1 min read
A Cosmic Necklace Larger than a Solar System

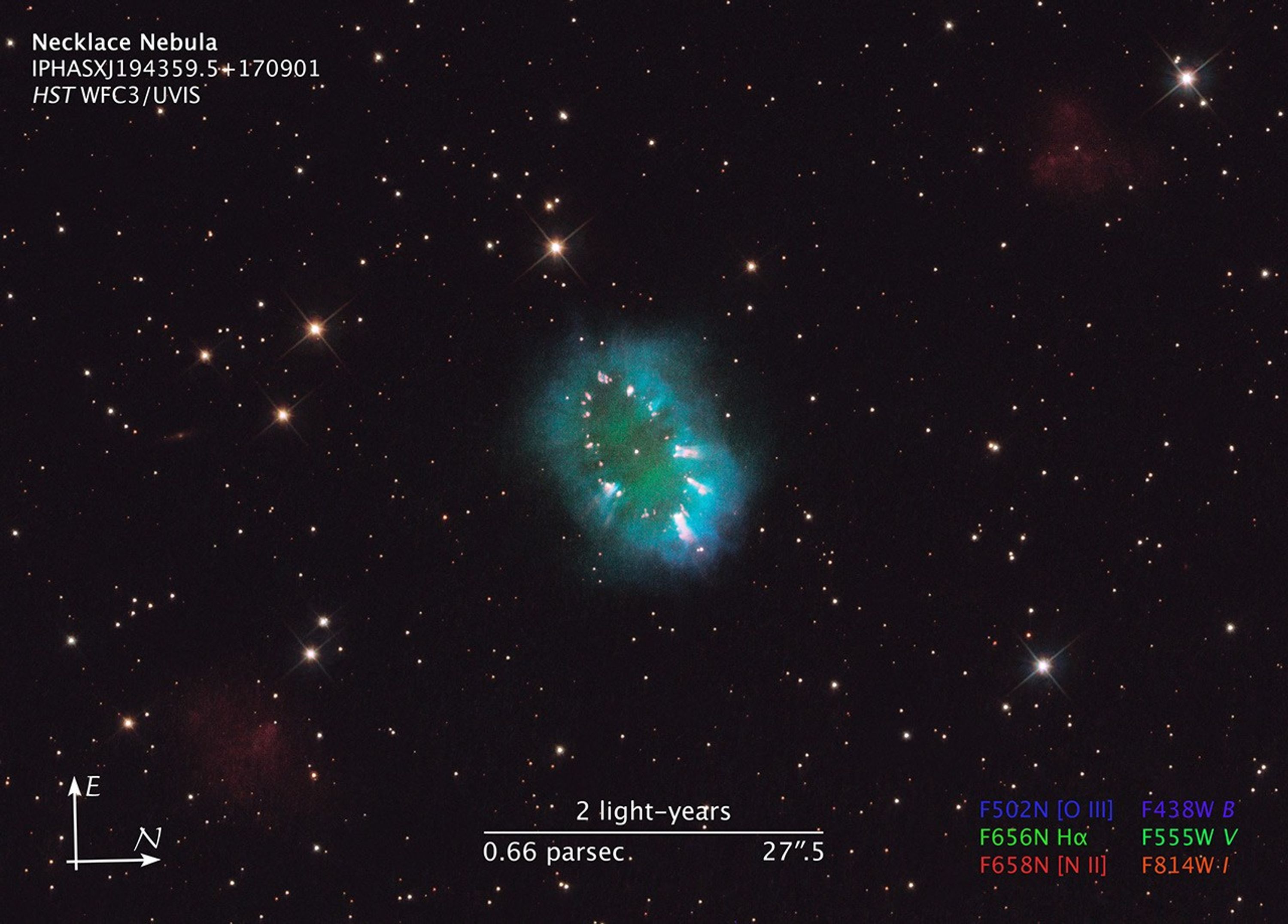
The Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) detector onboard Hubble was used to observe the Necklace Nebula on July 2, 2011. Hubble's WFC3 broadband filters, which show the colors of the galactic field stars, were used along with narrowband filters that show emission from the gases that make up the planetary nebula. In this composite image, ionized hydrogen gas is shown in blue, oxygen gas in green, and nitrogen gas in red. The field stars appear mainly white, with a reddish tint, which is indicative of the older population stars that make up the disk of our Milky Way galaxy.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.19h 43m 59.49s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.17° 9' 1.08"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Sagitta
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 15,000 light-years or 4,600 parsecs
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.1.7 arcminutes (7.6 light-years or 2.3 parsecs) wide
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposal 12675: K. Noll, Z. Levay, M. Livio, C. Christian, H. Bond, L. Frattare, M. Mutchler, T. Borders, and W. Januszewski (Hubble Heritage Team/STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.July 2, 2011, Exposure Time: 44 minutes
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F502N ([O III]), F438W (B), F656N (H-alpha), F555W (V), F658N ([N II]), and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Necklace Nebula, PN G054.2-03.4
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planetary Nebula
- Release DateAugust 11, 2011
- Science ReleaseHubble Offers a Dazzling View of the ‘Necklace’ Nebula
- Credit

Color Info
Color InfoA brief description of the methods used to convert telescope data into the color image being presented.
This image is a composite of many separate exposures made by the WFC3/UVIS instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope using six different filters, three broadband filters, and three narrowband filters. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F502N ([O III]) + F438W (B) Green: F656N (H-alpha) + F555W (V) Red: F658N ([N II]) + F814W (I)
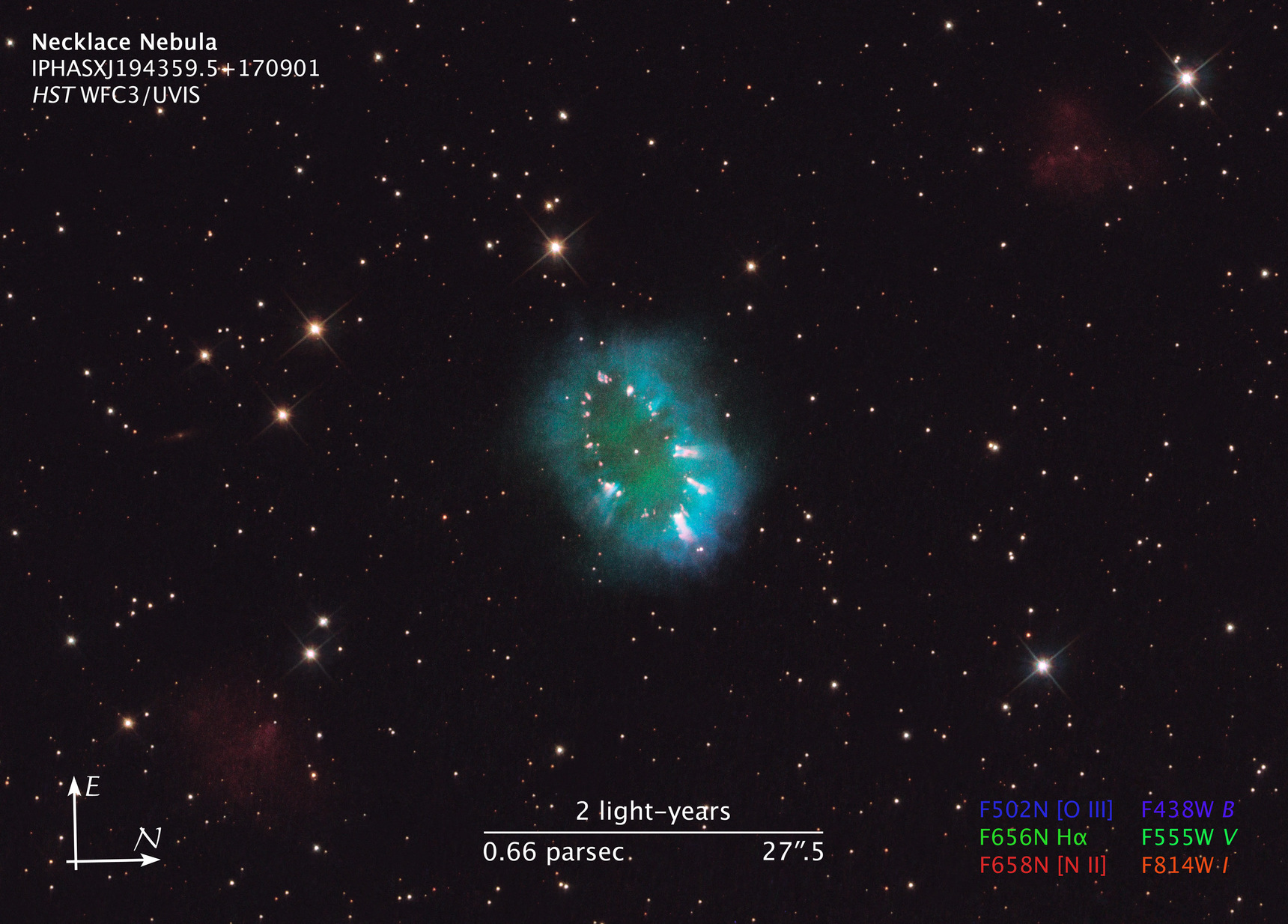
Compass and Scale
Compass and ScaleAn astronomical image with a scale that shows how large an object is on the sky, a compass that shows how the object is oriented on the sky, and the filters with which the image was made.
Related Images & Videos
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov