1 min read
Brown Dwarf Discovered Around Star Gliese 229
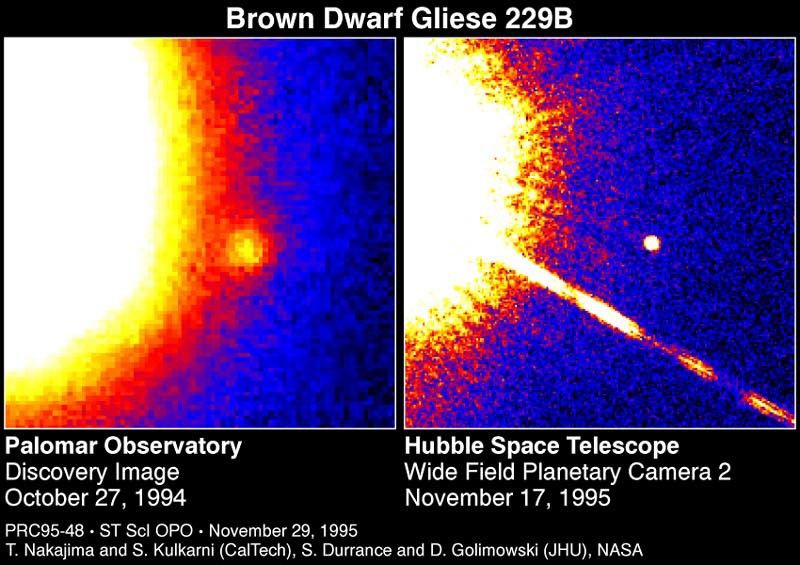
These two false-color telescope images reveal the faintest object ever seen around a star beyond our Sun, and the first unambiguous detection of a brown dwarf. The brown dwarf, called GL229B, orbits the red dwarf star Gliese 229, located approximately 18 light-years away in the constellation Lepus. The brown dwarf is about 20-50 times the mass of Jupiter, but is so dense it is about the same diameter as Jupiter (80,000 miles).
Brown dwarfs are a mysterious class of long-sought objects that form the same way stars do, by condensing out of a cloud of hydrogen gas. However, they do not accumulate enough mass to sustain nuclear fusion at their core, which make stars shine.
[left] - The brown dwarf (center) was first observed in far red light October 27, 1994 using the adaptive optics device and a 60-inch reflecting telescope on Palomar Mountain in California. Another year was required to confirm that the object was actually gravitationally bound to the companion star. GL229B is at least four billion miles from its companion star, roughly the separation between the planet Pluto and our Sun. Even though a cornograph on the detector masked most of the light from the star, which is off the left edge of the image, it is so bright relative to the brown dwarf the glare floods the detector.
[right] - This image of the GL229B (center) was taken with Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera-2, in far red light, on November 17, 1995. The Hubble observations will be used to accurately measure the brown dwarf's distance from Earth, and yield preliminary data on its orbital period, which may eventually offer clues to the dwarf's origin. Though the star Gliese 229 is off the edge of the image, it is so bright it floods Hubble detector. The diagonal line is a diffraction spike produced by the telescope's optical system.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.06h 10m 35.11s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-21° 51' 17.6"
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Gliese 229, GL229, Gliese 229b, GL229b
- Release DateNovember 29, 1995
- Science ReleaseAstronomers Announce First Clear Evidence of a Brown Dwarf
- CreditLeft image: T. Nakajima (Caltech), S. Durrance (JHU); Right image: S. Kulkarni (Caltech), D.Golimowski (JHU) and NASA
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov






























