1 min read
CHXR 73 A and B – Red Dwarf and Substellar Companion
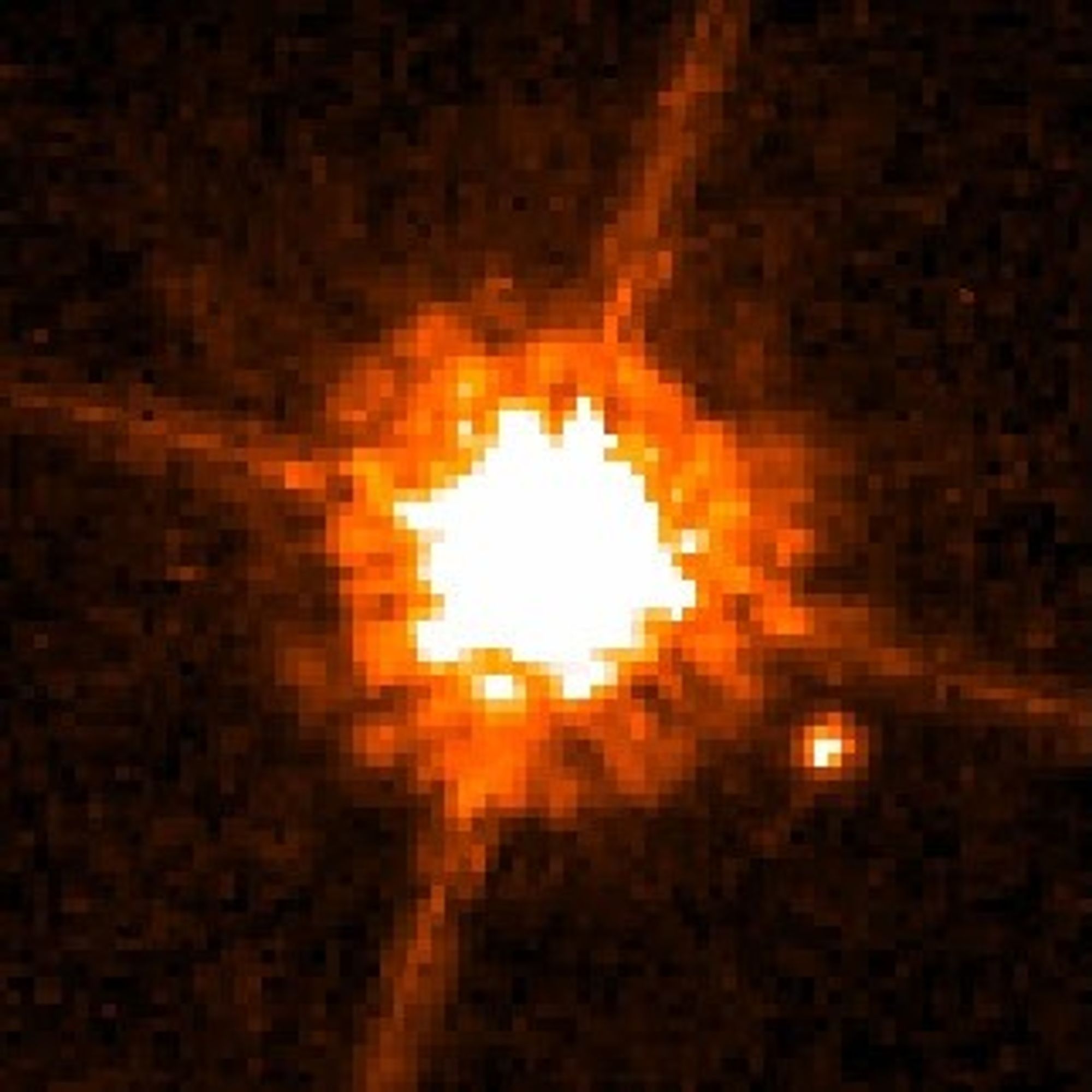

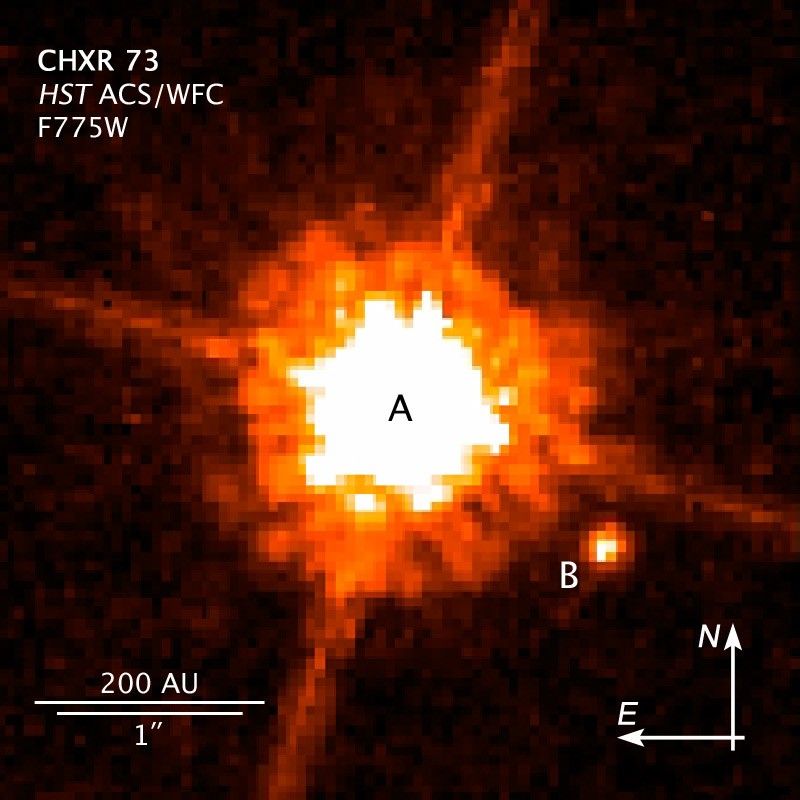
This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image shows one of the smallest objects ever seen around a normal star. Astronomers believe the object is a brown dwarf because it is 12 times more massive than Jupiter. The brown dwarf candidate, called CHXR 73 B, is the bright spot at lower right. It orbits a red dwarf star, dubbed CHXR 73, which is a third less massive than the Sun. At 2 million years old, the star is very young when compared with our middle-aged 4.6-billion-year-old Sun.
CHXR 73 B orbits 19.5 billion miles from its star, or roughly 200 times farther than Earth is from the Sun.
The star looks significantly larger than CHXR 73 B because it is much brighter than its companion. CHXR 73 B is 1/100 as bright as its star. The cross-shaped diffraction spikes around the star are artifacts produced within the telescope's optics. The star is 500 light-years away from Earth.
Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys snapped the image in near-infrared light on Feb. 10 and 15, 2005. The color used in the image does not reflect the object's true color.
Members of the research team are K. L. Luhman, Penn State University; J. C. Wilson, M. F. Skrutskie, M. J. Nelson, and D. E. Peterson, University of Virginia; W. Brandner, Max-Planck Institute for Astronomy; and J. D. Smith, M. C. Cushing, and E. Young, University of Arizona.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.11h 6m 29.29s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-77° 37' 33.99"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Chamaeleon
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Approximately 500 light-years (150 parsecs)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Full width of the image is 690 AU or 4"
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposal 10138: K. Luhman (Pennsylvania State University) and G. Fazio (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics). The science team includes: K. Luhman (Pennsylvania State University), J. Wilson (University of Virginia), W. Brandner (Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany), M. Skrutskie and M. Nelson (University of Virginia), J. Smith (Steward Observatory, University of Arizona), D.Peterson (University of Virginia), and M. Cushing and E. Young (Steward Observatory, University of Arizona). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 10, 2005, Exposure Time: 40 minutes
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F775W (SDSS i) and F850LP(SDSS z)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.CHXR 73 A and B
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Red Dwarf and Substellar Companion
- Release DateSeptember 7, 2006
- Science ReleasePlanet Or Failed Star? NASA’s Hubble Telescope Photographs One of Smallest Stellar Companions Ever Seen
- Credit

This image was made using data from a single filter in the near-infrared part of the spectrum so it is in fact monochrome or black and white. The color results from mapping each brightness step in the grayscale image to a separate color, known as a color-mapped or color-indexed image. In this case the color scale is a ramp from black through red and orange to white.

Related Images & Videos

Artist's View of Red Dwarf and Substellar Companion
This is an artist's concept of the red dwarf star CHXR 73 (upper left) and its companion CHXR 73 B in the foreground (lower right) weighing in at 12 Jupiter masses. CHXR 73 B is one of the smallest companion objects ever seen around a normal star beyond our Sun. Estimated to be...
CHXR 73 A and B - Red Dwarf and Substellar Companion (Annotated)
This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image shows one of the smallest objects ever seen around a normal star. Astronomers believe the object is a brown dwarf because it is 12 times more massive than Jupiter. The brown dwarf candidate, called CHXR 73 B, is the bright spot at lower...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov

























