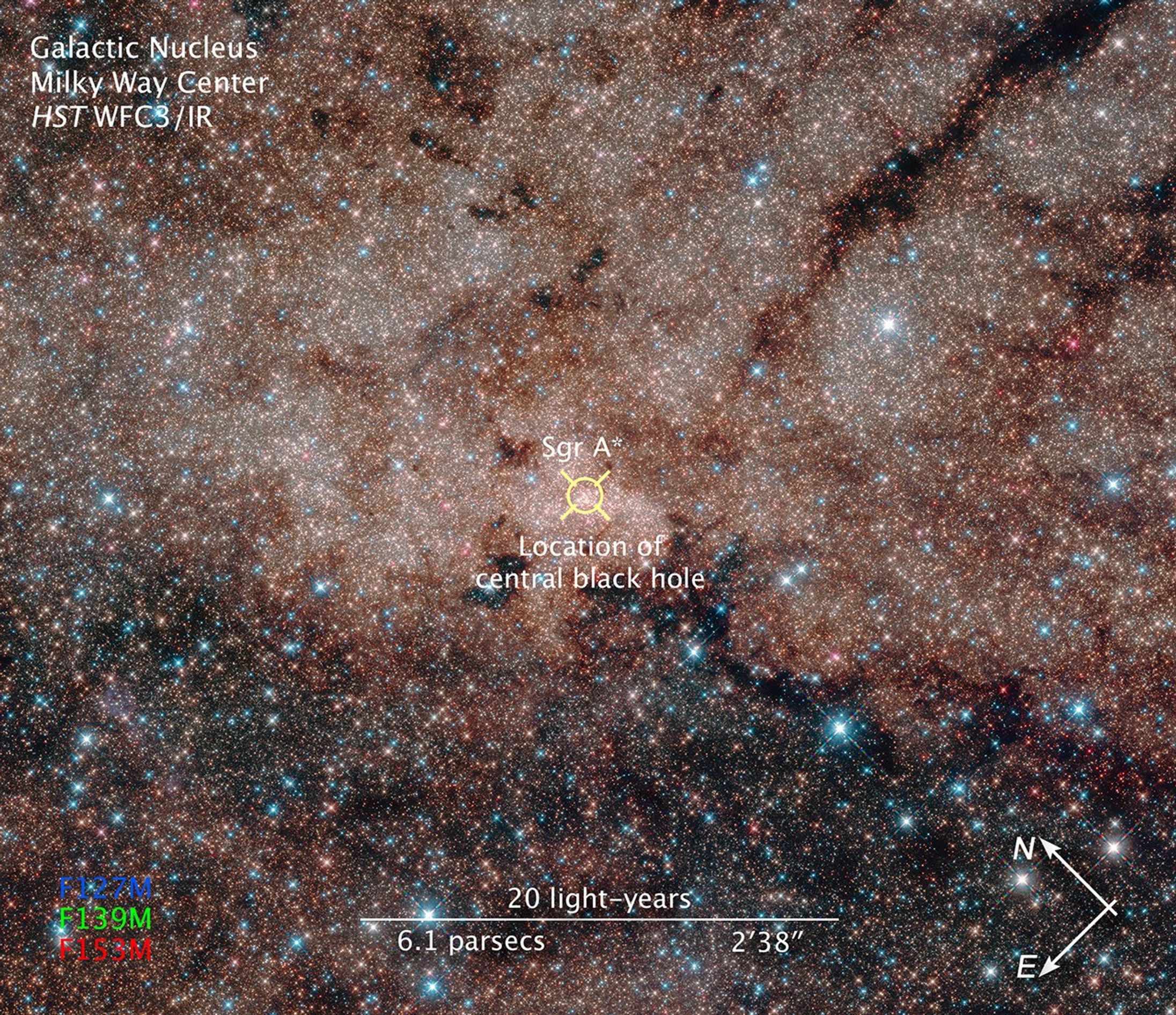

Compass and Scale Image for Milky Way Center
This annotated, infrared image from the Hubble Space Telescope shows the scale of the galactic core. The locator mark in the middle designates the galaxy's nucleus, which is home to a central, supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A* (pronounced Sagittarius A-star).

Zoom into the Center of Our Galaxy
This video sequence zooms into the Hubble Space Telescope view of the galactic core. Hubble's infrared vision pierced the dusty heart of our Milky Way galaxy to reveal more than half a million stars at its core. Except for a few blue, foreground stars, the stars are part of the...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov