1 min read
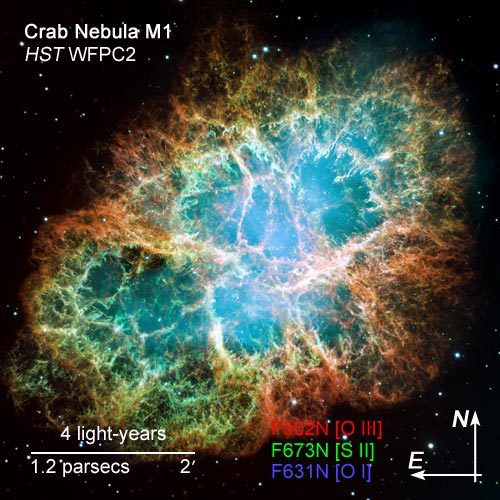
A Giant Hubble Mosaic of the Crab Nebula

This is a mosaic image, one of the largest ever taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of the Crab Nebula, a six-light-year-wide expanding remnant of a star's supernova explosion. Japanese and Chinese astronomers recorded this violent event nearly 1,000 years ago in 1054, as did, almost certainly, Native Americans.
The orange filaments are the tattered remains of the star and consist mostly of hydrogen. The rapidly spinning neutron star embedded in the center of the nebula is the dynamo powering the nebula's eerie interior bluish glow. The blue light comes from electrons whirling at nearly the speed of light around magnetic field lines from the neutron star. The neutron star, like a lighthouse, ejects twin beams of radiation that appear to pulse 30 times a second due to the neutron star's rotation. A neutron star is the crushed ultra-dense core of the exploded star.
The Crab Nebula derived its name from its appearance in a drawing made by Irish astronomer Lord Rosse in 1844, using a 36-inch telescope. When viewed by Hubble, as well as by large ground-based telescopes such as the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope, the Crab Nebula takes on a more detailed appearance that yields clues into the spectacular demise of a star, 6,500 light-years away.
The newly composed image was assembled from 24 individual Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 exposures taken in October 1999, January 2000, and December 2000. The colors in the image indicate the different elements that were expelled during the explosion. Blue in the filaments in the outer part of the nebula represents neutral oxygen, green is singly-ionized sulfur, and red indicates doubly-ionized oxygen.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 34m 32.0s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.22° 0' 51.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Taurus
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The distance to NGC 1952 is 6500 light-years (2.0 kpc).
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is 6 arcminutes along the bottom (12 light-years or 3.7 pc).
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble image was created from HST data from proposal 8222: J. Hester and A. Loll (Arizona State University), W. Blair and R. Sankrit (Johns Hopkins University), and P.Scowen (Arizona State University). D. de Martin (www.skyfactory.org, Venice, Italy) also helped in the creation of this image. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.October 1999, January 2000, and December 2000
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F502N ([O III]), F631N ([O I]), F673N ([S II])
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Crab Nebula, NGC 1952
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Remnant
- Release DateDecember 1, 2005
- Science ReleaseA Giant Hubble Mosaic of the Crab Nebula
- Credit

Blue: F631N ([O I]) Green: F673N ([S II]) Red: F502N ([O III])
Related Images & Videos

Crab Nebula: A Dead Star Creates Celestial Havoc
This composite image of the Crab Nebula uses data from three of NASA's Great Observatories. The Chandra X-ray image is shown in light blue, the Hubble Space Telescope optical images are in green and dark blue, and the Spitzer Space Telescope's infrared image is in red. The size...
Zoom into the Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula is an expanding remnant of a star's supernova explosion. Located 6,500 light-years away, this glowing relic has been expanding since the star exploded, and it is now approximately 11 light-years in width. The orange filaments are the tattered remains of the star...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov




























